Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pronouns Chart
Pronouns Chart
Uploaded by
Euej FyuCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ndebele Word CategoriesDocument4 pagesNdebele Word CategoriesCarl Ushe100% (1)
- Kahn Lily Valijarvi Riittaliisa West Greenlandic An EssentiaDocument357 pagesKahn Lily Valijarvi Riittaliisa West Greenlandic An EssentiaPaolo Lastname100% (3)
- Pronouns Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesPronouns Lesson PlanAshford Thom100% (1)
- Teach Yourself Latin PDFDocument342 pagesTeach Yourself Latin PDFIcaro S.100% (12)
- Pronoun Cases and Types English Composition 1Document5 pagesPronoun Cases and Types English Composition 1Helen ZakiNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDDocument41 pagesParts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDDenna Refnaldi SatryaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Grammar NotesDocument68 pagesDetailed Grammar NotesHani MhmoudNo ratings yet
- English: Kinds of PronounsDocument9 pagesEnglish: Kinds of PronounsMarynell ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDDocument42 pagesParts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDFirda JinanNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech 2Document14 pagesParts of Speech 2cagasanjelian112001No ratings yet
- Semi dETAILED LESSON PLAN IN eNGLISHDocument3 pagesSemi dETAILED LESSON PLAN IN eNGLISHMarie Michelle Dellatan Laspiñas60% (5)
- Pronouns: Refuerzo, Reyes, Santos, UyDocument26 pagesPronouns: Refuerzo, Reyes, Santos, UydeniseNo ratings yet
- Grammar Elfrida BakaraDocument34 pagesGrammar Elfrida BakaraLesbra SandyNo ratings yet
- Subject VERB AgreementDocument3 pagesSubject VERB Agreementlalinuz42No ratings yet
- PronounDocument24 pagesPronounTaha HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Erisa Newati SihombingDocument38 pagesGrammar Erisa Newati SihombingLesbra SandyNo ratings yet
- The Pronouns: and Its ClassificationDocument14 pagesThe Pronouns: and Its Classificationelvismar osorioNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument16 pagesPronounsfatimatuzahra503No ratings yet
- What Is A PronounDocument9 pagesWhat Is A PronounJOSE MANUEL EspirituNo ratings yet
- Packet UpdatedDocument70 pagesPacket UpdatedTien Thanh Le,No ratings yet
- Aula 2 - Pronouns Fran VieiraDocument19 pagesAula 2 - Pronouns Fran VieirafelippeavlisNo ratings yet
- Parts of The SpeechDocument7 pagesParts of The SpeechJessica MereyNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNS - Kelompok 12Document9 pagesPRONOUNS - Kelompok 12Meriliana Candra DeviNo ratings yet
- TSL 1024 Language Description: Sem. 2/ 2016 Week 2Document29 pagesTSL 1024 Language Description: Sem. 2/ 2016 Week 2Miziana Suhana Binti Saboo IPGKPINo ratings yet
- l1 Parts of SpeechDocument54 pagesl1 Parts of SpeechNeilJohn MogatoNo ratings yet
- Types of Pronoun: TheyDocument3 pagesTypes of Pronoun: TheyMr. AK RajNo ratings yet
- University of Technology - English - Language - First - Year - 2018 - 2019Document47 pagesUniversity of Technology - English - Language - First - Year - 2018 - 2019Sajad HayderNo ratings yet
- Pronoun - Types of Pronouns With Useful Examples - Pronouns ListDocument16 pagesPronoun - Types of Pronouns With Useful Examples - Pronouns ListAdelina Elena Ghiuţă100% (1)
- Esl2O: Lesson 1.3 Pronoun-Antecedent AgreementDocument32 pagesEsl2O: Lesson 1.3 Pronoun-Antecedent Agreementjannica yzabelNo ratings yet
- Grammatical Usage of PronounsDocument60 pagesGrammatical Usage of PronounsMuffin DyNo ratings yet
- Pronouns Its TypesDocument6 pagesPronouns Its TypesMuhammad AdilNo ratings yet
- English Master Series - DAY 5Document8 pagesEnglish Master Series - DAY 5Bharath TejaNo ratings yet
- Tugas PronounsDocument4 pagesTugas PronounsputuNo ratings yet
- Grammar Complete NotesDocument34 pagesGrammar Complete Notesfarhad.mr37100% (1)
- Pronouns 1Document2 pagesPronouns 1SMbunnyleeNo ratings yet
- Eng Plus - Parts of SpeechDocument25 pagesEng Plus - Parts of SpeechJia DagandanNo ratings yet
- Pronoun: LECTURER: Surya Kelana Putra, S.Pd.I., M.HumDocument25 pagesPronoun: LECTURER: Surya Kelana Putra, S.Pd.I., M.HumTEGUH SIHOTANGNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronoun: You, He, She, It, We They, Me, Him, Her, Us, and Them Are All PersonalDocument12 pagesPersonal Pronoun: You, He, She, It, We They, Me, Him, Her, Us, and Them Are All PersonalWH LimNo ratings yet
- Lb. Engleza - Lectia5Document5 pagesLb. Engleza - Lectia5Anonymous KfIlaN0No ratings yet
- PronounsDocument23 pagesPronounssharmishtharoy08No ratings yet
- Pronoun Bhs InggrisDocument45 pagesPronoun Bhs InggrisCut Raudahtul FitriNo ratings yet
- 5) Types of Pronouns PDFDocument3 pages5) Types of Pronouns PDFmarcela noemiNo ratings yet
- Pronouns PDFDocument3 pagesPronouns PDFgleeNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument43 pagesPronounsanneNo ratings yet
- Pronoun 2.0Document10 pagesPronoun 2.0Norielyn DamasoNo ratings yet
- Pronoun PDFDocument10 pagesPronoun PDFJhona Joyce Barron WPNo ratings yet
- Test 2Document2 pagesTest 2Arsenio ManuelNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronoun A Detailed Lesson Plan in EnglishDocument6 pagesPersonal Pronoun A Detailed Lesson Plan in EnglishIvy AlmenianaNo ratings yet
- English LecturesDocument6 pagesEnglish LecturesAndrei Sy JaviertoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 PronounsDocument22 pagesLesson 6 Pronounstalanikola.insiangNo ratings yet
- Week No 2 PronounsDocument32 pagesWeek No 2 PronounsMuhammad Nouman YasinNo ratings yet
- Functional English Lecture # 3 (Pronoun and Its Kinds by Sumair Arslan)Document16 pagesFunctional English Lecture # 3 (Pronoun and Its Kinds by Sumair Arslan)RNG mrcoolNo ratings yet
- Pronouns 100425004955 Phpapp01Document41 pagesPronouns 100425004955 Phpapp01John Harvey Magos0% (1)
- Learn Pronouns As Part of Speech For Bank & SSC Exams - English Notes in PDFDocument11 pagesLearn Pronouns As Part of Speech For Bank & SSC Exams - English Notes in PDFZEE zeeNo ratings yet
- Unit Three 3 PronounsDocument9 pagesUnit Three 3 Pronounskatia oussNo ratings yet
- SpeechDocument15 pagesSpeechMahboob RiazNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Tugas Kelompok Sejarah Scrapbook CoklatDocument14 pagesPresentasi Tugas Kelompok Sejarah Scrapbook CoklatKartika Tri YamaryantiNo ratings yet
- Study Notes On English Grammar - PRONOUNS - SSC CGL 2017 - SSC CGL, CHSL, Railway Exam Preparation - SSC AddaDocument5 pagesStudy Notes On English Grammar - PRONOUNS - SSC CGL 2017 - SSC CGL, CHSL, Railway Exam Preparation - SSC AddaRatanhari NagargojeNo ratings yet
- Grammar G - 9 - 12Document18 pagesGrammar G - 9 - 12DreadNo ratings yet
- G - 11 GRAMMAR (Complete)Document10 pagesG - 11 GRAMMAR (Complete)abdullahharoonabbasi13No ratings yet
- Parts of Speech 3Document48 pagesParts of Speech 3Taleb AbboudNo ratings yet
- I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesI. ObjectivesAnonymous YwtZrxp100% (1)
- Img 9209Document2 pagesImg 9209Euej FyuNo ratings yet
- Img 9207Document2 pagesImg 9207Euej FyuNo ratings yet
- Img 9211Document2 pagesImg 9211Euej FyuNo ratings yet
- Reading Exercise 3Document4 pagesReading Exercise 3Euej FyuNo ratings yet
- Img 9205Document2 pagesImg 9205Euej FyuNo ratings yet
- Img 9206Document2 pagesImg 9206Euej FyuNo ratings yet
- TextDocument1 pageTextEuej FyuNo ratings yet
- Topic 13 SapientiaDocument7 pagesTopic 13 SapientiaÁngela Naranjo GómezNo ratings yet
- Materi Bahasa Inggris Meeting 234567Document23 pagesMateri Bahasa Inggris Meeting 234567Dian MardiantiNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics of Part of Speech of The Old English Period: Adjective, VerbDocument6 pagesGeneral Characteristics of Part of Speech of The Old English Period: Adjective, VerbНиколетта ГеоргиешNo ratings yet
- Self Learning Kit These Are Those AreDocument11 pagesSelf Learning Kit These Are Those Areelyssa marie pradoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3. Possessive NounsDocument28 pagesLesson 3. Possessive NounsZerene Joy ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Mentorsentencesept19 23Document2 pagesMentorsentencesept19 23api-262537403No ratings yet
- English (Skill 25)Document2 pagesEnglish (Skill 25)Ayu SetyyaNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive WorksheetDocument5 pagesActive and Passive WorksheetEmanAbdel-HaqNo ratings yet
- Easy English GrammarDocument71 pagesEasy English GrammarRanga RagavanNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb Agreement: Lesson No.Document16 pagesSubject-Verb Agreement: Lesson No.mariamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Filial CamanaDocument20 pagesLesson 2 Filial CamanaJessicaK.CutipaNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb Agreement DocumentsDocument8 pagesSubject-Verb Agreement DocumentsAnalyn Lyzzaine PradelaNo ratings yet
- St. Thomas Aquinas School: Kinds of Sentence and Transformation of SentenceDocument3 pagesSt. Thomas Aquinas School: Kinds of Sentence and Transformation of SentenceMathew V SajiNo ratings yet
- USAGE in Spite of Despite However AlthoughDocument10 pagesUSAGE in Spite of Despite However Althoughalan subagioNo ratings yet
- Writ. Supp. 1 - Sentence Structure 1Document16 pagesWrit. Supp. 1 - Sentence Structure 1Uğur KaramanNo ratings yet
- Gerunds PDFDocument3 pagesGerunds PDFAira LimbocNo ratings yet
- Prep TestDocument11 pagesPrep TestRudy PutroNo ratings yet
- Adverb Quiz PDFDocument12 pagesAdverb Quiz PDFRaquelNo ratings yet
- Functional English-IIDocument25 pagesFunctional English-IIMemon MemonNo ratings yet
- Imperative SentenceDocument9 pagesImperative SentencesHAWON0% (1)
- December 23 Dawn VocabularyDocument2 pagesDecember 23 Dawn VocabularyZubbi RamzNo ratings yet
- Count NounsDocument6 pagesCount NounsEva.lineNo ratings yet
- MTB Module 10Document5 pagesMTB Module 10Mary Joy RellomaNo ratings yet
- Adverbs Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesAdverbs Lesson PlanMegan ParkerNo ratings yet
- Self Study IiDocument9 pagesSelf Study IiFanny M DuarteNo ratings yet
- Nouns, Pronouns and Noun PhraseDocument53 pagesNouns, Pronouns and Noun Phrasemomobear152No ratings yet
- Cleft SentencesDocument2 pagesCleft Sentencestanja glisic100% (1)
Pronouns Chart
Pronouns Chart
Uploaded by
Euej FyuOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pronouns Chart
Pronouns Chart
Uploaded by
Euej FyuCopyright:
Available Formats
George Mason University Writing Center
writingcenter.gmu.edu
The wcenter@gmu.edu
Writing Center 703.993.1200
Pronouns
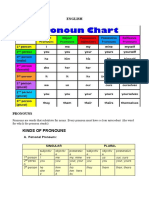
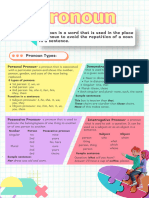
A pronoun is used in place of a noun. Different forms are used to show person, number, gender, and case. There
are personal, interrogative, indefinite, demonstrative, and reflexive pronouns.
• A personal pronoun refers to one or more individuals or things. Personal pronouns may be in the
nominative, objective or possessive case.
Singular Nominative Objective Possessive Possessive
(used in the place (used after (as an adjective) (as a pronoun)
of a subject) verbs)
1st person I me my mine
2nd person you you your yours
3rd person masculine he him his his
3rd person feminine she her her hers
3rd person gender- they* them* theirs theirs*
neutral*
3rd person inanimate it it its its
*see reverse side of this handout, “Pronoun/antecedent agreement”
Plural Nominative Objective Possessive Possessive
(as an adjective) (as a pronoun)
1st person we us our ours
2nd person you you your yours
3rd person they them their theirs
For example: I took my sister to her doctor.
She gave us a new table for our kitchen.
• An interrogative pronoun is used to ask a question. Interrogative pronouns include: who, whom, whose,
what, and which.
For example: Who left the light on?
Which book is yours?
• A relative pronoun introduces a relative clause, relating groups of words to nouns or other pronouns.
For example: Matt was the one who built the picnic table.
The house, which has a garden in bloom, is very inviting.
• An indefinite pronoun refers to a general person or thing. Singular indefinite pronouns include: one, each
either, neither, everyone, no one, anybody, somebody, nobody, everybody, anyone, and someone. Plural
indefinite pronouns include: several, both, many, and few.
For example: No one has a good idea for the workshop. (singular)
Many go on vacation in August. (plural)
The indefinite pronouns some, none, all, most, and any can be singular or plural depending on the meaning of the
sentence.
© The George Mason University Writing Center 2014
For example: Some of the work is done. (singular)
Some of the marks come off easily. (plural)
• A demonstrative pronoun identifies or points out a noun. The demonstrative pronouns include: that, this,
these, those, and such.
For example: This is more expensive than that.
These are my favorites, not those.
• A reflexive pronoun refers to a noun and provides emphasis or shows distinction from others. Reflexive
pronouns are formed with the suffixes –self and –selves.
For example: Bianca made the cake by herself.
Erin and Renee tried to occupy themselves when work was slow.
Pronoun and antecedent agreement
The guidelines for Standard American Written English dictate that a pronoun must “agree” in person and number
with its antecedent, the word that the pronoun replaces or the word to which it refers.
Incorrect: Students should be careful about checking the grammar in her writing.*
Correct: Students should be careful about checking the grammar in their writing.
A student should be careful about checking grammar in her writing.
A student should be careful about checking grammar in their writing.
As illustrated by the last example, the use of “their” to refer to a third-person, gender-neutral singular noun is
becoming acceptable among readers and writers who are tired of using “he or she” repeatedly or who
acknowledge that many people prefer to be referred to using gender-neutral pronouns. For this reason, the writing
center supports the use of the singular “they” and “them.” We recommend, however, that writers be aware of their
audiences when deciding to use the singular “they” or “them” in their writing. Professors or supervisors may
correct such usage when they see it.
• Antecedents joined by the word and take plural pronouns.
For example: Lisa and Tracy are writing their papers.
• Use a singular pronoun to refer to two or more singular antecedents joined by the words or or nor.
For example: Ben or James will read his essay.
• When there is more than one type of antecedent – a singular and a plural – joined by the words or or nor, the
pronoun agrees with the closest antecedent.
For example: The teacher or the students will have their way.
The students or the teacher will have her way.
Vague pronoun reference
In conversation, the words it and they are often used to make vague reference to people and situations. In writing,
more precise identification is needed.
Vague: The history test was made up of multiple choice questions. This disturbed us.
Better: The history test was made up of multiple choice questions. This failure to
evaluate students’ analytic abilities disturbed us.
Last updated 9/8/2016
© The George Mason University Writing Center 2016
You might also like
- Ndebele Word CategoriesDocument4 pagesNdebele Word CategoriesCarl Ushe100% (1)
- Kahn Lily Valijarvi Riittaliisa West Greenlandic An EssentiaDocument357 pagesKahn Lily Valijarvi Riittaliisa West Greenlandic An EssentiaPaolo Lastname100% (3)
- Pronouns Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesPronouns Lesson PlanAshford Thom100% (1)
- Teach Yourself Latin PDFDocument342 pagesTeach Yourself Latin PDFIcaro S.100% (12)
- Pronoun Cases and Types English Composition 1Document5 pagesPronoun Cases and Types English Composition 1Helen ZakiNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDDocument41 pagesParts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDDenna Refnaldi SatryaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Grammar NotesDocument68 pagesDetailed Grammar NotesHani MhmoudNo ratings yet
- English: Kinds of PronounsDocument9 pagesEnglish: Kinds of PronounsMarynell ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDDocument42 pagesParts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDFirda JinanNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech 2Document14 pagesParts of Speech 2cagasanjelian112001No ratings yet
- Semi dETAILED LESSON PLAN IN eNGLISHDocument3 pagesSemi dETAILED LESSON PLAN IN eNGLISHMarie Michelle Dellatan Laspiñas60% (5)
- Pronouns: Refuerzo, Reyes, Santos, UyDocument26 pagesPronouns: Refuerzo, Reyes, Santos, UydeniseNo ratings yet
- Grammar Elfrida BakaraDocument34 pagesGrammar Elfrida BakaraLesbra SandyNo ratings yet
- Subject VERB AgreementDocument3 pagesSubject VERB Agreementlalinuz42No ratings yet
- PronounDocument24 pagesPronounTaha HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Erisa Newati SihombingDocument38 pagesGrammar Erisa Newati SihombingLesbra SandyNo ratings yet
- The Pronouns: and Its ClassificationDocument14 pagesThe Pronouns: and Its Classificationelvismar osorioNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument16 pagesPronounsfatimatuzahra503No ratings yet
- What Is A PronounDocument9 pagesWhat Is A PronounJOSE MANUEL EspirituNo ratings yet
- Packet UpdatedDocument70 pagesPacket UpdatedTien Thanh Le,No ratings yet
- Aula 2 - Pronouns Fran VieiraDocument19 pagesAula 2 - Pronouns Fran VieirafelippeavlisNo ratings yet
- Parts of The SpeechDocument7 pagesParts of The SpeechJessica MereyNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNS - Kelompok 12Document9 pagesPRONOUNS - Kelompok 12Meriliana Candra DeviNo ratings yet
- TSL 1024 Language Description: Sem. 2/ 2016 Week 2Document29 pagesTSL 1024 Language Description: Sem. 2/ 2016 Week 2Miziana Suhana Binti Saboo IPGKPINo ratings yet
- l1 Parts of SpeechDocument54 pagesl1 Parts of SpeechNeilJohn MogatoNo ratings yet
- Types of Pronoun: TheyDocument3 pagesTypes of Pronoun: TheyMr. AK RajNo ratings yet
- University of Technology - English - Language - First - Year - 2018 - 2019Document47 pagesUniversity of Technology - English - Language - First - Year - 2018 - 2019Sajad HayderNo ratings yet
- Pronoun - Types of Pronouns With Useful Examples - Pronouns ListDocument16 pagesPronoun - Types of Pronouns With Useful Examples - Pronouns ListAdelina Elena Ghiuţă100% (1)
- Esl2O: Lesson 1.3 Pronoun-Antecedent AgreementDocument32 pagesEsl2O: Lesson 1.3 Pronoun-Antecedent Agreementjannica yzabelNo ratings yet
- Grammatical Usage of PronounsDocument60 pagesGrammatical Usage of PronounsMuffin DyNo ratings yet
- Pronouns Its TypesDocument6 pagesPronouns Its TypesMuhammad AdilNo ratings yet
- English Master Series - DAY 5Document8 pagesEnglish Master Series - DAY 5Bharath TejaNo ratings yet
- Tugas PronounsDocument4 pagesTugas PronounsputuNo ratings yet
- Grammar Complete NotesDocument34 pagesGrammar Complete Notesfarhad.mr37100% (1)
- Pronouns 1Document2 pagesPronouns 1SMbunnyleeNo ratings yet
- Eng Plus - Parts of SpeechDocument25 pagesEng Plus - Parts of SpeechJia DagandanNo ratings yet
- Pronoun: LECTURER: Surya Kelana Putra, S.Pd.I., M.HumDocument25 pagesPronoun: LECTURER: Surya Kelana Putra, S.Pd.I., M.HumTEGUH SIHOTANGNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronoun: You, He, She, It, We They, Me, Him, Her, Us, and Them Are All PersonalDocument12 pagesPersonal Pronoun: You, He, She, It, We They, Me, Him, Her, Us, and Them Are All PersonalWH LimNo ratings yet
- Lb. Engleza - Lectia5Document5 pagesLb. Engleza - Lectia5Anonymous KfIlaN0No ratings yet
- PronounsDocument23 pagesPronounssharmishtharoy08No ratings yet
- Pronoun Bhs InggrisDocument45 pagesPronoun Bhs InggrisCut Raudahtul FitriNo ratings yet
- 5) Types of Pronouns PDFDocument3 pages5) Types of Pronouns PDFmarcela noemiNo ratings yet
- Pronouns PDFDocument3 pagesPronouns PDFgleeNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument43 pagesPronounsanneNo ratings yet
- Pronoun 2.0Document10 pagesPronoun 2.0Norielyn DamasoNo ratings yet
- Pronoun PDFDocument10 pagesPronoun PDFJhona Joyce Barron WPNo ratings yet
- Test 2Document2 pagesTest 2Arsenio ManuelNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronoun A Detailed Lesson Plan in EnglishDocument6 pagesPersonal Pronoun A Detailed Lesson Plan in EnglishIvy AlmenianaNo ratings yet
- English LecturesDocument6 pagesEnglish LecturesAndrei Sy JaviertoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 PronounsDocument22 pagesLesson 6 Pronounstalanikola.insiangNo ratings yet
- Week No 2 PronounsDocument32 pagesWeek No 2 PronounsMuhammad Nouman YasinNo ratings yet
- Functional English Lecture # 3 (Pronoun and Its Kinds by Sumair Arslan)Document16 pagesFunctional English Lecture # 3 (Pronoun and Its Kinds by Sumair Arslan)RNG mrcoolNo ratings yet
- Pronouns 100425004955 Phpapp01Document41 pagesPronouns 100425004955 Phpapp01John Harvey Magos0% (1)
- Learn Pronouns As Part of Speech For Bank & SSC Exams - English Notes in PDFDocument11 pagesLearn Pronouns As Part of Speech For Bank & SSC Exams - English Notes in PDFZEE zeeNo ratings yet
- Unit Three 3 PronounsDocument9 pagesUnit Three 3 Pronounskatia oussNo ratings yet
- SpeechDocument15 pagesSpeechMahboob RiazNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Tugas Kelompok Sejarah Scrapbook CoklatDocument14 pagesPresentasi Tugas Kelompok Sejarah Scrapbook CoklatKartika Tri YamaryantiNo ratings yet
- Study Notes On English Grammar - PRONOUNS - SSC CGL 2017 - SSC CGL, CHSL, Railway Exam Preparation - SSC AddaDocument5 pagesStudy Notes On English Grammar - PRONOUNS - SSC CGL 2017 - SSC CGL, CHSL, Railway Exam Preparation - SSC AddaRatanhari NagargojeNo ratings yet
- Grammar G - 9 - 12Document18 pagesGrammar G - 9 - 12DreadNo ratings yet
- G - 11 GRAMMAR (Complete)Document10 pagesG - 11 GRAMMAR (Complete)abdullahharoonabbasi13No ratings yet
- Parts of Speech 3Document48 pagesParts of Speech 3Taleb AbboudNo ratings yet
- I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesI. ObjectivesAnonymous YwtZrxp100% (1)
- Img 9209Document2 pagesImg 9209Euej FyuNo ratings yet
- Img 9207Document2 pagesImg 9207Euej FyuNo ratings yet
- Img 9211Document2 pagesImg 9211Euej FyuNo ratings yet
- Reading Exercise 3Document4 pagesReading Exercise 3Euej FyuNo ratings yet
- Img 9205Document2 pagesImg 9205Euej FyuNo ratings yet
- Img 9206Document2 pagesImg 9206Euej FyuNo ratings yet
- TextDocument1 pageTextEuej FyuNo ratings yet
- Topic 13 SapientiaDocument7 pagesTopic 13 SapientiaÁngela Naranjo GómezNo ratings yet
- Materi Bahasa Inggris Meeting 234567Document23 pagesMateri Bahasa Inggris Meeting 234567Dian MardiantiNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics of Part of Speech of The Old English Period: Adjective, VerbDocument6 pagesGeneral Characteristics of Part of Speech of The Old English Period: Adjective, VerbНиколетта ГеоргиешNo ratings yet
- Self Learning Kit These Are Those AreDocument11 pagesSelf Learning Kit These Are Those Areelyssa marie pradoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3. Possessive NounsDocument28 pagesLesson 3. Possessive NounsZerene Joy ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Mentorsentencesept19 23Document2 pagesMentorsentencesept19 23api-262537403No ratings yet
- English (Skill 25)Document2 pagesEnglish (Skill 25)Ayu SetyyaNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive WorksheetDocument5 pagesActive and Passive WorksheetEmanAbdel-HaqNo ratings yet
- Easy English GrammarDocument71 pagesEasy English GrammarRanga RagavanNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb Agreement: Lesson No.Document16 pagesSubject-Verb Agreement: Lesson No.mariamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Filial CamanaDocument20 pagesLesson 2 Filial CamanaJessicaK.CutipaNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb Agreement DocumentsDocument8 pagesSubject-Verb Agreement DocumentsAnalyn Lyzzaine PradelaNo ratings yet
- St. Thomas Aquinas School: Kinds of Sentence and Transformation of SentenceDocument3 pagesSt. Thomas Aquinas School: Kinds of Sentence and Transformation of SentenceMathew V SajiNo ratings yet
- USAGE in Spite of Despite However AlthoughDocument10 pagesUSAGE in Spite of Despite However Althoughalan subagioNo ratings yet
- Writ. Supp. 1 - Sentence Structure 1Document16 pagesWrit. Supp. 1 - Sentence Structure 1Uğur KaramanNo ratings yet
- Gerunds PDFDocument3 pagesGerunds PDFAira LimbocNo ratings yet
- Prep TestDocument11 pagesPrep TestRudy PutroNo ratings yet
- Adverb Quiz PDFDocument12 pagesAdverb Quiz PDFRaquelNo ratings yet
- Functional English-IIDocument25 pagesFunctional English-IIMemon MemonNo ratings yet
- Imperative SentenceDocument9 pagesImperative SentencesHAWON0% (1)
- December 23 Dawn VocabularyDocument2 pagesDecember 23 Dawn VocabularyZubbi RamzNo ratings yet
- Count NounsDocument6 pagesCount NounsEva.lineNo ratings yet
- MTB Module 10Document5 pagesMTB Module 10Mary Joy RellomaNo ratings yet
- Adverbs Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesAdverbs Lesson PlanMegan ParkerNo ratings yet
- Self Study IiDocument9 pagesSelf Study IiFanny M DuarteNo ratings yet
- Nouns, Pronouns and Noun PhraseDocument53 pagesNouns, Pronouns and Noun Phrasemomobear152No ratings yet
- Cleft SentencesDocument2 pagesCleft Sentencestanja glisic100% (1)