Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2004 - Scalar Implicaturen Pi - 21
2004 - Scalar Implicaturen Pi - 21
Uploaded by
George MartinezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2004 - Scalar Implicaturen Pi - 21
2004 - Scalar Implicaturen Pi - 21
Uploaded by
George MartinezCopyright:
Available Formats
SCALAR
I M P L I C A T U RP
EoSL/ A R t r yr H E N o M E N AA/ N D T H ES y N T A x / e n n c u n r t c sT N T E R F A C E 79
78 S T R U C T U R EASN D B E Y O N D
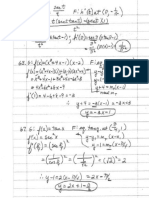
as I din't eat a string of DE-heads C-commanding it, clearly only the closestrelevant head may
work with. Let me use a simple example. Consider a sentencesuch
will be (117a); after closure' it will agreewith the NPI (however, you will want to cash this in formally):
any potato. Before closure, its logical form
be (117b):
(t20) [ . . . NEG. . . . t . . . NEG. . . . t . . . Npr . . . ] . . . I . . . l
I atex))
potatoi[I atet,]l + r solllsepiootato';(],x lt
(ll7) a. not (anyerpr
6. O^enot(anyrloypotatol[I ateq]l + VgeA r I atex))
somee(oy'(potato')(l,x
(117a)] must be This, given my mapping hypothesis, forces the closest DE-head to act as the scope
According to (116), the closureof a sentence0 [i.e., in this case,
of g removed' That is, site for universal closure (and hence as the level at which the condition on strength-
stronger than q', which is identical to $ with all occurrences
ening must be checked).What happensabove that level (i.e., how many negative
(117b) must be strongerthan
operatorsthere may be) remains without consequence.2T
I atex)) To sum up, my hypothesisis that NPIs are parasitic on weak quantifiersand close
(11S) - somen'(Potato')(l.x
off quantificationally the domain (or situation) variable implicit in the former. In
(117a)is well de- positive contexts,this constitutesa loss of information with respectto plain exis-
since (117b) is in fact strongerthan (118), the result of closing
quantifier restricted to domain- tentials;in negative contexts,it leads, instead,to strengthening.Hence, pragmatic
fined. Essentially, O is u pt.roppositional universal
that the result must entail the meaning of and/or morphological considerationsprevent NPIs from occurring in positive con-
extending functions. The presuppositionis
texts (not embeddedunder a DE-head). The NPIs involve a comparisonof domains
the correspondingsentencewith some.
conditions (asproposedby K&L) but not alexicalized scale (like scalar terms).
Usually quantificational closure is taken to be subject to mapping
(Diesing tggil.we may exploit this general line of approach to closure to enforce
(presentin the lexical entry of NPIs)
tt. r.quir.ment that domain-extendingfunctions 4.3. Intervention
it. First, observe that in the
must be eventually closed. Here is one way of executing
relevant alternatives is done through The approachto NPIs outlined above capturestheir sensitivity to DE-contexts, a
case of scalar terms, the individuation of the
with eachother). property NPIs sharewith SIs. However, the two phenomenaalso differ in some im-
lexically specified scales(a list of words in paradigmaticopposition
morphology to flag that their use may portant respects.One difference between the two phenomenais the flip-flop versus
Becauseof this, scalar terms need no special
on the other hand, are not coded in roofing effects. This difference, too, now makes sense.The SIs are in turn inserted
lead to strengthening.Quantificational domains,
So if one wants to signal domain andremoved acrossDE-operators,in a pistonlike fashion becausethe scalarrequire-
lexicalized scalesUut in covert domain variables.
device specialized to this task' mentsare checkedat every stepof the derivation (as is necessaryto keep the strength-
expansion,one must resortto some morphological
relations. It is thus to be expected enedmeaning stronger)-whence the flip-flop effect. The NPIs, per contra, are not
RnA morphological featuresenter into agreement
suitable head, part of scales.They involve a generalizationover quantificational domains that must
that the morphology of NPIs must agreewith the morphology of some
with, for example, interroga- lead to a stronger statementthan plain indefinites. In virtue of their parasitic nature,
just as, say, wh-words must enter into such a relation
counts as a suitabile head. Given the they are subject to a constraint that relates their contribution to that of their host.
iiur.o.piementizers. The secondissueis what
(any other choice would lead the interpre- Roofing follows from this. In particular, I suggest (in the spirit of much previous
semanticsof NPIs, it must be a DE-head
carry a feature that, when work) that this constraint takes the form of a morphological requirement. If their
tive componentto crash).So we may assumethat DE-heads
in syntax possible scope sites specialmorphology (necessaryto signal potential domain widening) enters into an
active, must be checkedby an NPI. This feature marks
now obvious: agreementrelation with a negative head (the only kind of heads they could agree
for closure, the relevant mapping hypothesis being
with, in virtue of their semantics),then roofing follows from the properties of agree-
ment (e.g., the probe must seek out the closest goal). But even if such a mor-
(l 19) The domainof a +DE-headmapsonto the scopeof O'
phological requirement were not there, if strengtheningor blocking is just freely
have to be checked,the empirical effects of roofing would also be expected:in the presence
To recapitulate, supposean NPI is selectedin an enumeration.There will
feature that will consti- of c-commandingnegative heads,we would always have a site at which strength-
a head with the appropriate semantic quality and an active
will lead the derivation ening can be satisfied (namely, the closest one), and nothing that happensthere-
tute the domain oi quantificational closure.Any other option
after would affect that.
to crash either in the syntax or in the semantics'26
clo- So we have a proposal that does arguably improve some on the previous seman-
As an immediate consequenceof this way of implementing quantificational
heads), we get an ac- tic ones that directly inspired it, namely K&L's, Krifka's, and Lahiri's. With respect
sure (through a feature that may be associatedwith negative
If you have an NPI and to K&L, besidesthe generalissuesjust mentioned,we no longer haveto posit a specific
count of why NPI licensing is subject to a roofing constraint.
You might also like
- Carson Histotecnologia PDFDocument417 pagesCarson Histotecnologia PDFPaola Froster100% (1)
- CAT G3500 Gas Engine Maintenance ScheduleDocument3 pagesCAT G3500 Gas Engine Maintenance ScheduleQaiser Iqbal67% (6)
- 2004 - Scalar Implicaturen Pi - 19Document1 page2004 - Scalar Implicaturen Pi - 19George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2004 - Scalar Implicaturen Pi - 20Document1 page2004 - Scalar Implicaturen Pi - 20George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2004 - Scalar Implicaturen Pi - 11Document1 page2004 - Scalar Implicaturen Pi - 11George MartinezNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Imaging Group, EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland: C Edric Vonesch, Thierry Blu and Michael UnserDocument4 pagesBiomedical Imaging Group, EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland: C Edric Vonesch, Thierry Blu and Michael UnserajuNo ratings yet
- 2004 - Scalar Implicaturen Pi - 23Document1 page2004 - Scalar Implicaturen Pi - 23George MartinezNo ratings yet
- CS772 Lec21Document18 pagesCS772 Lec21Yuvraj PardeshiNo ratings yet
- 2004 - Scalar Implicaturen Pi - 26Document1 page2004 - Scalar Implicaturen Pi - 26George MartinezNo ratings yet
- Larson GIlfeather Commutats Modulo The Compact Operators of Certain CSL Algebras IIDocument12 pagesLarson GIlfeather Commutats Modulo The Compact Operators of Certain CSL Algebras IIManar MaherNo ratings yet
- BBPS Kennedy03 PDFDocument8 pagesBBPS Kennedy03 PDFCyz RobertNo ratings yet
- Peaks Theory and The Excursion Set Approach: Aseem Paranjape & Ravi K. ShethDocument10 pagesPeaks Theory and The Excursion Set Approach: Aseem Paranjape & Ravi K. ShethAmirNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Gradients On Higher Dimensional Sierpinski GasketsDocument9 pagesHarmonic Gradients On Higher Dimensional Sierpinski GasketsKaruna SangamNo ratings yet
- A Data Oriented Parsing Model ForDocument8 pagesA Data Oriented Parsing Model ForLucas BorgesNo ratings yet
- Grainflow ShapefactorDocument4 pagesGrainflow Shapefactortoufik saouchiNo ratings yet
- Uri Keshet, Ofir Arad, and Yuri Lyubarski (Dated: October 21, 2019)Document11 pagesUri Keshet, Ofir Arad, and Yuri Lyubarski (Dated: October 21, 2019)Carlos FazNo ratings yet
- 6 - Further Properties of SPs - System PerformanceDocument43 pages6 - Further Properties of SPs - System PerformanceCamNo ratings yet
- Kolmogorov-Arnold NetworksDocument48 pagesKolmogorov-Arnold NetworksI TNo ratings yet
- On The Induction Operations For Shift Subspace and Cellular AutomstaDocument20 pagesOn The Induction Operations For Shift Subspace and Cellular AutomstaNeptali_RomeroNo ratings yet
- Towards A Semantic Theory of Dynamic BindingDocument29 pagesTowards A Semantic Theory of Dynamic BindingMarco CocchiNo ratings yet
- Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN)Document50 pagesMulti-Layer Perceptron (MLP) Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN)rako2736No ratings yet
- (1991) Hornik (Neural Netw.)Document7 pages(1991) Hornik (Neural Netw.)MaxNo ratings yet
- ML Unit-5Document22 pagesML Unit-5Mohammed Amir ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Main Body, Closing and Questions Answer KeysDocument4 pagesMain Body, Closing and Questions Answer KeysSara HddNo ratings yet
- SPE8352 Dstanalysis Withpressure Dependent Rockandfluid PropertiesDocument9 pagesSPE8352 Dstanalysis Withpressure Dependent Rockandfluid PropertiesSofiaNo ratings yet
- Edwards 1977Document17 pagesEdwards 1977ZeusJonathanBautistaGranadosNo ratings yet
- Neural Nets 4 Recurrent Neural Nets: WikipediaDocument4 pagesNeural Nets 4 Recurrent Neural Nets: Wikipediachuck212No ratings yet
- Classical Prelim VersionDocument6 pagesClassical Prelim VersionNida RazzaqNo ratings yet
- Thesis Cuni - CZDocument8 pagesThesis Cuni - CZdwf6nx2z100% (1)
- Testing Modularity of Local SupervisorsDocument7 pagesTesting Modularity of Local SupervisorsfhamdiNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free Apuntes Sintaxis InglesaDocument3 pagesWuolah Free Apuntes Sintaxis InglesakotyNo ratings yet
- Percolation Fractal Exponents Without Fractals and A New Conservation Law in DiffusionDocument8 pagesPercolation Fractal Exponents Without Fractals and A New Conservation Law in Diffusionياسر عوض اللّهNo ratings yet
- Kernels Regularization and Differential EquationsDocument16 pagesKernels Regularization and Differential EquationsAniAceNo ratings yet
- Z = Jωl While Capacitors Are Represented: Summary And ReviewDocument3 pagesZ = Jωl While Capacitors Are Represented: Summary And ReviewYogi Foto Copy0% (1)
- Eigenvalue Problem For A Class of Fractional Elliptic OperatorsDocument11 pagesEigenvalue Problem For A Class of Fractional Elliptic Operatorssoumyajit ghoshNo ratings yet
- 2304.09221 Convergence of Stochastic Gradient Descent UnderDocument14 pages2304.09221 Convergence of Stochastic Gradient Descent UnderhongnhNo ratings yet
- ParCFD11 LysenkoDocument19 pagesParCFD11 LysenkoOpenFOAM DocsNo ratings yet
- Elaborating Domain DescriptionsDocument9 pagesElaborating Domain DescriptionsIvan José VarzinczakNo ratings yet
- Sparsistency of The Edge Lasso Over GraphsDocument9 pagesSparsistency of The Edge Lasso Over GraphsAnonymous BkmsKXzwyKNo ratings yet
- Rosenzweig 1999 0165Document3 pagesRosenzweig 1999 0165Particle Beam Physics LabNo ratings yet
- Li - Neuronal NetworkDocument7 pagesLi - Neuronal Networkgabriela apreuteseiNo ratings yet
- Taylor & Francis, Ltd. American Statistical AssociationDocument8 pagesTaylor & Francis, Ltd. American Statistical AssociationWameath SalbiNo ratings yet
- Quantifying The Vanishing Gradient and Long Distance Dependency Problem in Recursive Neural Networks and Recursive LstmsDocument7 pagesQuantifying The Vanishing Gradient and Long Distance Dependency Problem in Recursive Neural Networks and Recursive Lstmsvungochuy-tdhNo ratings yet
- ML UNIT-4 Chapter-1 Instance Based LearningDocument23 pagesML UNIT-4 Chapter-1 Instance Based LearningDivya Sri M.V.No ratings yet
- Simsekli 17 ADocument10 pagesSimsekli 17 AFebry MulyaNo ratings yet
- Re8ection K.: X-Ray Transmission Surfaces D. GDocument9 pagesRe8ection K.: X-Ray Transmission Surfaces D. Gcristhian alvarezNo ratings yet
- On The Abundance of Extreme Voids II: A Survey of Void Mass FunctionsDocument11 pagesOn The Abundance of Extreme Voids II: A Survey of Void Mass FunctionsAdonai Jireh Dionne BaliteNo ratings yet
- A Simple Theory For Seismic Diffractions - Trorey 1970Document23 pagesA Simple Theory For Seismic Diffractions - Trorey 1970Rafik Et-TrabelsiNo ratings yet
- PLS PDFDocument8 pagesPLS PDFnorma9No ratings yet
- QRB-Domains and The Probabilistic PowerdomainDocument14 pagesQRB-Domains and The Probabilistic PowerdomainRaghuram GudeNo ratings yet
- ML Unit-4 Instance Based LearningDocument10 pagesML Unit-4 Instance Based LearningDivya Sri M.V.No ratings yet
- Artigo MLSP Atenuacao MultiplasDocument6 pagesArtigo MLSP Atenuacao MultiplasfarzinshamsNo ratings yet
- Segment GrammarDocument27 pagesSegment GrammarGURUDUTTA PALNo ratings yet
- 10 MDOF Formulation UofPDocument26 pages10 MDOF Formulation UofPIoannis BazosNo ratings yet
- How To Construct Deep Recurrent Neural NetworksDocument13 pagesHow To Construct Deep Recurrent Neural Networksomonait17No ratings yet
- Laplace TransformDocument5 pagesLaplace TransformjohnNo ratings yet
- Transformer-Xl Attentive Language Models Beyond A Fixed-Length ContextDocument22 pagesTransformer-Xl Attentive Language Models Beyond A Fixed-Length Contextsalman younusNo ratings yet
- Steady OpenfoamDocument10 pagesSteady Openfoamhafidh farisiNo ratings yet
- Estimating Steganographic Fisher Information in Real ImagesDocument15 pagesEstimating Steganographic Fisher Information in Real ImagessooshkyNo ratings yet
- Dalalyan - 2017 - Theoretical Guarantees For Approximate Sampling From Smooth and Log-Concave DensitiesDocument26 pagesDalalyan - 2017 - Theoretical Guarantees For Approximate Sampling From Smooth and Log-Concave DensitiesAlex LeviyevNo ratings yet
- Anderson Jackson 1967 Fluid Mechanical Description of Fluidized Beds PDFDocument13 pagesAnderson Jackson 1967 Fluid Mechanical Description of Fluidized Beds PDFAbgail PinheiroNo ratings yet
- A1902010105 002Document1 pageA1902010105 002George MartinezNo ratings yet
- A1902020108 004Document1 pageA1902020108 004George MartinezNo ratings yet
- A1902010105 004Document1 pageA1902010105 004George MartinezNo ratings yet
- A1902010105 005Document1 pageA1902010105 005George MartinezNo ratings yet
- A1901020107 002Document1 pageA1901020107 002George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2 3 PR QR0001Document1 page2 3 PR QR0001George MartinezNo ratings yet
- A1901020107 003Document1 pageA1901020107 003George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2012 RealRecordRacialAttitudesSocialTrendsAmericanLife 19Document1 page2012 RealRecordRacialAttitudesSocialTrendsAmericanLife 19George MartinezNo ratings yet
- A1901020107 007Document1 pageA1901020107 007George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2 3 PR QR0005Document1 page2 3 PR QR0005George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2020 Joss Neurodiffeq 002Document1 page2020 Joss Neurodiffeq 002George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2 3 PR QR0007Document1 page2 3 PR QR0007George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2012 RealRecordRacialAttitudesSocialTrendsAmericanLife 24Document1 page2012 RealRecordRacialAttitudesSocialTrendsAmericanLife 24George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2 3 PR QR0004Document1 page2 3 PR QR0004George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 1 S 3 DDocument1 page1 S 3 DGeorge MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2 3 PR QR0006Document1 page2 3 PR QR0006George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 1 S 3 FDocument1 page1 S 3 FGeorge MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2012 RealRecordRacialAttitudesSocialTrendsAmericanLife 23Document1 page2012 RealRecordRacialAttitudesSocialTrendsAmericanLife 23George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2012 RealRecordRacialAttitudesSocialTrendsAmericanLife 21Document1 page2012 RealRecordRacialAttitudesSocialTrendsAmericanLife 21George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 1409.1549v1 013Document1 page1409.1549v1 013George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2012 RealRecordRacialAttitudesSocialTrendsAmericanLife 22Document1 page2012 RealRecordRacialAttitudesSocialTrendsAmericanLife 22George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 1409.1549v1 023Document1 page1409.1549v1 023George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2012 RealRecordRacialAttitudesSocialTrendsAmericanLife 20Document1 page2012 RealRecordRacialAttitudesSocialTrendsAmericanLife 20George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 1409.1549v1 018Document1 page1409.1549v1 018George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 1409.1549v1 028Document1 page1409.1549v1 028George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2012 RealRecordRacialAttitudesSocialTrendsAmericanLife 15Document1 page2012 RealRecordRacialAttitudesSocialTrendsAmericanLife 15George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 1409.1549v1 007Document1 page1409.1549v1 007George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 1409.1549v1 010Document1 page1409.1549v1 010George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 1409.1549v1 002Document1 page1409.1549v1 002George MartinezNo ratings yet
- 1409.1549v1 004Document1 page1409.1549v1 004George MartinezNo ratings yet
- Report On VSATDocument19 pagesReport On VSATchinu meshramNo ratings yet
- Rose Water OintmentDocument1 pageRose Water OintmentThomas Niccolo Filamor ReyesNo ratings yet
- EZVIZ - Apps4u StoreDocument1 pageEZVIZ - Apps4u StorePak UliNo ratings yet
- Cash Out With WhatsappDocument22 pagesCash Out With WhatsappIDRIS JAMIUNo ratings yet
- CHWW What Makes Up A CommunityDocument2 pagesCHWW What Makes Up A CommunityJev DumasisNo ratings yet
- Phyu Phyu Lwin CVDocument5 pagesPhyu Phyu Lwin CVphuy phyu100% (1)
- TCVN 4513-1988 Internal Water Supply - Design Standard PDFDocument37 pagesTCVN 4513-1988 Internal Water Supply - Design Standard PDFDoThanhTungNo ratings yet
- DB en Macx MCR T Ui Up 104595 en 10Document49 pagesDB en Macx MCR T Ui Up 104595 en 10Dante LupuNo ratings yet
- TextsDocument10 pagesTextsapi-446884620No ratings yet
- Chemistry Test 11 Chap 1-5Document2 pagesChemistry Test 11 Chap 1-5Sabitra RudraNo ratings yet
- Developer Report PDFDocument65 pagesDeveloper Report PDFAnonymous JyKPfbZBQNo ratings yet
- Cockateil Pairing DetailsDocument4 pagesCockateil Pairing DetailsWaseem UllahNo ratings yet
- Adime Malnutrition and OncolgyDocument6 pagesAdime Malnutrition and Oncolgyapi-300587226100% (1)
- Ingovern Series Electronic Engine Speed Governor Instruction ManualDocument44 pagesIngovern Series Electronic Engine Speed Governor Instruction Manualfelipe floresNo ratings yet
- Modelo Listening Exam c1 2014junio Task 1MODELODocument1 pageModelo Listening Exam c1 2014junio Task 1MODELOtereNo ratings yet
- 4.contour Flow Conditioner PDFDocument14 pages4.contour Flow Conditioner PDFFIRMANSYAHNo ratings yet
- OpsCenter 7.6 Performance and Tuning GuideDocument50 pagesOpsCenter 7.6 Performance and Tuning GuideNitesh RoyNo ratings yet
- Integrated Door Motor Controller User Manual: Shenyang Bluelight Automatic Technology Co., LTDDocument56 pagesIntegrated Door Motor Controller User Manual: Shenyang Bluelight Automatic Technology Co., LTDJulio Cesar GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Ageing Aura and Vanitas in Art Greek LauDocument31 pagesAgeing Aura and Vanitas in Art Greek LautaraselbulbaNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs Capsule For SBI/IBPS/RRB PO Mains Exam 2021 - Part 2Document253 pagesCurrent Affairs Capsule For SBI/IBPS/RRB PO Mains Exam 2021 - Part 2King SammyNo ratings yet
- 001 GEYSERSD23Final PDFDocument100 pages001 GEYSERSD23Final PDFVasu ThakurNo ratings yet
- En PL Da220c5300 5 (8) 080104 JDocument36 pagesEn PL Da220c5300 5 (8) 080104 Jluisleao1982No ratings yet
- Comandos de ScilabDocument11 pagesComandos de ScilabAlejandro Galindo Vega0% (1)
- Joint Summary SheetDocument1 pageJoint Summary Sheetchandana kumarNo ratings yet
- Important People - Exercises 2 PDFDocument2 pagesImportant People - Exercises 2 PDFDiana BerariNo ratings yet
- Summer Farm: By: Norman Maccaig Group: Camila Luna and Estrella LinDocument8 pagesSummer Farm: By: Norman Maccaig Group: Camila Luna and Estrella LinJamieDuncanNo ratings yet
- CICSDB2 Guide NotesDocument4 pagesCICSDB2 Guide Notesshobhit10aprilNo ratings yet
- Islam A Challenge To Religion by G. A. ParwezDocument359 pagesIslam A Challenge To Religion by G. A. ParwezJamshed IqbalNo ratings yet