Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Normal Values
Normal Values
Uploaded by
JOHN CARLO APATANOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Normal Values
Normal Values
Uploaded by
JOHN CARLO APATANCopyright:
Available Formats
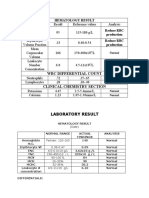
Reference Definition Term Boards Review Reference Definition
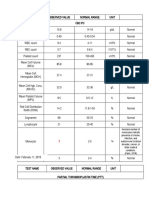
NORMAL VALUES
Males: 13-18 g/dL; Females: 12-16 g/dL Normal hemoglobin levels
Males: 42-52 %; Females: 35-47% Normal hematocrit levels
4000 - 11 000 cu/mm Normal RBC count
80 to 100 fl Normal MCV
150 000 to 450 000 count/uL Normal platelet count
5000-10 000 Normal WBC count
Low MCV and MCH indicate microcytic anemia (seen in
iron deficiency anemia) while high MCV and MCH
indicate macrocytic anemia (seen in pernicious and This is how mean corpuscular volume (MCV) and mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) indicate anemia -- they
folic acid deficiency anemia) are the best indicators of such
2-9 minutes Normal bleeding time
11-13 seconds Normal prothrombin time
< 1.1 Normal INR
25-40 seconds Normal activated parital thromboplastin time
< 0.5 mg/dL) Normal D-dimer
1.5 to 2.5 x Heparin therapeutic range
1.5 to 2.0 x Warfarin therapeutic range
0.5 to 1.2 mg/dL Normal serum bilirubin
5 to 20 mg/dL Normal BUN
0.5 to 1.2 mg/dL Normal creatinine
10:1 BUN:Creatinine ratio
110 to 120 mL/min or 1.67 to 2.5 mL/second Urine creatinine clearance - this is the best indicate of glomerular function
8 to 48 U/L Normal aspartate aminotransferase
7 to 55 U/L Normal alanine aminotransferase
10 to 140 U/L Normal serum lipase
40 to 140 U/L Normal serum amylase
125 mL/min Normal GFR
3.5 to 5 g/dL Normal serum albumin
2.5 to 8 mg/dL Normal serum uric acid levels
40 to 80 mcg/dL (average: 35 to 65 mcg/dL) Normal serum ammonia levels
0.5 to 1.0 mmol/L Normal serum lactate levels
The BUN:Creatinine ratio is increased where BUN is higher than Crea but crea Decreased GFR, high BUN/CREA, high BUN:Crea, high These are the laboratory manifestations of pre-renal AKI which reabsorbs water and Na due to RAA because of
ratio is still the same SG and urine osmolality, low urine Na decreased renal blood flow (GFR, BUN/CREA, BUN:Crea ratio, SG, urine osmolality, urine Na)
Decreased GFR, high BUN/CREA, low BUN:Crea, low
SG and urine osmolality, and high urine Na ++ These are the laboratory manfiestations of intra-renal AKI which has increased permeability due to direct renal
proteinuria damage including the glomerulus (GFR, BUN/CREA, BUN:Crea ratio, SG, urine osmolality, urine Na)
These are the laboratory manifestations of initial post-renal AKI due to obstruction of the ureter and bladder
Decreased GFR, high BUN/CREA, High BUN:Crea, high causing low excretion and increased reabsorption (GFR, BUN/CREA, BUN:Crea ratio, SG, urine osmolality,
SG and urine osmolality, low urine Na urine Na)
These are the laboratory manifestations of post post-renal AKI where the damage has occurred in the renal
Decreased GFR, high BUN/CREA, low BUN:Crea, low tubules causing decreased reabsorption and increased excretion (GFR, BUN/CREA, BUN:Crea ratio, SG, urine
SG and urine osmolality, and high urine Na osmolality, urine Na)
7.35-7.45 This is the normal values for blood pH
35-45 mmHg This is the normal values for PaCO2
22-26 mEq/L This is the normal values for HCO3
80-100 mmHg This is the normal values for PaO2
135-145 mEq/L Normal serum sodium levels
3.5 to 5.0 mEq/L Normal serum potassium levels
9 to 10 mg/dL Normal serum calcium levels
1.3 to 2.5 mEq/L Normal serum magnesium levels
2.5 to 4.5 mg/dL Normal serum phosphorus levels
275-295 mOsm/L Normal serum osmolality
1200 to 1500 mL/day Normal urine output in a day
More than 1.0 mL/kg/hr (preschool onwards); more
than 1.5 mL/kg/hr (toddler); more than 2 mL/kg/hr
(infants) Normal urine output for children 5
More than 0.5 mL/kg/hr or 30 mL/hour Normal urine output for adults
< 400-500 mL/day Levels indicating oliguria
< 100 mL/day Levels indicating anuria
4000 to 5000 mL/day Levels indicating polyuria or water intake that may lead to psychogenic diabetes insipidus
Amber or straw Normal urine color in urinalysis
4.5 to 8.0 (average: 6) - slightly acidic Normal urine pH in urinalysis
1.010 to 1.025 Normal urine specific gravity
Absent Normal urine protein levels in urinalysis
0-5/hpf or absent Normal RBC levels in urinalysis
0-5/hpf or absent Normal WBC levels in urinalysis
Absent Normal pus amount in urinalysis
Absent Normal glucose amount in urinalysis
Absent Normal ketone amount in urinalysis
0 to 4 Normal amount of casts in urinalysis
RBC, WBC, and pus The presence of these in urinalysis indicate UTI
Glucose, ketones, and casts The presence of these in urinalysis indicate DKA
Fr 7.5 to 8.5 / 23 cm ET tube size and length of insertion for males
Fr 6.5 to 7.5 /. 21 cm ET tube size and length of insertion for females
Fr 4 / age/2 +13 if oral or 15 if nasal ET tube size and length of insertion for children
SBP + 2DBP / 3 70 to 100 mmHg Normal MAP
2 to 5 mmHg // 3 to 8 cmH2O Normal CVP in mmHg or cmH2O
5 to 12 mmHg Normal left atrial pressure and pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
4 to 6 LPM Normal cardiac output
60 to 70 mL Normal stroke volume
10 to 20 mmHg // 5-10 to 15 mmHg Normal ICP
60 to 70 mmHg Normal CPP
0.04 seconds Time of a small box in ECG
0.20 seconds Time of a big box in ECG
0.1 mV Voltage of a small box
1 P wave : 1 QRS complex Normal P wave
0.12 to 0.20 seconds Normal PR segment
0.08 to 0.10 seconds Normal QRS complex
Flat; isoelectric Normal ST segment
0.32 to 0.44 seconds Normal QT interval
Upright T wave Normal T wave
50 to 200 J Cardioversion in J
360 J Monophasic defibrillation in J
120 to 200 J Biphasic defibrillation in J
< 15% or < 750 mL Class I hypovolemic shock in % of body water or mL of blood
15% to 30% or 750 to 1500 mL Class II hypovolemic shock in % of body water or mL of blood
30% to 40% or 1500 to 2000 mL Class III hypovolemic shock in % of body water or mL of blood
> 40% or >2000 mL Class IV hypovolemic shock in % of body water or mL of blood
9% [4.5% if anterior or posterior] Adult head TBSA
18% each side, anterior or posterior (can be 9% for
upper and lower portion) Adult torso TBSA
9% [4.5% if upper or posterior arm] Adult arm TBSA
18% [9% if anterior or posterior] Adult leg TBSA
1% [no divisions] Adult perineum TBSA
18% [9% if anterior or posterior] Infant head TBSA
18% same as adults Infant torso TBSA
9% same as adults Infant arm TBSA
14% [7% if anterior or posterior] Infant leg TBSA
TBSA x weight in kg x 4 = 50% in the first 8 hours and
50% in the remaining 16 hours Parkland formula
1% = 1 palm Palmar method
150 to 200 mg/dL These are the normal values for cholesterol levels
140 to 200 mg/dL These are the normal values for triglyceride levels
30 to 70 mg/dL These are the normal HDL levels
< 130 mg/dL These are the normal LDL levels Needs fasting prior blood measurement (10 hours)
70 to 110 mg/dL Normal fasting blood glucose
111 to 125 mg/dL Pre-diabetic fasting blood glucose
More than 125 mg/dL Diabetic FBS Needs fasting prior blood measurement (8-10 hours, NEVER 12 HOURS)
170 to 200 mg/dL Normal blood glucose immediate post-prandial
190 to 230 mg/dL Pre-diabetic blood glucose immediate post-prandial
220 to 300 mg/dL Diabetic blood glucose immediate post-prandial
2 hours post-prandial; multiples of 2 120 to 140 mg/dL Normal blood glucose 2 hours post-prandial
140 to 160 mg/dL Pre-diabetic blood glucose 2 hours post-prandial
More than 200 mg/dL Diabetic blood glucose 2 hours post-prandial
1 mukhang 7 below 5.7% Below 5.7% Normal HbA1C
5.7 to 6.4% Pre-diabetic HbA1C
Above 6.5% Diabetic HbA1C
Reference Definition Term Boards Review Reference Definition
Clark's rule, Young's rule, and Fried's rule (until 2
years old) These are formula for estimating child dosages based on adult doses
2.2 lbs This is the equivalent of one pound in kilograms
Adult dose x weight in lbs. / 150 This is the formula for Clark's rule
Adult dose x age in years / age in years + 12 This is the formula for Young's rule
Adult dose x age in months / 150 This is the formula for Fried's rule
(Desired dose / stock) x quantity = amount This is the accurate calculation of drug dosage
0.7 to 6.8 mg/24 hours Normal levels of VMA Avoid coffee, chocolate, tea, bananas, vanilla, and aspirin before VMA test
Myoglobin - within 2 to 4 hours
Troponin (I) and CKMB - within 3 to 4 hours
Creatine phosphokinase - within 4 to 6 hours Less than 0.6 ng/mL (greater than 1.5 ng/mL indicates
LDH - within 6 to 12 hours MI) Normal serum troponin I
75 to 200 ng/dL Normal T3 levels
4.5 to 11.5 mcg/dL Normal T4 levels
0 to 15 mmHg or 75 to 180 mmH2O Normal opening pressure of CSF
50 to 80 mg/dL Normal CSF glucose levels
20 to 50 mg/dL Normal CSF protein levels
0-8/mm3 (average of 5/mm3) Normal CSF WBC levels
10 to 20 mcg/dL Normal serum acetaminophen levels
10 to 20 mcg/dL Normal serum phenytoin levels
10 to 20 mcg/dL Normal serum theophylline levels
5 to 12 mcg/dL Normal serum carbamazepine (tegretol) levels
5 to 10 mcg/dL Normal serum gentamycin sulfate levels
5 to 8 mg/dL Normal serum therapeutic magnesium sulfate levels
0.6 to 1.2 (to 1.5) mEq/L Normal serum therapeutic lithium levels
300 to 700 umol/L or 50 to 100 mcg/mL Normal serum therapeutic valproic acid levels
Expose affected lung (side-lying opposite direction of
affected lung) Position after thoracentesis
Semi-Fowler's with affected arm abducted and
elevated Position after modified radical mastectomy
Orthopneic position Position for patients with COPD
Right side-lying Position post-liver biopsy
Supine (FOB) Position post-kidney biopsy
Lateral Position post tonsillectomy
Flat/supine Position after oil-based (pantopaque) myelography
Semi-Fowler's Position after water-based (metrizamide) myelography
Lateral Position post UGI endoscopy
Left lateral Position during colonoscopy
Semi-Fowler's Position post-incisional cholecystectomy
Semi-Fowler's Position for patients with MI
High-Fowler's Position for patients with heart failure
Semi-Fowler's Position for patients who had supratentorial craniotomy
Flat Position for patients who had infratentorial craniotomy
Semi-Fowler's Position during gastrostomy
Trendelenburg Position during change of IV tubing or insertion of central access or TPN into subclavian vein
Legs on dependent position Position for patients with arterial insufficiency
Legs on elevated position (higher than the level of the
heart) Position for patients with venous insufficiency
Upright/sitting Position for patients with autonomic hyperreflexia
Flat Position for patients with spinal cord injury
Flat Position for patients post-lumbar laminectomy
Left lateral Position during enema procedures
Lithotomy Position during cystoscopy
Trendelenburg Position during labor with prolapsed umbilical cord
Modified Trendelenburg Position during shock
Dorsal recumbent Position post-abdominal surgery or during female catheterization
Reference Definition Term Boards Review Reference Definition
Reference Definition Term Boards Review Reference Definition
Reference Definition Term Boards Review Reference Definition
Reference Definition Term Boards Review Reference Definition
Reference Definition Term Boards Review Reference Definition
Reference Definition Term Boards Review Reference Definition
You might also like
- NP1 CHN 2018 PDFDocument86 pagesNP1 CHN 2018 PDFJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- LBOBI12 XB1 Group7 Lab-Activity20 Solidum TanDocument13 pagesLBOBI12 XB1 Group7 Lab-Activity20 Solidum TanFernando Martin BarbaNo ratings yet
- Exampro GCSE Biology: B3.2 TransportDocument22 pagesExampro GCSE Biology: B3.2 TransportMeera Para100% (1)
- Labs Finals Case PreDocument4 pagesLabs Finals Case Prereized02No ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument2 pagesAnemiaRed DiggerNo ratings yet
- Examination Done Date Results Normal Values Significance or Relevance To Patient's Condition UrinalysisDocument10 pagesExamination Done Date Results Normal Values Significance or Relevance To Patient's Condition UrinalysisStephanie Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test W/ Normal Values Result Interpretat ION Significance Nursing Responsibility RE MA RKSDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Test W/ Normal Values Result Interpretat ION Significance Nursing Responsibility RE MA RKSjanna mae patriarcaNo ratings yet
- Group F DXDocument2 pagesGroup F DXmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- CBC March 11, 2016 Test Result Normal Values InterpretationDocument3 pagesCBC March 11, 2016 Test Result Normal Values InterpretationBernaline KatadaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostics CVDDocument4 pagesDiagnostics CVDZmiaNo ratings yet
- February 28,2011Document3 pagesFebruary 28,2011Beth PascuaNo ratings yet
- Adult Transfusion GuidelinesDocument18 pagesAdult Transfusion GuidelinesConnor ScanlonNo ratings yet
- Laboratory FindingsDocument51 pagesLaboratory FindingsALYSSA PACHECONo ratings yet
- VI. Laboratory ResultsDocument5 pagesVI. Laboratory ResultsCendaña LorelynNo ratings yet
- Clinical Laboratory Tests RangesDocument31 pagesClinical Laboratory Tests RangesjenvarmatNo ratings yet
- Lab ValuesDocument11 pagesLab ValuesJess MontgomeryNo ratings yet
- Normal RangesDocument1 pageNormal RangesLayalNo ratings yet
- Nurseslabs Lab Values PDFDocument2 pagesNurseslabs Lab Values PDFJan BularioNo ratings yet
- Case Study #3 Renal 1. LabDocument9 pagesCase Study #3 Renal 1. LabLindrit AliuNo ratings yet
- CS - LDPDocument2 pagesCS - LDPNicole ArandingNo ratings yet
- Reference ValuesDocument18 pagesReference Valueslucidnox21No ratings yet
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) : Anemia Infection InflammationDocument4 pagesComplete Blood Count (CBC) : Anemia Infection Inflammationbobovovo bobovovoNo ratings yet
- La Salle University: Name of Laboratory/ Diagnostic Test Result Normal Values Interpretation/ Analysis CBCDocument2 pagesLa Salle University: Name of Laboratory/ Diagnostic Test Result Normal Values Interpretation/ Analysis CBCKristine NacuaNo ratings yet
- Test Patient Value Normal Range Result Interpretation Cortisol LevelDocument2 pagesTest Patient Value Normal Range Result Interpretation Cortisol LevelKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNo ratings yet
- Section of Hematology Test Indication Normal Value Result InterpretationDocument4 pagesSection of Hematology Test Indication Normal Value Result Interpretationnerissa_villanueva3523No ratings yet
- Hemolytic Disease of The NewbornDocument47 pagesHemolytic Disease of The NewbornJanine CabreraNo ratings yet
- LabsDocument3 pagesLabsKate Leysa MamonNo ratings yet
- Nurseslabs Lab ValuesDocument2 pagesNurseslabs Lab ValuesJiro ManawariNo ratings yet
- Metabolic PanelDocument2 pagesMetabolic PanelRajeshNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Study: Complete Blood CountDocument5 pagesLaboratory Study: Complete Blood CountNicole Angeli ManuelNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Results & InterpretationDocument11 pagesLaboratory Results & InterpretationLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory TestDocument3 pagesLaboratory TestKim TangoNo ratings yet
- LAB & DIAGNOSTIC TEST (TAHBSO) - Garcia, Jimlord A.Document7 pagesLAB & DIAGNOSTIC TEST (TAHBSO) - Garcia, Jimlord A.Jimlord GarciaNo ratings yet
- XL AdaDocument2 pagesXL AdaDinesh SreedharanNo ratings yet
- References: Treatment, Page 227-229Document6 pagesReferences: Treatment, Page 227-229Nur AzzahanaNo ratings yet
- Only Only: Labs As Indicated Result Normal Labs As Indicated Result NormalDocument13 pagesOnly Only: Labs As Indicated Result Normal Labs As Indicated Result NormalStacey Struck MyersNo ratings yet
- DiagnosticDocument2 pagesDiagnosticakroma092No ratings yet
- Vi. Laboratory Examinations Findings and InterpretationDocument14 pagesVi. Laboratory Examinations Findings and InterpretationStephanie Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Nonmalignant Hematologic DisordersDocument97 pagesManagement of Patients With Nonmalignant Hematologic DisordersJulia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- WBC Differential Count Clinical Chemistry Section: Hematology Result Reduce RBC Production Reduce RBC ProductionDocument10 pagesWBC Differential Count Clinical Chemistry Section: Hematology Result Reduce RBC Production Reduce RBC ProductionknicknucksNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4. Laboratory StudiesDocument6 pagesLesson 4. Laboratory StudiesJhendave TromansNo ratings yet
- Https:Jetmapp - orbundsis.com:Einstein-freshair:Videos::102793DigitalDownload LabValues NurseInTheMaking 2pagesDocument5 pagesHttps:Jetmapp - orbundsis.com:Einstein-freshair:Videos::102793DigitalDownload LabValues NurseInTheMaking 2pagesamazonian005100% (1)
- Corse in The WardDocument8 pagesCorse in The WardMichelle FactoNo ratings yet
- 37.0 Low 90.5 High: Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal NormalDocument2 pages37.0 Low 90.5 High: Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal NormalLinsae TroyNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresDocument6 pagesDiagnostic and Laboratory Proceduresmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Hemogram: RBC:: Normocytic Normochromic Cells Comments: No Hemoparasites Seen. Platelets:: Adequate On The SmearDocument8 pagesHemogram: RBC:: Normocytic Normochromic Cells Comments: No Hemoparasites Seen. Platelets:: Adequate On The SmearMadhu SUDANAN.A.S.BNo ratings yet
- My Important DocumentsDocument12 pagesMy Important DocumentsNivein's BiG WolrdNo ratings yet
- Invest and Medication 1Document9 pagesInvest and Medication 1RajaNo ratings yet
- Print Notes Analysis of The Urine and Other Body FluidsDocument11 pagesPrint Notes Analysis of The Urine and Other Body FluidsVenice Natasha B. GalgalaNo ratings yet
- Reference ValuesDocument3 pagesReference ValuesShaira MukaramNo ratings yet
- 63 Must Know Lab Values Cheat Sheet - NCLEX (Caribbean Nurses of Puerto Rico and Latin America) PDFDocument4 pages63 Must Know Lab Values Cheat Sheet - NCLEX (Caribbean Nurses of Puerto Rico and Latin America) PDFChristineBiankii100% (1)
- Lab ProceduresDocument7 pagesLab Procedureslaurie.charlynjaneNo ratings yet
- Labs To Know For NCLEX ReviewDocument4 pagesLabs To Know For NCLEX ReviewKatherineNo ratings yet
- Lab and Diagnostic Test (Liver Cancer) 1Document3 pagesLab and Diagnostic Test (Liver Cancer) 1Ericka VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Signs and Symptoms Reason For Admission: Elective Repeat CSDocument4 pagesAssessment of Signs and Symptoms Reason For Admission: Elective Repeat CSSistine Rose LabajoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostics and Laboratory ProceduresDocument2 pagesDiagnostics and Laboratory Procedureskevnique11No ratings yet
- Diagnostic and LaboratoryDocument2 pagesDiagnostic and LaboratoryMva AgueroNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood CountDocument1 pageComplete Blood CountRona PieNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts For An NCLEX-RN Cram SheetDocument3 pagesKey Concepts For An NCLEX-RN Cram Sheetema100% (2)
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Asthma Vs COPD PDFDocument10 pagesAsthma Vs COPD PDFJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Where The Dream and The Dreamer Become ONEDocument5 pagesWhere The Dream and The Dreamer Become ONEJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Olivarez CollegeDocument2 pagesOlivarez CollegeJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Expanded Program of ImmunizationDocument9 pagesExpanded Program of ImmunizationJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Apatan, John Carlo S. RNDocument143 pagesApatan, John Carlo S. RNJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Lilly Wiggill Copy of Disorders Packet PDFDocument9 pagesLilly Wiggill Copy of Disorders Packet PDFJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Img 20230409 0001Document1 pageImg 20230409 0001JOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- SIH C: Prepared By: John Carlo S. Apatan SNDocument8 pagesSIH C: Prepared By: John Carlo S. Apatan SNJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- PB2 NP2Document26 pagesPB2 NP2JOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- COPD Chronic Bronchitis EmphysemaDocument3 pagesCOPD Chronic Bronchitis EmphysemaJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever Human: ImmunodeficiencyDocument9 pagesTyphoid Fever Human: ImmunodeficiencyJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesDischarge PlanJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus NCPDocument6 pagesDiabetes Mellitus NCPJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Radio Phenomenal Script BroadcastingDocument4 pagesRadio Phenomenal Script BroadcastingJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Apatan, John Carlo SenaderoDocument1 pageApatan, John Carlo SenaderoJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Smoking EffectsDocument1 pageSmoking EffectsJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The FootDocument1 pageAnatomy of The FootJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- 259Document1 page259JOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 21 ConvertDocument6 pagesPDF Document 21 ConvertJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- JOHN CARLO APATAN - Mental Health Status AssessmentDocument5 pagesJOHN CARLO APATAN - Mental Health Status AssessmentJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- John Carlo Apatan - Checklist On Discontinuing An IV InfusionDocument2 pagesJohn Carlo Apatan - Checklist On Discontinuing An IV InfusionJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- APATANDocument27 pagesAPATANJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario Cva Group 1 NCM 116Document24 pagesCase Scenario Cva Group 1 NCM 116JOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- JOHN CARLO APATAN - Checklist On Tracheostomy CareDocument3 pagesJOHN CARLO APATAN - Checklist On Tracheostomy CareJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communicationarm AnimalsDocument8 pagesTherapeutic Communicationarm AnimalsJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Ramipril For CHFDocument13 pagesRamipril For CHFYennyTjuatjaNo ratings yet
- MN - B4 Revision LessonDocument34 pagesMN - B4 Revision Lessonspamzz063No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System: Temple College EMS ProfessionsDocument39 pagesMusculoskeletal System: Temple College EMS ProfessionsSinga Manja MengaumNo ratings yet
- Science 6: Let'S Work Together!Document26 pagesScience 6: Let'S Work Together!Xivaughn SebastianNo ratings yet
- BLOOD - REVIEWERDocument6 pagesBLOOD - REVIEWERVanya YeleniaNo ratings yet
- SATYAM Projects 2016-17Document2 pagesSATYAM Projects 2016-17rushi.baplNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science Chapter05 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument7 pagesGrade 9 Science Chapter05 The Fundamental Unit of Lifequreshiroshaan673No ratings yet
- Introduction To Psychology (2022)Document642 pagesIntroduction To Psychology (2022)hongnhung.tgdd2018No ratings yet
- Perio 3Document6 pagesPerio 3Bea YmsnNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document209 pagesBook 1Camilo Arturo Suarez Ballesteros100% (1)
- Chapter 21 - Blood Vessels and CirculationDocument13 pagesChapter 21 - Blood Vessels and CirculationSameer AkhtarNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System ReviewerDocument9 pagesThe Integumentary System ReviewerleyluuuuuhNo ratings yet
- Print NeuroDocument18 pagesPrint Neurokai jaeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 2 Lab Manual 1616118382Document107 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 2 Lab Manual 1616118382Chu NamNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology June 2002 P1 Specimen PaperDocument13 pagesCSEC Biology June 2002 P1 Specimen PaperJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- Hematology: Shukur Wasman Smail PHD Student in ImmunologyDocument12 pagesHematology: Shukur Wasman Smail PHD Student in ImmunologyShukr Wesman BlbasNo ratings yet
- Chronic Venous Congestion of Lung, Liver and SpleenDocument24 pagesChronic Venous Congestion of Lung, Liver and SpleenSanjana YadwadNo ratings yet
- 2009 HAYES - FRYLING Psychological Events and Constructs - An Alliance With SmithDocument9 pages2009 HAYES - FRYLING Psychological Events and Constructs - An Alliance With SmithFelix NogueiraNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Semester SystemchemistryDocument3 pagesSyllabus Semester Systemchemistrylearning2earninngNo ratings yet
- Thematic Module 1: Introduction To General Anatomy. Anatomy of BonesDocument10 pagesThematic Module 1: Introduction To General Anatomy. Anatomy of BonesAnimesh DasNo ratings yet
- MS NeurosurgeryDocument60 pagesMS NeurosurgeryAdeel Rauf100% (1)
- المستندDocument7 pagesالمستندمحمود محمدNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ecology: September 2019Document10 pagesIntroduction To Ecology: September 2019Ela Mae SayodNo ratings yet
- Abdomen and Pelvis Aimc AcademiaDocument10 pagesAbdomen and Pelvis Aimc AcademiaDoctor MS 1320No ratings yet
- Amylase Enzyme ThesisDocument6 pagesAmylase Enzyme Thesischristinajohnsonanchorage100% (2)
- Cell, Basic Structure of All Living Creatures: Life Science, Human BiologyDocument11 pagesCell, Basic Structure of All Living Creatures: Life Science, Human BiologyAshleigh Jenson WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- School: San Agustin Elementary School Grade Level: Six Teacher: Jonalvin A. Ke Learning Area: Science Date: SEPTEMBER 5, 2018 (WEDNESDAY)Document3 pagesSchool: San Agustin Elementary School Grade Level: Six Teacher: Jonalvin A. Ke Learning Area: Science Date: SEPTEMBER 5, 2018 (WEDNESDAY)Jonalvin KENo ratings yet
- Ikan BotokDocument16 pagesIkan BotokMUHAMMAD NUR MARDIANTONo ratings yet