Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsEndocrine
Endocrine
Uploaded by
Priya SaikiaThe document provides information about the endocrine system through diagrams and flowcharts. It compares the endocrine and nervous systems, outlines the main types of hormones and secondary messenger systems. It also summarizes:
1. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland relationship and feedback mechanisms.
2. The thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and endocrine pancreas functions.
3. Calcium homeostasis involving the parathyroid gland, vitamin D, and calcitonin.
The document aims to help students learn about the key components and functions of the endocrine system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Black's Medical DictionaryDocument849 pagesBlack's Medical Dictionaryanon-97048197% (30)
- The Digestive System A Level NotesDocument7 pagesThe Digestive System A Level Noteselendria100% (1)
- Endocrine System: EndocrinologyDocument10 pagesEndocrine System: EndocrinologyAnya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands: Secretion and Action of HormonesDocument18 pagesEndocrine Glands: Secretion and Action of HormonesAnkur HazraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - 2023Document61 pagesChapter 9 - 2023ngoclan4304No ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGYDocument8 pagesENDOCRINOLOGYshaairatogleNo ratings yet
- 17.2 Hormones Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pages17.2 Hormones Anatomy and PhysiologyPrincess RuthNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 2Document22 pagesChapter1 2Thea NatacNo ratings yet
- Neuroendocrine System NotesDocument9 pagesNeuroendocrine System Notestara.mehrNo ratings yet
- Endokrinologi Reproduksi: Bayu Kurniawan, DRDocument48 pagesEndokrinologi Reproduksi: Bayu Kurniawan, DRdocbay100% (1)
- Endocrine DrugsDocument172 pagesEndocrine DrugsAlvim Tiel FactorNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: EndocrineDocument210 pagesPharmacology: EndocrineSharifa Darayan100% (1)
- Endocrine System: Navigation SearchDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Navigation SearchAnnagella De JesusNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Lec 1Document26 pagesEndocrine System Lec 1Fadli IlhamNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Harliansyah Dept Biochemistry University of YARSIDocument26 pagesEndocrine System: Harliansyah Dept Biochemistry University of YARSIAnonymous 7r6o3g4jNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13 EditDocument10 pagesExercise 13 EditSamantha De JesusNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry - PITUITARY HORMONES TRANSDocument7 pagesClinical Chemistry - PITUITARY HORMONES TRANSCamella Beatrice Lujan ValleNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionaudreyNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Endocrinology 2020Document37 pagesBasic Principles of Endocrinology 2020K ZarabianNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemJessica Glitter100% (2)
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandDocument32 pagesHypothalamus and Pituitary Glandyararadwan56No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument70 pagesEndocrine SystemKELVINNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument120 pagesBasicsbiniam MesfinNo ratings yet
- Hormones 080623Document83 pagesHormones 080623Rao Asad MubeenNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument86 pagesEndocrine PhysiologySabbir AhmedNo ratings yet
- CH 16 Endocrine TableDocument9 pagesCH 16 Endocrine TablebetazenNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Apllied ScienceDocument44 pagesEndocrinology Apllied ScienceAdam PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Describe Hormones and Their CompositionDocument7 pagesDescribe Hormones and Their CompositionShahzaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 17 PhysiologyDocument49 pagesChapter - 17 PhysiologyAhsanullah PathanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandDocument9 pagesEndocrine GlandKUNAL1221No ratings yet
- Metabolic & Endocrine DiseasesDocument280 pagesMetabolic & Endocrine DiseasesHussenNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Citation NeededDocument8 pagesEndocrine System: Citation NeededAsif Hassan BiswasNo ratings yet
- NOTES Endocrinology ToxicologyDocument52 pagesNOTES Endocrinology ToxicologyRenz Gerard AmorNo ratings yet
- Discussion Notes AnaphyDocument36 pagesDiscussion Notes Anaphyjade tanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System/socialDocument33 pagesEndocrine System/socialrpant3165No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Physiology Chapter 14 Endocrine System NotesDocument13 pagesHuman Anatomy Physiology Chapter 14 Endocrine System Notesadarshjain816No ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument32 pagesEndocrine PhysiologyAziem ShazwanNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument12 pagesEndocrinologyNathaniel Derige AndesNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Anterior Pituitary and HypothalamusDocument121 pagesDisorders of The Anterior Pituitary and Hypothalamusbiniam MesfinNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: DR - Entissar Mansour 2O16-2017Document162 pagesEndocrine System: DR - Entissar Mansour 2O16-2017Zainab Alshamary100% (1)
- EndocrineDocument12 pagesEndocrinejamille consingNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesEndocrine SystemElaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezDocument144 pagesEndocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezTrixie Rose Ebona CortezNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 8 EndocrineDocument4 pagesLecture - 8 EndocrineBafrin ShaqlawaNo ratings yet
- MRGR Endocrine System Ysh17Document29 pagesMRGR Endocrine System Ysh17Yash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Science Glands SlidesDocument13 pagesScience Glands SlidesAte DannyNo ratings yet
- 1-Endocrine 1Document23 pages1-Endocrine 1محمد عليNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument10 pagesEndocrine System13PLAN, SENTH RUEN, ANo ratings yet
- evaluatedSLK On The Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesevaluatedSLK On The Endocrine SystemMilagrosBautistaNo ratings yet
- Anterior Pituitary GlandDocument33 pagesAnterior Pituitary Glandmarianne.erdooNo ratings yet
- 9F. Endokrin 2Document53 pages9F. Endokrin 2Irfan Maulana AjiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physology 2023 SharedDocument121 pagesEndocrine Physology 2023 SharedputracahyaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Endocrine SystemDocument43 pagesDrugs Affecting The Endocrine SystemJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Endocrine-SystemLabActivityDocument5 pagesEndocrine-SystemLabActivityMrs Robert IrwinNo ratings yet
- Hormon Hipotalamus Dan Hipofisis Compatibility ModeDocument35 pagesHormon Hipotalamus Dan Hipofisis Compatibility ModeVennia Riskia TristiantiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction & Endocrinology 1: Hypothalamus and PituitaryDocument41 pagesReproduction & Endocrinology 1: Hypothalamus and PituitaryabdulNo ratings yet
- Topic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesDocument18 pagesTopic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesHaris AliNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Consists of Hormones Secreted by Glands Traveling Through The Blood To Target TissuesDocument16 pagesThe Endocrine System Consists of Hormones Secreted by Glands Traveling Through The Blood To Target TissuesAljon AniesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemKAUSTUBH SAWANTNo ratings yet
- Hormones (Short Version)Document80 pagesHormones (Short Version)Vivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument8 pagesNcert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and Integrationginnisingh524No ratings yet
- Endocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandEndocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PLM Screening ActivityDocument8 pagesPLM Screening Activityjamie mutucNo ratings yet
- 2009 Fee ScheduleDocument1,123 pages2009 Fee ScheduleNicole HillNo ratings yet
- Pharynx: DissectionDocument23 pagesPharynx: DissectionrajtanniruNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue: D. Urinary BladderDocument3 pagesEpithelial Tissue: D. Urinary BladderNuhu SibaNo ratings yet
- Review Questions Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesReview Questions Fluid and Electrolytesmarie100% (13)
- Freedive Earth - The Mammalian Diving ReflexDocument5 pagesFreedive Earth - The Mammalian Diving ReflexAryaNo ratings yet
- Lee Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesLee Endocrine SystemLouise Mica LeeNo ratings yet
- Addison's DiseaseDocument17 pagesAddison's DiseaseMah Jezthy100% (1)
- CSEC Biology June 2013 P2 PDFDocument16 pagesCSEC Biology June 2013 P2 PDFJoy Boehmer100% (1)
- HealthDocument16 pagesHealthMaria Lucille Mejias IINo ratings yet
- Management of Compromised Residual Ridge PDFDocument73 pagesManagement of Compromised Residual Ridge PDFmarwa100% (1)
- Tounge Thrust SwallowingDocument2 pagesTounge Thrust SwallowinglexerdowsalternativeNo ratings yet
- LP IcuDocument15 pagesLP IcuMario Kape100% (1)
- Corrections and Additions To Taxonomists' Glossary of Mosquito AnatomyDocument17 pagesCorrections and Additions To Taxonomists' Glossary of Mosquito AnatomymokarahNo ratings yet
- HEMA-1 Up To PG 30.-1-31Document31 pagesHEMA-1 Up To PG 30.-1-31Angela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Peadiatric History Taking: Patient IdentificationDocument7 pagesPeadiatric History Taking: Patient Identificationpriyanjali sainiNo ratings yet
- GroomingDocument17 pagesGroomingKishor RaskarNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsDocument30 pagesCoordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsSarah CruzNo ratings yet
- How Did We Find Out About Blood - Isaac AsimovDocument27 pagesHow Did We Find Out About Blood - Isaac AsimovCristo A. BojorquezNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Fisiologi Sistem Kemih ManusiaDocument104 pagesRangkuman Fisiologi Sistem Kemih ManusiaPAP BungsuNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System Pmls 2 Lecture 3 PrelimsDocument8 pagesThe Circulatory System Pmls 2 Lecture 3 PrelimsNunai SalipadaNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH 6 Life Process Part-II - Class 10th Science Study RankersDocument7 pagesNotes of CH 6 Life Process Part-II - Class 10th Science Study RankerssamyNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Nervous ControlDocument5 pagesChemical and Nervous ControlNico BereberNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Occlusion JipsDocument7 pagesConcepts of Occlusion JipsDRPRIYA007No ratings yet
- Life Processes 1Document36 pagesLife Processes 1Generic nameNo ratings yet
- @soyeb - Aftab Earthworm, Cockroach, Frog Ncert NotesDocument17 pages@soyeb - Aftab Earthworm, Cockroach, Frog Ncert NotesKrutiNo ratings yet
- TXB Anomali RadenDocument10 pagesTXB Anomali Radenayu waodeNo ratings yet
- Puberty and Its Disorders Puberty and Its DisordersDocument57 pagesPuberty and Its Disorders Puberty and Its DisordersYeltserNo ratings yet
Endocrine
Endocrine
Uploaded by
Priya Saikia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views28 pagesThe document provides information about the endocrine system through diagrams and flowcharts. It compares the endocrine and nervous systems, outlines the main types of hormones and secondary messenger systems. It also summarizes:
1. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland relationship and feedback mechanisms.
2. The thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and endocrine pancreas functions.
3. Calcium homeostasis involving the parathyroid gland, vitamin D, and calcitonin.
The document aims to help students learn about the key components and functions of the endocrine system.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information about the endocrine system through diagrams and flowcharts. It compares the endocrine and nervous systems, outlines the main types of hormones and secondary messenger systems. It also summarizes:
1. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland relationship and feedback mechanisms.
2. The thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and endocrine pancreas functions.
3. Calcium homeostasis involving the parathyroid gland, vitamin D, and calcitonin.
The document aims to help students learn about the key components and functions of the endocrine system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views28 pagesEndocrine
Endocrine
Uploaded by
Priya SaikiaThe document provides information about the endocrine system through diagrams and flowcharts. It compares the endocrine and nervous systems, outlines the main types of hormones and secondary messenger systems. It also summarizes:
1. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland relationship and feedback mechanisms.
2. The thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and endocrine pancreas functions.
3. Calcium homeostasis involving the parathyroid gland, vitamin D, and calcitonin.
The document aims to help students learn about the key components and functions of the endocrine system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 28
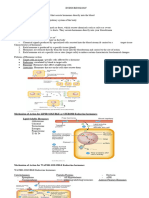
Diagrams & Flowcharts – Endocrine System
Instruction: Date: 17/07/2023
1. Write the diagrams/flow charts neatly with proper Labeling in 100page unruled
notebook
2. Submit your assignment to the respective Table Teacher on time
3. Clarify your doubts with teacher concerned.
4. Submit the assignment by August 28th 2023
1. General Endocrinology
Comparison between Endocrine and Nervous System
Features Endocrine System Nervous System
Communication Method Secretes hormones; hormones are A nerve signal causes
transported within the blood & neurotransmitter release from a
distributed to target cells throughout neuron into a synaptic cleft
body
Target of Stimulation Any cell in the body with a receptor for Other neurons, muscle cells & gland
the hormone cells
Response Time Relatively slow reaction time: seconds to Rapid reaction time: Typically
minutes to hours milliseconds or seconds
Range of Effect Typically has widespread effects Typically has localized specific
throughout the body effects in the body
Duration of Response Long-lasting: minutes to days to weeks: Short- term: Milliseconds,
may continue after stimulus is removed terminates with removal of stimulus
Types of Hormones & Second messenger system
Hormones That Use Hormones That Use the Adenylyl Hormones That Use the
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Cyclase–cAMP Second Messenger Phospholipase C Second
Signaling System Messenger System
Fibroblast growth Adrenocorticotropic hormone Angiotensin II (vascular
factor (ACTH) smooth muscle)
Growth hormone Angiotensin II (epithelial Catecholamines (α
Insulin cells) receptors)
Insulin-like growth Calcitonin Gonadotropin-releasing
factor-1 Catecholamines (â receptors) hormone (GnRH)
Leptin Corticotropin-releasing Growth hormone–
Prolactin hormone (CRH) releasing hormone
Follicle-stimulating hormone (GHRH)
(FSH) Parathyroid hormone
Glucagon (PTH)
Growth hormone–releasing Oxytocin
hormone (GHRH) Thyrotropin-releasing
Luteinizing hormone (LH) hormone (TRH)
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Vasopressin (V1 receptor,
Somatostatin vascular smooth muscle)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
(TSH)
Vasopressin (V2 receptor,
epithelial cells)
Feedback Mechanisms
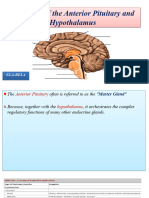
2. HYPOTHALAMUS & PITUTARY
Growth Hormone
Milk Ejection Reflex
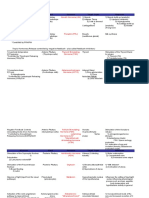
3. THYROID GLAND
4. ADRENAL GLAND
5. ENDOCRINE PANCREAS
Pathophysiology of Diabetes mellitus & its complication
6. CALCIUM HOMEOSTASIS (PARA THYROID, VIT D, CALCITONIN)
7. OTHERS
You might also like
- Black's Medical DictionaryDocument849 pagesBlack's Medical Dictionaryanon-97048197% (30)
- The Digestive System A Level NotesDocument7 pagesThe Digestive System A Level Noteselendria100% (1)
- Endocrine System: EndocrinologyDocument10 pagesEndocrine System: EndocrinologyAnya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands: Secretion and Action of HormonesDocument18 pagesEndocrine Glands: Secretion and Action of HormonesAnkur HazraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - 2023Document61 pagesChapter 9 - 2023ngoclan4304No ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGYDocument8 pagesENDOCRINOLOGYshaairatogleNo ratings yet
- 17.2 Hormones Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pages17.2 Hormones Anatomy and PhysiologyPrincess RuthNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 2Document22 pagesChapter1 2Thea NatacNo ratings yet
- Neuroendocrine System NotesDocument9 pagesNeuroendocrine System Notestara.mehrNo ratings yet
- Endokrinologi Reproduksi: Bayu Kurniawan, DRDocument48 pagesEndokrinologi Reproduksi: Bayu Kurniawan, DRdocbay100% (1)
- Endocrine DrugsDocument172 pagesEndocrine DrugsAlvim Tiel FactorNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: EndocrineDocument210 pagesPharmacology: EndocrineSharifa Darayan100% (1)
- Endocrine System: Navigation SearchDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Navigation SearchAnnagella De JesusNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Lec 1Document26 pagesEndocrine System Lec 1Fadli IlhamNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Harliansyah Dept Biochemistry University of YARSIDocument26 pagesEndocrine System: Harliansyah Dept Biochemistry University of YARSIAnonymous 7r6o3g4jNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13 EditDocument10 pagesExercise 13 EditSamantha De JesusNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry - PITUITARY HORMONES TRANSDocument7 pagesClinical Chemistry - PITUITARY HORMONES TRANSCamella Beatrice Lujan ValleNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionaudreyNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Endocrinology 2020Document37 pagesBasic Principles of Endocrinology 2020K ZarabianNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemJessica Glitter100% (2)
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandDocument32 pagesHypothalamus and Pituitary Glandyararadwan56No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument70 pagesEndocrine SystemKELVINNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument120 pagesBasicsbiniam MesfinNo ratings yet
- Hormones 080623Document83 pagesHormones 080623Rao Asad MubeenNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument86 pagesEndocrine PhysiologySabbir AhmedNo ratings yet
- CH 16 Endocrine TableDocument9 pagesCH 16 Endocrine TablebetazenNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Apllied ScienceDocument44 pagesEndocrinology Apllied ScienceAdam PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Describe Hormones and Their CompositionDocument7 pagesDescribe Hormones and Their CompositionShahzaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 17 PhysiologyDocument49 pagesChapter - 17 PhysiologyAhsanullah PathanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandDocument9 pagesEndocrine GlandKUNAL1221No ratings yet
- Metabolic & Endocrine DiseasesDocument280 pagesMetabolic & Endocrine DiseasesHussenNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Citation NeededDocument8 pagesEndocrine System: Citation NeededAsif Hassan BiswasNo ratings yet
- NOTES Endocrinology ToxicologyDocument52 pagesNOTES Endocrinology ToxicologyRenz Gerard AmorNo ratings yet
- Discussion Notes AnaphyDocument36 pagesDiscussion Notes Anaphyjade tanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System/socialDocument33 pagesEndocrine System/socialrpant3165No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Physiology Chapter 14 Endocrine System NotesDocument13 pagesHuman Anatomy Physiology Chapter 14 Endocrine System Notesadarshjain816No ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument32 pagesEndocrine PhysiologyAziem ShazwanNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument12 pagesEndocrinologyNathaniel Derige AndesNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Anterior Pituitary and HypothalamusDocument121 pagesDisorders of The Anterior Pituitary and Hypothalamusbiniam MesfinNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: DR - Entissar Mansour 2O16-2017Document162 pagesEndocrine System: DR - Entissar Mansour 2O16-2017Zainab Alshamary100% (1)
- EndocrineDocument12 pagesEndocrinejamille consingNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesEndocrine SystemElaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezDocument144 pagesEndocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezTrixie Rose Ebona CortezNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 8 EndocrineDocument4 pagesLecture - 8 EndocrineBafrin ShaqlawaNo ratings yet
- MRGR Endocrine System Ysh17Document29 pagesMRGR Endocrine System Ysh17Yash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Science Glands SlidesDocument13 pagesScience Glands SlidesAte DannyNo ratings yet
- 1-Endocrine 1Document23 pages1-Endocrine 1محمد عليNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument10 pagesEndocrine System13PLAN, SENTH RUEN, ANo ratings yet
- evaluatedSLK On The Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesevaluatedSLK On The Endocrine SystemMilagrosBautistaNo ratings yet
- Anterior Pituitary GlandDocument33 pagesAnterior Pituitary Glandmarianne.erdooNo ratings yet
- 9F. Endokrin 2Document53 pages9F. Endokrin 2Irfan Maulana AjiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physology 2023 SharedDocument121 pagesEndocrine Physology 2023 SharedputracahyaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Endocrine SystemDocument43 pagesDrugs Affecting The Endocrine SystemJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Endocrine-SystemLabActivityDocument5 pagesEndocrine-SystemLabActivityMrs Robert IrwinNo ratings yet
- Hormon Hipotalamus Dan Hipofisis Compatibility ModeDocument35 pagesHormon Hipotalamus Dan Hipofisis Compatibility ModeVennia Riskia TristiantiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction & Endocrinology 1: Hypothalamus and PituitaryDocument41 pagesReproduction & Endocrinology 1: Hypothalamus and PituitaryabdulNo ratings yet
- Topic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesDocument18 pagesTopic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesHaris AliNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Consists of Hormones Secreted by Glands Traveling Through The Blood To Target TissuesDocument16 pagesThe Endocrine System Consists of Hormones Secreted by Glands Traveling Through The Blood To Target TissuesAljon AniesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemKAUSTUBH SAWANTNo ratings yet
- Hormones (Short Version)Document80 pagesHormones (Short Version)Vivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument8 pagesNcert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and Integrationginnisingh524No ratings yet
- Endocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandEndocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PLM Screening ActivityDocument8 pagesPLM Screening Activityjamie mutucNo ratings yet
- 2009 Fee ScheduleDocument1,123 pages2009 Fee ScheduleNicole HillNo ratings yet
- Pharynx: DissectionDocument23 pagesPharynx: DissectionrajtanniruNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue: D. Urinary BladderDocument3 pagesEpithelial Tissue: D. Urinary BladderNuhu SibaNo ratings yet
- Review Questions Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesReview Questions Fluid and Electrolytesmarie100% (13)
- Freedive Earth - The Mammalian Diving ReflexDocument5 pagesFreedive Earth - The Mammalian Diving ReflexAryaNo ratings yet
- Lee Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesLee Endocrine SystemLouise Mica LeeNo ratings yet
- Addison's DiseaseDocument17 pagesAddison's DiseaseMah Jezthy100% (1)
- CSEC Biology June 2013 P2 PDFDocument16 pagesCSEC Biology June 2013 P2 PDFJoy Boehmer100% (1)
- HealthDocument16 pagesHealthMaria Lucille Mejias IINo ratings yet
- Management of Compromised Residual Ridge PDFDocument73 pagesManagement of Compromised Residual Ridge PDFmarwa100% (1)
- Tounge Thrust SwallowingDocument2 pagesTounge Thrust SwallowinglexerdowsalternativeNo ratings yet
- LP IcuDocument15 pagesLP IcuMario Kape100% (1)
- Corrections and Additions To Taxonomists' Glossary of Mosquito AnatomyDocument17 pagesCorrections and Additions To Taxonomists' Glossary of Mosquito AnatomymokarahNo ratings yet
- HEMA-1 Up To PG 30.-1-31Document31 pagesHEMA-1 Up To PG 30.-1-31Angela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Peadiatric History Taking: Patient IdentificationDocument7 pagesPeadiatric History Taking: Patient Identificationpriyanjali sainiNo ratings yet
- GroomingDocument17 pagesGroomingKishor RaskarNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsDocument30 pagesCoordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsSarah CruzNo ratings yet
- How Did We Find Out About Blood - Isaac AsimovDocument27 pagesHow Did We Find Out About Blood - Isaac AsimovCristo A. BojorquezNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Fisiologi Sistem Kemih ManusiaDocument104 pagesRangkuman Fisiologi Sistem Kemih ManusiaPAP BungsuNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System Pmls 2 Lecture 3 PrelimsDocument8 pagesThe Circulatory System Pmls 2 Lecture 3 PrelimsNunai SalipadaNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH 6 Life Process Part-II - Class 10th Science Study RankersDocument7 pagesNotes of CH 6 Life Process Part-II - Class 10th Science Study RankerssamyNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Nervous ControlDocument5 pagesChemical and Nervous ControlNico BereberNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Occlusion JipsDocument7 pagesConcepts of Occlusion JipsDRPRIYA007No ratings yet
- Life Processes 1Document36 pagesLife Processes 1Generic nameNo ratings yet
- @soyeb - Aftab Earthworm, Cockroach, Frog Ncert NotesDocument17 pages@soyeb - Aftab Earthworm, Cockroach, Frog Ncert NotesKrutiNo ratings yet
- TXB Anomali RadenDocument10 pagesTXB Anomali Radenayu waodeNo ratings yet
- Puberty and Its Disorders Puberty and Its DisordersDocument57 pagesPuberty and Its Disorders Puberty and Its DisordersYeltserNo ratings yet