Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson Acid-Base Equilibria
Lesson Acid-Base Equilibria
Uploaded by
VECNACopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Assignment 1 GRAD 2019Document4 pagesAssignment 1 GRAD 2019RamonErnestoICNo ratings yet
- Jack Westin MCAT Content General ChemistryDocument25 pagesJack Westin MCAT Content General ChemistryLora100% (1)
- DISA Parts and Services Catalogue 2019Document141 pagesDISA Parts and Services Catalogue 2019Yanto Daryanto100% (2)
- The Case of The Port of Antwerp PDFDocument11 pagesThe Case of The Port of Antwerp PDFCastilla CarlosNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal (Jkuat)Document108 pagesProject Proposal (Jkuat)Florian Osore86% (7)
- WiFi Function Manual of Charge Point-181030 PDFDocument16 pagesWiFi Function Manual of Charge Point-181030 PDFfreesonNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases PDFDocument2 pagesAcids and Bases PDFAnonymous qz4jWTNo ratings yet
- AcidDocument26 pagesAcidFarhan Sahariar Akondo OrvilNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Acids and BasesDocument4 pagesLesson 5: Acids and BasesBellay KaleesiyNo ratings yet
- Org and Inorg Chem 1ST Year MedtechDocument11 pagesOrg and Inorg Chem 1ST Year MedtechALEXANDRA MAE MAIPIDNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Acids and BasesDocument4 pagesUnit 4 - Acids and BasesbuchienjoyerNo ratings yet
- Chem 213 Module 5A-Aqueous Soln and Chemical EquilibriaDocument7 pagesChem 213 Module 5A-Aqueous Soln and Chemical EquilibriaNatalie GaidNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Acid Base Equilibria and Salt EquilibriaDocument11 pagesModule 6 Acid Base Equilibria and Salt EquilibriaaerizyphrNo ratings yet
- Bronsted-Lowry Acids and BasesDocument28 pagesBronsted-Lowry Acids and Basesreajustin13No ratings yet
- Chapter 16auDocument97 pagesChapter 16auShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Bacal ChempitDocument7 pagesBacal Chempit3J'sNet.Print 3J'sNo ratings yet
- CN 9Document59 pagesCN 9Shaira Jane AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Acids BasesDocument57 pagesAcids BasesJrtNo ratings yet
- Non-Aqueous TitrationsDocument40 pagesNon-Aqueous TitrationsAhmed Imran100% (2)
- AcidDocument5 pagesAcidSandraNo ratings yet
- Non Aqueous Titrations: Deokate U. ADocument26 pagesNon Aqueous Titrations: Deokate U. Aanon_68001775No ratings yet
- 1 ST Lecture Acia, Base and SaltDocument34 pages1 ST Lecture Acia, Base and Saltسارة صباح عيدان عليNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 4 - Module 2Document12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 4 - Module 2Jirah GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base ChemistryDocument12 pagesAcid-Base ChemistryNOBLEMANNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument25 pagesAcids and BasesKim SeungminNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document100 pagesChapter 16gycht672qdNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method: Jayson Nota Maria Angelica BalicocoDocument21 pagesScientific Method: Jayson Nota Maria Angelica BalicocoGrace Ann ArimadoNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmaceutical Chemistry 15Document108 pagesBasic Pharmaceutical Chemistry 15Gideon AntwiNo ratings yet
- CN 9Document73 pagesCN 9Shaira Jane AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 PPT 2Document108 pagesTopic 8 PPT 2rashadco786No ratings yet
- Acids BaseDocument31 pagesAcids BaseBharath M BNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM LAB - PH and BuffersDocument4 pagesBIOCHEM LAB - PH and BuffersLyanne SoNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base TheoryDocument2 pagesAcid and Base Theoryusulasia777No ratings yet
- Finals - Acid Base Equilibria: OutlineDocument17 pagesFinals - Acid Base Equilibria: OutlineJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Non-Aqueous Titrimetry AnalDocument29 pages4 - Non-Aqueous Titrimetry AnalMtw WondNo ratings yet
- Topic 8.1 IB ChemistryDocument36 pagesTopic 8.1 IB ChemistryFrank AlfanoNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base-Property-If-Water 1Document10 pagesAcid-Base-Property-If-Water 1Robelle Grace M. CulaNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument25 pagesAcid BaseMuhammad Yaser RayyanNo ratings yet
- PH and pOH ReviewerDocument7 pagesPH and pOH ReviewerFaller, Fiona Luie C.No ratings yet
- Bronsted-Lowry TheoryDocument2 pagesBronsted-Lowry TheoryNkosi JupiterNo ratings yet
- Bronsted-Lowry TheoryDocument2 pagesBronsted-Lowry TheoryNkosi JupiterNo ratings yet
- Bronsted-Lowry TheoryDocument2 pagesBronsted-Lowry TheoryNkosi JupiterNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument34 pagesAcids, Bases and SaltsV de VendettaNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument50 pagesAcids and BasesMimi G. TrosioNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Equilibria and Salt EquilibriaDocument11 pagesAcid Base Equilibria and Salt EquilibriaAMEER HANAFI JIKIRI. JUL-ASRINo ratings yet
- AQA 21 Acids Base and BuffersDocument16 pagesAQA 21 Acids Base and Buffersleonidas.wujieweiNo ratings yet
- Brønsted-Lowry Concept of Acids and Bases Chemistry 2 Grade 12 Sabuco Reniel M.Document26 pagesBrønsted-Lowry Concept of Acids and Bases Chemistry 2 Grade 12 Sabuco Reniel M.Niel SabucoNo ratings yet
- Anions, Although Few Cases of Cations Acting As: B + H BHDocument38 pagesAnions, Although Few Cases of Cations Acting As: B + H BHArei DizonNo ratings yet
- Acid and BasesDocument43 pagesAcid and BasesRobin TimkangNo ratings yet
- Am Topic 8 AnskeyDocument64 pagesAm Topic 8 Anskeyturtle42012No ratings yet
- Difference Between Acid and Base - Honeylyn ViejoDocument2 pagesDifference Between Acid and Base - Honeylyn ViejoJamaica SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Chem Lec 4 - TransesDocument7 pagesChem Lec 4 - TransesGelyn Marie LobresNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 (STEM) : Quarter 4 - Module 3 & 4Document9 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 (STEM) : Quarter 4 - Module 3 & 4Alexa ValdezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Inorganic ChemDocument27 pagesChapter 4-Inorganic ChemMark Harold GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Water PH Acid Base BufferDocument3 pagesWater PH Acid Base BufferMuhammad YaseenNo ratings yet
- محاضرة 6 (ن)Document22 pagesمحاضرة 6 (ن)انمي العراقNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibria 6B: Arrhenius Theory Bronsted-Lowry Theory Lewis TheoryDocument3 pagesIonic Equilibria 6B: Arrhenius Theory Bronsted-Lowry Theory Lewis TheoryTan Zhi JieNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Theories 1Document42 pagesAcid-Base Theories 1api-234133814No ratings yet
- Conjugate AcidDocument7 pagesConjugate AcidManP13No ratings yet
- GC2 Q4 L4stemDocument45 pagesGC2 Q4 L4stemeli candazaNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument15 pagesAcids and BasesNjabulo Ah AhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers - Week 10-11 - Electrolytes, Acid Base, PH and BufferDocument67 pagesChemistry For Engineers - Week 10-11 - Electrolytes, Acid Base, PH and Buffernttkim0201No ratings yet
- The Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Redhaired Mummies and Giants of The United StatesDocument7 pagesRedhaired Mummies and Giants of The United StatesMaria StancanNo ratings yet
- Pep - Monetary Policy (Final Term Report)Document21 pagesPep - Monetary Policy (Final Term Report)Fiza Abdul HameedNo ratings yet
- Job Description MatrixDocument1 pageJob Description Matrixkristenjohansen90% (10)
- Translating Humor in Dubbing and SubtitlingDocument8 pagesTranslating Humor in Dubbing and SubtitlingJane Hartnett0% (1)
- Compression Molding and Injection MoldDocument23 pagesCompression Molding and Injection MoldKodhansNo ratings yet
- Building Services Branch Testing and Commissioning ProcedureDocument211 pagesBuilding Services Branch Testing and Commissioning ProcedurePHYRAK100% (1)
- From Novice To Expert Theory - Lucille Alkhaldi BSN RNDocument11 pagesFrom Novice To Expert Theory - Lucille Alkhaldi BSN RNmaha_alkhaldi100% (1)
- Indium ISAFE OverviewDocument12 pagesIndium ISAFE OverviewShahinsha SNo ratings yet
- Weisman (1996) A Concept Analysis of EmpathyDocument7 pagesWeisman (1996) A Concept Analysis of EmpathyBenjamin Varas ArnelloNo ratings yet
- JutlandicDocument24 pagesJutlandicmorenojuanky3671No ratings yet
- Non-Local Consciousness and The Anthropo PDFDocument4 pagesNon-Local Consciousness and The Anthropo PDFtoffaloniNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in ScienceJesza May JuabanNo ratings yet
- Unification SensibilityDocument3 pagesUnification SensibilityAhsan LavaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications Petrucci 10th Edition Test BankDocument34 pagesGeneral Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications Petrucci 10th Edition Test Bankservantmerceryxfced100% (37)
- Renewable Energy Sources: A Laboratory Manual ForDocument22 pagesRenewable Energy Sources: A Laboratory Manual ForMadhupur PolytechnicNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Stuttering Foundations and Clinical Applications 0131573101Document24 pagesTest Bank For Stuttering Foundations and Clinical Applications 0131573101JimmyHaynessfmg100% (46)
- G10-2nd-Q-review Sheets-Chem-Chap7, 8.1, 8.2Document8 pagesG10-2nd-Q-review Sheets-Chem-Chap7, 8.1, 8.2Karim Ahmed100% (1)
- NPCIL Electronics PaperDocument9 pagesNPCIL Electronics Papernetcity143No ratings yet
- English 9thDocument1 pageEnglish 9thAlrayyan RashidNo ratings yet
- Creative Clothing TLPDocument11 pagesCreative Clothing TLPapi-245252207No ratings yet
- 5 MSHMS Course DescriptionsDocument1 page5 MSHMS Course DescriptionsJay BagayasNo ratings yet
- For Review OAPDocument144 pagesFor Review OAPKim John Rull NateNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Essential Cell Biology 4th Edition Bruce Alberts PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Essential Cell Biology 4th Edition Bruce Alberts PDF Full Chaptermilreis.cunettew2ncs100% (19)
- WWW Mytechnosoft Com Tibco Difference-between-bw5-And-bw6 PHPDocument3 pagesWWW Mytechnosoft Com Tibco Difference-between-bw5-And-bw6 PHPsabarin_72No ratings yet
- Nonverbal CommunicationDocument23 pagesNonverbal CommunicationNaman Agarwal100% (1)
Lesson Acid-Base Equilibria
Lesson Acid-Base Equilibria
Uploaded by
VECNAOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Acid-Base Equilibria
Lesson Acid-Base Equilibria
Uploaded by
VECNACopyright:
Available Formats
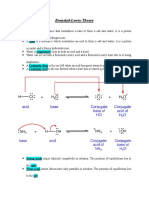
ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA
Acid Base
● Tastes sour ● Tastes bitter
● Cause dyes to ● Feel soapy
change color
Definition Acid Base
Arrhenius Increases [H⁺] when Increases [OH⁻]
dissolved in solution when dissolved in
solution
Bronsted- H⁺ donor H⁺ acceptor
Lowry
ARRHENIUS — it is acceptable to represent the proton in aqueous
solution as H⁺ or as H₃O⁺. the formula H⁺ is less
Acid Base cumbersome in calculations involving hydrogen ion
concentrations and in calculations involving equilibrium
● An acid is a ● A base is a constants, whereas H₃O⁺ is more useful in a discussion of
substance that, substance that, Brønsted acid-base properties.
when dissolved in when dissolved in
water, increases water, increases CONJUGATE ACIDS AND BASES
the concentration the concentration
of hydrogen ions of hydroxide ions ● In any acid-base equilibrium, both the forward
reaction (to the right) and the reverse reaction (to
the left) involve proton transfer
– the arrhenius concept of acids and bases, while useful, is
rather limited. For one thing, it is restricted to aqueous
solutions only.
BRONSTED-LOWRY — an acid and a base such as HA and A- that differ only in
the presence or absence of a proton are called a conjugate
Brønsted Acid Brønsted Base acid-base pair
● A substance that ● A substance that ● Two formula that differ by H⁺ are called a
donates a proton accepts a proton conjugate acid-base pair
(H⁺) (H⁺) ● Reactions between acids and bases always yield
their conjugate bases and acids
— their concept is based on the fact that acid-base reactions
involve the transfer of H⁺ ions from one substance to
another
WATER AS A PROTON ACCEPTOR
● When a hydrogen ion is formed in water, it does
not exist alone for long!
● H-bonds form with water forming hydronium ion
1 OUT OF [TOTAL PAGE NUMBER]
substance is one which can
both donate hydrogen ions
(protons) and also accept
them
All amphiprotic substances are also amphoteric.
Not all amphoteric are amphiprotic (there are amphoteric
substances which don’t either donate or accept hydrogen
ions when they act as acids or bases)
RELATIVE STRENGTHS OF ACIDS AND BASES AUTOIONIZATION OF WATER
● The stronger an acid, the weaker its conjugate base, ● Water is amphoteric
and ● In pure water, a few molecules act as bases an a
● The stronger the base, the weaker its conjugate few act as acids
acid. ● This is referred to as autoionization
WHAT IS DIFFERENT ABOUT WATER?
● Water can act as a Bronsted base and accept a
proton from an acid
● It can also donate a proton and act as an acid
● This makes water amphiprotic and amphoteric
○ An amphiprotic/amphoteric substance acts
as a base when combined with something
more strongly acidic that itself and as an
acid when combined with something more
strongly basic than itself
Amphiprotic Amphoteric
An amphiprotic (‘amphi’ - Amphoteric means that a
means both; ‘protic’ - substance has reactions as
refers to the proton) both acid and base
2 OUT OF [TOTAL PAGE NUMBER]
You might also like
- Assignment 1 GRAD 2019Document4 pagesAssignment 1 GRAD 2019RamonErnestoICNo ratings yet
- Jack Westin MCAT Content General ChemistryDocument25 pagesJack Westin MCAT Content General ChemistryLora100% (1)
- DISA Parts and Services Catalogue 2019Document141 pagesDISA Parts and Services Catalogue 2019Yanto Daryanto100% (2)
- The Case of The Port of Antwerp PDFDocument11 pagesThe Case of The Port of Antwerp PDFCastilla CarlosNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal (Jkuat)Document108 pagesProject Proposal (Jkuat)Florian Osore86% (7)
- WiFi Function Manual of Charge Point-181030 PDFDocument16 pagesWiFi Function Manual of Charge Point-181030 PDFfreesonNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases PDFDocument2 pagesAcids and Bases PDFAnonymous qz4jWTNo ratings yet
- AcidDocument26 pagesAcidFarhan Sahariar Akondo OrvilNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Acids and BasesDocument4 pagesLesson 5: Acids and BasesBellay KaleesiyNo ratings yet
- Org and Inorg Chem 1ST Year MedtechDocument11 pagesOrg and Inorg Chem 1ST Year MedtechALEXANDRA MAE MAIPIDNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Acids and BasesDocument4 pagesUnit 4 - Acids and BasesbuchienjoyerNo ratings yet
- Chem 213 Module 5A-Aqueous Soln and Chemical EquilibriaDocument7 pagesChem 213 Module 5A-Aqueous Soln and Chemical EquilibriaNatalie GaidNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Acid Base Equilibria and Salt EquilibriaDocument11 pagesModule 6 Acid Base Equilibria and Salt EquilibriaaerizyphrNo ratings yet
- Bronsted-Lowry Acids and BasesDocument28 pagesBronsted-Lowry Acids and Basesreajustin13No ratings yet
- Chapter 16auDocument97 pagesChapter 16auShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Bacal ChempitDocument7 pagesBacal Chempit3J'sNet.Print 3J'sNo ratings yet
- CN 9Document59 pagesCN 9Shaira Jane AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Acids BasesDocument57 pagesAcids BasesJrtNo ratings yet
- Non-Aqueous TitrationsDocument40 pagesNon-Aqueous TitrationsAhmed Imran100% (2)
- AcidDocument5 pagesAcidSandraNo ratings yet
- Non Aqueous Titrations: Deokate U. ADocument26 pagesNon Aqueous Titrations: Deokate U. Aanon_68001775No ratings yet
- 1 ST Lecture Acia, Base and SaltDocument34 pages1 ST Lecture Acia, Base and Saltسارة صباح عيدان عليNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 4 - Module 2Document12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 4 - Module 2Jirah GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base ChemistryDocument12 pagesAcid-Base ChemistryNOBLEMANNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument25 pagesAcids and BasesKim SeungminNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document100 pagesChapter 16gycht672qdNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method: Jayson Nota Maria Angelica BalicocoDocument21 pagesScientific Method: Jayson Nota Maria Angelica BalicocoGrace Ann ArimadoNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmaceutical Chemistry 15Document108 pagesBasic Pharmaceutical Chemistry 15Gideon AntwiNo ratings yet
- CN 9Document73 pagesCN 9Shaira Jane AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 PPT 2Document108 pagesTopic 8 PPT 2rashadco786No ratings yet
- Acids BaseDocument31 pagesAcids BaseBharath M BNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM LAB - PH and BuffersDocument4 pagesBIOCHEM LAB - PH and BuffersLyanne SoNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base TheoryDocument2 pagesAcid and Base Theoryusulasia777No ratings yet
- Finals - Acid Base Equilibria: OutlineDocument17 pagesFinals - Acid Base Equilibria: OutlineJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Non-Aqueous Titrimetry AnalDocument29 pages4 - Non-Aqueous Titrimetry AnalMtw WondNo ratings yet
- Topic 8.1 IB ChemistryDocument36 pagesTopic 8.1 IB ChemistryFrank AlfanoNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base-Property-If-Water 1Document10 pagesAcid-Base-Property-If-Water 1Robelle Grace M. CulaNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument25 pagesAcid BaseMuhammad Yaser RayyanNo ratings yet
- PH and pOH ReviewerDocument7 pagesPH and pOH ReviewerFaller, Fiona Luie C.No ratings yet
- Bronsted-Lowry TheoryDocument2 pagesBronsted-Lowry TheoryNkosi JupiterNo ratings yet
- Bronsted-Lowry TheoryDocument2 pagesBronsted-Lowry TheoryNkosi JupiterNo ratings yet
- Bronsted-Lowry TheoryDocument2 pagesBronsted-Lowry TheoryNkosi JupiterNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument34 pagesAcids, Bases and SaltsV de VendettaNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument50 pagesAcids and BasesMimi G. TrosioNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Equilibria and Salt EquilibriaDocument11 pagesAcid Base Equilibria and Salt EquilibriaAMEER HANAFI JIKIRI. JUL-ASRINo ratings yet
- AQA 21 Acids Base and BuffersDocument16 pagesAQA 21 Acids Base and Buffersleonidas.wujieweiNo ratings yet
- Brønsted-Lowry Concept of Acids and Bases Chemistry 2 Grade 12 Sabuco Reniel M.Document26 pagesBrønsted-Lowry Concept of Acids and Bases Chemistry 2 Grade 12 Sabuco Reniel M.Niel SabucoNo ratings yet
- Anions, Although Few Cases of Cations Acting As: B + H BHDocument38 pagesAnions, Although Few Cases of Cations Acting As: B + H BHArei DizonNo ratings yet
- Acid and BasesDocument43 pagesAcid and BasesRobin TimkangNo ratings yet
- Am Topic 8 AnskeyDocument64 pagesAm Topic 8 Anskeyturtle42012No ratings yet
- Difference Between Acid and Base - Honeylyn ViejoDocument2 pagesDifference Between Acid and Base - Honeylyn ViejoJamaica SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Chem Lec 4 - TransesDocument7 pagesChem Lec 4 - TransesGelyn Marie LobresNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 (STEM) : Quarter 4 - Module 3 & 4Document9 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 (STEM) : Quarter 4 - Module 3 & 4Alexa ValdezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Inorganic ChemDocument27 pagesChapter 4-Inorganic ChemMark Harold GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Water PH Acid Base BufferDocument3 pagesWater PH Acid Base BufferMuhammad YaseenNo ratings yet
- محاضرة 6 (ن)Document22 pagesمحاضرة 6 (ن)انمي العراقNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibria 6B: Arrhenius Theory Bronsted-Lowry Theory Lewis TheoryDocument3 pagesIonic Equilibria 6B: Arrhenius Theory Bronsted-Lowry Theory Lewis TheoryTan Zhi JieNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Theories 1Document42 pagesAcid-Base Theories 1api-234133814No ratings yet
- Conjugate AcidDocument7 pagesConjugate AcidManP13No ratings yet
- GC2 Q4 L4stemDocument45 pagesGC2 Q4 L4stemeli candazaNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument15 pagesAcids and BasesNjabulo Ah AhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers - Week 10-11 - Electrolytes, Acid Base, PH and BufferDocument67 pagesChemistry For Engineers - Week 10-11 - Electrolytes, Acid Base, PH and Buffernttkim0201No ratings yet
- The Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Redhaired Mummies and Giants of The United StatesDocument7 pagesRedhaired Mummies and Giants of The United StatesMaria StancanNo ratings yet
- Pep - Monetary Policy (Final Term Report)Document21 pagesPep - Monetary Policy (Final Term Report)Fiza Abdul HameedNo ratings yet
- Job Description MatrixDocument1 pageJob Description Matrixkristenjohansen90% (10)
- Translating Humor in Dubbing and SubtitlingDocument8 pagesTranslating Humor in Dubbing and SubtitlingJane Hartnett0% (1)
- Compression Molding and Injection MoldDocument23 pagesCompression Molding and Injection MoldKodhansNo ratings yet
- Building Services Branch Testing and Commissioning ProcedureDocument211 pagesBuilding Services Branch Testing and Commissioning ProcedurePHYRAK100% (1)
- From Novice To Expert Theory - Lucille Alkhaldi BSN RNDocument11 pagesFrom Novice To Expert Theory - Lucille Alkhaldi BSN RNmaha_alkhaldi100% (1)
- Indium ISAFE OverviewDocument12 pagesIndium ISAFE OverviewShahinsha SNo ratings yet
- Weisman (1996) A Concept Analysis of EmpathyDocument7 pagesWeisman (1996) A Concept Analysis of EmpathyBenjamin Varas ArnelloNo ratings yet
- JutlandicDocument24 pagesJutlandicmorenojuanky3671No ratings yet
- Non-Local Consciousness and The Anthropo PDFDocument4 pagesNon-Local Consciousness and The Anthropo PDFtoffaloniNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in ScienceJesza May JuabanNo ratings yet
- Unification SensibilityDocument3 pagesUnification SensibilityAhsan LavaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications Petrucci 10th Edition Test BankDocument34 pagesGeneral Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications Petrucci 10th Edition Test Bankservantmerceryxfced100% (37)
- Renewable Energy Sources: A Laboratory Manual ForDocument22 pagesRenewable Energy Sources: A Laboratory Manual ForMadhupur PolytechnicNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Stuttering Foundations and Clinical Applications 0131573101Document24 pagesTest Bank For Stuttering Foundations and Clinical Applications 0131573101JimmyHaynessfmg100% (46)
- G10-2nd-Q-review Sheets-Chem-Chap7, 8.1, 8.2Document8 pagesG10-2nd-Q-review Sheets-Chem-Chap7, 8.1, 8.2Karim Ahmed100% (1)
- NPCIL Electronics PaperDocument9 pagesNPCIL Electronics Papernetcity143No ratings yet
- English 9thDocument1 pageEnglish 9thAlrayyan RashidNo ratings yet
- Creative Clothing TLPDocument11 pagesCreative Clothing TLPapi-245252207No ratings yet
- 5 MSHMS Course DescriptionsDocument1 page5 MSHMS Course DescriptionsJay BagayasNo ratings yet
- For Review OAPDocument144 pagesFor Review OAPKim John Rull NateNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Essential Cell Biology 4th Edition Bruce Alberts PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Essential Cell Biology 4th Edition Bruce Alberts PDF Full Chaptermilreis.cunettew2ncs100% (19)
- WWW Mytechnosoft Com Tibco Difference-between-bw5-And-bw6 PHPDocument3 pagesWWW Mytechnosoft Com Tibco Difference-between-bw5-And-bw6 PHPsabarin_72No ratings yet
- Nonverbal CommunicationDocument23 pagesNonverbal CommunicationNaman Agarwal100% (1)