Professional Documents
Culture Documents
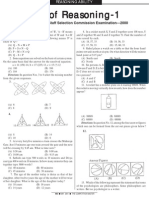
Reasoning 2
Reasoning 2
Uploaded by
Sushant RanjanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reasoning 2
Reasoning 2
Uploaded by
Sushant RanjanCopyright:
Available Formats
Reasoning 2
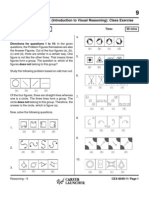
Odd One Out, Input / Output flow charts, Visual Reasoning,
Matrix & Cube based problems, Binary logic (Truth & Lie), Misc problems
Number of Questions : 45 CEX–0508/20
Directions for questions 1 to 4: Each of the following questions has four terms out of which three are
similar due to some common characteristic. Find the odd one out which does not share that common
characteristic with the other three.
1. (a) 12 (b) 36 (c) 80 (d) 148
2. (a) Violet (b) Brown (c) Orange (d) Indigo
3. (a) Yard (b) Metre (c) Kilogram (d) Inch
4. (a) CDE (b) OPQ (c) QST (d) LMN
Directions for questions 5 and 6: A word arrangement machine when given an input line of words,
rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input rearrangement.
Input : its easy to swim with the stream
Step I : easy its to swim with the stream
Step II : easy to swim with the stream its
Step III : easy stream to swim with the its
Step IV : easy stream to with the swim its
Step V : easy stream the to with swim its
Step VI : easy stream the with to swim its
5. What would be the step IV for the following input “will we go for a party tonight”?
(a) a go will we tonight party for
(b) a go we will tonight party for
(c) for go we will tonight party a
(d) a go will tonight we party for
6. What will be the final step for the following input “I had dinner at Hilton towers today”?
(a) Step III (b) Step IV (c) Step V (d) Step VI
Non-CAT Exams / Reasoning – 2 Page 1
Direction for questions 7 to 9: Whiz kids have designed a new computer. A set of numbers is fed to it as
Input and certain operations are performed on them according to defined rules of rearrangement. A sample
input and steps for rearrangement are given below. Answer the questions that follow.
Input: 16 9 4 49 1 36 25 100 64 81
Step 1 : 4 3 2 7 1 6 5 10 8 9
Step 2 : 8 6 4 14 2 12 10 20 16 18
Step 3 : 64 36 16 196 4 144 100 400 256 324
Step 4 : 32 18 8 98 2 72 50 200 128 162
Step 5 : 42 28 18 108 12 82 60 210 138 172
(Step 5 is the final step.)
7. Which one of the following will be Step 5, i.e. the final step, for the following input?
Input: 121 196 169 4 36 225 256 25 1 289
(a) 252 412 348 18 82 460 522 60 12 588
(b) 252 402 348 18 82 460 522 60 12 588
(c) 262 402 348 18 82 460 522 60 12 588
(d) 252 402 348 18 82 460 532 60 12 588
(e) 252 402 348 18 92 460 532 60 12 588
8. The following is Step 3 for a certain input:
Step 3: 36 324 3364 3844 4356 6400 10000 12100 1936 400
Which of the following is the original input?
(a) 9 81 841 961 1089 1600 2500 3025 484 100
(b) 9 64 841 961 1089 1600 2500 3025 484 100
(c) 9 81 841 961 1089 1681 2500 3025 484 100
(d) 16 81 841 961 1089 1600 2500 3025 484 100
(e) 16 81 841 961 1089 1600 2500 3025 484 121
9. The following is Step 4, for a certain input:
Input: 128 338 450 648 968 1152 1568 1682
Which of the following is the original input?
(a) 64 169 225 324 484 676 784 841
(b) 64 169 225 324 384 576 784 841
(c) 64 169 225 334 384 576 784 841
(d) 74 169 225 334 384 576 784 841
(e) 64 169 225 324 484 576 784 841
Page 2 Non-CAT Exams / Reasoning – 2
Directions for questions 10 to 14: In the given questions, the Problem Figures themselves are also the
Answer Figures. Out of the five figures (a, b, c, d and e), four are similar in a certain way. One figure is not
like the other four. That means four figures form a group. The question is: which of the figure does not
belong to this group?
Study the following problem based on odd man out.
(a ) (b ) (c) (d ) (e )
Of the five figures, four are straight-lines whereas one is a circle. The four lines form a group. The circle
does not belong to this group. Therefore, the answer is the circle, which is figure (a).
Now, solve the following questions.
10.
(a ) (b ) (c) (d ) (e )
11.
(a ) (b ) (c) (d ) (e )
12.
(a ) (b ) (c) (d ) (e )
13.
(a ) (b ) (c) (d ) (e )
14.
(a ) (b ) (c) (d ) (e )
Non-CAT Exams / Reasoning – 2 Page 3
Directions for questions 15 to 19: In these questions, there are two sets of figures. The Problem Figures
and the Answer Figures. The five Problem Figures make a series. That means they change from left to right
in a specific order. The question is, if the figures continue to change in the same order, what should the
sixth figure be?
Study the following problem based on series.
Problem Figures Answ er Figures
(a ) (b ) (c) (d ) (e )
In the example above, as you go from left to right, you find the line across the Problem Figures falling
downward. The question is, if the line continues to fall, what will be its next, i.e. sixth position? The answer
would be: it would fall further from the horizontal.
Now, look at the Answer Figures. You find that Answer Figure (c) is the correct answer.
Now, solve the following questions.
Problem Figures Answer Figures
O = =
X
15. =
X X S C
(a ) (b ) (c) (d ) (e )
16.
(a ) (b ) (c) (d ) (e )
17.
(a ) (b ) (c) (d ) (e )
18.
(a ) (b ) (c) (d ) (e )
19.
(a ) (b ) (c) (d ) (e )
Page 4 Non-CAT Exams / Reasoning – 2
Directions for questions 20 to 23: Answer the Directions for questions 27 and 28: Answer the
questions on the basis of the information given below. questions on the basis of the information given below.
A large cube is painted on all six faces and cut A large cube was painted on all six faces and then
into 27 smaller but identical cubes. cut into smaller but identical cubes. Among these
cubes there were 24 which had exactly one face
20. How many of the smaller cubes have no face painted.
painted at all?
(a) 0 (b) 2 27. In how many smaller cubes was the original
(c) 1 (d) 3 large cube cut into?
(a) 125 (b) 216
21. How many of the smaller cubes have exactly (c) 64 (d) 27
one face painted?
(a) 3 (b) 9 28. How many of the smaller cubes had exactly
(c) 6 (d) 12 two faces painted ?
(a) 12 (b) 8
22. How many of the smaller cubes have exactly (c) 24 (d) 48
two faces painted?
(a) 4 (b) 12 Directions for questions 29 and 30: On the planet
(c) 20 (d) 16 Mars, the Martians invented a new symbol based
mathematical operation system which helps them
23. How many of the smaller cubes have exactly in calculation based on the conditions given below.
three faces painted? Now answer the following questions based on these
(a) 0 (b) 4 conditions.
(c) 12 (d) 8
1. A % B * C implies that sum of B and C is
Directions for questions 24 to 26: Answer the subtracted from product of A and B.
questions on the basis of information given below. 2. A ? B ω C implies that difference between A
and B is multiplied by C.
A large cube painted on all six faces is cut into 343 3. A + B × C implies that square of sum of A and
smaller but identical cubes. C is added to B.
4. A $ B ! C implies that C is subtracted from
24. How many of the smaller cubes have exactly sum of squares of A and B.
one face painted?
(a) 125 (b) 216 29. 23 % 4 * 70 = p
(c) 150 (d) 175 p $ 25 ! 100 = ?
(a) 947 (b) 749
25. How many of the smaller cubes have exactly (c) 849 (d) 948
two faces painted ?
(a) 90 (b) 120 30. 43 ? 34 ω 3 = y
(c) 60 (d) 30 11 + y × 15 = ?
(a) 703 (b) 578
26. How many of the smaller cubes have exactly (c) 670 (d) 576
three faces painted ?
(a) 4 (b) 12
(c) 8 (d) 16
Non-CAT Exams / Reasoning – 2 Page 5
31. Find out the missing number/letter shown by Down - 1 : A three-digit number divisible by 25.
the question mark (?) in the matrix given Down - 3 : A three-digit prime number having 9
below. as its unit’s digit.
3C 2B 4A Note: Across - 1 means the number should be filled
in the grid horizontally starting from the cell
27A ? 64C number 1. Similarly, Down - 1 means the
9C 4A 16B
number should be filled in the grid vertically
starting from the cell number 1.
(a) 8B (b) 16C
(c) 8C (d) 12B 34. The sum of the digits filled in cell number 1
and cell number 6 is
32. Select a suitable number from the four (a) 9 (b) 13 (c) 16
alternatives that would complete the following (d) 4 (e) 12
number matrix.
35. What could be the possible value of the digit
1 1 2 filled in the cell number 8, if the number filled
2 3 3 in Down - 2 is a prime number?
3 ? 6 (a) 1 (b) 3 (c) 7
(a) 4 (b) 14 (d) 9 (e) 4
(c) 9 (d) 19
36.
33. In the following question, a number matrix is A B C
given. These number follow a certain trend,
row-wise or column-wise. Find out the trend D E (5) F
and choose the missing character
accordingly.
G (8) H I(6 )
3 4 ?
7 9 8 Given above is a 3 × 3 grid with each unit box
21 36 72 filled with natural numbers less than 10. All
the nine boxes are filled with distinct natural
(a) 6 (b) 9
numbers. If the sum of numbers in each row,
(c) 12 (d) 18
each column and each of the diagonals is
15, then which of the following numbers is
Directions for questions 34 and 35: Answer the
filled in box C?
questions on the basis of the information given below.
(a) 6 (b) 2 (c) 3
There is a (3 × 3) grid which have cells numbered
(d) 7 (e) 8
from 1 to 9. The cells of the grid have to be filled as
per the information provided below.
37. Find the term in place of question mark (?).
1 2 3
3C 7B 5A
4 5 6
8A ? 1B
7 8 9
Across - 1 : A three-digit perfect cube having its 4B 2A 9C
sum of digits equal to 18.
Across - 4 : A three-digit perfect cube. (a) 8C (b) 6B (c) 6C (d) 8A
Page 6 Non-CAT Exams / Reasoning – 2
38. Which number should come in place of ‘x’ 42. TIGER : COBRA : : EAGLE : ____
and ‘y’ respectively? (a) NGBYN (b) NHAYN
(c) MHAZM (d) MGBXM
y
Directions for questions 43 to 45: Answer the
x 48 questions on the basis of the information given below.
There are only four members in a family – P, Q, R
and S. P and R form a couple. When asked about
6 4 12
their relationships, following were their replies:
3 2 2 6 i. P: Q is my son. S is my mother.
ii. Q: P is my mother. S is my grandmother.
iii. R: P is my wife. Q is my son.
(a) 24 and 72 (b) 36 and 1008
iv. S: Q is my granddaughter. R is my daughter.
(c) 36 and 64 (d) 24 and 1152
43. If only P always speaks the truth, then who
Directions for questions 39 to 41: Answer the
always lied?
questions on the basis of the information given below.
(a) Q (b) R
A numerical machine accepts two values X and Y.
(c) S (d) Can’t be determined
Then it updates these values as X = XY and Y = Y + 1
in every step. The machine stops at X ≥ N. 44. If only P always speaks the truth, then how
X = 2, Y = 3 and N = 5040. is R related to Q?
39. How many steps are performed before the (a) Father (b) Mother
machine stops? (c) Son (d) Daughter
(a) 3 (b) 4
(c) 5 (d) 6 45. If R always speaks the truth, then how is
Q related to S?
40. The final values of X and Y are (a) Father (b) Grandmother
(a) 5040, 7 (b) 5040, 8 (c) Grandson (d) Can’t be determined
(c) 5760, 7 (d) 5760, 8
41. If machine stops at X > N rather than at
X ≥ N, then the final value of X is
(a) 40320 (b) 5040
(c) 720 (d) 360
Non-CAT Exams / Reasoning – 2 Page 7
Answers and Explanations
1 d 2 b 3 c 4 c 5 a 6 c 7 b 8 a 9 e 10 c
11 e 12 a 13 d 14 e 15 a 16 a 17 d 18 b 19 d 20 c
21 c 22 b 23 d 24 c 25 c 26 c 27 c 28 c 29 c 30 a
31 a 32 c 33 b 34 a 35 a 36 b 37 c 38 d 39 c 40 b
41 a 42 a 43 c 44 b 45 d
1. d Except 148, the other three terms can be expressed 12. a Every figure has one long line that contains three
as n3 + n2 (12 = 23 + 22; 36 = 33 + 32; 80 = 43 + 42). perpendicular small lines. Among the three lines two
are of the same type and one is different. The two of
2. b Except Brown, the other three are colours of Rainbow the same type are always in the opposite direction,
(VIBGYOR). except in figure (a).
3. c Except ‘Kilogram’, the other three are units of length. 13. d In all the other figures there are 5 petals shaded on the
right side and 3 shaded on the left side. In figure (d),
4. c Except in QST, the other three group of letters have there are 5 petals shaded on the left and 3 shaded on
consecutive letters. the right.
For questions 5 and 6: The logic for the set is that the word 14. e The objects remain the same in all figures. The three
which comes first alphabetically is placed in the first position
objects, X, O and ↑ always have a gap of one space
in the first step. In the second step, the word which should
come next alphabetically is placed in the last position and this between them and in the given order in anticlockwise
alternating pattern follows. direction. In figure (e), the order is clockwise.
5. a Input : will we go for a party tonight 15. a The four elements together are moving one step ACW
Step I : a will we go for party tonight in all the boxes. The elements among themselves are
Step II : a will we go party tonight for then moving one step CW and the first element (the
Step III : a go will we party tonight for small circle) gets replaced by 'S' in box-2. In box-3 of
Step IV : a go will we tonight party for the problem figure, the elements among themselves
Hence, the answer is option (a) move 2 steps CW and the second element (the element
'S') gets replaced by '='. In box-4, elements now move
6. c Input : I had dinner at Hilton towers today 3 steps CW and the third element (the ‘X') gets replaced
Step I : at I had dinner Hilton towers today by the 'arrow' symbol. The logic then continues to
Step II : at I had Hilton towers today dinner increase by one for the elements to move among
Step III : at had I Hilton towers today dinner themselves in subsequent boxes.
Step IV : at had I towers today Hilton dinner
Step V : at had I today towers Hilton dinner 16. a Mark the curves in the first box of the problem figure
Hence, the answer is option (c). as shown here.
1
7. b 8. a 9. e
2 5
10. c In all the other figures we have boxes opening in all 3 4
four directions, i.e. left, right, top and bottom. In figure
(c), we have two boxes opening towards right and In box-2 only curve no.1 has flipped. In box-3 the next
none towards top. two curves namely 2 & 3 have flipped while the other
three are same. In box-4, the curve numbers 4, 5 and
11. e In all the other figures, the O, P and X are present 1 have flipped and in box-5, curve 2 has flipped. So
while the other two objects are new. In figure (e) the the sequence of flipping is happening in an ACW
X is replaced by a ' ' and hence there are three new manner. Hence, the answer is (a) as two curves
objects. bearing numbers 3 and 4 should flip and the others
would remain the same.
Page 8 Non-CAT Exams / Reasoning – 2
17. d Mark the elements in the first box of the problem figure 26. c 8 cubes have exactly three faces painted.
as shown here.
For questions 27 and 28:
2
It is given that there were 24 cubes which had exactly one
1 face painted.
4 Now, 6(n – 2)2 = 24
3 ⇒ (n – 2)2 = 4
In box-2, element-1 flips in the opposite direction, the ∴ n=4
'U-tip' of element-3 slides down from top to bottom and
element-4 flips in opposite direction. Moving ACW, in 27. c Maximum number of cubes = 43 = 64.
box-3, element-3 flips opposite, the 'U-tip' of
element-4 slides down from top to bottom and 28. c Number of smaller cubes which had exactly two faces
element-2 flips in opposite direction. Extending this logic painted = 12(4 – 2) = 24 .
of "Flip-Down-Flip" till the final box, we get the answer
as (d). 29. c Using condition (1), the resultant of first row = Product
of 23 and 4 – Sum of 4 and 70 = 92 – 74 = 18
18. b The arrow inside the circle rotates 45°, 90°, 135°, 180° Using condition (4), the resultant of second row
and 225° clockwise. The object outside gets replaced = Sum of squares of 18 and 25 – 100
by a new one, as it rotates from one corner to another = (18)2 + (25)2 –100 = 324 + 625 – 100 = 849.
in anticlockwise direction. Every time it reaches a
corner, it rotates at the same place by 90° clockwise in 30. a Using condition (2), the resultant of first row = Product
the next figure. of 3 and difference between 43 and 34
= 3 × (43 – 34) = 3 × 9 = 27
19. d Each object moves one place down. As it does so, it Using condition (3), the resultant of second row
flips over. The object in the middle position gets replaced = Square of the sum of 15 and 11 is added to 27
and a new object comes in the bottommost position. = (15 + 11)2 + 27 = 676 + 27 = 703.
31. a In each row out of the letters A, B and C each of these
For questions 20 to 23:
letters must appear once and only once.
Total number of cubes = 27
In each column
Now, 27 = 3 × 3 × 3
1st number × 3rd number = 2nd number.
∴n = 3
Hence, the term replacing (?) would be (2 × 4)B
Number of cubes having exactly 3 painted faces = 8.
i.e. 8B.
Number of cubes having only two painted faces
= 12(n – 2) = 12(3 – 2) = 12.
32. c Value in the middle column is half of the product of
Number of cubes having only one painted face
values in other columns.
= (n – 2)2 × 6 = (3 – 2)2 × 6 = 6.
Number of cubes having no painted faces =(n – 2)3 = 1. 1
Hence, required number = × 6 × 3 = 9.
2
20. c Only one cube has no face painted at all.
33. b Bottom most element in each coloumn is product of the
21. c 6 cubes have only one face painted. above two elements of the same column.
Hence, required number is 9 as 9 × 8 = 72.
22. b 12 cubes have exactly two faces painted.
For questions 34 and 35:
23. d 8 cubes have exactly three faces painted.
1 2 3
For questions 24 to 26:
Total number of cubes = 343
343 = 7 × 7 × 7
4 5 6
∴ n=7
7 8 9
Number of cubes having three visible faces = 8.
Number of cubes having exactly two visible faces Across - 1: A 3 digit perfect cube having sum of digits = 18.
= 12(n – 2) = 12(5) = 60 3 digits perfect cube are 125, 216, 343, 512, 729
Number of cubes having only one visible face
∴ Only Possible number is 729.
= (7 – 2)2 × 6 = 52 × 6 = 150.
1 2 3
24. c 150 cubes have exactly one face painted. 7 2 9
25. c 60 cubes have exactly two faces painted.
Non-CAT Exams / Reasoning – 2 Page 9
Across - 4: A 3 digit perfect cube which could be one of the 41. a
216, 512, 729 because down - 1 is a three-digit number divisible
by 25.
Updated Updated
If 216 ⇒ Down - 3 will become 969 ≠ not a prime number. Step Initial X Initial Y Is X > N ?
X = XY Y = Y + 1
729 ⇒ Down - 3 will become 999 ≠ not a prime number. 1 2 3 6 4 FALSE
⇒ 512 is the value in (Across - 4) as 929 is a prime number. 2 6 4 24 5 FALSE
⇒ Since (Down - 1) is divisible by 25. Therefore, the units 3 24 5 120 6 FALSE
digit has to be zero.
Hence, matrix will be: 4 120 6 720 7 FALSE
5 720 7 5040 8 FALSE
1 2 3
7 2 9 6 5040 8 40320 9 TRUE
4 5 6
5 1 2 Hence, (a) is the correct option.
7 8 9
O 9 42. a T(20) – 17 = C(3)
I(9) + 6 = O(15)
G(7) – 5 = B(2)
34. a Required sum = 7 + 2 = 9. E(5) + 13 = R(18)
R(18) – 17 = A(1)
35. a Option (a) is the correct choice. As 211 is a prime
Similarly,
number. E(5) –17 = N(14)
A(1) + 6 = G(7)
36. b The grid will be like G(7) – 5 = B(2)
L(12) + 13 = Y(25)
A (4 ) B (9 ) C (2 ) E(5) –17 = N(14)
Hence, NGBYN is the answer.
D (3 ) E (5 ) F(7 )
For questions 43 to 45:
H (1 ) I(6 ) If P speaks truth then,
G (8)
S (– )
Hence option (b) is the correct choice. N o te: (+) rep re se nts m ale
P R
(–) re pre se n ts fem ale
37. c The sum of the numbers of each row/column is 15 Q (+)
and each row/column has one A, one B and one C.
Hence, the missing term is 6C. Genders of P and R are not known. Since only P always
speaks the truth, at least 1 statement of each of Q, R and S
38. d Each number in the circle from the second last row must be false. Since S is grandmother of Q, other statement of
onwards is the product of the numbers in the two Q must be false. This implies P is not mother of Q i.e. P is father
circles immediately below it. of Q.
Therefore, x = 6 × 4 = 24 and y = 24 × 48 = 1152.
43. c Clearly Q is grandson of S and R is daughter-in-law of
Directions for questions 39 to 41: S. Hence, S always lied.
Updated Updated 44. b R is mother of Q.
Step Initial X Initial Y Is X > N?
X = XY Y = Y + 1
45. d If R speaks the truth.
1 2 3 6 4 FALSE
(+ )R P (–)
2 6 4 24 5 FALSE
3 24 5 120 6 FALSE Q (+)
4 120 6 720 7 FALSE Nothing can be said about the relation of S with
anyone.
5 720 7 5040 8 TRUE
39. c 40. b
Page 10 Non-CAT Exams / Reasoning – 2
You might also like
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)From EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- SOF Level 2 IMO Class 5Document5 pagesSOF Level 2 IMO Class 5amarpreetsethi100% (6)
- Visual Reasoning 1Document17 pagesVisual Reasoning 1Arpit Singh100% (5)
- AMC Year3and4 3Document84 pagesAMC Year3and4 3jun zhang0% (1)
- Terex RT 780. 80 Ton RTDocument20 pagesTerex RT 780. 80 Ton RTBhavana Kewlani67% (3)
- Maxsurf TutorialDocument169 pagesMaxsurf TutorialJayjay Rindole BalingbingNo ratings yet
- Final Report On WaterproofingDocument35 pagesFinal Report On WaterproofingAlOk100% (2)
- Ntse Phase - I: Mat (Paper # 02)Document19 pagesNtse Phase - I: Mat (Paper # 02)ketan sumanNo ratings yet
- VMC National Admission Test 2018-19Document7 pagesVMC National Admission Test 2018-19Samvid Pundir83% (6)
- Ntse Mat TestDocument20 pagesNtse Mat TestAnimesh AnshNo ratings yet
- IX To X Entrance Test Sample Paper-2Document20 pagesIX To X Entrance Test Sample Paper-2Mahendra TakNo ratings yet
- 2017 Imas 1st UpDocument9 pages2017 Imas 1st UpDarma YasaNo ratings yet
- 2023 WMC Junior Secondary (Warm Up Round) - Grade 8&9Document6 pages2023 WMC Junior Secondary (Warm Up Round) - Grade 8&9smakheleNo ratings yet
- Class X Sample Question and For Mock Test AlsoDocument7 pagesClass X Sample Question and For Mock Test AlsoHetal PanchmiyaNo ratings yet
- 2015 Paper SSC CGL-16AugDocument20 pages2015 Paper SSC CGL-16AugRaghu RamNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Solved PapersDocument5 pagesSSC CGL Solved PapersDhananjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Class 6thDocument8 pagesSample Paper Class 6thAditya khandelwalNo ratings yet
- STEM Critical Thinking Practice Test-2Document33 pagesSTEM Critical Thinking Practice Test-2shalafat7No ratings yet
- Class - IX Go X - Sample Paper-2Document20 pagesClass - IX Go X - Sample Paper-2J SoujanyaNo ratings yet
- Class: 1 (Syllabus & Sample Questions)Document2 pagesClass: 1 (Syllabus & Sample Questions)JdhNo ratings yet
- IOM Class1Document2 pagesIOM Class1Muthu KumarNo ratings yet
- Preliminary DPP-3 (IOQM 2022)Document9 pagesPreliminary DPP-3 (IOQM 2022)Lakshya TomarNo ratings yet
- 2016 WMI Grade 5 Questions Part 1Document3 pages2016 WMI Grade 5 Questions Part 1doggylover100% (1)
- Amc2015 MPDocument10 pagesAmc2015 MPtham luongNo ratings yet
- Cube and Dice ExplanationDocument6 pagesCube and Dice Explanationavilal padiyanNo ratings yet
- Mat & Sat-03Document36 pagesMat & Sat-03RamNagalNo ratings yet
- PracticeDocument10 pagesPracticesaNo ratings yet
- Ikmc Class 11&12 2015-2023Document70 pagesIkmc Class 11&12 2015-2023belucky81No ratings yet
- Phase - Ii Question Paper Class - VDocument10 pagesPhase - Ii Question Paper Class - Vsnsarangi06No ratings yet
- WEB SUPPORT: The Pearson Guide To Bank Clerical Recruitment ExaminationDocument35 pagesWEB SUPPORT: The Pearson Guide To Bank Clerical Recruitment ExaminationAkshat GoelNo ratings yet
- Amc2016 UPDocument9 pagesAmc2016 UPPEIHONG WANGNo ratings yet
- 3 Point Problems: Singapore Math Kangaroo Contest 2015 - StudentDocument7 pages3 Point Problems: Singapore Math Kangaroo Contest 2015 - StudentRPNo ratings yet
- 2017 Upper Primary Division First Round PaperDocument8 pages2017 Upper Primary Division First Round PaperLuong Vu100% (1)
- Sat Math Practice Test 5Document9 pagesSat Math Practice Test 5wwwmacyNo ratings yet
- Contest A: 5 Annual American Mathematics Contest 10Document9 pagesContest A: 5 Annual American Mathematics Contest 10elitefireninjaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper: National Cyber OlympiadDocument3 pagesSample Paper: National Cyber OlympiadApoorv SaraogeeNo ratings yet
- Usa Amc 10 2012Document10 pagesUsa Amc 10 2012dreamsheikhNo ratings yet
- 2022 AMC12 de Eng Vie DADocument19 pages2022 AMC12 de Eng Vie DAbenjamin lenaNo ratings yet
- Class: 6 (Syllabus & Sample Questions) : International Olympiad of Mathematics-iOM'16Document2 pagesClass: 6 (Syllabus & Sample Questions) : International Olympiad of Mathematics-iOM'16Sohom MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- 2023 WMC Upper Primary (Warm Up Round) - Grade 6&7Document6 pages2023 WMC Upper Primary (Warm Up Round) - Grade 6&7smakheleNo ratings yet
- Kangaroo Math 2019Document8 pagesKangaroo Math 2019ธนเสฐฐ์ กิตติวรรธโนทัยNo ratings yet
- 2020 CadetDocument6 pages2020 CadetjeeshikaNo ratings yet
- 2020 AMC 8 - Trivial Math PracticeDocument14 pages2020 AMC 8 - Trivial Math PracticeMinh BuiNo ratings yet
- Amc 10A: 19th AnnualDocument30 pagesAmc 10A: 19th AnnualNguyễn LiamNo ratings yet
- 2sec I PDFDocument12 pages2sec I PDFpriti089No ratings yet
- 2023 WMC Senior Secondary (Warm Up Round) - Grade 10-12Document5 pages2023 WMC Senior Secondary (Warm Up Round) - Grade 10-12smakheleNo ratings yet
- Tttttest of R Estofr Estofr Estofr Est of Reasoning-1 Easoning-1 Easoning-1 Easoning-1 Easoning-1Document5 pagesTttttest of R Estofr Estofr Estofr Est of Reasoning-1 Easoning-1 Easoning-1 Easoning-1 Easoning-1Sharique AlamNo ratings yet
- 2019 MMC MPDocument10 pages2019 MMC MPJomar EjedioNo ratings yet
- 2017 AMC 12A Problems and Solutions: Problem 1Document5 pages2017 AMC 12A Problems and Solutions: Problem 1Ahmet Arduç100% (1)
- Study Material For Class IXDocument21 pagesStudy Material For Class IXCHARAN 8BNo ratings yet
- Study Material For Class IXDocument21 pagesStudy Material For Class IXCHARAN 8BNo ratings yet
- SSC Statistical Investigators ExamDocument12 pagesSSC Statistical Investigators Examsat100% (2)
- PLC Educators: Series Completion E-BookDocument6 pagesPLC Educators: Series Completion E-BookExamseggNo ratings yet
- X Class Section 1Document5 pagesX Class Section 1rohit29agrawalNo ratings yet
- Contest A: 55 Annual American Mathematics Contest 12Document8 pagesContest A: 55 Annual American Mathematics Contest 12elitefireninjaNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips Imo Class 4Document4 pagesQdoc - Tips Imo Class 4Gaurav JoshiNo ratings yet
- Wmi 2013 Logic Ques PDFDocument6 pagesWmi 2013 Logic Ques PDFcindyNo ratings yet
- Autumn Mock AMC 10 v4Document4 pagesAutumn Mock AMC 10 v4Jessica LiuNo ratings yet
- AMC 12 Mock Test Problems: Problem 1Document8 pagesAMC 12 Mock Test Problems: Problem 1Karl Henry M. DahaoNo ratings yet
- Master Fundamental Concepts of Math Olympiad: Maths, #1From EverandMaster Fundamental Concepts of Math Olympiad: Maths, #1No ratings yet
- As Referenced by ASME B20.1 For Use in Conjunction With That StandardDocument26 pagesAs Referenced by ASME B20.1 For Use in Conjunction With That StandardimazaxNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: ReferencesDocument7 pagesAcknowledgement: Referencesdwayne420No ratings yet
- CUK ConverterDocument13 pagesCUK ConverterpakalagopalNo ratings yet
- Hse PlanDocument44 pagesHse PlanSheldon Van RooyenNo ratings yet
- Optical Micros PDFDocument24 pagesOptical Micros PDFsensoham03No ratings yet
- Intro To Signal Processing 2021Document510 pagesIntro To Signal Processing 2021crypto fanbaby0% (1)
- Visual-Vestibular Interaction and Treatment of Dizziness: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesVisual-Vestibular Interaction and Treatment of Dizziness: A Case ReportsoumenNo ratings yet
- Transdisciplinary Urbanism and CultureDocument236 pagesTransdisciplinary Urbanism and CultureZenón Rizo Fernández100% (1)
- De Cuong On He Mon Tieng Anh Lop 6 Len Lop 7Document14 pagesDe Cuong On He Mon Tieng Anh Lop 6 Len Lop 7Quang Hưng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Russian Involvement in Eastern Europe's Petroleum Industry - The Case of Bulgaria 2005Document41 pagesRussian Involvement in Eastern Europe's Petroleum Industry - The Case of Bulgaria 2005stephenNo ratings yet
- X9 User Manual: ImportantDocument28 pagesX9 User Manual: ImportantWolleo LW100% (1)
- AX33 XXDocument21 pagesAX33 XXLuz Rito Gomez ColungaNo ratings yet
- Annual Barangay Youth Investment Plan (Abyip)Document5 pagesAnnual Barangay Youth Investment Plan (Abyip)Rhyss Malinao BurandayNo ratings yet
- Physics Challenge Dec14Document2 pagesPhysics Challenge Dec14John DixonNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 High Performance Liquid Chromatography HPLCDocument57 pagesUnit 8 High Performance Liquid Chromatography HPLCNathanianNo ratings yet
- Biblical Hermeneutics (PDFDrive)Document56 pagesBiblical Hermeneutics (PDFDrive)Temesgn Amello100% (2)
- E123-02 (2012) Standard Specification For ApparatusDocument6 pagesE123-02 (2012) Standard Specification For ApparatusAhmed AlzubaidiNo ratings yet
- NepalDocument22 pagesNepalDarya KhanNo ratings yet
- The Charter Oak Brunch MenuDocument1 pageThe Charter Oak Brunch MenuEllenFortNo ratings yet
- Butuan Doctors' College: Unit 1: Level of Complexity and Anatomical PrinciplesDocument4 pagesButuan Doctors' College: Unit 1: Level of Complexity and Anatomical PrinciplesKlynt BasadreNo ratings yet
- MANDAYADocument22 pagesMANDAYAAndengBaduriaNo ratings yet
- Class 6 NSTSE PQP 10-Papers 2019-20 2-In-A4 PDFDocument85 pagesClass 6 NSTSE PQP 10-Papers 2019-20 2-In-A4 PDFSanjib Mandal100% (3)
- Snell Manuscript (Keelys Secrets)Document5 pagesSnell Manuscript (Keelys Secrets)Gregg Martin100% (2)
- Audio Test For TWS EarphoneDocument12 pagesAudio Test For TWS EarphoneprabhatmitNo ratings yet
- Methane MSDSDocument2 pagesMethane MSDSa0% (1)
- New Text DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Text DocumentGzim DragushaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Week 7Document5 pages11 - Week 7Christine Bernadette MacinasNo ratings yet