Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes - Respiration in Organisms
Notes - Respiration in Organisms
Uploaded by
Divyanshi BansalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes - Respiration in Organisms
Notes - Respiration in Organisms
Uploaded by
Divyanshi BansalCopyright:
Available Formats
NOTES – RESPIRATION IN
ORGANISMS
CELL: All organisms are made of small, microscopic units called CELLS.
A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism. Each
cell of an organism performs different tasks: nutrition, transport, excretion
and reproduction.
The increase in the supply of oxygen results in the complete breakdown of
lactic acid into carbon dioxide and water.
BREATHING RATE: On an average an adult human being breathes about
15-18 times in a minute. During, heavy exercise breathing rate can extend
up to 25 times per minute.
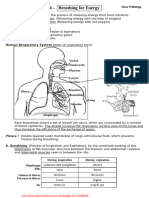
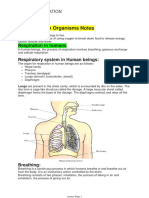
BREATHING PROCESS:
INHALATION -> NASAL CAVITY -> LUNGS (PRESENT IN THE
CHEST CAVITY AND IT IS SURROUNDED BY RIBS ON BOTH SIDES)
-> DIAPHRAGM (FORMS THE FLOOR OF CHEST CAVITY)
BREATHE FOR BETTER LIFE:
Regular traditional breathing exercise can increase the capacity of lungs to
take in more air. Thus, more oxygen can be supplied to the body cells
resulting in release of more energy.
INHALED AIR: 21% OXYGEN, 0.04% CARBON DIOXIDE
EXHALED AIR: 16.4% OXYGEN, 4.4% CARBON DIOXIDE
COCKROACH:
It has small openings on the sides of the body called spiracles.
They have a network of air tubes called trachea for the exchange of
gases.
INHALATION: Oxygen -> spiracles -> tracheal tubes -> diffuses into
body tissue -> every cell of the body
EXHALATION: Carbon Dioxide from cell-> tracheal tubes-> spiracles ->
atmosphere.
You might also like
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument9 pagesRespiration in Organismsshreya kashyapNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument7 pagesRespiration NotesTamisha JacobsNo ratings yet
- Bio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .Document21 pagesBio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .naazim mohamedNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Document19 pagesAnimal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Abhishek Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Notebook Work Respiration in OrganismsDocument4 pagesNotebook Work Respiration in OrganismsachlaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 (A) Human and Social BiologyDocument4 pagesWeek 7 (A) Human and Social BiologyBeyonce SkekelNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument5 pagesRespirationDivyansh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - RespirationDocument22 pagesLife Processes - RespirationraghavrungtambwaNo ratings yet
- MLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDocument4 pagesMLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDivyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- Bio Form 4 Chap 7Document15 pagesBio Form 4 Chap 7Lim Hong ShengNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument3 pagesRespiration in Organismschrisbronzel56No ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument36 pagesRESPIRATIONnyemarichardssvgNo ratings yet
- What Is Respiration?Document8 pagesWhat Is Respiration?Waleed Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Bio NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 11 Bio NotesArabella ShepherdNo ratings yet
- Sheniblog-Class 9 Biology Chapter 4 (Eng Med) NotesDocument3 pagesSheniblog-Class 9 Biology Chapter 4 (Eng Med) Notesdevu fav MohanNo ratings yet
- Human and Social Biology The Respiratory System 10 1 and 2Document35 pagesHuman and Social Biology The Respiratory System 10 1 and 2Science,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Respiration and BreathingDocument57 pagesRespiration and BreathingHarvagale BlakeNo ratings yet
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4edain84No ratings yet
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Faida Hamid87% (23)
- Class 7 RespirationDocument5 pagesClass 7 RespirationGopi SNo ratings yet
- Grade X Biology Ch-5 Notes-3 RespirationDocument8 pagesGrade X Biology Ch-5 Notes-3 Respirationreshma.dhairyasinghNo ratings yet
- B7-CBSE-Respiration in OrganismDocument29 pagesB7-CBSE-Respiration in OrganismSwyamjeet PradhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Exercise Question and AnswersDocument5 pagesChapter 8 Exercise Question and AnswersPooja AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Spyros Filippas A4 Biology Term ProjectDocument12 pagesSpyros Filippas A4 Biology Term Projectpipis pipasNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Human Respiratory SystemWei Ling KuahNo ratings yet
- Biology 11 BODY SYSTEMSDocument13 pagesBiology 11 BODY SYSTEMSkatwal09No ratings yet
- Respiratory System of Frog: External RespirationDocument3 pagesRespiratory System of Frog: External RespirationShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument7 pagesRespiration in Organismschristopher thomasNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.3 - Human Respiratory SystemDocument29 pagesTopic 2.3 - Human Respiratory Systembienfrancis.reyes.jhsNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument17 pagesRespiration in OrganismsSaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument35 pagesRespirationnabeeha malhiNo ratings yet
- L - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkDocument7 pagesL - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkNotImmortalNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument11 pagesRESPIRATIONCREATIVING TAMILANNo ratings yet
- Respiration HandoutDocument4 pagesRespiration Handoutkiran2000tripathiNo ratings yet
- Respiration Science AssessmentDocument19 pagesRespiration Science Assessmentmarta.amsNo ratings yet
- Lec 17 Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesLec 17 Circulatory SystemEnmuskNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System-11 By:-Dr. Hazim AL-RawiDocument12 pagesThe Respiratory System-11 By:-Dr. Hazim AL-RawiDrAli Al-FendiNo ratings yet
- E Book Bio English 03Document42 pagesE Book Bio English 03sanjNo ratings yet
- Notes RespirationDocument6 pagesNotes Respirationakheel7353No ratings yet
- Biology - Respiration & The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesBiology - Respiration & The Respiratory SystemMegan TaylorNo ratings yet
- DoydoyDocument3 pagesDoydoyAngie ZayasNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument6 pagesRespiration in OrganismsAdityaNo ratings yet
- Lec-18 - Respiratory & Excretory SystemDocument23 pagesLec-18 - Respiratory & Excretory Systemfahadkhanbd911No ratings yet
- G7 ScienceDocument27 pagesG7 Scienceranjan.kvisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 1 NotesLim Zhi EnNo ratings yet
- Breathing and RespirationDocument30 pagesBreathing and Respirationhamzahazard527No ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From SUPERCOPDocument8 pagesMaterial Downloaded From SUPERCOPfast-track for n2021No ratings yet
- 1r3ntvbfve - Ipa Kelas 8 Bab 9Document19 pages1r3ntvbfve - Ipa Kelas 8 Bab 9aulyamaltha.2008No ratings yet
- Respiratory System in Human BeingsDocument11 pagesRespiratory System in Human BeingsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Biology GCE Study BuddyDocument45 pagesRespiration: Biology GCE Study BuddyMaleeha HumayunNo ratings yet
- Breathing & RespirationDocument81 pagesBreathing & RespirationGreta SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Respiration: - Respiration Is The Release of Energy From Food Substances in All Living CellsDocument8 pagesRespiration: - Respiration Is The Release of Energy From Food Substances in All Living CellsMandla RebirthNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument24 pagesRespiration and Gas ExchangeEizelle100% (2)
- Life Processes (Respiration)Document2 pagesLife Processes (Respiration)Farid AhemadNo ratings yet
- Life Process RespirationDocument51 pagesLife Process RespirationJatin Kalra 10 DNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System NotesDocument4 pagesRespiratory System NotesFlare FlareonNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesThe Respiratory SystemmvslikavNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Img 1578Document24 pagesImg 1578Divyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- Email WritingDocument9 pagesEmail WritingDivyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- NOTES - Nutrion in PlantsDocument1 pageNOTES - Nutrion in PlantsDivyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- Math Mock Paper, 2023-24 Objective Paper Class - 7 Term - 1 (2023 - 24)Document6 pagesMath Mock Paper, 2023-24 Objective Paper Class - 7 Term - 1 (2023 - 24)Divyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- Notebook Work How State Govt. Works - 2023-24Document2 pagesNotebook Work How State Govt. Works - 2023-24Divyanshi BansalNo ratings yet