Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Soil Mechanics
Soil Mechanics
Uploaded by
Jennifer Rebadeo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageSoil mechanics is the study of physical properties of soil and its engineering applications. Geotechnical engineering applies principles of soil mechanics to solve practical problems involving natural materials found near the Earth's surface, such as soil. Key goals are ensuring safe structures with minimal settling or collapse. Some important soil types include silt, granular soils, and cohesive soils. Particle size analysis methods like sieve analysis and hydrometer analysis are used to characterize soils. Important soil properties include void ratio, porosity, saturation, moisture content, unit weight, and relative density.
Original Description:
Soil Mechanics Lecture Notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSoil mechanics is the study of physical properties of soil and its engineering applications. Geotechnical engineering applies principles of soil mechanics to solve practical problems involving natural materials found near the Earth's surface, such as soil. Key goals are ensuring safe structures with minimal settling or collapse. Some important soil types include silt, granular soils, and cohesive soils. Particle size analysis methods like sieve analysis and hydrometer analysis are used to characterize soils. Important soil properties include void ratio, porosity, saturation, moisture content, unit weight, and relative density.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageSoil Mechanics
Soil Mechanics
Uploaded by
Jennifer RebadeoSoil mechanics is the study of physical properties of soil and its engineering applications. Geotechnical engineering applies principles of soil mechanics to solve practical problems involving natural materials found near the Earth's surface, such as soil. Key goals are ensuring safe structures with minimal settling or collapse. Some important soil types include silt, granular soils, and cohesive soils. Particle size analysis methods like sieve analysis and hydrometer analysis are used to characterize soils. Important soil properties include void ratio, porosity, saturation, moisture content, unit weight, and relative density.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
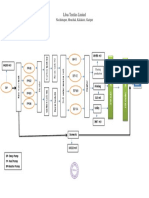
Soil mechanics study of the physical properties of Silt – microscopic fraction that consist of very fine
soil quarts grains and fragments of micaceous minerals.
Soils engineering is the application of the principles Granular soils- Exhibiting large bearing capacities
of soil mechanics to practical problems. and
Geotechnical engineering is the subdiscipline of experiencing relatively small settlements
civil engineering that involves natural materials
Cohesive soils -They tend to have lower shear
found close to the surface of the earth.
strength. They can be plastic and compressible.
Soil- uncemented aggregate of mineral grains and
decaying organic matter 1. Sieve Analysis
to ensure a safe structure free from unduesettling • For particle sizes larger than 0.075 mm in diameter
and/or collapse.
2. Hydrometer Analysis
Karl Terzaghi Presided the first conference of the
• For particle sizes smaller than 0.075 mm in
International Society of Soil Mechanics and diameter
Foundation
Engineering (ISSMFE) in 1936 at Harvard University
A given volume of soil in natural occurrence consists
Igneous rocks - Formed by solidification of molten of solid particles and the void spaces between the
magma particles.
Sedimentary rocks- Formed by the accumulated If the entire void space is filled with water, it is
deposit of soil particles referred to as a saturated soil.
Metamorphic rocks - Formed by the process of However, if the void is partially filled with water, it
changing the composition and texture of rocks is a moist soil.
1. Mechanical (physical) weathering Void Ratio (e) is defined as the ratio of the volume
of voids to the volume of solids. It is expressed in
• Caused by the expansion or contraction of rocks
decimals.
from which the continuous gain and loss of heat
Porosity (n) is defined as the ratio of the volume of
2. Chemical weathering
voids to the total volume of the soil aggregate.
• The original rock minerals are transformed into
Degree of Saturation (S), in %, is defined as the ratio
new minerals by chemical reaction.
of the volume of water to the volume of voids
An important characteristic of residual soil is the
Moisture Content ( w), also referred to as water
gradation of particle size.
content, is defined as the ratio of the weight of
transported soil, regardless of the agent that water to the weight of solids in a given volume of
performed the transportation soil
Cohesionless – particles do not tend to stick Unit weight (γ), also called moist unit weight, is the
together weight of soil per unit volume
Cohesive – characterized by very small particle size Dry unit weight (γd) is the weight of soil solid per
where surface chemical effects predominate. unit volume
Organic – typically spongy, crumble, and Relative density – commonly used to indicate the in
compressible. situ denseness and looseness of granular soil.
You might also like
- Project Muhammad SahabiDocument56 pagesProject Muhammad SahabiAbdullahi MuhammadNo ratings yet
- The Ice Age - A Very Short IntroductionDocument201 pagesThe Ice Age - A Very Short IntroductionElena María Hernández Medinilla100% (2)
- Physical Characteristics of Soils: Chapter TwoDocument63 pagesPhysical Characteristics of Soils: Chapter TwoMinilik Tikur SewNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument16 pages1 IntroductionelafsweeddNo ratings yet
- Ceng 401-Lecture #1 - Introduction-Review of Soil Mechanics - 034400-1Document5 pagesCeng 401-Lecture #1 - Introduction-Review of Soil Mechanics - 034400-1Haphiz JusuNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document45 pagesModule 1carldomingoNo ratings yet
- File13572 PDFDocument52 pagesFile13572 PDFZhwan AnwarNo ratings yet
- 2-Physical Characterstics of SoilDocument14 pages2-Physical Characterstics of SoilleeNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering-I: As Per KTU SyllabusDocument68 pagesGeotechnical Engineering-I: As Per KTU SyllabusshahzilezNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Lecture 2Document8 pagesCH-2 Lecture 2Daniel SolomonNo ratings yet
- Prelim Notes 1Document7 pagesPrelim Notes 1Umyfp IsdNo ratings yet
- Soil I Lecture 2Document6 pagesSoil I Lecture 2hadushNo ratings yet
- Soil 2Document30 pagesSoil 2Usman PervaizNo ratings yet
- Description and Classification of Soils: Instructor: Associate Prof. Ts. Dr. Mohamad Yusri AmanDocument92 pagesDescription and Classification of Soils: Instructor: Associate Prof. Ts. Dr. Mohamad Yusri Amanfuad haziqNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics NotesDocument20 pagesSoil Mechanics Notessandeep singhNo ratings yet
- Soil, Plant, Water RelationshipDocument3 pagesSoil, Plant, Water RelationshipLADY MARIELLE GAYOSANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document11 pagesChapter 1Fenta NebiyouNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Soil Mechanics and Types of SoilsDocument19 pages1.introduction To Soil Mechanics and Types of SoilsMehboob KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23Document32 pagesChapter 23Barnababas BeyeneNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics - I: Department of Civil EngineeringDocument60 pagesSoil Mechanics - I: Department of Civil EngineeringAman JainNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No. 01 - TribunaloDocument7 pagesProblem Set No. 01 - TribunaloLormelyn TribunaloNo ratings yet
- Soil Chapter - OneDocument5 pagesSoil Chapter - OneebirahimmusanNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics JottingDocument23 pagesSoil Mechanics JottingKunbi Santos-ArinzeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1&2-Origin and Simple Soil Properties PDFDocument48 pagesChapter 1&2-Origin and Simple Soil Properties PDFMeski TayeNo ratings yet
- 1 Geological Formation of Soils and TypesDocument48 pages1 Geological Formation of Soils and TypesMuaz HararNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics I-1Document48 pagesSoil Mechanics I-1yonatanNo ratings yet
- Soil Science MergeDocument135 pagesSoil Science MergeSajeebChandraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SWPRDocument16 pagesChapter 2 SWPRdereje werkuNo ratings yet
- Soil MechanicsDocument18 pagesSoil MechanicsGV Rama Subba RaoNo ratings yet
- Soil MechanicsDocument119 pagesSoil MechanicsDoan Duy Thinh100% (3)
- Soil Mechanics IntroductionDocument24 pagesSoil Mechanics IntroductionKenyi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- المستندDocument5 pagesالمستندoo625253No ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics-2017Document20 pagesSoil Mechanics-2017Beethovengg BeethovenggNo ratings yet
- ECE 301 Soil Mechanics IDocument24 pagesECE 301 Soil Mechanics IDanielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SWP P PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 2 SWP P PDFShita AlemieNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Lecture NotesDocument61 pagesSoil Mechanics Lecture NotesDias Bakhtiyarov75% (4)
- CN 301 Chapter 2Document50 pagesCN 301 Chapter 2Ahmed Badr MabroukNo ratings yet
- Unit I Soil Properties: Soil Mechanics Is A Discipline of Civil Engineering Involving The Study of Soil, ItsDocument77 pagesUnit I Soil Properties: Soil Mechanics Is A Discipline of Civil Engineering Involving The Study of Soil, ItsArun ECENo ratings yet
- 3-Module Iii-Soil PropertiesDocument13 pages3-Module Iii-Soil PropertiesTrazon Triestian Pedrera CardeñoNo ratings yet
- Soil Deposits and Grain Size AnalysisDocument23 pagesSoil Deposits and Grain Size AnalysisMary Lourielle0% (1)
- University of Gondar: Institutes of Technology Department of Civil EngineeringDocument43 pagesUniversity of Gondar: Institutes of Technology Department of Civil EngineeringnahomNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Assignment 1Document3 pagesSoil Mechanics Assignment 1rish02kumarNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Soil Mechanics-I: Lecture Two Physical Characteristics of SoilsDocument9 pagesCH-2 Soil Mechanics-I: Lecture Two Physical Characteristics of SoilsAbera Mamo JaletaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Geotchnical Engineering The Historical PerspectiveDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Geotchnical Engineering The Historical PerspectiveJohnfrey MarigzaNo ratings yet
- Pp-Soil Origin and DevelopmentDocument176 pagesPp-Soil Origin and DevelopmentNelzen GarayNo ratings yet
- Cement Bound Road Based MaterialsDocument133 pagesCement Bound Road Based MaterialsViviMoraRuizNo ratings yet
- Introduction - Soil Mechanics NotesDocument3 pagesIntroduction - Soil Mechanics NotesErika TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Irriagtion Sessional RE CE 1006 16-01-2020Document70 pagesIrriagtion Sessional RE CE 1006 16-01-2020arnob hridoy100% (3)
- Chapter - Two 2. Soil-Water-Plant RelationshipsDocument12 pagesChapter - Two 2. Soil-Water-Plant RelationshipsbulchaNo ratings yet
- Soil Physical Properties2020 LastDocument5 pagesSoil Physical Properties2020 LastKernisha AdamsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 SWP RelationshipDocument72 pagesChapter 4 SWP Relationshipyabsiradaniel930No ratings yet
- Sci 1304Document129 pagesSci 1304Hunegnaw AynalemNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 MINERAL AGGREGATESDocument10 pagesLesson 2 MINERAL AGGREGATESDeniell Kahlil Kyro GabonNo ratings yet
- The Nature of SoilsDocument96 pagesThe Nature of SoilsMohammed OumerNo ratings yet
- SoilDocument13 pagesSoilXDXDXDNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Notes (Gte-1)Document44 pagesUnit 1 Notes (Gte-1)Sri Gaja Govind Babu100% (1)
- File13572 PDFDocument66 pagesFile13572 PDFZhwan AnwarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 ToeflDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 ToeflSiti AisyahNo ratings yet
- Reading Text KuisDocument3 pagesReading Text KuisJhoni IskanNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers For Gis Interview: Que:What Is GIS?Document12 pagesQuestions and Answers For Gis Interview: Que:What Is GIS?shivlakhara144No ratings yet
- OlogeDocument9 pagesOlogealaniade94No ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument101 pagesEarth ScienceSoma Chakraborty100% (1)
- Abstracte - Conf Geoheritage 2018Document85 pagesAbstracte - Conf Geoheritage 2018Monica MacoveiNo ratings yet
- DEM and GIS-based Hypsometric Analysis To Study TectonicsDocument15 pagesDEM and GIS-based Hypsometric Analysis To Study TectonicsedihidayatNo ratings yet
- Horák-Terra Et Al 2020Document13 pagesHorák-Terra Et Al 2020Camila Mota MendesNo ratings yet
- Soal Pat Bahasa InggrisDocument7 pagesSoal Pat Bahasa Inggriskurnia valentinaNo ratings yet
- 1844 r0 Afcons Agra MetroDocument73 pages1844 r0 Afcons Agra MetrodebapriyoNo ratings yet
- Confined Unconfined AquiferDocument23 pagesConfined Unconfined Aquiferpranjal singhNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of ChinaDocument1 pageTopographic Map of ChinaHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- Resilient Farm & Homestead, Revised: TOCDocument2 pagesResilient Farm & Homestead, Revised: TOCChelsea Green Publishing100% (1)
- Water Flow Chart-July-22Document1 pageWater Flow Chart-July-22Faisal Sr. ExecutiveNo ratings yet
- Q2.6 Seafloor SpreadingDocument18 pagesQ2.6 Seafloor SpreadingJhon KyleNo ratings yet
- 10.water 13 00905Document35 pages10.water 13 00905WIta DeuterNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Revision Spreadsheet - EcologyDocument7 pagesIB Biology Revision Spreadsheet - Ecologypari meharunkarNo ratings yet
- Hickey-Vargas Et Al., 2016Document18 pagesHickey-Vargas Et Al., 2016Joel Arriagada CortesNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Skepticism For Busy PeopleDocument97 pagesGlobal Warming Skepticism For Busy PeoplefallaxtNo ratings yet
- 1 4 Sea Floor SpreadingDocument20 pages1 4 Sea Floor SpreadingNeil De Guzman100% (1)
- Accumulation of Microplastic On Shorelines Worldwide-Sources and SinksDocument5 pagesAccumulation of Microplastic On Shorelines Worldwide-Sources and SinkslixiaoluhjNo ratings yet
- Iraq GeographyDocument121 pagesIraq Geographykusay.wheib kusay.wheibNo ratings yet
- Water Security KosovoDocument211 pagesWater Security KosovoJumbo SmithNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Sub-Soil Geotechnical PropertiesDocument9 pagesAssessment of Sub-Soil Geotechnical PropertiesDenis Akingbaso100% (1)
- Costa Rica - MPG - 2007 PDFDocument11 pagesCosta Rica - MPG - 2007 PDFEdward CuipaNo ratings yet
- G7Q4LAS1W1Document7 pagesG7Q4LAS1W1Hazel RecañaNo ratings yet
- Reference Fo DesignDocument19 pagesReference Fo DesignketemaNo ratings yet
- DCG5122 - Geodesy 1 - JUN16Document11 pagesDCG5122 - Geodesy 1 - JUN16mashitohNo ratings yet
- Air Masses MonsoonDocument14 pagesAir Masses MonsoonMikaelia NesbethNo ratings yet