Professional Documents
Culture Documents
COSMAN1 Learning Packet 1 Introductionto Cost Accounting
COSMAN1 Learning Packet 1 Introductionto Cost Accounting
Uploaded by
Alexander QuemadaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
COSMAN1 Learning Packet 1 Introductionto Cost Accounting
COSMAN1 Learning Packet 1 Introductionto Cost Accounting
Uploaded by
Alexander QuemadaCopyright:
Available Formats
Ateneo de Zamboanga University
School of Management and Accountancy
Accountancy Department
LEARNING PACKET
COSMAN1, Session 2, First Semester, SY 2020-21
LEARNING PACKET 1
TOPIC: Introduction to Cost Accounting
I. CONCEPT NOTES
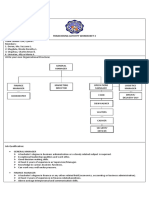
Purpose of Accounting?
-to provide financial information about an economic entity to different types of users
Investors
Creditors Financial
External
Government Accounting
Others
Users
Board of
Directors Managerial
Internal
Managers Accounting
Employees
Comparison
Financial Accounting Managerial Accounting
• Primary Users are external • Primary Users are internal
• Focus is historical information • Focus is future prospects
• Purpose is to communicate the financial • Purpose is to help managers and owners make
position and performance of a company decision to fulfill organization’s goals
• Information is mostly financial in nature • Information is both financial and non-financial
• Uses standards (IFRS, GAAP) that is required in nature
to be followed • No standards required to be followed
Cost Accounting
• It is the intersection between financial and management accounting because it addresses
informational demands of both financial and management accounting by providing information
to external and internal parties.
Relationship with Financial accounting - Inventory Valuation (production of units render cost, and cost
accounting gives financial information about costs related to production of a product)
Relationship with Managerial accounting - Decision making (costs incurred can be used for projection in
budgeting and forecasting, for pricing decisions, performance evaluation, and other management-
related tasks)
Interrelationship between the three disciplines:
• Cost information collected will be recorded in the journals, and these costs are used to plan and
decide for future prospects by managers
• To better use the cost information, managers should strategize on how to use capabilities and
opportunities to accomplish its objectives-thus the birth of strategic cost management
Strategic Cost Management
• Describes cost management that specifically focuses on strategic issues
• Questions that help managers formulate strategy:
1. Customers
2. Market
3. Capabilities
4. Funding
One specific strategy is to focus on our Value Chain Analysis
Value Chain
is the sequence of business functions in which customer usefulness is added to products.
Business Functions include:
A. Research and Development
B. Design of products and services
C. Production
D. Marketing
E. Distribution
F. Customer Service
Administrative Functions (accounting, HR, IT) support the business function
Supply chain
the parts of the value chain associated with producing and delivering a product or service, which
are production and distribution
describes the flow of goods, services, and information from the initial sources of materials and
services to the delivery of products to consumers, regardless of whether those activities occur in
the same organization or in other organizations
Key Success Factors
• Cost and Efficiency
• Quality
• Time
• Innovation
Professional Ethics
• Enron, WorldCom, Arthur Andersen eroded public confidence in corporations
• Earnings Management- any accounting method or practice used by managers or accountants to deliberately
adjust a company's profit to meet a predetermined internal or external target
Statement of Ethical Professional Practice
• CMAs are required to adhere to these set of standards which focuses on
A. Competence (level of professional expertise)
B. Confidentiality (appropriate use of confidential information)
C. Integrity (Mitigate conflict of interest, avoid discredit the profession)
D. Credibility (communicate information fairly and objectively)
You might also like
- Assignment Cover Page: Example: BUSM4535Document15 pagesAssignment Cover Page: Example: BUSM4535Vu Anh Quang100% (2)
- DaburDocument18 pagesDaburSwati0101100% (1)
- Final Exam Marketing PDFDocument17 pagesFinal Exam Marketing PDFPrashant GautamNo ratings yet
- Marketing AssignmentDocument14 pagesMarketing Assignmentvineel kumarNo ratings yet
- Lec 01 Cost and Management AccDocument53 pagesLec 01 Cost and Management AccMd Shawfiqul IslamNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting, Also Known As Management Accounting, Is The Process of Identifying, MeasuringDocument11 pagesManagerial Accounting, Also Known As Management Accounting, Is The Process of Identifying, MeasuringJeffrey De LeonNo ratings yet
- Fa Class Notes UplodedDocument252 pagesFa Class Notes UplodedDurvas Karmarkar100% (1)
- Financial AccountingDocument252 pagesFinancial AccountingSonia Dhar100% (1)
- Cost Accounting PDFDocument35 pagesCost Accounting PDFSanta-ana Jerald JuanoNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting (MA)Document114 pagesManagement Accounting (MA)Shivangi Patel100% (1)
- 1.1 Evolution of Management Accounting - Part 1Document23 pages1.1 Evolution of Management Accounting - Part 1Dabbie JoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Cost Accounting Chapter - IDocument10 pagesChapter One: Cost Accounting Chapter - IlemiNo ratings yet
- Fma CH 1 IntroductionDocument32 pagesFma CH 1 IntroductionHabtamuNo ratings yet
- Chapetr1-Overview of Cost and Management AccountingDocument12 pagesChapetr1-Overview of Cost and Management AccountingNetsanet BelayNo ratings yet
- Accounting For ManagersDocument224 pagesAccounting For Managershabtamu100% (1)
- Cost & Mgt. Acct - I, Lecture Note - Chapter 1 & 2Document35 pagesCost & Mgt. Acct - I, Lecture Note - Chapter 1 & 2Yonas BamlakuNo ratings yet
- Fmac Chapter One CpuDocument121 pagesFmac Chapter One CpuMasresha Tasew100% (1)
- MA Lecture 1 - Introduction To MA (6 Slides Per Page)Document8 pagesMA Lecture 1 - Introduction To MA (6 Slides Per Page)surangauorNo ratings yet
- Management Accountancy: MM/EBM 2153Document37 pagesManagement Accountancy: MM/EBM 2153Anuruddha RajasuriyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1-Financial AccountingDocument85 pagesChapter-1-Financial AccountingHabesh FilmsNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Chapter 1Document30 pagesManagement Accounting Chapter 1dawsonNo ratings yet
- Module 1-1 Cost Accounting FundamentalsDocument9 pagesModule 1-1 Cost Accounting FundamentalsClaire BarbaNo ratings yet
- Cost Managemet Acc Capter 1Document13 pagesCost Managemet Acc Capter 118FB014 Hridoy PalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management AccountingDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Management AccountingSwapnil Singh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Advanced Management Accounting: Dr. Ronny Andesto, S.E., M.M Program Magister Akuntansi Universitas Mercu Buana 2018Document30 pagesAdvanced Management Accounting: Dr. Ronny Andesto, S.E., M.M Program Magister Akuntansi Universitas Mercu Buana 2018dhianNo ratings yet
- 1 - Overview of AccountingDocument49 pages1 - Overview of AccountingGeraldine Lop-nao GermanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter12024Document23 pagesChapter12024govindam.mittalNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: S.Y. BmsDocument36 pagesManagement Accounting: S.Y. BmsYashwardhan KrNo ratings yet
- University of London (LSE)Document33 pagesUniversity of London (LSE)Dương DươngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document26 pagesChapter 1Robel HabtamuNo ratings yet
- MA Lecture 1 - Introduction To MA (3 Slides Per Page)Document15 pagesMA Lecture 1 - Introduction To MA (3 Slides Per Page)surangauorNo ratings yet
- MPA 602: Cost and Managerial AccountingDocument42 pagesMPA 602: Cost and Managerial AccountingMd. ZakariaNo ratings yet
- MAC 307 Updated Lecture Slides 05112021Document317 pagesMAC 307 Updated Lecture Slides 05112021Denny ChakauyaNo ratings yet
- 1 CombinedDocument405 pages1 CombinedMansi aggarwal 171050No ratings yet
- The Accountant'S Role in The Organization: Iii. Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesThe Accountant'S Role in The Organization: Iii. Lecture Notesgkmishra2001 at gmail.com100% (1)
- BIT 163 Introduction To AccountingDocument26 pagesBIT 163 Introduction To AccountingBalach MalikNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Management AccountingDocument16 pagesMODULE 1 Management AccountingABEL, CHARLYN JOY LUARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document23 pagesChapter 1Nandini SinhaNo ratings yet
- American College of Technology Department of Business Studies Mba ProgramDocument37 pagesAmerican College of Technology Department of Business Studies Mba ProgramTeke TarekegnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AccountingDocument43 pagesIntroduction To AccountingDonnieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Intro - CLC - HandoutDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - Intro - CLC - HandoutMai ChiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Managerial AccountingDocument22 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Managerial AccountingviraNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting !!Document5 pagesManagerial Accounting !!Putri Utami WulandariNo ratings yet
- Maryland International College: Accounting and Finance For ManagersDocument26 pagesMaryland International College: Accounting and Finance For ManagersANTENEH ENDALE DILNESSANo ratings yet
- Introduction To AccountingDocument10 pagesIntroduction To AccountingMary HealyNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1Document66 pagesChapter One 1Kirubel SolomonNo ratings yet
- BBAW2103 Topic 1Document30 pagesBBAW2103 Topic 1MOHD SYUKRI BIN ABDUL WAHAB STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Cost and Management Accounting IDocument77 pagesCost and Management Accounting Iasressherute70No ratings yet
- Introduction of AccountingDocument13 pagesIntroduction of AccountingJuliet OllaminaNo ratings yet
- Cost and Management AccountingDocument51 pagesCost and Management Accountingabhijeet0% (1)
- Introduction To Managerial AccountingDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Managerial Accountingpvsk17072005No ratings yet
- Unit - 1 محاسبه اداريهDocument29 pagesUnit - 1 محاسبه اداريهsuperstreem.9No ratings yet
- Managerial AccountingDocument5 pagesManagerial Accountingjaninemaeserpa14No ratings yet
- Group Buad 803Document7 pagesGroup Buad 803oluseyi osifuwaNo ratings yet
- Introudction To Management Accounting RevisedDocument27 pagesIntroudction To Management Accounting RevisedraghbendrashahNo ratings yet
- ACC-223 SIM Week-1-3 ULOaDocument13 pagesACC-223 SIM Week-1-3 ULOaChara etangNo ratings yet
- MCOM2001 Managerial Decisions AccountingDocument241 pagesMCOM2001 Managerial Decisions AccountingspymeherNo ratings yet
- 1 - Objectives, Role and Scope of Management AccountingDocument11 pages1 - Objectives, Role and Scope of Management Accountingmymy100% (2)
- Chater OneDocument12 pagesChater OneFasiko AsmaroNo ratings yet
- L2 Management AccountingDocument23 pagesL2 Management Accountingvidisha sharmaNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Unit1Document5 pagesManagement Accounting Unit1manikasehgal2No ratings yet
- Introduction To Cost Accounting: This Chapter IncludesDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Cost Accounting: This Chapter IncludesMuhammad BasitNo ratings yet
- The Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successFrom EverandThe Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- FINAL Is PAPER DaguroMarcosQuemadaDocument18 pagesFINAL Is PAPER DaguroMarcosQuemadaAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS TAX..docx - PROBLEM SET Problem 1 VAT-Exempt Transactions Determine Which Transaction(s) Is (Are) Exempt From VAT. 1. SDocument1 pageBUSINESS TAX..docx - PROBLEM SET Problem 1 VAT-Exempt Transactions Determine Which Transaction(s) Is (Are) Exempt From VAT. 1. SAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- Alex MarketDocument2 pagesAlex MarketAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- Pa REDIDocument2 pagesPa REDIAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- ACARecos CommsDocument3 pagesACARecos CommsAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- Franchising Activity Worksheet 3Document4 pagesFranchising Activity Worksheet 3Alexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- mrktg01 Week2Document15 pagesmrktg01 Week2Alexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- Letter For BB DezDocument1 pageLetter For BB DezAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- Litmin PresentationDocument2 pagesLitmin PresentationAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- SONNET 116 LessonDocument3 pagesSONNET 116 LessonAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Alexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- 12222Document9 pages12222Alexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- ETHICS Post Module Activity#4Document4 pagesETHICS Post Module Activity#4Alexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- ETHICS A - SYNTHESIS IntegrationDocument7 pagesETHICS A - SYNTHESIS IntegrationAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- B U S E C O 1: Theory of Individual BehaviorDocument29 pagesB U S E C O 1: Theory of Individual BehaviorAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- Part Two: Supply and Demand I: How Markets WorkDocument42 pagesPart Two: Supply and Demand I: How Markets WorkAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- Cell Name Original Value Final ValueDocument25 pagesCell Name Original Value Final ValueAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- Baluan TimelineDocument6 pagesBaluan TimelineAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- Baluan TimelineDocument6 pagesBaluan TimelineAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- Baluan TimelineDocument6 pagesBaluan TimelineAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- AlallDocument4 pagesAlallAlexander Quemada100% (1)
- Nature of Inquiry and Research: Some Research Ethics PrinciplesDocument11 pagesNature of Inquiry and Research: Some Research Ethics PrinciplesAlexander QuemadaNo ratings yet
- CRMDocument25 pagesCRMpuneeta chughNo ratings yet
- Final Project of Cost AccountingDocument16 pagesFinal Project of Cost AccountingMariya Saeed100% (1)
- 2nd Year Resume Writing Guidelines - StudentDocument44 pages2nd Year Resume Writing Guidelines - StudentDYPUSM WECNo ratings yet
- Demand and SupplyDocument15 pagesDemand and SupplytagashiiNo ratings yet
- Marketing - Positioning and Communication StrategyDocument9 pagesMarketing - Positioning and Communication StrategyMuskanNo ratings yet
- Indus Motor Company PakistanDocument73 pagesIndus Motor Company PakistanMalik Nasir AbbasNo ratings yet
- Best LinkedIn Invitations - 2018 Guide To Connecting (With Templates)Document7 pagesBest LinkedIn Invitations - 2018 Guide To Connecting (With Templates)Sabina vlaicuNo ratings yet
- 9 External Environment Factors That Affect BusinessDocument5 pages9 External Environment Factors That Affect BusinessHasan NaseemNo ratings yet
- Socialmediastrategy 230315074626 7ef0c173Document6 pagesSocialmediastrategy 230315074626 7ef0c173SAQUIB ALAMNo ratings yet
- Brighter Smiles For The Masses - Colgate vs. P&G - Group 10Document10 pagesBrighter Smiles For The Masses - Colgate vs. P&G - Group 10sneha upadhyayNo ratings yet
- CLV Csi ProjectDocument13 pagesCLV Csi ProjectSrisha Prasad RathNo ratings yet
- Knowledgeable Sales Person Who Can Act As A Trusted AdvisorDocument1 pageKnowledgeable Sales Person Who Can Act As A Trusted AdvisorProjNo ratings yet
- Summary Chapter 1 Creating Blue Ocean Mirza M Abdullah 2655 SMDocument2 pagesSummary Chapter 1 Creating Blue Ocean Mirza M Abdullah 2655 SMabd.mirza2627No ratings yet
- Trabalho de Campo 3 de InglesDocument12 pagesTrabalho de Campo 3 de InglesBEBITO MIZENo ratings yet
- Choco MallowDocument17 pagesChoco MallowNickenson Cruz CauilanNo ratings yet
- Flare Fragrance Case-NPD Group 8Document6 pagesFlare Fragrance Case-NPD Group 8Abhi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Amway BrandingDocument2 pagesAmway BrandingSophia PhoebeNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Corona BeerDocument7 pagesCase Analysis Corona Beerfbl3No ratings yet
- Class 5 - TM Theory 2021-22Document4 pagesClass 5 - TM Theory 2021-22UTKARSH PANDEYNo ratings yet
- The 4Ps and 4 As of Rural MarketingDocument6 pagesThe 4Ps and 4 As of Rural MarketinggunjanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document40 pagesChapter 8Ahmed Ali DhakuNo ratings yet
- Internal Analysis (IFE)Document37 pagesInternal Analysis (IFE)mughni5000No ratings yet
- Advertising and Promotions - ADVT706Document395 pagesAdvertising and Promotions - ADVT706hibha moosaNo ratings yet
- Dma602 Marketing CommunicationDocument42 pagesDma602 Marketing CommunicationBen OusoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Advantages of Distribution Management System and Growing Importance of Distribution For Strategic AdvantageDocument24 pagesLesson 6 - Advantages of Distribution Management System and Growing Importance of Distribution For Strategic AdvantageIris Cristine GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Advertising Agency Internship ReportDocument63 pagesAdvertising Agency Internship Reportkotojef674No ratings yet