Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 6
Assignment 6
Uploaded by
Warda HanifOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 6
Assignment 6
Uploaded by
Warda HanifCopyright:
Available Formats
Distance Protection Relays
Types of Distance Protection Relays
There are several types of distance protection relays, including:
1. Impedance (Z) Relays: These relays operate by measuring the impedance between the relay
location and the fault point. They are sensitive to changes in the system's impedance due to fault
conditions and can be classified into the following subtypes:
Mho (Circle) Relays: These are the most common type of impedance relays. They use a circle
diagram to determine the operating characteristics, which are typically set to protect a specific
line length and configuration.
Modified Mho Relays: These are variations of the mho relay that include features like offset
mho and quadrilateral characteristics to accommodate specific system conditions.
Offset Mho Relays: These relays are designed to provide more accurate protection for lines
with significant charging currents by incorporating an offset characteristic.
2. Reactance (X) Relays: Reactance relays measure the reactance of the system impedance rather
than the absolute impedance. They are typically used in systems where the impedance variation
due to fault is predominantly inductive or capacitive.
3. Admittance (Y) Relays: Admittance relays measure the admittance between the relay location and
the fault point. They are mainly used for protection against faults involving parallel branches or
systems with variable loads.
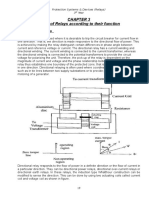
Working Principal And Uses of Distance Protection Relays:
A distance relay is a type of protection relay most often used for transmission line
protection. Distance relays measure the impedance from the installation side to the fault
location and operates in response to changes in the ratio of measured current and voltage
Distance protection is a type of protection relay that operates on the principle of impedance
measurement to detect and isolate faults in a power system. Here's a point by point
explanation of its working principle:
1. Impedance measurement: Distance protection relays measure the impedance of the
power system using the voltage and current signals at the relaying point. Impedance is the
ratio of voltage to current in a circuit, and it varies depending on the distance between the
relay and the fault.
2. Impedance characteristic: The relay's impedance characteristic is a plot of the measured
impedance versus the distance from the relay. This characteristic is programmed into the
relay and is based on the characteristics of the power system components.
3. Fault detection: When a fault occurs in the power system, the impedance measured by the
relay changes, and the impedance characteristic is used to determine the location of the
fault. The relay compares the measured impedance to the impedance characteristic and
operates if the measured impedance falls outside the characteristic.
4. Zone settings: The impedance characteristic is divided into zones, and the relay is
programmed with zone settings. Each zone represents a distance from the relay, and the
zone settings determine the relay's operating time for faults in that zone. The time delay is
set to allow upstream protection to operate before the distance protection operates.
5. Fault clearing: When the relay operates, it sends a trip signal to the circuit breaker to
isolate the fault. The trip signal is sent after the time delay set by the zone settings has
elapsed. The circuit breaker opens, and the fault is cleared.
In summary, distance protection relays detect faults by measuring the impedance of the
power system and comparing it to a programmed impedance characteristic. The relay
operates if the measured impedance falls outside the characteristic and sends a trip signal
to the circuit breaker to isolate the fault.
Three step Protection of transmission line
In order to cover a section of the line and to provide back-up protection to remote sections,
three main protection zones are set up with the following criteria .
Zone 1: this is set to protect between 80% of the line length AB.
Zone 2: this is set to protect 100% of the line length AB, plus at least 50% of the
shortest adjacent line BC and operates with time delay t2.
Zone 3: this is set to protect 100% of the two lines AB, BC, plus about 25% of the
third line CD and operates with time delay t3. In the project the starting element will
be the quadrilateral distance measuring element. It is not affected by the arc resistance
and least affected by the power swing. The remaining two elements will be reactance
measuring elements .
You might also like
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Trilogy of Wireless Power: Basic principles, WPT Systems and ApplicationsFrom EverandTrilogy of Wireless Power: Basic principles, WPT Systems and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Over Current Relay Types and ApplicationsDocument11 pagesOver Current Relay Types and ApplicationskishansaiNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsFrom EverandA Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Architectural Emi Shielding PDFDocument229 pagesArchitectural Emi Shielding PDFluxof100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Modern Electrical Substations - Part 2 - R2Document22 pagesFundamentals of Modern Electrical Substations - Part 2 - R2Harish De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Power System Protection Lecture 2: Protection Paradigms - Apparatus ProtectionDocument7 pagesFundamentals of Power System Protection Lecture 2: Protection Paradigms - Apparatus Protectionsunny1725No ratings yet
- Report On Radial Feeder ProtectionDocument20 pagesReport On Radial Feeder ProtectionSubhamGangdeb78% (9)
- Protection and Switchgear Important QuestionsDocument38 pagesProtection and Switchgear Important QuestionsAkhil Surya0% (1)
- Topic 7: Pilot ProtectionDocument49 pagesTopic 7: Pilot ProtectionMohammedNasserNo ratings yet
- Distribution Overcurrent Protection and CoordinationDocument52 pagesDistribution Overcurrent Protection and CoordinationRonieboy Baliber CairoNo ratings yet
- SGP 6Document7 pagesSGP 6Soumajit PoddarNo ratings yet
- Web - Itu.edu - TR Yumakk Downloads Lab Notes Distance Protection v1Document6 pagesWeb - Itu.edu - TR Yumakk Downloads Lab Notes Distance Protection v1sunitharajababuNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection Lec 3Document16 pagesPower System Protection Lec 3DobaNo ratings yet
- Principles and Characteristics of Distance ProtectionDocument5 pagesPrinciples and Characteristics of Distance ProtectionFrancisco MartinezNo ratings yet
- Distance Protection of Series Compensated Transmission LineDocument9 pagesDistance Protection of Series Compensated Transmission Lineyand_carlosNo ratings yet
- Introduction ProtectionDocument15 pagesIntroduction ProtectionAyushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-2Document27 pagesUnit 1-2yogesh.pdy7No ratings yet
- Report On Radial Feeder ProtectionDocument15 pagesReport On Radial Feeder ProtectionHarshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Protection System 1 To 150Document95 pagesElectrical Protection System 1 To 150Anirban Bandyopadhyay50% (2)
- Basic Line ProtectionDocument30 pagesBasic Line ProtectionMaduike Obinna HenryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Det50083 PTSBDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Det50083 PTSBNUR RABBIATUL ADAWIYAH MOHAMMADNo ratings yet
- Electrical NotesDocument22 pagesElectrical NotesJamil AhmadNo ratings yet
- Pp01to09 Into+DefDocument10 pagesPp01to09 Into+DefBenhur A. PossattoNo ratings yet
- Long Transmission Lines: Since Long Lines Are Highly Subjected To Power Swings (Load SheddingDocument4 pagesLong Transmission Lines: Since Long Lines Are Highly Subjected To Power Swings (Load Sheddingkrishna chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- PSP ImpDocument36 pagesPSP ImpHarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Distance Protection RelayDocument2 pagesDistance Protection RelayThirumalNo ratings yet
- UniMasr.com 79e3983af376cc3e0a3c7adef354815eDocument60 pagesUniMasr.com 79e3983af376cc3e0a3c7adef354815eBala MNo ratings yet
- Zone of ProtectionDocument17 pagesZone of ProtectionAkimeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3nassim.1979No ratings yet
- Chapter 1-2-3Document170 pagesChapter 1-2-3Nitish Nageshwara RaoNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of Distance Relay For Transmission Line ProtectionDocument10 pagesModeling and Simulation of Distance Relay For Transmission Line Protectionයෙදුම් Karunarathna100% (1)
- Radial Feeder ProtectionDocument6 pagesRadial Feeder ProtectionSrivalli ReddyNo ratings yet
- Distance Protection Relay - FinalDocument16 pagesDistance Protection Relay - FinalDilina Iroshan DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Principle of Power SystemDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Principle of Power SystemSurendra PanditNo ratings yet
- Basic Power Protection Relaying Manual PDFDocument407 pagesBasic Power Protection Relaying Manual PDFmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Protection of Feeder and Transmission LinesDocument6 pagesProtection of Feeder and Transmission LinesKetan KishoreNo ratings yet
- Power System ProtectionDocument6 pagesPower System ProtectionGaurav RaiNo ratings yet
- Protection of Electrical SystemDocument34 pagesProtection of Electrical SystemDan C. LabagnoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Electrical Protection SystemDocument101 pagesChapter-3 Electrical Protection Systemgerrzen64No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Slides 2023Document52 pagesUnit 4 Slides 2023Theko LeroyatvarsityNo ratings yet
- Line ProtectionDocument91 pagesLine Protectionhafiz_hazreen100% (1)
- İnstruction To System ProtectionDocument91 pagesİnstruction To System ProtectionSuat KaracanNo ratings yet
- Development of Distance Relay in Matlab: Jayant Lamture, A. P. VaidyaDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Distance Relay in Matlab: Jayant Lamture, A. P. VaidyahasanNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document105 pagesCH 1Haben Mekonen NegidNo ratings yet
- Protection Basic (Traditional) - IDAHO PowerDocument93 pagesProtection Basic (Traditional) - IDAHO PowerLiang CheNo ratings yet
- Application of Zone 3 Distance Relays On Transmission LinesDocument6 pagesApplication of Zone 3 Distance Relays On Transmission LinesLog in 2007No ratings yet
- D1 DisDocument299 pagesD1 DisShahin AsadiFardNo ratings yet
- PSP PresentationDocument7 pagesPSP PresentationTahmid Mohammad RongonNo ratings yet
- Zones of Protection and General Principles of ProtectionDocument5 pagesZones of Protection and General Principles of ProtectionFuadNo ratings yet
- Chp-1-Part-1 Fund. of Protection and RelaysDocument97 pagesChp-1-Part-1 Fund. of Protection and RelaysSentex Habasha100% (1)
- Types of ProtectionDocument9 pagesTypes of Protectionkxalxo7637No ratings yet
- Power Systems Dr.Document3 pagesPower Systems Dr.eng mabenkNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection: Topic: IntroductionDocument19 pagesPower System Protection: Topic: Introductionayan PatelNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Power System ProtectionDocument15 pagesFundamentals of Power System Protectionty14344100% (1)
- Principio de ProteccionesDocument5 pagesPrincipio de ProteccionesBrenda Naranjo MorenoNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection - Part 08Document16 pagesPower System Protection - Part 08Rahul MandalNo ratings yet
- Protection of Power SystemDocument5 pagesProtection of Power SystemOdai SalehNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Distribution of Electric Power CourseFrom EverandDistribution of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Distribution of Electric Power CourseNo ratings yet
- Exp 5Document4 pagesExp 5Warda HanifNo ratings yet
- Lab - Manual 1Document1 pageLab - Manual 1Warda HanifNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1+2Document15 pagesLecture 1+2Warda HanifNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document2 pagesAssignment 4Warda HanifNo ratings yet
- Service ManualDocument72 pagesService ManualezequielNo ratings yet
- Marantz AV 9000 Service ManualDocument49 pagesMarantz AV 9000 Service ManualsrinivasanNo ratings yet
- S2D2Direction Finding Basics and MethodsDocument55 pagesS2D2Direction Finding Basics and Methodsjosestalin120No ratings yet
- Classification of Electronic FiltersDocument9 pagesClassification of Electronic FiltersSanjay CrNo ratings yet
- 275 053 Dayton Audio ND25FN 4 SpecificationsDocument1 page275 053 Dayton Audio ND25FN 4 SpecificationsjoseNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Sansui 1978Document8 pagesCatalogue Sansui 1978P HandokoNo ratings yet
- Audio SpotlightDocument40 pagesAudio SpotlightAbhishek BendigeriNo ratings yet
- Millimeter-Wave Technology and Research Trends For 5G Access and Wireless Transmission Applications An Industry ViewDocument1 pageMillimeter-Wave Technology and Research Trends For 5G Access and Wireless Transmission Applications An Industry ViewBry ZeosNo ratings yet
- Panomera Muswe PanonyeredzaDocument177 pagesPanomera Muswe PanonyeredzaAbraham MakameraNo ratings yet
- Communication Chapter OneDocument10 pagesCommunication Chapter OneMustafa Alobaidi100% (2)
- EuroTel Med Power UHF-VHF Air-Cooled Series Ed 2013Document6 pagesEuroTel Med Power UHF-VHF Air-Cooled Series Ed 2013elang_tyoNo ratings yet
- Ifmar WC 8th Offroad 2014Document21 pagesIfmar WC 8th Offroad 2014Marcio PisiNo ratings yet
- Chirp RadarDocument64 pagesChirp RadarLuis Gonzalo Baldeon HuanquiNo ratings yet
- 05 UMTS Uplink Interference AnalysisDocument4 pages05 UMTS Uplink Interference AnalysisJames BaileyNo ratings yet
- WF - Hytera PD56X VHF&UHF1 Service Manual 04-02-14Document160 pagesWF - Hytera PD56X VHF&UHF1 Service Manual 04-02-14A&A LABORATORIO100% (1)
- Product Specifications: KSM8 Dualdyne Handheld Dynamic Vocal MicrophoneDocument1 pageProduct Specifications: KSM8 Dualdyne Handheld Dynamic Vocal Microphone21BVC120Jhewin FrankNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Ee 301Document2 pagesTutorial 2 Ee 301PulkitNo ratings yet
- Electrical Specifications: 8-Port Planar Array Antenna, 2300-2400 MHZ, 90° HPBW, 1X RetDocument5 pagesElectrical Specifications: 8-Port Planar Array Antenna, 2300-2400 MHZ, 90° HPBW, 1X RetIkie BarieNo ratings yet
- GIC Catalogue - 022011 2 PDFDocument74 pagesGIC Catalogue - 022011 2 PDFvicky_doshi096004No ratings yet
- AppendixDocument19 pagesAppendixDr-Eng Imad A. ShaheenNo ratings yet
- Panasonic TX p50gw10 Gpf12de Chassis SM (ET)Document134 pagesPanasonic TX p50gw10 Gpf12de Chassis SM (ET)Luděk CsibaNo ratings yet
- 5G For Future Wireless NetworksDocument712 pages5G For Future Wireless Networkskabi6713No ratings yet
- Mototrbo Portable Dep 450 Basic Service ManualDocument95 pagesMototrbo Portable Dep 450 Basic Service ManualAyon BaxterNo ratings yet
- Datasheet A25-4102920-AMT02 (Rev 0)Document6 pagesDatasheet A25-4102920-AMT02 (Rev 0)djebinNo ratings yet
- Rctproah PDF 1630245401Document122 pagesRctproah PDF 1630245401張允執No ratings yet
- Ocean Rescue EPIRB1-user-manualDocument16 pagesOcean Rescue EPIRB1-user-manualrfpedleyNo ratings yet
- YAYAADocument35 pagesYAYAAhandika pratamaNo ratings yet
- FBB150 Installation Manual 2014Document88 pagesFBB150 Installation Manual 2014Yanko150No ratings yet
- Groovy ICP ETCHER SST G Vinogradov - Apr05Document7 pagesGroovy ICP ETCHER SST G Vinogradov - Apr05Peter-sagami100% (1)