Professional Documents
Culture Documents
16) Unstable Angina
16) Unstable Angina
Uploaded by
Aris PaparisCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Vasovagal Reflex SyndromeDocument19 pagesVasovagal Reflex SyndromeJalalludin AnNo ratings yet
- Osce Notes - Myocardial InfarctionDocument10 pagesOsce Notes - Myocardial InfarctionmmmalcampoNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument9 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromegojigef236No ratings yet
- NSTEMIDocument29 pagesNSTEMIGeanina Creanga100% (1)
- Specialty Medicine: CardiologyDocument326 pagesSpecialty Medicine: Cardiologyjames.a.blairNo ratings yet
- Cardio BBDocument73 pagesCardio BBايات عبدالرحمنNo ratings yet
- Unstable AnginaDocument20 pagesUnstable AnginaMoon AudioNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: Prepared by Chan Xinyi Supervisor: DR HASHAIRIDocument22 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome: Prepared by Chan Xinyi Supervisor: DR HASHAIRIbobby redlandNo ratings yet
- Topic:: Unstable AnginaDocument44 pagesTopic:: Unstable AnginaApurba100% (1)
- St-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: PGI Barrantes, Lloyd DanielDocument28 pagesSt-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: PGI Barrantes, Lloyd DanielLloyd Daniel BarrantesNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy-Handbook-9th-Edition (1) - Halaman-48-58 - CompressedDocument11 pagesPharmacotherapy-Handbook-9th-Edition (1) - Halaman-48-58 - Compressedyour happinesNo ratings yet
- 11-Acs2 StemiDocument33 pages11-Acs2 Stemiمحمد بن الصادقNo ratings yet
- ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction (Stemi) : Present byDocument29 pagesST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction (Stemi) : Present byReema AlamriNo ratings yet
- Step Up To MedicineDocument68 pagesStep Up To MedicineAmadou N'Dow100% (1)
- AcsDocument20 pagesAcsTitanSeptiansyahNo ratings yet
- Lirerature Review NSTEMI Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument6 pagesLirerature Review NSTEMI Diagnosis and TreatmentNgurah WigantaraNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument67 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeAdam SmithNo ratings yet
- Angina and MIDocument68 pagesAngina and MIAndrassy Twinkle AlineaNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument53 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseJoel CanenciaNo ratings yet
- Acs TrombolitikDocument55 pagesAcs TrombolitikDiana IswardhaniNo ratings yet
- Differences BTW ACS, Stable AnginaDocument7 pagesDifferences BTW ACS, Stable AnginaCarmenhNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction: Classification of ACSDocument7 pagesMyocardial Infarction: Classification of ACSMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Chest PainDocument50 pagesChest PainGrafu Andreea AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Acs 11 190524110746Document46 pagesAcs 11 190524110746Obakeng MandaNo ratings yet
- Satjit Bhusri, MD Cardiologist Lenox Hill Hospital: Jeff Chianfagna Rpa-CDocument76 pagesSatjit Bhusri, MD Cardiologist Lenox Hill Hospital: Jeff Chianfagna Rpa-CAjaz JunachNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome-SignedDocument3 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome-Signedابو الجودNo ratings yet
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument13 pagesAcute Myocardial InfarctionSajjad KabirNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain Notes USMLE Step 3Document3 pagesChest Pain Notes USMLE Step 3kisria100% (1)
- Chest Pain Protocol in EDDocument3 pagesChest Pain Protocol in EDshahidchaudharyNo ratings yet
- Management of ArrhythmiasDocument4 pagesManagement of ArrhythmiasAray Al-AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndromes AlgorithmDocument5 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromes AlgorithmLiuk IrawatiNo ratings yet
- Chestpainandacspathway PDFDocument28 pagesChestpainandacspathway PDFfebryNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument20 pagesMyocardial InfarctionRio Ramon HilarioNo ratings yet
- Summary 2012 Esc GuidelinesDocument10 pagesSummary 2012 Esc GuidelinesNick StamatiadisNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain. Surgical Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)Document21 pagesChest Pain. Surgical Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)Hanif ZamriNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain Pres WebinarDocument28 pagesChest Pain Pres Webinarteukureza fatwaNo ratings yet
- ACS Recognition ECG InterpretationDocument73 pagesACS Recognition ECG InterpretationJoel ChongNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument46 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeEmma Andaya100% (1)
- Acute Coronay Syndrome - BACCDocument72 pagesAcute Coronay Syndrome - BACCYeyen Devyanti HandokoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document11 pagesLecture 7Grafu Andreea AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument42 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeGorgieNo ratings yet
- Acute MIDocument4 pagesAcute MICasuga, Jessica Carmela F.No ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument48 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeAchmad ulil Albab100% (1)
- Coronay Artery Disease: Dr. Bibek Poudel Department of Medicine City Medical College HospitalDocument22 pagesCoronay Artery Disease: Dr. Bibek Poudel Department of Medicine City Medical College HospitalitsmailbbkNo ratings yet
- 2014 AHA/ACC Guideline For The Management of Patients Wit H Non-ST-Elevation Acute Coronar y Syndromes: Executive SummaryDocument32 pages2014 AHA/ACC Guideline For The Management of Patients Wit H Non-ST-Elevation Acute Coronar y Syndromes: Executive SummaryEmmieNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome ACSDocument9 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome ACSChen BrionesNo ratings yet
- Step 2 CK Review - CardiologyDocument28 pagesStep 2 CK Review - Cardiologyrsmd1986100% (1)
- 12 Hours: Continue To Monitor: High-Risk NSTEACSDocument1 page12 Hours: Continue To Monitor: High-Risk NSTEACSMeita ReligiaNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients With Acute Biologic CrisisDocument72 pagesCare of Patients With Acute Biologic CrisisJames QuilingNo ratings yet
- Fac Thrombolysis 2007Document36 pagesFac Thrombolysis 2007Tri Harjono0% (1)
- 9 CsaDocument34 pages9 Csaمحمد بن الصادقNo ratings yet
- MTB Cardiology NotesDocument11 pagesMTB Cardiology Noteskabal321No ratings yet
- MTB Cardiology NotesDocument7 pagesMTB Cardiology Noteskabal321No ratings yet
- Pocket Card Myocardial Infarction January 2024Document7 pagesPocket Card Myocardial Infarction January 2024تمارا مقداديNo ratings yet
- ACS-Karim AbdellatifDocument10 pagesACS-Karim AbdellatifKarim AbdellatifNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support in Adults (ACLS) : SubtitleDocument30 pagesAdvanced Cardiovascular Life Support in Adults (ACLS) : SubtitleMohamad El SharNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeFrom EverandCardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeNo ratings yet
- 10) Elbow JointDocument2 pages10) Elbow JointAris PaparisNo ratings yet
- 9-Histogenesis of The Intercellular Substance of The Connective Tissue-Pro Alpha Chain - Alpha Chain - ProCollagen - TropoCollagenDocument2 pages9-Histogenesis of The Intercellular Substance of The Connective Tissue-Pro Alpha Chain - Alpha Chain - ProCollagen - TropoCollagenAris PaparisNo ratings yet
- 15) Stable AnginaDocument3 pages15) Stable AnginaAris PaparisNo ratings yet
- 8) Chronic Cor PulmonaleDocument2 pages8) Chronic Cor PulmonaleAris PaparisNo ratings yet
- 17) AMI 1Document3 pages17) AMI 1Aris PaparisNo ratings yet
- 4 - Multi-Stratified Epithelia. Function, Structure, TypesDocument2 pages4 - Multi-Stratified Epithelia. Function, Structure, TypesAris PaparisNo ratings yet
16) Unstable Angina
16) Unstable Angina
Uploaded by
Aris PaparisOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
16) Unstable Angina
16) Unstable Angina
Uploaded by
Aris PaparisCopyright:
Available Formats
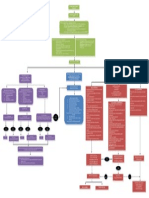
Q16) Unstable angina (UA) (uni book)
Definition: Unstable angina is an acute or subacute coronarogenic myocardial ischemia,
which does not lead to development of necrosis. It is classified into:
Newly appeared angina
Accelerating stable angina
Angina at rest
Early post-infarction angina upto 14 days after AMI
Pathogenesis
The destabilized atherosclerotic plaque lead to the formation of a thrombus, which
obliterates the coronary arteries partially or totally. The fibrinolytic system gets activated
and is capable of restoring the patency of the vessel but in the rest of the 20-40% critical
stenosis with/without an added spasm is responsible.
Braunwald's classification of unstable angina (book)
Clinical presentation :
- angina at rest
- less effort provokes pain
- pain propagates to more places
- pain duration is increased
NB: The destabilisation of the coronary plaque requires an urgent hospitalisation.
Hence the moment of plaque activation is important .
Diagnosis
Any stress tests in the acute phase are prohibited (bicycle ergometer, treadmill)
Check serum level of troponins
ECG - ST depression
Radioisotope scintography
contrast CT
positron emitted tomography (PET)
Coronary angiography (gold standard) is combined with intracoranary
echocardiography to rule out CAD.
unstable angina is divided into:
1. troponin (+) = indicaton of coronary angioraphy
2. troponin (-) = requires a stress test before hospital discharge and then every
6-12 months.
Treatment
UA patients are hospitalised in ICU, where they receive:
sedation
oxygen
anticoagulants e.g unfractionated Heparin can be started about 1000 U/hour,
following day, low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) is given i.e. Arixtra 2.5mg/day
subcutaneoulsy.
Nitrates can be given to abolish chest pain (but don't affect the prognosis)
Beta blockers for CAD treatment
Calcium channel blockers given if angina persists or spasms suspected.
Statins also used to treat CAD
High risk patient e.g. who are troponin (+), with persistent angina, hemodynamically
unstable, are given coronary angiography followed by revascularisation procedure
(PTCA or CABG). The rest of the patients, who have been stabilised, a stress test if
performed , if + they are referred to a cathlab for coronary angiography.
You might also like
- Vasovagal Reflex SyndromeDocument19 pagesVasovagal Reflex SyndromeJalalludin AnNo ratings yet
- Osce Notes - Myocardial InfarctionDocument10 pagesOsce Notes - Myocardial InfarctionmmmalcampoNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument9 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromegojigef236No ratings yet
- NSTEMIDocument29 pagesNSTEMIGeanina Creanga100% (1)
- Specialty Medicine: CardiologyDocument326 pagesSpecialty Medicine: Cardiologyjames.a.blairNo ratings yet
- Cardio BBDocument73 pagesCardio BBايات عبدالرحمنNo ratings yet
- Unstable AnginaDocument20 pagesUnstable AnginaMoon AudioNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: Prepared by Chan Xinyi Supervisor: DR HASHAIRIDocument22 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome: Prepared by Chan Xinyi Supervisor: DR HASHAIRIbobby redlandNo ratings yet
- Topic:: Unstable AnginaDocument44 pagesTopic:: Unstable AnginaApurba100% (1)
- St-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: PGI Barrantes, Lloyd DanielDocument28 pagesSt-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: PGI Barrantes, Lloyd DanielLloyd Daniel BarrantesNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy-Handbook-9th-Edition (1) - Halaman-48-58 - CompressedDocument11 pagesPharmacotherapy-Handbook-9th-Edition (1) - Halaman-48-58 - Compressedyour happinesNo ratings yet
- 11-Acs2 StemiDocument33 pages11-Acs2 Stemiمحمد بن الصادقNo ratings yet
- ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction (Stemi) : Present byDocument29 pagesST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction (Stemi) : Present byReema AlamriNo ratings yet
- Step Up To MedicineDocument68 pagesStep Up To MedicineAmadou N'Dow100% (1)
- AcsDocument20 pagesAcsTitanSeptiansyahNo ratings yet
- Lirerature Review NSTEMI Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument6 pagesLirerature Review NSTEMI Diagnosis and TreatmentNgurah WigantaraNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument67 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeAdam SmithNo ratings yet
- Angina and MIDocument68 pagesAngina and MIAndrassy Twinkle AlineaNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument53 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseJoel CanenciaNo ratings yet
- Acs TrombolitikDocument55 pagesAcs TrombolitikDiana IswardhaniNo ratings yet
- Differences BTW ACS, Stable AnginaDocument7 pagesDifferences BTW ACS, Stable AnginaCarmenhNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction: Classification of ACSDocument7 pagesMyocardial Infarction: Classification of ACSMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Chest PainDocument50 pagesChest PainGrafu Andreea AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Acs 11 190524110746Document46 pagesAcs 11 190524110746Obakeng MandaNo ratings yet
- Satjit Bhusri, MD Cardiologist Lenox Hill Hospital: Jeff Chianfagna Rpa-CDocument76 pagesSatjit Bhusri, MD Cardiologist Lenox Hill Hospital: Jeff Chianfagna Rpa-CAjaz JunachNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome-SignedDocument3 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome-Signedابو الجودNo ratings yet
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument13 pagesAcute Myocardial InfarctionSajjad KabirNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain Notes USMLE Step 3Document3 pagesChest Pain Notes USMLE Step 3kisria100% (1)
- Chest Pain Protocol in EDDocument3 pagesChest Pain Protocol in EDshahidchaudharyNo ratings yet
- Management of ArrhythmiasDocument4 pagesManagement of ArrhythmiasAray Al-AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndromes AlgorithmDocument5 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromes AlgorithmLiuk IrawatiNo ratings yet
- Chestpainandacspathway PDFDocument28 pagesChestpainandacspathway PDFfebryNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument20 pagesMyocardial InfarctionRio Ramon HilarioNo ratings yet
- Summary 2012 Esc GuidelinesDocument10 pagesSummary 2012 Esc GuidelinesNick StamatiadisNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain. Surgical Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)Document21 pagesChest Pain. Surgical Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)Hanif ZamriNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain Pres WebinarDocument28 pagesChest Pain Pres Webinarteukureza fatwaNo ratings yet
- ACS Recognition ECG InterpretationDocument73 pagesACS Recognition ECG InterpretationJoel ChongNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument46 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeEmma Andaya100% (1)
- Acute Coronay Syndrome - BACCDocument72 pagesAcute Coronay Syndrome - BACCYeyen Devyanti HandokoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document11 pagesLecture 7Grafu Andreea AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument42 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeGorgieNo ratings yet
- Acute MIDocument4 pagesAcute MICasuga, Jessica Carmela F.No ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument48 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeAchmad ulil Albab100% (1)
- Coronay Artery Disease: Dr. Bibek Poudel Department of Medicine City Medical College HospitalDocument22 pagesCoronay Artery Disease: Dr. Bibek Poudel Department of Medicine City Medical College HospitalitsmailbbkNo ratings yet
- 2014 AHA/ACC Guideline For The Management of Patients Wit H Non-ST-Elevation Acute Coronar y Syndromes: Executive SummaryDocument32 pages2014 AHA/ACC Guideline For The Management of Patients Wit H Non-ST-Elevation Acute Coronar y Syndromes: Executive SummaryEmmieNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome ACSDocument9 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome ACSChen BrionesNo ratings yet
- Step 2 CK Review - CardiologyDocument28 pagesStep 2 CK Review - Cardiologyrsmd1986100% (1)
- 12 Hours: Continue To Monitor: High-Risk NSTEACSDocument1 page12 Hours: Continue To Monitor: High-Risk NSTEACSMeita ReligiaNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients With Acute Biologic CrisisDocument72 pagesCare of Patients With Acute Biologic CrisisJames QuilingNo ratings yet
- Fac Thrombolysis 2007Document36 pagesFac Thrombolysis 2007Tri Harjono0% (1)
- 9 CsaDocument34 pages9 Csaمحمد بن الصادقNo ratings yet
- MTB Cardiology NotesDocument11 pagesMTB Cardiology Noteskabal321No ratings yet
- MTB Cardiology NotesDocument7 pagesMTB Cardiology Noteskabal321No ratings yet
- Pocket Card Myocardial Infarction January 2024Document7 pagesPocket Card Myocardial Infarction January 2024تمارا مقداديNo ratings yet
- ACS-Karim AbdellatifDocument10 pagesACS-Karim AbdellatifKarim AbdellatifNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support in Adults (ACLS) : SubtitleDocument30 pagesAdvanced Cardiovascular Life Support in Adults (ACLS) : SubtitleMohamad El SharNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeFrom EverandCardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeNo ratings yet
- 10) Elbow JointDocument2 pages10) Elbow JointAris PaparisNo ratings yet
- 9-Histogenesis of The Intercellular Substance of The Connective Tissue-Pro Alpha Chain - Alpha Chain - ProCollagen - TropoCollagenDocument2 pages9-Histogenesis of The Intercellular Substance of The Connective Tissue-Pro Alpha Chain - Alpha Chain - ProCollagen - TropoCollagenAris PaparisNo ratings yet
- 15) Stable AnginaDocument3 pages15) Stable AnginaAris PaparisNo ratings yet
- 8) Chronic Cor PulmonaleDocument2 pages8) Chronic Cor PulmonaleAris PaparisNo ratings yet
- 17) AMI 1Document3 pages17) AMI 1Aris PaparisNo ratings yet
- 4 - Multi-Stratified Epithelia. Function, Structure, TypesDocument2 pages4 - Multi-Stratified Epithelia. Function, Structure, TypesAris PaparisNo ratings yet