Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Document (4) - 1
Document (4) - 1
Uploaded by
Justin DugangCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- EM WavesDocument2 pagesEM WavesMyyo TabunoNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattDocument21 pagesUnit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10: Types-and-Applications-of-EM-wavesDocument32 pagesSCIENCE 10: Types-and-Applications-of-EM-wavesInsigne HarietteNo ratings yet
- What Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Document11 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Rodrigo SeriozaNo ratings yet
- What Are Electromagnetic Waves?Document8 pagesWhat Are Electromagnetic Waves?Jay Marie OcampoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumTanish100% (1)
- General Informatio NDocument15 pagesGeneral Informatio NJenny RoblesNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves 2023Document6 pagesElectromagnetic Waves 2023llindoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Wave HandoutDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic Wave HandoutARLENE POMBONo ratings yet
- 7 Types of Electromagnetic WavesDocument6 pages7 Types of Electromagnetic WavesAbigail Domingo100% (1)
- Electromagnetic RadiationDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic RadiationAyman BashirNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic SpectrumDocument6 pagesElectro Magnetic SpectrumarhamNo ratings yet
- Module 8 PhysicsDocument7 pagesModule 8 PhysicsLopez AeraNo ratings yet
- Name Wavelength : Gamma Ray E KeDocument3 pagesName Wavelength : Gamma Ray E KeJose Andrei Dalisay PagsinohinNo ratings yet
- Spectrum) of Electromagnetic Radiation and Their RespectiveDocument10 pagesSpectrum) of Electromagnetic Radiation and Their RespectiveJabez Edwin SivaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument5 pagesScienceAriana LaynoNo ratings yet
- (51014) Javier Prelab6Document2 pages(51014) Javier Prelab6Jesse JavierNo ratings yet
- Science Report Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument24 pagesScience Report Electromagnetic SpectrumJedí BelanoNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document13 pagesScience 10Joel De LeonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EM SpectrumDocument8 pagesIntroduction To EM SpectrumKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- Copy 2nd QuarterDocument30 pagesCopy 2nd QuarterLiwayway MadaliNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes No. 19 Regions of The Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio WavesDocument4 pagesConcept Notes No. 19 Regions of The Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio WavesLunaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumAndres GalarragaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation Frequency Wavelength Speed of Light Photon SpectrumDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation Frequency Wavelength Speed of Light Photon SpectrumFOODHEALTHNo ratings yet
- Waves in The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument13 pagesWaves in The Electromagnetic SpectrumD AngelaNo ratings yet
- Elctronic RadiationDocument4 pagesElctronic RadiationTia WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Microwaves - Can Penetrate The Atmosphere ofDocument2 pagesMicrowaves - Can Penetrate The Atmosphere ofSpade WattpadNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Module 1Document20 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 1Ma'am LeiNo ratings yet
- 7 Types of Electromagnetic WavesDocument2 pages7 Types of Electromagnetic Wavesvee propaganda100% (1)
- Physics1101 - Course MaterialDocument332 pagesPhysics1101 - Course MaterialAhmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Radio WavesDocument4 pagesRadio WavesSophia Nicole ZaraNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum: Juan Carlos Isaza Jacome Byron Cubides Romero Duvan Reyes SaenzDocument20 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum: Juan Carlos Isaza Jacome Byron Cubides Romero Duvan Reyes SaenzJuan Carlos Isaza JacomeNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument13 pages3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumMadiha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WaveDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic WavewerewolfNo ratings yet
- How Radiation Works: Light Radio)Document2 pagesHow Radiation Works: Light Radio)NabilaPutriClpdhiNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 1Document15 pagesScience Reviewer 1Symon MarianoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument43 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumxunxhineNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document38 pagesScience 10Angelo LiwanagNo ratings yet
- Science 10 SECOND QuarterDocument152 pagesScience 10 SECOND QuarterAPPLE GRACE MARIE SEBASTIAN100% (1)
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrummuddasarhussain739No ratings yet
- Science Reviewer q2Document6 pagesScience Reviewer q2Samuel IdoNo ratings yet
- Team Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksDocument12 pagesTeam Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksJOHN ASHLEY RANIN CARIAGANo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum FormsDocument32 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum FormsRuih PadillaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Electromagnetic WavesDocument10 pagesPhysics: Electromagnetic WavesBen Hemert G. Jumao-asNo ratings yet
- Inbound 4743556798129293898Document8 pagesInbound 4743556798129293898Samantha GabrielNo ratings yet
- Physics: Electromagnetic WavesDocument11 pagesPhysics: Electromagnetic WavesBen Hemert G. Jumao-asNo ratings yet
- Alison ProjectDocument8 pagesAlison Projectjalefaye abapoNo ratings yet
- The Application of Electromagnetic WavesDocument6 pagesThe Application of Electromagnetic WaveszeromanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument54 pagesElectromagnetic WavesPortia A. EgkenNo ratings yet
- Blue Red and Yellow Illustrative Science Electromagnetic Radiation Educational PresentationDocument26 pagesBlue Red and Yellow Illustrative Science Electromagnetic Radiation Educational PresentationAsma AmpangNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument8 pagesScienceapi-398255504No ratings yet
- Applications of MicrowavesDocument6 pagesApplications of MicrowavesorculloNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjektDocument12 pagesPhysics Projektrupendrajain20No ratings yet
- C12 Electromagnetic WavesDocument48 pagesC12 Electromagnetic WavesRosemarie Cabanilla50% (2)
- Electromagnetic Spectrum and BandwidthDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum and BandwidthJennybabe NapolesNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument33 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and The Electromagnetic SpectrumDanae Forrester100% (1)
- EM Waves - UPHDocument20 pagesEM Waves - UPHSHIVA THAVANI100% (1)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument27 pagesElectromagnetic WavesKatrinaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q2W3-4Document15 pagesScience 10 - Q2W3-4quackity obamaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 2Document4 pagesTutorial Chapter 2batrisyaNo ratings yet
- CP Phys CH 2 Web RevDocument8 pagesCP Phys CH 2 Web RevMichelle MuliawidjajaNo ratings yet
- CAPE Physics Workshop Workbook 2021 - Unit 1Document41 pagesCAPE Physics Workshop Workbook 2021 - Unit 1Kenya LevyNo ratings yet
- Use The Passage To Answer Questions 4 - 5Document4 pagesUse The Passage To Answer Questions 4 - 5Melvin CabonegroNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Performance Flight TestingDocument284 pagesAircraft Performance Flight TestingIoannis PerperisNo ratings yet
- Linearized Dynamics Equations For The Balance and Steer of A Bicycle: A Benchmark and ReviewDocument63 pagesLinearized Dynamics Equations For The Balance and Steer of A Bicycle: A Benchmark and ReviewVictor MagriNo ratings yet
- Yousefi Saleh2015 Article Three DimensionalSuctionFlowCoDocument14 pagesYousefi Saleh2015 Article Three DimensionalSuctionFlowCoasdasddasNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic MotionDocument18 pagesSimple Harmonic Motionieja03100% (2)
- CH 12 Physics AnswersDocument21 pagesCH 12 Physics AnswersSam Likes HamNo ratings yet
- Sound PDFDocument4 pagesSound PDFNgoc Vũ TrầnNo ratings yet
- Module IVDocument25 pagesModule IVVinay KashyapNo ratings yet
- Clicker Questions For Vectors 1Document7 pagesClicker Questions For Vectors 1Gersson Alejandro LoperaNo ratings yet
- Motion, Speed, Acceleration, Velocity, and ForceDocument26 pagesMotion, Speed, Acceleration, Velocity, and ForceKersy Mere FajardoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Explainer - Velocity - NagwaDocument34 pagesLesson Explainer - Velocity - NagwaMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- All About TrigonometryDocument13 pagesAll About TrigonometryAhmad100% (1)
- Sheet (5) - Dynamics PDFDocument2 pagesSheet (5) - Dynamics PDFahmedmohammeda829No ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument4 pagesKinema Ticssheden0320No ratings yet
- Ripamonti Folleto PDFDocument4 pagesRipamonti Folleto PDFDavid CarrilloNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Aqwa Suite Articulations & ANSYS Aqwa Suite Articulations & Multi-Body Multi-Body Problems ProblemsDocument9 pagesANSYS Aqwa Suite Articulations & ANSYS Aqwa Suite Articulations & Multi-Body Multi-Body Problems ProblemsPatrick SilvaNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 8 and 15 Electromagnetic Waves and Communicationommunication SystemsystemsDocument13 pagesPhysics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 8 and 15 Electromagnetic Waves and Communicationommunication SystemsystemsJaseela NaufalNo ratings yet
- Vector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics: Distributed Forces: Moments of InertiaDocument19 pagesVector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics: Distributed Forces: Moments of InertiaMamdouh GhzawiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Fluid Flow in PipesDocument42 pagesLecture 6 - Fluid Flow in PipesPercival ArcherNo ratings yet
- Sph3u - Quiz 4 - Review - SolutionsDocument6 pagesSph3u - Quiz 4 - Review - Solutionsapi-601648218No ratings yet
- Vehicle Dynamics Session 3 Tire Fundamental Characteristics and Dynamic PerformanceDocument36 pagesVehicle Dynamics Session 3 Tire Fundamental Characteristics and Dynamic PerformanceHarish SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Vibration Measurement EquipmentsDocument19 pagesVibration Measurement EquipmentsReyvel MugarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document41 pagesLecture 14Boyi EnebinelsonNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engines: Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of LagosDocument4 pagesThermal Engines: Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of LagosSaheed LawansonNo ratings yet
- CE222 Problem Set 1Document6 pagesCE222 Problem Set 1Mehmet ArasNo ratings yet
- Ship Hydrodynamics - Lecture - Notes - Part - 8 - Propeller - TestsDocument12 pagesShip Hydrodynamics - Lecture - Notes - Part - 8 - Propeller - TestsOdpewğw RlelelwNo ratings yet
- Modeling of A Three-Axes MEMS Gyroscope With Feedforward PI Quadrature CompensationDocument10 pagesModeling of A Three-Axes MEMS Gyroscope With Feedforward PI Quadrature CompensationDavide MaranoNo ratings yet
Document (4) - 1
Document (4) - 1
Uploaded by
Justin DugangOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Document (4) - 1
Document (4) - 1
Uploaded by
Justin DugangCopyright:
Available Formats
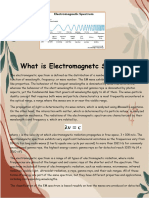
The electromagnetic (EM) spectrum is the range of all types of EM radiation.
Radiation is
energy that travels and spreads out as it goes – the visible light that comes from a lamp in
your house and the radio waves that come from a radio station are two types of
electromagnetic radiation. The other types of EM radiation that make up the
electromagnetic spectrum are microwaves, infrared light, ultraviolet light, X-rays and
gamma-rays.
In 1887 Heinrich Hertz demonstrated the existence of the
waves and predicted by James C. Maxwell by producing radio
waves in his laboratory.
Heinrich Hertz James C. Maxwell
(Who demonstrate the existence ( Who predicted the existence
of electromagnetic waves) of electromagnetic waves)
Why is the electromagnetic spectrum important? Significance of Electromagnetic Spectrum
Nonetheless, the main significance of the electromagnetic spectrum is that it can be used to classify
electromagnetic waves and arrange them according to their different frequencies or wavelengths.
The electromagnetic (EM) spectrum is the range of all types of EM radiation. Radiation is energy that
travels and spreads out as it goes – the visible light that comes from a lamp in your house and the radio
waves that come from a radio station are two types of electromagnetic radiation. The other types of EM
radiation that make up the electromagnetic spectrum are microwaves, infrared light, ultraviolet light, X-
rays and gamma-rays.
Description
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation. A radio wave has a
much wavelength than visible light. Humans use radio waves
extensively for communications.
Radio waves are the waves having the longest
wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum. These waves are a
kind of electromagnetic radiation and have a frequency from high
300 GHz to low as 3 kHz though somewhere it is defined above 3
GHz as microwaves.
Most radio waves pass freely through Earth’s atmosphere. However, some frequencies
can reflected or absorbed by the charged particles in the ionosphere.
Characteristics
Property 1: Radio waves are a form of radiation known as electromagnetic waves. The
wavelength of radio waves is longer than the infrared light. Property 2: Radio waves can
travel for a long distance. Property 3: Radio waves can penetrate through materials.
Uses
Various frequencies of radio waves are used for
television and FM and AM radio broadcasts, military
communications, mobile phones, ham radio,
wireless computer networks, and numerous other
communications applications.
James Clerk Maxwell who made the first prediction about radio waves but it was Heinrich Hurts who
showed that radio waves can be produced and transmitted.
James Clerk Maxwell Heinrich Hurts
Description
Microwaves are defined as electromagnetic radiations with a
frequency ranging between 300 MHz to 300 GHz. In contrast, the
wavelength ranges from 1 mm to around 30 cm. Microwave radiation
is commonly referred to as microwaves. They fall between infrared
radiation and radio waves in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Properties of Microwave
Microwaves are reflected by metal surfaces.
They pass through glass and plastics.
They can pass through the atmosphere. …
Water absorbs a particular frequency of microwaves. …
Microwave transmission is affected by wave effects like reflection, refraction,
diffraction, and interference.
Uses
The uses of the microwave are similar to that of radio waves.
They are used in communications, radio astronomy, remote
sensing, radar, and of course, owing to their heating
application, they are used in cooking as well.
Microwaves are used in spacecraft communication, and
much of the world’s data, TV, and telephone
communications are transmitted long distances by
microwaves between ground stations and
communications satellites. Microwaves are also employed in microwave ovens and in radar
technology.
Description
Infrared radiation (IR), sometimes referred to simply as infrared, is a region of
the electromagnetic radiation spectrum where
wavelengths range from about 700 nanometers (nm)
to 1 millimeter (mm). Infrared waves are longer than
those of visible light, but shorter than those of radio
waves.
Infrared waves, or infrared light, are part of the
electromagnetic spectrum. People encounter Infrared
waves every day; the human eye cannot see it, but
humans can detect it as heat. A remote control uses
light waves just beyond the visible spectrum of light—infrared light waves—to
change channels on your TV.
Characteristics
The origin is from an alteration in electron movement. Wavelength range from
710 nm to 1 mm. Frequency range from 430 THz to 300 GHz. Infrared radiation
is a Transverse wave.
Uses
Infrared is used in a variety of applications.
Among the most well-known are heat sensors,
thermal imaging and night vision equipment.
In communications and networking, infrared
light is used in wired and wireless operations.
Around 1800, the German-born British-
astronomer William Herschel discovered
infrared radiation. He did so with a simple
experiment in which he dispersed sunlight
through a prism and placed a thermometer at
the location of each color.
Frederick William Herschel
Description
Visible light waves are the only wavelengths of the
electromagnetic spectrum that humans can see. The
different wavelengths of visible light are seen as the colors of
the rainbow: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and
violet.
The visible light spectrum is the segment of the
electromagnetic spectrum that the human eye can view.
More simply, this range of wavelengths is called visible light.
Typically, the human eye can detect wavelengths from 380
to 700 nanometers.
Uses
Visible light is the light we can see, so is used in photography and illumination. It is
also used in fibre optic communications, where coded pulses of light travel through
glass fibres from a source to a receiver.
The 3 uses of visible light are fibre optic communications, photography, and
electronic devices.
Newton’s Rainbow. In the 1660s, English physicist and mathematician Isaac
Newton began a series of experiments with sunlight and prisms. He
demonstrated that clear white light was composed of seven visible colors.
Perhaps the most important characteristic of
visible light is color. Color is both an inherent
property of light and an artifact of the cells in
the human eye. Objects don’t “have” color,
according to The Physics Hypertextbook
Description
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a form of non-
ionizing radiation that is emitted by the
sun and artificial sources, such as tanning
beds. While it has some benefits for
people, including the creation of Vitamin
D, it also can cause health risks. Our
natural source of UV radiation: The sun.
Characteristics
Ultraviolet (UV) light is a type of electromagnetic radiation
that has shorter wavelengths than visible light. This means
that UV light has a higher frequency than visible light. It is categorized as electromagnetic radiation with
wavelengths between 10 and 400 nanometers (nm).
Uses
UV radiation is widely used in industrial processes and in
medical and dental practices for a variety of purposes, such as
killing bacteria, creating fluorescent effects, curing inks and
resins, phototherapy and suntanning. Different UV wavelengths
and intensities are used for different purposes.
On 22 February 1801, Johann Wilhelm Ritter discovered UV radiation in
Jena. In general, this achievement is less well known than his work on
galvanism. Ritter was the creator of modern electrochemistry.
Description
X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, similar to visible light. Unlike light,
however, x-rays have higher energy and can pass through most objects, including the
body. Medical x-rays are used to generate images of tissues and structures inside the
body.
X-rays are high-frequency, and thus high-energy, electromagnetic radiation. They have
wavelengths ranging from 0.01 to 10 nanometres, and thus frequencies from 3×1019
to 3×1016 Hz. They are found to reside between ultraviolet radiation and gamma rays
on the electromagnetic spectrum
Properties of X-Rays
They have a shorter wavelength of the electromagnetic spectrum. Requires high voltage to produce X-
Rays. They are used to capture the human skeleton defects. They travel in a straight line and do not carry
an electric charge with them.
Uses
X-ray radiography: Detects bone fractures, certain tumors and
other abnormal masses, pneumonia, some types of injuries,
calcifications, foreign objects, or dental problems.
X-rays are not only used to form diagnoses but also to help with
treatment, check on progression of a condition or injury, and to
assess progress following treatment.
Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen reported the discovery of X-rays in December 1895
after seven weeks of assiduous work during which he had studied the
properties of this new type of radiation able to go through screens of notable
thickness. He named them X-rays to underline the fact that their nature was
unknown.
Description
A gamma ray is electromagnetic radiation of the shortest
wavelength and highest energy. Gamma-ray radiation has
wavelengths generally smaller than a few tenths of an
angstrom (10−10 meter), and gamma-ray photons have
energies greater than tens of thousands of electron volts.
Gamma rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation
that results from a redistribution of electric charge
within a nucleus. Gamma rays are essentially very
energetic X rays ; the distinction between the two is not
based on their intrinsic nature but rather on their
origins.
Characteristics of Gamma Rays
They have the shortest wavelength among the electromagnetic spectrum, with a
wavelength no shorter than 0.01 nanometer or 10 picometers. They have the highest
frequencies among the electromagnetic spectrum. Gamma frequency is commonly
greater than 1019 Hz.
Uses
Gamma rays are ionizing electromagnetic
radiation, obtained by the decay of an atomic
nucleus. Gamma rays are more penetrating,
in matter, and can damage living cells to a
great extent. Gamma rays are used in
medicine (radiotherapy), industry
(sterilization and disinfection) and the
nuclear industry.
Sterilize medical equipment.
Sterilize food (irradiated food)
Used as tracers in medicine.
French chemist Paul Villard first identified gamma rays in 1900 from the
element radium, which had been isolated by Marie and Pierre Curie just two
years before.
You might also like
- EM WavesDocument2 pagesEM WavesMyyo TabunoNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattDocument21 pagesUnit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10: Types-and-Applications-of-EM-wavesDocument32 pagesSCIENCE 10: Types-and-Applications-of-EM-wavesInsigne HarietteNo ratings yet
- What Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Document11 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Rodrigo SeriozaNo ratings yet
- What Are Electromagnetic Waves?Document8 pagesWhat Are Electromagnetic Waves?Jay Marie OcampoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumTanish100% (1)
- General Informatio NDocument15 pagesGeneral Informatio NJenny RoblesNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves 2023Document6 pagesElectromagnetic Waves 2023llindoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Wave HandoutDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic Wave HandoutARLENE POMBONo ratings yet
- 7 Types of Electromagnetic WavesDocument6 pages7 Types of Electromagnetic WavesAbigail Domingo100% (1)
- Electromagnetic RadiationDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic RadiationAyman BashirNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic SpectrumDocument6 pagesElectro Magnetic SpectrumarhamNo ratings yet
- Module 8 PhysicsDocument7 pagesModule 8 PhysicsLopez AeraNo ratings yet
- Name Wavelength : Gamma Ray E KeDocument3 pagesName Wavelength : Gamma Ray E KeJose Andrei Dalisay PagsinohinNo ratings yet
- Spectrum) of Electromagnetic Radiation and Their RespectiveDocument10 pagesSpectrum) of Electromagnetic Radiation and Their RespectiveJabez Edwin SivaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument5 pagesScienceAriana LaynoNo ratings yet
- (51014) Javier Prelab6Document2 pages(51014) Javier Prelab6Jesse JavierNo ratings yet
- Science Report Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument24 pagesScience Report Electromagnetic SpectrumJedí BelanoNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document13 pagesScience 10Joel De LeonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EM SpectrumDocument8 pagesIntroduction To EM SpectrumKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- Copy 2nd QuarterDocument30 pagesCopy 2nd QuarterLiwayway MadaliNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes No. 19 Regions of The Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio WavesDocument4 pagesConcept Notes No. 19 Regions of The Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio WavesLunaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumAndres GalarragaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation Frequency Wavelength Speed of Light Photon SpectrumDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation Frequency Wavelength Speed of Light Photon SpectrumFOODHEALTHNo ratings yet
- Waves in The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument13 pagesWaves in The Electromagnetic SpectrumD AngelaNo ratings yet
- Elctronic RadiationDocument4 pagesElctronic RadiationTia WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Microwaves - Can Penetrate The Atmosphere ofDocument2 pagesMicrowaves - Can Penetrate The Atmosphere ofSpade WattpadNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Module 1Document20 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 1Ma'am LeiNo ratings yet
- 7 Types of Electromagnetic WavesDocument2 pages7 Types of Electromagnetic Wavesvee propaganda100% (1)
- Physics1101 - Course MaterialDocument332 pagesPhysics1101 - Course MaterialAhmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Radio WavesDocument4 pagesRadio WavesSophia Nicole ZaraNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum: Juan Carlos Isaza Jacome Byron Cubides Romero Duvan Reyes SaenzDocument20 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum: Juan Carlos Isaza Jacome Byron Cubides Romero Duvan Reyes SaenzJuan Carlos Isaza JacomeNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument13 pages3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumMadiha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WaveDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic WavewerewolfNo ratings yet
- How Radiation Works: Light Radio)Document2 pagesHow Radiation Works: Light Radio)NabilaPutriClpdhiNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 1Document15 pagesScience Reviewer 1Symon MarianoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument43 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumxunxhineNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document38 pagesScience 10Angelo LiwanagNo ratings yet
- Science 10 SECOND QuarterDocument152 pagesScience 10 SECOND QuarterAPPLE GRACE MARIE SEBASTIAN100% (1)
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrummuddasarhussain739No ratings yet
- Science Reviewer q2Document6 pagesScience Reviewer q2Samuel IdoNo ratings yet
- Team Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksDocument12 pagesTeam Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksJOHN ASHLEY RANIN CARIAGANo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum FormsDocument32 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum FormsRuih PadillaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Electromagnetic WavesDocument10 pagesPhysics: Electromagnetic WavesBen Hemert G. Jumao-asNo ratings yet
- Inbound 4743556798129293898Document8 pagesInbound 4743556798129293898Samantha GabrielNo ratings yet
- Physics: Electromagnetic WavesDocument11 pagesPhysics: Electromagnetic WavesBen Hemert G. Jumao-asNo ratings yet
- Alison ProjectDocument8 pagesAlison Projectjalefaye abapoNo ratings yet
- The Application of Electromagnetic WavesDocument6 pagesThe Application of Electromagnetic WaveszeromanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument54 pagesElectromagnetic WavesPortia A. EgkenNo ratings yet
- Blue Red and Yellow Illustrative Science Electromagnetic Radiation Educational PresentationDocument26 pagesBlue Red and Yellow Illustrative Science Electromagnetic Radiation Educational PresentationAsma AmpangNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument8 pagesScienceapi-398255504No ratings yet
- Applications of MicrowavesDocument6 pagesApplications of MicrowavesorculloNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjektDocument12 pagesPhysics Projektrupendrajain20No ratings yet
- C12 Electromagnetic WavesDocument48 pagesC12 Electromagnetic WavesRosemarie Cabanilla50% (2)
- Electromagnetic Spectrum and BandwidthDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum and BandwidthJennybabe NapolesNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument33 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and The Electromagnetic SpectrumDanae Forrester100% (1)
- EM Waves - UPHDocument20 pagesEM Waves - UPHSHIVA THAVANI100% (1)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument27 pagesElectromagnetic WavesKatrinaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q2W3-4Document15 pagesScience 10 - Q2W3-4quackity obamaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 2Document4 pagesTutorial Chapter 2batrisyaNo ratings yet
- CP Phys CH 2 Web RevDocument8 pagesCP Phys CH 2 Web RevMichelle MuliawidjajaNo ratings yet
- CAPE Physics Workshop Workbook 2021 - Unit 1Document41 pagesCAPE Physics Workshop Workbook 2021 - Unit 1Kenya LevyNo ratings yet
- Use The Passage To Answer Questions 4 - 5Document4 pagesUse The Passage To Answer Questions 4 - 5Melvin CabonegroNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Performance Flight TestingDocument284 pagesAircraft Performance Flight TestingIoannis PerperisNo ratings yet
- Linearized Dynamics Equations For The Balance and Steer of A Bicycle: A Benchmark and ReviewDocument63 pagesLinearized Dynamics Equations For The Balance and Steer of A Bicycle: A Benchmark and ReviewVictor MagriNo ratings yet
- Yousefi Saleh2015 Article Three DimensionalSuctionFlowCoDocument14 pagesYousefi Saleh2015 Article Three DimensionalSuctionFlowCoasdasddasNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic MotionDocument18 pagesSimple Harmonic Motionieja03100% (2)
- CH 12 Physics AnswersDocument21 pagesCH 12 Physics AnswersSam Likes HamNo ratings yet
- Sound PDFDocument4 pagesSound PDFNgoc Vũ TrầnNo ratings yet
- Module IVDocument25 pagesModule IVVinay KashyapNo ratings yet
- Clicker Questions For Vectors 1Document7 pagesClicker Questions For Vectors 1Gersson Alejandro LoperaNo ratings yet
- Motion, Speed, Acceleration, Velocity, and ForceDocument26 pagesMotion, Speed, Acceleration, Velocity, and ForceKersy Mere FajardoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Explainer - Velocity - NagwaDocument34 pagesLesson Explainer - Velocity - NagwaMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- All About TrigonometryDocument13 pagesAll About TrigonometryAhmad100% (1)
- Sheet (5) - Dynamics PDFDocument2 pagesSheet (5) - Dynamics PDFahmedmohammeda829No ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument4 pagesKinema Ticssheden0320No ratings yet
- Ripamonti Folleto PDFDocument4 pagesRipamonti Folleto PDFDavid CarrilloNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Aqwa Suite Articulations & ANSYS Aqwa Suite Articulations & Multi-Body Multi-Body Problems ProblemsDocument9 pagesANSYS Aqwa Suite Articulations & ANSYS Aqwa Suite Articulations & Multi-Body Multi-Body Problems ProblemsPatrick SilvaNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 8 and 15 Electromagnetic Waves and Communicationommunication SystemsystemsDocument13 pagesPhysics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 8 and 15 Electromagnetic Waves and Communicationommunication SystemsystemsJaseela NaufalNo ratings yet
- Vector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics: Distributed Forces: Moments of InertiaDocument19 pagesVector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics: Distributed Forces: Moments of InertiaMamdouh GhzawiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Fluid Flow in PipesDocument42 pagesLecture 6 - Fluid Flow in PipesPercival ArcherNo ratings yet
- Sph3u - Quiz 4 - Review - SolutionsDocument6 pagesSph3u - Quiz 4 - Review - Solutionsapi-601648218No ratings yet
- Vehicle Dynamics Session 3 Tire Fundamental Characteristics and Dynamic PerformanceDocument36 pagesVehicle Dynamics Session 3 Tire Fundamental Characteristics and Dynamic PerformanceHarish SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Vibration Measurement EquipmentsDocument19 pagesVibration Measurement EquipmentsReyvel MugarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document41 pagesLecture 14Boyi EnebinelsonNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engines: Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of LagosDocument4 pagesThermal Engines: Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of LagosSaheed LawansonNo ratings yet
- CE222 Problem Set 1Document6 pagesCE222 Problem Set 1Mehmet ArasNo ratings yet
- Ship Hydrodynamics - Lecture - Notes - Part - 8 - Propeller - TestsDocument12 pagesShip Hydrodynamics - Lecture - Notes - Part - 8 - Propeller - TestsOdpewğw RlelelwNo ratings yet
- Modeling of A Three-Axes MEMS Gyroscope With Feedforward PI Quadrature CompensationDocument10 pagesModeling of A Three-Axes MEMS Gyroscope With Feedforward PI Quadrature CompensationDavide MaranoNo ratings yet