Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsGen - Chem - R1
Gen - Chem - R1
Uploaded by
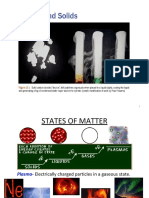
Kevin JamilThere are four main types of intermolecular forces: dipole-dipole forces, ion-dipole forces, hydrogen bonding, and dispersion forces. Dispersion forces arise from temporary dipoles induced in molecules and generally increase with molar mass. Liquids have stronger intermolecular forces than gases but weaker than solids. Strong intermolecular forces result in high boiling points, high surface tension, and high viscosity. Crystalline solids have long-range order defined by a unit cell, while amorphous solids lack long-range order. The phase and properties of a substance depend on temperature, pressure, and the types of intermolecular forces present.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Pt. Duta Utama Tehnik Abadi: Blasting & PaintingDocument3 pagesPt. Duta Utama Tehnik Abadi: Blasting & Paintingmarifa tullahNo ratings yet
- Neither Physics Nor Chemistry A History of Quantum Chemistry (Transformations Studies in The History of Science and Technology) (PRG)Document367 pagesNeither Physics Nor Chemistry A History of Quantum Chemistry (Transformations Studies in The History of Science and Technology) (PRG)yyyyy100% (1)
- ASTM E1675 2phase Geothermal Fluids SamplingDocument9 pagesASTM E1675 2phase Geothermal Fluids SamplingHasby AbdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsDocument31 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Liquids and Solidsvpetro250No ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces in Liquids and Solids: Course Outcome 1Document8 pagesIntermolecular Forces in Liquids and Solids: Course Outcome 1Angelika ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Q1 Week 1Document74 pagesQ1 Week 1Bukhari DiangkaNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsDocument55 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsSadia afrinNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Q1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q1 ReviewerDuke FaciolNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument14 pagesChemistry ReviewerJaliesa Ann ValdezNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2Document10 pagesGen Chem 2eeiarias0503No ratings yet
- Phase: Goodluck! Fighting Tayo!!!Document21 pagesPhase: Goodluck! Fighting Tayo!!!Jamilla KimNo ratings yet
- Chang - Lecture Slides of Chap11-Intermolecular ForcesDocument35 pagesChang - Lecture Slides of Chap11-Intermolecular ForcesJiselle GoconNo ratings yet
- Che 1010 Imf Phase EquilibriaDocument47 pagesChe 1010 Imf Phase EquilibriaRobert SimazuoNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Bonding in SolidsDocument27 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Bonding in Solidsmhay martinezNo ratings yet
- IMF Liquids and SolidsDocument29 pagesIMF Liquids and SolidsAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsDocument54 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Liquids and Solidscarl jason talanNo ratings yet
- Trans Organic Chemistry Chapter3Document3 pagesTrans Organic Chemistry Chapter3jilldlrs06No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Intermolecular ForcesDocument36 pagesLesson 1 Intermolecular ForcesCrisanta GanadoNo ratings yet
- Pointers in Gen Chem 2Document1 pagePointers in Gen Chem 2regalaallyn52No ratings yet
- General Chemistry IIDocument8 pagesGeneral Chemistry IIJoven EstebanNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsDocument58 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsEmir YükselNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument37 pagesIntermolecular ForcesJohnnardBelenNo ratings yet
- 1-IMF and Solids LiquidsDocument56 pages1-IMF and Solids LiquidsMyka Jen UlitaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 11: Liquids and Intermolecular Forces: - GasesDocument22 pagesCh. 11: Liquids and Intermolecular Forces: - GasesJozel Bryan Mestiola TerrìbleNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM II Kulang PaDocument12 pagesGEN CHEM II Kulang Pasara joyce pinedaNo ratings yet
- GenChem 2 ReviewerDocument13 pagesGenChem 2 ReviewerPia Aure MartinezNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 002Document7 pagesGen Chem 002jazz vergsNo ratings yet
- Phyphar Chapter 2Document7 pagesPhyphar Chapter 2KATHLEEN CALALANGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document28 pagesChapter 1yaqoobNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Ii LecturesDocument18 pagesGen Chem Ii LecturesHANNA ROLISH DIGAMONNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocument107 pagesIntermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenGopal GopinathNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument58 pagesIntermolecular ForcesChristine Joy De OcampoNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Liquids and SolidsDocument58 pagesTopic 6 - Liquids and SolidsKenneth DalionNo ratings yet
- GenChem (Lesson 1)Document2 pagesGenChem (Lesson 1)abgolena5238valNo ratings yet
- 4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedDocument23 pages4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedFN5052023 PRAMITA MAHENDRANNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem w1-2Document6 pagesGen Chem w1-2Cyril FaithNo ratings yet
- Properties of Solids and LiquidsDocument3 pagesProperties of Solids and LiquidsMalvin Roix OrenseNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesLesson 2 - Chemical BondingJanchel BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Intermolecular ForcesDocument81 pagesChapter 11 Intermolecular ForcesFABIO DE LIMANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chem ReviewerDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Chem ReviewerMatt DLSNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: © 20 Pearson Education, IncDocument26 pagesIntermolecular Forces: © 20 Pearson Education, IncKJ AlinsasaguinNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument5 pagesChemkerwin OligarioNo ratings yet
- LessonPPT1 KMTDocument64 pagesLessonPPT1 KMTRaiv LondresNo ratings yet
- Inter Molecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsDocument53 pagesInter Molecular Forces and Liquids and Solidsdevender singh100% (2)
- Intramolecular Forces (Chemical Bonding) : Ionic BondDocument27 pagesIntramolecular Forces (Chemical Bonding) : Ionic BondVince ShaneNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory and Intermolecular Forces of Liquid and Solid PDFDocument70 pagesKinetic Theory and Intermolecular Forces of Liquid and Solid PDFMiguel RañadaNo ratings yet
- GenChem2 ReviewerDocument9 pagesGenChem2 ReviewerAshley TupasNo ratings yet
- The Kinetic Molecular ModelDocument9 pagesThe Kinetic Molecular ModelSaralyn Mawallil AmilhamjaNo ratings yet
- 3 GenchemDocument6 pages3 GenchemAthena PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document4 pagesModule 1welpNo ratings yet
- General - Chemistry-ReviewerDocument11 pagesGeneral - Chemistry-ReviewerShiela Mae VisayaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem IMFADocument2 pagesGen Chem IMFArhonz.hildawaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - States of Matter (Chemy)Document64 pagesLecture 3 - States of Matter (Chemy)NUR EZZAIFAH BINTI AKBAR NAWAB FS21110068No ratings yet
- 3.1.3 - BondingDocument15 pages3.1.3 - BondingaprildazzleNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and SolidsDocument49 pagesIntermolecular Forces, Liquids, and SolidsfuatNo ratings yet
- Atomic BondingDocument20 pagesAtomic BondingVladimir Pascua CanaoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2Document1 pageGeneral Chemistry 2SET B-Veniegas Jhonn LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular ModelDocument3 pagesKinetic Molecular ModelChristine FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesChemistry 2 RevieweralicolipanoNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document3 pagesChem 1Nico San AgustinNo ratings yet
- First Quarter: Week - 1: General ChemistryDocument9 pagesFirst Quarter: Week - 1: General ChemistryPerlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 11 - Intermolecular - Forces Solids and LiquidsDocument88 pagesChapter - 11 - Intermolecular - Forces Solids and Liquidsbuse.kilicNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Calculations Involving SolutionsDocument45 pagesCalculations Involving SolutionsArthur LaurelNo ratings yet
- 212 - Problem Set 1Document2 pages212 - Problem Set 1everyoneMDNo ratings yet
- Innovations in AerosolDocument42 pagesInnovations in AerosolHely PatelNo ratings yet
- Koretsky CHDocument122 pagesKoretsky CHflowerlily629100% (3)
- Kollicoat ProtectDocument10 pagesKollicoat ProtectAshok LenkaNo ratings yet
- Fusion Bead XRFDocument6 pagesFusion Bead XRFAnindya RoyNo ratings yet
- Mole Fraction Volume FractionDocument9 pagesMole Fraction Volume FractionameyckulkarniNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Di Deionised WaterDocument4 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Di Deionised Watercgjp120391No ratings yet
- Cross Flow Filtration HandbookDocument21 pagesCross Flow Filtration Handbooksahar vahdatifarNo ratings yet
- Proceeding Book SIBE 2017Document625 pagesProceeding Book SIBE 2017Yochanan meisandroNo ratings yet
- Sociological TheoriesDocument55 pagesSociological TheoriesBUNNy RaoNo ratings yet
- Reactor Design For Methanol SynthesisDocument12 pagesReactor Design For Methanol SynthesisYashaswini Nagaraj100% (1)
- 1.2.2 Thermodynamics and HYSYS - 5 PDFDocument26 pages1.2.2 Thermodynamics and HYSYS - 5 PDFWelisson SilvaNo ratings yet
- Scholar 2017Document1 pageScholar 2017AKSHET PATIALNo ratings yet
- Distillation: C H E 2 4 6 Separation ProcessDocument41 pagesDistillation: C H E 2 4 6 Separation ProcessnorazifahNo ratings yet
- Effect of Salinity On Physical and Chemical Properties of Soils of Khulna RegionDocument17 pagesEffect of Salinity On Physical and Chemical Properties of Soils of Khulna Regioncurzonbd100% (1)
- CH 4 To 5 PDFDocument3 pagesCH 4 To 5 PDFRafael Yubrán HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drilling and Cementing Lab ManualDocument22 pagesDrilling and Cementing Lab ManualTheo AnkamahNo ratings yet
- Design of A Cryogenic Grinding System For SpicesDocument10 pagesDesign of A Cryogenic Grinding System For Spicesdeepakkumar2626No ratings yet
- Hot Dip GalvanizingDocument50 pagesHot Dip GalvanizingkevinNo ratings yet
- Production ChemistDocument2 pagesProduction Chemistapi-122049623No ratings yet
- FST 313-316 MDocument1 pageFST 313-316 MRachael JosephNo ratings yet
- Aeration, Coagulation and Flocculation Processes in Water Treatment Plant: Case Study Water Treatment Plant Around Maiduguri, Borno State Nigeria.Document4 pagesAeration, Coagulation and Flocculation Processes in Water Treatment Plant: Case Study Water Treatment Plant Around Maiduguri, Borno State Nigeria.AJER JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Is SP 23 1982 PDFDocument151 pagesIs SP 23 1982 PDFMano MaddulaNo ratings yet
- Inventory StatusDocument19 pagesInventory StatusMuhaiminul IslamNo ratings yet
- WFC Gap AnalysisDocument2 pagesWFC Gap AnalysisDilodilaver DilaverNo ratings yet
- Marcet Boiler: Thermodynamics LabDocument5 pagesMarcet Boiler: Thermodynamics LabShiyas Basheer100% (1)
Gen - Chem - R1
Gen - Chem - R1
Uploaded by
Kevin Jamil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesThere are four main types of intermolecular forces: dipole-dipole forces, ion-dipole forces, hydrogen bonding, and dispersion forces. Dispersion forces arise from temporary dipoles induced in molecules and generally increase with molar mass. Liquids have stronger intermolecular forces than gases but weaker than solids. Strong intermolecular forces result in high boiling points, high surface tension, and high viscosity. Crystalline solids have long-range order defined by a unit cell, while amorphous solids lack long-range order. The phase and properties of a substance depend on temperature, pressure, and the types of intermolecular forces present.
Original Description:
h
Original Title
Gen.-Chem.-R1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThere are four main types of intermolecular forces: dipole-dipole forces, ion-dipole forces, hydrogen bonding, and dispersion forces. Dispersion forces arise from temporary dipoles induced in molecules and generally increase with molar mass. Liquids have stronger intermolecular forces than gases but weaker than solids. Strong intermolecular forces result in high boiling points, high surface tension, and high viscosity. Crystalline solids have long-range order defined by a unit cell, while amorphous solids lack long-range order. The phase and properties of a substance depend on temperature, pressure, and the types of intermolecular forces present.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesGen - Chem - R1
Gen - Chem - R1
Uploaded by
Kevin JamilThere are four main types of intermolecular forces: dipole-dipole forces, ion-dipole forces, hydrogen bonding, and dispersion forces. Dispersion forces arise from temporary dipoles induced in molecules and generally increase with molar mass. Liquids have stronger intermolecular forces than gases but weaker than solids. Strong intermolecular forces result in high boiling points, high surface tension, and high viscosity. Crystalline solids have long-range order defined by a unit cell, while amorphous solids lack long-range order. The phase and properties of a substance depend on temperature, pressure, and the types of intermolecular forces present.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
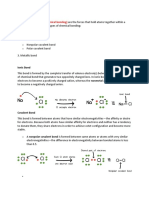
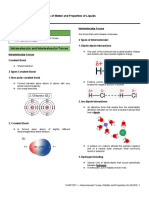
GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 Hydrogen Bond
Special dipole-dipole interaction
between the hydrogen atom in a polar
Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and
N-H, O-H, or F-H bond and an
Solids
electronegative O, N, or F atom.
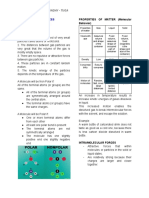
Phase
Properties of Liquids
Homogeneous part of the system in
contact with other parts of the system Surface Tension
but separated from them by a well- Amount of energy required to stretch
defined boundary. or increase the surface of a liquid by a
2 Phases: Solid- ice; Liquid- water unit area.
Strong intermolecular forces
Intermolecular Forces High surface tension
Attractive forces between molecules. Cohesion
Intramolecular Forces Intermolecular attraction between like
molecules.
Hold atoms together in a molecule.
Adhesion
**Generally, intermolecular forces are much
weaker than intramolecular forces. Attraction between unlike molecules.
“Measure” of Intermolecular Force Viscosity
boiling point Measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow.
Strong intermolecular forces
melting point
High viscosity
^Hvap
^Hfus
Crystalline Solid
^Hsub
Possesses rigid and long-range order.
4 Types of Intermolecular Forces In a crystalline solid, atoms, molecules
or ions occupy specific (predictable)
Dipole-Dipole Forces positions.
Attractive forces between polar Amorphous Solid
molecules.
Does not possess a well-defined
Ion-Dipole Forces arrangement and long-range
molecular order.
Attractive forces between an ion and a
polar molecule. Unit Cell
Dispersion Forces Basic repeating structural unit of a
crystalline solid.
Attractive forces that arise as a result
of temporary dipoles induced in atoms At Lattice Points
or molecules.
- Polarizability is the ease with Atoms
which the electron distribution in Molecules
the atom or molecule can be Ion
distorted.
- Polarizability increases with: 7 Basic Unit Cells
greater number of electrons Simple Cubic
more diffuse electron cloud Tetragonal
**Dispersion forces usually increase with Orthorhombic
molar mass. Rhombohedral
Monoclinic
Triclinic Vapor pressure measured when a
Hexagonal dynamic equilibrium exists between
condensation and evaporation.
3 Types of Cubic Unit Cells
Dynamic Equilibrium
Simple Cubic
- 1 atom/unit cell Rate of condensation = Rate of
Body-Centered Cubic
- 2 atoms/unit cell evaporation
Face-Centered Cubic Molar Heat of Vaporization (^Hvap)
- 4 atoms/unit cell
Energy required to vaporize 1 mole of
Types of Crystals a liquid at its boiling point.
Ionic Crystals
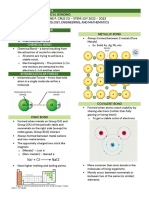
Lattice points occupied by cations and Boiling Point
anions.
Held together by electrostatic Temperature at which the (equilibrium)
attraction. vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to
Hard, brittle, high melting point. the external pressure.
Poor conductor of heat and electricity. Normal Boiling Point
Covalent Crystals Temperature at which a liquid boil
Lattice points occupied by atoms. when the external pressure is 1 atm.
Held together by covalent bonds. Critical Temperature (Tc)
Hard, high melting point.
Poor conductor of heat and electricity. Temperature above which the gas
cannot be made to liquefy, no matter
Molecular Crystals how great the applied pressure.
Lattice points occupied by molecules. Critical Pressure (Pc)
Held together by intermolecular forces.
Soft, low melting point. Minimum pressure that must be
applied to bring about liquefaction at
Poor conductor of heat and electricity.
the critical temperature.
Metallic Crystals
**Melting point of a solid or the Freezing
Lattice points occupied by metal point of a liquid is the temperature at which
atoms. the solid and liquid phases coexist in
Held together by metallic bonds.
Soft to hard, low to high melting point. equilibrium.
Good conductors of heat and
electricity. Molar Heat of Fusion (^Hfus)
Energy required to melt 1 mole of a
Amorphous Solid solid substance at its freezing point.
Does not possess a well-defined Molar Heat of Sublimation (^Hsub)
arrangement and long-range
Energy required to sublime 1 mole of a
molecular order.
solid.
Glass
Phase Diagram
Optically transparent fusion product of
inorganic materials that has cooled to Summarizes the conditions at which a
a rigid state without crystallizing. substance exists as a solid, liquid, or
gas.
Equilibrium Vapor Pressure
© Yasmin Bucay
You might also like
- Pt. Duta Utama Tehnik Abadi: Blasting & PaintingDocument3 pagesPt. Duta Utama Tehnik Abadi: Blasting & Paintingmarifa tullahNo ratings yet
- Neither Physics Nor Chemistry A History of Quantum Chemistry (Transformations Studies in The History of Science and Technology) (PRG)Document367 pagesNeither Physics Nor Chemistry A History of Quantum Chemistry (Transformations Studies in The History of Science and Technology) (PRG)yyyyy100% (1)
- ASTM E1675 2phase Geothermal Fluids SamplingDocument9 pagesASTM E1675 2phase Geothermal Fluids SamplingHasby AbdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsDocument31 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Liquids and Solidsvpetro250No ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces in Liquids and Solids: Course Outcome 1Document8 pagesIntermolecular Forces in Liquids and Solids: Course Outcome 1Angelika ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Q1 Week 1Document74 pagesQ1 Week 1Bukhari DiangkaNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsDocument55 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsSadia afrinNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Q1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q1 ReviewerDuke FaciolNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument14 pagesChemistry ReviewerJaliesa Ann ValdezNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2Document10 pagesGen Chem 2eeiarias0503No ratings yet
- Phase: Goodluck! Fighting Tayo!!!Document21 pagesPhase: Goodluck! Fighting Tayo!!!Jamilla KimNo ratings yet
- Chang - Lecture Slides of Chap11-Intermolecular ForcesDocument35 pagesChang - Lecture Slides of Chap11-Intermolecular ForcesJiselle GoconNo ratings yet
- Che 1010 Imf Phase EquilibriaDocument47 pagesChe 1010 Imf Phase EquilibriaRobert SimazuoNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Bonding in SolidsDocument27 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Bonding in Solidsmhay martinezNo ratings yet
- IMF Liquids and SolidsDocument29 pagesIMF Liquids and SolidsAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsDocument54 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Liquids and Solidscarl jason talanNo ratings yet
- Trans Organic Chemistry Chapter3Document3 pagesTrans Organic Chemistry Chapter3jilldlrs06No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Intermolecular ForcesDocument36 pagesLesson 1 Intermolecular ForcesCrisanta GanadoNo ratings yet
- Pointers in Gen Chem 2Document1 pagePointers in Gen Chem 2regalaallyn52No ratings yet
- General Chemistry IIDocument8 pagesGeneral Chemistry IIJoven EstebanNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsDocument58 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsEmir YükselNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument37 pagesIntermolecular ForcesJohnnardBelenNo ratings yet
- 1-IMF and Solids LiquidsDocument56 pages1-IMF and Solids LiquidsMyka Jen UlitaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 11: Liquids and Intermolecular Forces: - GasesDocument22 pagesCh. 11: Liquids and Intermolecular Forces: - GasesJozel Bryan Mestiola TerrìbleNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM II Kulang PaDocument12 pagesGEN CHEM II Kulang Pasara joyce pinedaNo ratings yet
- GenChem 2 ReviewerDocument13 pagesGenChem 2 ReviewerPia Aure MartinezNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 002Document7 pagesGen Chem 002jazz vergsNo ratings yet
- Phyphar Chapter 2Document7 pagesPhyphar Chapter 2KATHLEEN CALALANGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document28 pagesChapter 1yaqoobNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Ii LecturesDocument18 pagesGen Chem Ii LecturesHANNA ROLISH DIGAMONNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocument107 pagesIntermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenGopal GopinathNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument58 pagesIntermolecular ForcesChristine Joy De OcampoNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Liquids and SolidsDocument58 pagesTopic 6 - Liquids and SolidsKenneth DalionNo ratings yet
- GenChem (Lesson 1)Document2 pagesGenChem (Lesson 1)abgolena5238valNo ratings yet
- 4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedDocument23 pages4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedFN5052023 PRAMITA MAHENDRANNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem w1-2Document6 pagesGen Chem w1-2Cyril FaithNo ratings yet
- Properties of Solids and LiquidsDocument3 pagesProperties of Solids and LiquidsMalvin Roix OrenseNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesLesson 2 - Chemical BondingJanchel BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Intermolecular ForcesDocument81 pagesChapter 11 Intermolecular ForcesFABIO DE LIMANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chem ReviewerDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Chem ReviewerMatt DLSNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: © 20 Pearson Education, IncDocument26 pagesIntermolecular Forces: © 20 Pearson Education, IncKJ AlinsasaguinNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument5 pagesChemkerwin OligarioNo ratings yet
- LessonPPT1 KMTDocument64 pagesLessonPPT1 KMTRaiv LondresNo ratings yet
- Inter Molecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsDocument53 pagesInter Molecular Forces and Liquids and Solidsdevender singh100% (2)
- Intramolecular Forces (Chemical Bonding) : Ionic BondDocument27 pagesIntramolecular Forces (Chemical Bonding) : Ionic BondVince ShaneNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory and Intermolecular Forces of Liquid and Solid PDFDocument70 pagesKinetic Theory and Intermolecular Forces of Liquid and Solid PDFMiguel RañadaNo ratings yet
- GenChem2 ReviewerDocument9 pagesGenChem2 ReviewerAshley TupasNo ratings yet
- The Kinetic Molecular ModelDocument9 pagesThe Kinetic Molecular ModelSaralyn Mawallil AmilhamjaNo ratings yet
- 3 GenchemDocument6 pages3 GenchemAthena PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document4 pagesModule 1welpNo ratings yet
- General - Chemistry-ReviewerDocument11 pagesGeneral - Chemistry-ReviewerShiela Mae VisayaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem IMFADocument2 pagesGen Chem IMFArhonz.hildawaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - States of Matter (Chemy)Document64 pagesLecture 3 - States of Matter (Chemy)NUR EZZAIFAH BINTI AKBAR NAWAB FS21110068No ratings yet
- 3.1.3 - BondingDocument15 pages3.1.3 - BondingaprildazzleNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and SolidsDocument49 pagesIntermolecular Forces, Liquids, and SolidsfuatNo ratings yet
- Atomic BondingDocument20 pagesAtomic BondingVladimir Pascua CanaoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2Document1 pageGeneral Chemistry 2SET B-Veniegas Jhonn LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular ModelDocument3 pagesKinetic Molecular ModelChristine FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesChemistry 2 RevieweralicolipanoNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document3 pagesChem 1Nico San AgustinNo ratings yet
- First Quarter: Week - 1: General ChemistryDocument9 pagesFirst Quarter: Week - 1: General ChemistryPerlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 11 - Intermolecular - Forces Solids and LiquidsDocument88 pagesChapter - 11 - Intermolecular - Forces Solids and Liquidsbuse.kilicNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Calculations Involving SolutionsDocument45 pagesCalculations Involving SolutionsArthur LaurelNo ratings yet
- 212 - Problem Set 1Document2 pages212 - Problem Set 1everyoneMDNo ratings yet
- Innovations in AerosolDocument42 pagesInnovations in AerosolHely PatelNo ratings yet
- Koretsky CHDocument122 pagesKoretsky CHflowerlily629100% (3)
- Kollicoat ProtectDocument10 pagesKollicoat ProtectAshok LenkaNo ratings yet
- Fusion Bead XRFDocument6 pagesFusion Bead XRFAnindya RoyNo ratings yet
- Mole Fraction Volume FractionDocument9 pagesMole Fraction Volume FractionameyckulkarniNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Di Deionised WaterDocument4 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Di Deionised Watercgjp120391No ratings yet
- Cross Flow Filtration HandbookDocument21 pagesCross Flow Filtration Handbooksahar vahdatifarNo ratings yet
- Proceeding Book SIBE 2017Document625 pagesProceeding Book SIBE 2017Yochanan meisandroNo ratings yet
- Sociological TheoriesDocument55 pagesSociological TheoriesBUNNy RaoNo ratings yet
- Reactor Design For Methanol SynthesisDocument12 pagesReactor Design For Methanol SynthesisYashaswini Nagaraj100% (1)
- 1.2.2 Thermodynamics and HYSYS - 5 PDFDocument26 pages1.2.2 Thermodynamics and HYSYS - 5 PDFWelisson SilvaNo ratings yet
- Scholar 2017Document1 pageScholar 2017AKSHET PATIALNo ratings yet
- Distillation: C H E 2 4 6 Separation ProcessDocument41 pagesDistillation: C H E 2 4 6 Separation ProcessnorazifahNo ratings yet
- Effect of Salinity On Physical and Chemical Properties of Soils of Khulna RegionDocument17 pagesEffect of Salinity On Physical and Chemical Properties of Soils of Khulna Regioncurzonbd100% (1)
- CH 4 To 5 PDFDocument3 pagesCH 4 To 5 PDFRafael Yubrán HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drilling and Cementing Lab ManualDocument22 pagesDrilling and Cementing Lab ManualTheo AnkamahNo ratings yet
- Design of A Cryogenic Grinding System For SpicesDocument10 pagesDesign of A Cryogenic Grinding System For Spicesdeepakkumar2626No ratings yet
- Hot Dip GalvanizingDocument50 pagesHot Dip GalvanizingkevinNo ratings yet
- Production ChemistDocument2 pagesProduction Chemistapi-122049623No ratings yet
- FST 313-316 MDocument1 pageFST 313-316 MRachael JosephNo ratings yet
- Aeration, Coagulation and Flocculation Processes in Water Treatment Plant: Case Study Water Treatment Plant Around Maiduguri, Borno State Nigeria.Document4 pagesAeration, Coagulation and Flocculation Processes in Water Treatment Plant: Case Study Water Treatment Plant Around Maiduguri, Borno State Nigeria.AJER JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Is SP 23 1982 PDFDocument151 pagesIs SP 23 1982 PDFMano MaddulaNo ratings yet
- Inventory StatusDocument19 pagesInventory StatusMuhaiminul IslamNo ratings yet
- WFC Gap AnalysisDocument2 pagesWFC Gap AnalysisDilodilaver DilaverNo ratings yet
- Marcet Boiler: Thermodynamics LabDocument5 pagesMarcet Boiler: Thermodynamics LabShiyas Basheer100% (1)