Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 - The Nervous System
Chapter 1 - The Nervous System
Uploaded by
Radha RamineniCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Thibarmy Program Fat LossDocument18 pagesThibarmy Program Fat LossWilliam Spratling86% (14)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputRy Pablo83% (41)
- Intensive Care Chart MalaysiaDocument1 pageIntensive Care Chart MalaysiaZan Ya100% (2)
- Neonatal Ventilation Made Easy Jaypee PDFDocument97 pagesNeonatal Ventilation Made Easy Jaypee PDFfloare de coltNo ratings yet
- Huberman Lab NotesDocument152 pagesHuberman Lab Notescan dagidir80% (5)
- Unit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsDocument13 pagesUnit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsIrene Caballero PicazoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Body Coordination 2.1 Body CoordinationDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Body Coordination 2.1 Body CoordinationMarcia PattersonNo ratings yet
- Neuron and Glial CellsDocument25 pagesNeuron and Glial Cellsfakhar aliNo ratings yet
- Week No 1 Quarter 3 - SCIENCEDocument2 pagesWeek No 1 Quarter 3 - SCIENCEwylen b. catamoraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Biology of MindDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - The Biology of MindCindy AvendanoNo ratings yet
- Biology Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesBiology Nervous SystemFatima PueblaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument43 pagesThe Nervous SystemmalakbasahalNo ratings yet
- Section 3.10 The Nervous System Guided NotesDocument3 pagesSection 3.10 The Nervous System Guided NotesNoelleNo ratings yet
- Nerve CellDocument14 pagesNerve CellRomelyn Grace BorbeNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesNervous Systemmercaderlorenzo9No ratings yet
- CBSE G+10 Control+and+coordination NotesDocument19 pagesCBSE G+10 Control+and+coordination Notesveerskucheriya.byjusNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - The Human Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesModule 2 - The Human Nervous SystemoyamaNo ratings yet
- Worksheetsmod1 69Document29 pagesWorksheetsmod1 69Jenairah VillamorNo ratings yet
- Synaptic Neurotransmission and Parts of The Brain NOTESDocument6 pagesSynaptic Neurotransmission and Parts of The Brain NOTESDaniNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument3 pagesCoordination and ResponseclintonbogololephojaneNo ratings yet
- Note 1 Nervous CoDocument8 pagesNote 1 Nervous ComalshiNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument86 pagesThe Nervous SystemNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Neurons 15032022 022019pmDocument9 pagesNeurons 15032022 022019pmayan khanNo ratings yet
- RBA Lesson 1 Reflexes and ReactionsDocument16 pagesRBA Lesson 1 Reflexes and ReactionsFelixdino09No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesIntroduction To The Nervous SystemSherwin UbandoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemPatricia BonganayNo ratings yet
- Psychology I - Unit IIIDocument22 pagesPsychology I - Unit IIIMark DarketNo ratings yet
- 11.6. The Nervous System and Sense OrgansDocument12 pages11.6. The Nervous System and Sense OrgansIsaac SiameNo ratings yet
- Transes Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesTranses Nervous SystemAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - GeneralDocument4 pagesNervous System - GeneralanenomeNo ratings yet
- Midterm Pharmacology 1Document89 pagesMidterm Pharmacology 1Hannah Mae RemorinNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Document5 pagesScience-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Marl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Nervous SystemA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- E.nervous System - 2404Document19 pagesE.nervous System - 2404Sireeshasenapathi Sireesha SenapathiNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemDeejay BeekayNo ratings yet
- Physiological PsychologyDocument13 pagesPhysiological Psychologyrye dzNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument3 pagesControl and CoordinationShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- SCience Group 1 q3 Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesSCience Group 1 q3 Nervous Systemapolancos50713No ratings yet
- Week 8 - Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesWeek 8 - Nervous Systemkyla columnaNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 SCI CH No.2Document10 pagesGRADE 8 SCI CH No.2MariamNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience ABCsDocument261 pagesNeuroscience ABCsxxx xxx100% (2)
- Rev Notes ch16 eDocument9 pagesRev Notes ch16 eEdgar LeungNo ratings yet
- LeaP Science 10 Q3 W3Document6 pagesLeaP Science 10 Q3 W3SHAIRA SOTOMAYORNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response in Animals - 052037Document8 pagesCoordination and Response in Animals - 052037MosesNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNervous Systemvictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q3 Week 3Document10 pagesScience 10 Q3 Week 3benitezednacNo ratings yet
- The Neuromuscular System and ExerciseDocument20 pagesThe Neuromuscular System and ExercisenofriNo ratings yet
- Analzying Sensory Somatic Responces - System Reinforcemnt Worksheet1Document2 pagesAnalzying Sensory Somatic Responces - System Reinforcemnt Worksheet1Creative DestinyNo ratings yet
- Analzying Sensory Somatic Responces - System Reinforcemnt Worksheet1Document2 pagesAnalzying Sensory Somatic Responces - System Reinforcemnt Worksheet1Phoebe Sudweste QuitanegNo ratings yet
- 14.coordination and ResponseDocument104 pages14.coordination and ResponseAli MirzaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesNervous Systemmohd nazmieNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For COT 1 Sy 2022-2023Document7 pagesLesson Plan For COT 1 Sy 2022-2023Romelyn Grace BorbeNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q3 Week 3Document10 pagesScience 10 Q3 Week 3John ver PitaoNo ratings yet
- Sight Smell Taste: Unit 2 InteractionDocument3 pagesSight Smell Taste: Unit 2 InteractionmarcNo ratings yet
- Types Structure and Function of NeuronsDocument7 pagesTypes Structure and Function of Neuronsvishnuchaudhari322No ratings yet
- (Human Behavior and Community Health Education) : Biological ViewpointDocument14 pages(Human Behavior and Community Health Education) : Biological ViewpointKirstenNo ratings yet
- Class X - Control and Co-OrdinationDocument9 pagesClass X - Control and Co-OrdinationHardik SinghNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Science 10 Week 3Document28 pages3rd Quarter Science 10 Week 3Aple RigorNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue 1Document16 pagesNervous Tissue 1sbk6gscsbtNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Revision Material Term 2 - 2023Document44 pagesLife Sciences Grade 12 Revision Material Term 2 - 2023paballorandomaccNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous Systemkmakabe78No ratings yet
- Lecture4 - The Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesLecture4 - The Nervous SystemVivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- G-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesG-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- Biology f4 NoteDocument68 pagesBiology f4 NoteE-SKUUL ACADEMYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Neurons and The Action PotentialDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Neurons and The Action PotentialRadha RamineniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Chemical MessengersDocument6 pagesChapter 3 - Chemical MessengersRadha RamineniNo ratings yet
- Brain Facts FlashcardsDocument24 pagesBrain Facts FlashcardsRadha RamineniNo ratings yet
- 2021 Admission-Requirements ENDocument68 pages2021 Admission-Requirements ENRadha RamineniNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument51 pagesBloodMeti TasisaNo ratings yet
- NUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityDocument4 pagesNUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Apache Skor 2Document8 pagesApache Skor 2DhaniNo ratings yet
- Mid Test FK, Bahasa Inggris 1, Ang.2021Document2 pagesMid Test FK, Bahasa Inggris 1, Ang.2021Ary MfNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPKyla Carbonel100% (2)
- MED2 Tut1 Inflammation Healing Quiz NG 2021Document2 pagesMED2 Tut1 Inflammation Healing Quiz NG 2021joshNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Assessment TheoryDocument23 pagesRespiratory Assessment TheoryPopa SimonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - BloodDocument33 pagesChapter 11 - BloodCORONEL, SOPHIANo ratings yet
- Organisation of The Organism PDFDocument79 pagesOrganisation of The Organism PDFrachit100% (2)
- 2018-Pathophysiology and Management of Intracranial Hypertension and Tissular Brain Hypoxia After Severe Traumatic Brain p01-13Document13 pages2018-Pathophysiology and Management of Intracranial Hypertension and Tissular Brain Hypoxia After Severe Traumatic Brain p01-13italofgNo ratings yet
- اسئلتيDocument9 pagesاسئلتيahmedNo ratings yet
- MSDS Medical Carbon DioxideDocument4 pagesMSDS Medical Carbon DioxideRachel LeeNo ratings yet
- Ascorbic Acid-A Potential Oxidant Scavenger and Its Role in Plant Development and Abiotic Stress ToleranceDocument17 pagesAscorbic Acid-A Potential Oxidant Scavenger and Its Role in Plant Development and Abiotic Stress ToleranceNil Andreu ToseteNo ratings yet
- Dopamine DRUG STUDY-ENDODocument3 pagesDopamine DRUG STUDY-ENDOaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Pex 03 09Document5 pagesPex 03 09Pamela Zegarra VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Brainwave-FrequenciesDocument8 pagesBrainwave-Frequenciesroy100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Care 5: Clinical Pharmacy Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument80 pagesPharmaceutical Care 5: Clinical Pharmacy Coronary Artery DiseaseJerson Aizpuro SuplementoNo ratings yet
- 2023 - A Patient's Guide To Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (Arnav Shetty, Peter M Baptista Jardín)Document81 pages2023 - A Patient's Guide To Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (Arnav Shetty, Peter M Baptista Jardín)César EscobarNo ratings yet
- NCPsDocument11 pagesNCPsJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- ABG Quiz by GroupDocument13 pagesABG Quiz by Grouplourd nabNo ratings yet
- 5 Ways To Reduce StressDocument5 pages5 Ways To Reduce StressDr. Lum FrundiNo ratings yet
- Vasopressors For ShockDocument21 pagesVasopressors For ShocknugrahaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: EssentialsDocument31 pagesThe Nervous System: EssentialsSunshine LabraNo ratings yet
- Class 5 - Science Chapter 3Document18 pagesClass 5 - Science Chapter 3deviNo ratings yet
- X - Biology - Chapter 6 - Life Processes: 2 MarksDocument11 pagesX - Biology - Chapter 6 - Life Processes: 2 Marksvalliammai thiagarajanNo ratings yet
Chapter 1 - The Nervous System
Chapter 1 - The Nervous System
Uploaded by
Radha RamineniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 - The Nervous System
Chapter 1 - The Nervous System
Uploaded by
Radha RamineniCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 - The Nervous System
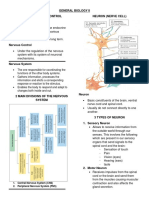
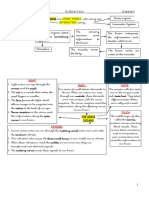
Basic Structure
Nervous System
It consists of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves
Made up of nerve cells and glial cells
Questions
1. What are the three parts of the nervous system?
2. What cell types make up the nervous system?
Neurons
Types of Neurons
Questions
1. What are the three main types of neurons?
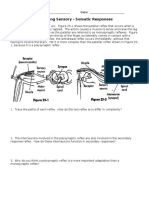
Sensory Neurons
Receptors
Sensory neurons work with receptors
Detect and respond to different attributes of the internal and
external environment
Sensitive to changes in:
Light stimuli
Sound stimuli
Mechanical stimuli
Chemical stimuli
Question
1. What do sensory neurons work with?
Chapter 1 - The Nervous System 1
2. What part of the nervous system detects and responds to
different attributes of the internal and external environment?
3. What do receptors do?
4. What kind of stimuli are receptors sensitive to?
Nociceptors
Activated when mechanical, thermal or chemical stimuli exceed a
certain intensity at which tissue damage can occur
Give rise to protective reflexes and to the sensation of pain.
Questions
1. When are nociceptors activated?
2. Activated when _________, _________, or _________ stimuli
exceed a certain intensity at which tissue damage can occur
3. What gives rise to protective reflexes and to the sensation of
pain?
4. What do nociceptors give rise to?
Motor Neurons
Control the activity of muscles
Questions
1. What type of neurons controls the activity of muscles?
2. What do motor neurons do?
Interneurons
In between sensory and motor neurons
The most common type of neuron in the human brain
Mediate simple reflexes
Responsible for the highest functions of the brain
Questions
1. What is the most numerous neuron in the human brain?
Chapter 1 - The Nervous System 2
2. Which type of neuron mediates simple reflexes?
3. Which type of neuron is responsible for the highest functions of the
brain?
4. What do interneurons do?
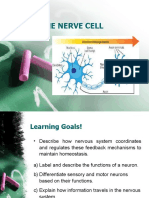
Neuron Structure
Neurons consist of:
The cell body
Two processes
Axon - Transmit info from the neuron onto other neurons that it is
connected to
Dendrite - Recieve the info being transmitted by the axons of
other neurons.
Synapses - Specialized contacts between the processes
Questions
1. What are the parts of a neuron?
2. What are the two processes in the neuron called?
3. What is another name for dendrite and axon?
4. What is the specialized contact between the processes called?
5. What part of the neuron transmits info from the neuron onto other
neurons that it is connected to?
6. What part of the neuron receives the information being transmitted b
other neurons?
7. What is a synapse?
8. What does an axon do?
9. What does a dendrite do?
Glial Cells
Contribute to the development of NS
Chapter 1 - The Nervous System 3
Question
1. Which cell contributes to the development of the NS?
Peripheral Nerves
Peripheral nerves connect sensory receptors and muscles to the brain and
spinal cord.
Questions
1. What do peripheral nerves do?
2. What connects sensory receptors and muscles to the brain and spinal
cord?
3. Peripheral nerves connect ___________ and ________ to the brain and
spinal cord.
Spinal Cord Functions
Two functions:
The seat of simple and complex reflexes
Forms highway between the body and brain
Questions
1. What are the functions of the spinal cord?
2. What part of the nervous system is the seat of simple and complex
reflexes?
3. What part of the nervous system forms a highway between the body and
brain?
Anatomy of the Brain
The brain consists of:
Brainstem
Questions
1. What are the parts of the brainstem?
Divided into the
Chapter 1 - The Nervous System 4
Hind-brain
Extension spinal cord
Contain networks of neurons that help with vital functions such as
breathing and blood pressure
The cerebellum arises from the roof of the hindbrain
Cerebellum - Plays a central role in the control and timing of
movements
Questions
1. Which part of the brainstem is an extension of the spinal
cord?
2. Which part of the brainstem contains networks of neurons that
help with vital functions such as breathing and blood
pressure?
3. What does the hindbrain do?
4. What part of the brain arises from the roof of the hindbrain?
5. What does the cerebellum arise from?
6. What does the cerebellum do?
7. What part of the brain plays a central role in the control and
timing of movements?
Mid-brain
It consists of groups of neurons that each use a specific
neurotransmitter and project to cerebral hemispheres.
Modulates activity in higher centres of the brain to mediate
functions such as sleep, attention, or reward
Questions
1. What does the midbrain do?
2. Which part of the brain modulates activity in higher centres of
the brain to mediate functions such as sleep, attention, or
Chapter 1 - The Nervous System 5
reward?
3. Which part of the brain consists of groups of neurons that
each use a specific neurotransmitter and project to cerebral
hemispheres?
4. The midbrain consists of groups of neurons that each use a
specific __________ and project to cerebral hemispheres.
Diencephalon
Divided into:
The thalamus
Relays impulses from all sensory systems to the CC,
which in turn sends messages back to the thalamus
The hypothalamus
Controls functions such as eating and drinking
Regulates the release of hormones involved in sexual
functions
Questions
1. What parts is the diencephalon divided into?
2. What do the thalamus and hypothalamus make up?
3. What does the thalamus do?
4. What does the hypothalamus do?
5. What part of the brain relays impulses from all sensory
systems to the CC?
6. What part of the brain controls functions such as eating
and drinking?
7. What part of the brain regulates the release of hormones
involved in sexual functions?
Cerebral Hemispheres
Consists of a
Chapter 1 - The Nervous System 6
Core
The basal ganglia
Cental role in the initiation and control of movement
Questions
1. What are the three parts of the cerebral hemispheres?
2. What do the basal ganglia do?
3. What part of the brain plays a central role in initiating and
controlling movement?
CC
Made up of a sheet of neurons that make up gray matter
The most highly developed area of the brain
Four times bigger than gorillas
Somaesthetic areas - sensory areas that receive signals from the
skin
Sensory receptors from one side of the body crossover to the
other side
Movements of the left side of the body are controlled by the
right cortex
The two cortex are connected by the corpus callosum, a fibre
tract
Required for:
Voluntary actions
Language
Speech
Higher functions
Speech is lateralized in the left hemisphere
Questions
Chapter 1 - The Nervous System 7
1. What part of the brain is made up of gray matter?
2. What type of matter is the CC made up of?
3. What is the most highly developed part of the brain?
4. What part of the brain is four times bigger than a gorilla?
5. The CC is four times bigger than a gorilla?
6. What are the somaesthetic areas of the brain?
7. What is the term for sensory areas in the CC that receive
signals from the skin?
8. Which fibre tract connects the hemispheres?
9. What are the four functions that the CC is required for?
10. In which hemisphere is speech laterlized?
The father of modern neuroscience was Ramon Y Cajal
Chapter 1 - The Nervous System 8
You might also like
- Thibarmy Program Fat LossDocument18 pagesThibarmy Program Fat LossWilliam Spratling86% (14)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputRy Pablo83% (41)
- Intensive Care Chart MalaysiaDocument1 pageIntensive Care Chart MalaysiaZan Ya100% (2)
- Neonatal Ventilation Made Easy Jaypee PDFDocument97 pagesNeonatal Ventilation Made Easy Jaypee PDFfloare de coltNo ratings yet
- Huberman Lab NotesDocument152 pagesHuberman Lab Notescan dagidir80% (5)
- Unit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsDocument13 pagesUnit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsIrene Caballero PicazoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Body Coordination 2.1 Body CoordinationDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Body Coordination 2.1 Body CoordinationMarcia PattersonNo ratings yet
- Neuron and Glial CellsDocument25 pagesNeuron and Glial Cellsfakhar aliNo ratings yet
- Week No 1 Quarter 3 - SCIENCEDocument2 pagesWeek No 1 Quarter 3 - SCIENCEwylen b. catamoraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Biology of MindDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - The Biology of MindCindy AvendanoNo ratings yet
- Biology Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesBiology Nervous SystemFatima PueblaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument43 pagesThe Nervous SystemmalakbasahalNo ratings yet
- Section 3.10 The Nervous System Guided NotesDocument3 pagesSection 3.10 The Nervous System Guided NotesNoelleNo ratings yet
- Nerve CellDocument14 pagesNerve CellRomelyn Grace BorbeNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesNervous Systemmercaderlorenzo9No ratings yet
- CBSE G+10 Control+and+coordination NotesDocument19 pagesCBSE G+10 Control+and+coordination Notesveerskucheriya.byjusNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - The Human Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesModule 2 - The Human Nervous SystemoyamaNo ratings yet
- Worksheetsmod1 69Document29 pagesWorksheetsmod1 69Jenairah VillamorNo ratings yet
- Synaptic Neurotransmission and Parts of The Brain NOTESDocument6 pagesSynaptic Neurotransmission and Parts of The Brain NOTESDaniNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument3 pagesCoordination and ResponseclintonbogololephojaneNo ratings yet
- Note 1 Nervous CoDocument8 pagesNote 1 Nervous ComalshiNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument86 pagesThe Nervous SystemNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Neurons 15032022 022019pmDocument9 pagesNeurons 15032022 022019pmayan khanNo ratings yet
- RBA Lesson 1 Reflexes and ReactionsDocument16 pagesRBA Lesson 1 Reflexes and ReactionsFelixdino09No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesIntroduction To The Nervous SystemSherwin UbandoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemPatricia BonganayNo ratings yet
- Psychology I - Unit IIIDocument22 pagesPsychology I - Unit IIIMark DarketNo ratings yet
- 11.6. The Nervous System and Sense OrgansDocument12 pages11.6. The Nervous System and Sense OrgansIsaac SiameNo ratings yet
- Transes Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesTranses Nervous SystemAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - GeneralDocument4 pagesNervous System - GeneralanenomeNo ratings yet
- Midterm Pharmacology 1Document89 pagesMidterm Pharmacology 1Hannah Mae RemorinNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Document5 pagesScience-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Marl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Nervous SystemA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- E.nervous System - 2404Document19 pagesE.nervous System - 2404Sireeshasenapathi Sireesha SenapathiNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemDeejay BeekayNo ratings yet
- Physiological PsychologyDocument13 pagesPhysiological Psychologyrye dzNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument3 pagesControl and CoordinationShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- SCience Group 1 q3 Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesSCience Group 1 q3 Nervous Systemapolancos50713No ratings yet
- Week 8 - Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesWeek 8 - Nervous Systemkyla columnaNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 SCI CH No.2Document10 pagesGRADE 8 SCI CH No.2MariamNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience ABCsDocument261 pagesNeuroscience ABCsxxx xxx100% (2)
- Rev Notes ch16 eDocument9 pagesRev Notes ch16 eEdgar LeungNo ratings yet
- LeaP Science 10 Q3 W3Document6 pagesLeaP Science 10 Q3 W3SHAIRA SOTOMAYORNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response in Animals - 052037Document8 pagesCoordination and Response in Animals - 052037MosesNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNervous Systemvictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q3 Week 3Document10 pagesScience 10 Q3 Week 3benitezednacNo ratings yet
- The Neuromuscular System and ExerciseDocument20 pagesThe Neuromuscular System and ExercisenofriNo ratings yet
- Analzying Sensory Somatic Responces - System Reinforcemnt Worksheet1Document2 pagesAnalzying Sensory Somatic Responces - System Reinforcemnt Worksheet1Creative DestinyNo ratings yet
- Analzying Sensory Somatic Responces - System Reinforcemnt Worksheet1Document2 pagesAnalzying Sensory Somatic Responces - System Reinforcemnt Worksheet1Phoebe Sudweste QuitanegNo ratings yet
- 14.coordination and ResponseDocument104 pages14.coordination and ResponseAli MirzaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesNervous Systemmohd nazmieNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For COT 1 Sy 2022-2023Document7 pagesLesson Plan For COT 1 Sy 2022-2023Romelyn Grace BorbeNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q3 Week 3Document10 pagesScience 10 Q3 Week 3John ver PitaoNo ratings yet
- Sight Smell Taste: Unit 2 InteractionDocument3 pagesSight Smell Taste: Unit 2 InteractionmarcNo ratings yet
- Types Structure and Function of NeuronsDocument7 pagesTypes Structure and Function of Neuronsvishnuchaudhari322No ratings yet
- (Human Behavior and Community Health Education) : Biological ViewpointDocument14 pages(Human Behavior and Community Health Education) : Biological ViewpointKirstenNo ratings yet
- Class X - Control and Co-OrdinationDocument9 pagesClass X - Control and Co-OrdinationHardik SinghNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Science 10 Week 3Document28 pages3rd Quarter Science 10 Week 3Aple RigorNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue 1Document16 pagesNervous Tissue 1sbk6gscsbtNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Revision Material Term 2 - 2023Document44 pagesLife Sciences Grade 12 Revision Material Term 2 - 2023paballorandomaccNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous Systemkmakabe78No ratings yet
- Lecture4 - The Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesLecture4 - The Nervous SystemVivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- G-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesG-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- Biology f4 NoteDocument68 pagesBiology f4 NoteE-SKUUL ACADEMYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Neurons and The Action PotentialDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Neurons and The Action PotentialRadha RamineniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Chemical MessengersDocument6 pagesChapter 3 - Chemical MessengersRadha RamineniNo ratings yet
- Brain Facts FlashcardsDocument24 pagesBrain Facts FlashcardsRadha RamineniNo ratings yet
- 2021 Admission-Requirements ENDocument68 pages2021 Admission-Requirements ENRadha RamineniNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument51 pagesBloodMeti TasisaNo ratings yet
- NUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityDocument4 pagesNUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Apache Skor 2Document8 pagesApache Skor 2DhaniNo ratings yet
- Mid Test FK, Bahasa Inggris 1, Ang.2021Document2 pagesMid Test FK, Bahasa Inggris 1, Ang.2021Ary MfNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPKyla Carbonel100% (2)
- MED2 Tut1 Inflammation Healing Quiz NG 2021Document2 pagesMED2 Tut1 Inflammation Healing Quiz NG 2021joshNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Assessment TheoryDocument23 pagesRespiratory Assessment TheoryPopa SimonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - BloodDocument33 pagesChapter 11 - BloodCORONEL, SOPHIANo ratings yet
- Organisation of The Organism PDFDocument79 pagesOrganisation of The Organism PDFrachit100% (2)
- 2018-Pathophysiology and Management of Intracranial Hypertension and Tissular Brain Hypoxia After Severe Traumatic Brain p01-13Document13 pages2018-Pathophysiology and Management of Intracranial Hypertension and Tissular Brain Hypoxia After Severe Traumatic Brain p01-13italofgNo ratings yet
- اسئلتيDocument9 pagesاسئلتيahmedNo ratings yet
- MSDS Medical Carbon DioxideDocument4 pagesMSDS Medical Carbon DioxideRachel LeeNo ratings yet
- Ascorbic Acid-A Potential Oxidant Scavenger and Its Role in Plant Development and Abiotic Stress ToleranceDocument17 pagesAscorbic Acid-A Potential Oxidant Scavenger and Its Role in Plant Development and Abiotic Stress ToleranceNil Andreu ToseteNo ratings yet
- Dopamine DRUG STUDY-ENDODocument3 pagesDopamine DRUG STUDY-ENDOaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Pex 03 09Document5 pagesPex 03 09Pamela Zegarra VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Brainwave-FrequenciesDocument8 pagesBrainwave-Frequenciesroy100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Care 5: Clinical Pharmacy Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument80 pagesPharmaceutical Care 5: Clinical Pharmacy Coronary Artery DiseaseJerson Aizpuro SuplementoNo ratings yet
- 2023 - A Patient's Guide To Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (Arnav Shetty, Peter M Baptista Jardín)Document81 pages2023 - A Patient's Guide To Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (Arnav Shetty, Peter M Baptista Jardín)César EscobarNo ratings yet
- NCPsDocument11 pagesNCPsJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- ABG Quiz by GroupDocument13 pagesABG Quiz by Grouplourd nabNo ratings yet
- 5 Ways To Reduce StressDocument5 pages5 Ways To Reduce StressDr. Lum FrundiNo ratings yet
- Vasopressors For ShockDocument21 pagesVasopressors For ShocknugrahaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: EssentialsDocument31 pagesThe Nervous System: EssentialsSunshine LabraNo ratings yet
- Class 5 - Science Chapter 3Document18 pagesClass 5 - Science Chapter 3deviNo ratings yet
- X - Biology - Chapter 6 - Life Processes: 2 MarksDocument11 pagesX - Biology - Chapter 6 - Life Processes: 2 Marksvalliammai thiagarajanNo ratings yet