Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anti-Viral Agents
Anti-Viral Agents
Uploaded by
Lily0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesAnti-viral drugs target viruses by exploiting differences between viral and host cell structures and functions. Acyclovir is a modified nucleoside that acts as a chain terminator during viral DNA replication, and has a high barrier to resistance due to requiring viral enzymes to activate it. Anti-influenza drugs like Tamiflu and Relenza mimic sialic acid to bind and inhibit the viral neuraminidase enzyme, while adamantanes block the M2 proton channel; resistance can emerge from single mutations. Effective anti-virals have characteristics like low side effects, broad activity, and targeting essential viral genes or proteins.
Original Description:
Original Title
Anti-viral agents
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAnti-viral drugs target viruses by exploiting differences between viral and host cell structures and functions. Acyclovir is a modified nucleoside that acts as a chain terminator during viral DNA replication, and has a high barrier to resistance due to requiring viral enzymes to activate it. Anti-influenza drugs like Tamiflu and Relenza mimic sialic acid to bind and inhibit the viral neuraminidase enzyme, while adamantanes block the M2 proton channel; resistance can emerge from single mutations. Effective anti-virals have characteristics like low side effects, broad activity, and targeting essential viral genes or proteins.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesAnti-Viral Agents
Anti-Viral Agents
Uploaded by
LilyAnti-viral drugs target viruses by exploiting differences between viral and host cell structures and functions. Acyclovir is a modified nucleoside that acts as a chain terminator during viral DNA replication, and has a high barrier to resistance due to requiring viral enzymes to activate it. Anti-influenza drugs like Tamiflu and Relenza mimic sialic acid to bind and inhibit the viral neuraminidase enzyme, while adamantanes block the M2 proton channel; resistance can emerge from single mutations. Effective anti-virals have characteristics like low side effects, broad activity, and targeting essential viral genes or proteins.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
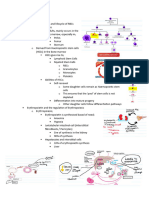
Anti-viral agents
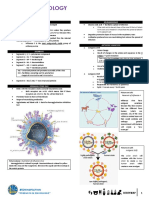
Virus
o Obligate intracellular parasite
o Virus replicates using host-cell machinery
o
Vaccines (Prophylactic) Anti-viral drugs
Live or inactive Difficult to develop
Given by governments/WHO Target group has varying
severities
Herd immunity or defined target
group
Targets for anti-viral drugs
o Substrate analogues
Competitive inhibitor
Rational drug design
When structure is known in depth
o Examples
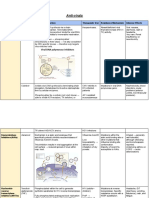
Acyclovir
Modified nucleoside -- Similar shape to Guanosine
o Chain terminator
Backs 3’ OH group
o Higher affinity for viral DNA
Given in unphosphorylated form
o Viral Thymidine Kinase phosphorylates
Resistance is rare
o Maps to the Thymidine Kinase
Mutation in Thymidine Kinase is rare because it
reduces fitness
Therefore HIGH BARRIER to mutation
Influenza
o The features of a good antiviral against influenza
Easy to administer
Low side effects
Effective against a range of influenza types
Targets unique and essential gene or function of virus
o Examples in antivirals;
Relenza and Tamiflu
Both mimic Sialic acid, therefore bind to Neuraminidase and prevent
virus entry and exit
o Have a higher affinity to Neuraminidase than Sialic acid
o Virus becomes ‘stuck’
Relenza
o Given as spray
Tamiflu
o Tablet
o Trials
Metanalysis by Cochrane
Shortens illness
4% of cases causes Nausea
Retrospective analysis (based on real life outcome)
Risk of death is halved if started within 4
hours of symptoms
Adamantanes
Cyclic amine
Discovery
o By-product of petroleum refinement
o By testing random chemicals
Acts on the M2 cell surface protein
o Amantane sits in the channel and blocks it
Therefore virus locked in endosome, cannot enter
cell
o Allows protons to get into the core of the virus and acidify it
There is resistance
o Single point mutation in M2
o Little cost to fitness
o Therefore drug becomes useless
o Examples of resistant strains
Most H3N2
Many H5N1
Swine flu PH1N1
Baloxavir
Acts on RNA polymerase
Patient gets better around 1 day sooner
o Kills virus in the nose and throat
Resistance
o Single point mutation in PAI38I
o Common in children
HIV
Combination therapy used
Slim chance that one genome acquires resistance to all
o Although
HIV is lifelong therefore long time for resistance to
occur
You might also like
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookFrom EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Assignment 2 MaterialsDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Materialspoornima patil100% (1)
- 3) DNA Replication-GenesDocument6 pages3) DNA Replication-GenesAlbertoNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument6 pagesAntiviral DrugsLori MoscaliucNo ratings yet
- Properties: Myxo-TypeDocument4 pagesProperties: Myxo-Typeحسين محمد مطرود كاظمNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 Introto VIRODocument3 pagesLesson 14 Introto VIROIsabella CeaNo ratings yet
- Influenza FixDocument19 pagesInfluenza FixZela yanti SahirNo ratings yet
- Anti Viral DrugsDocument3 pagesAnti Viral Drugsbilal ahmadNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument24 pagesAntiviral DrugsBurhan Nabi0% (1)
- Antiviral p1Document4 pagesAntiviral p1N Gv FcNo ratings yet
- Antiviral Agents: Dr. Roshna Sh. Aziz Department of Pharmacology School of Medicine University of SulaimaniDocument72 pagesAntiviral Agents: Dr. Roshna Sh. Aziz Department of Pharmacology School of Medicine University of Sulaimaniheta aprianaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Four (Clinical Virology)Document4 pagesLecture - Four (Clinical Virology)IM CTNo ratings yet
- Retroviridae - Equine Infectious AnemiaDocument7 pagesRetroviridae - Equine Infectious AnemiaELIJAH EUMIR CUNANANNo ratings yet
- Antiviral Agents: Viruses Are Obligate Cellular Parasites Composed of Nucleic AcidDocument47 pagesAntiviral Agents: Viruses Are Obligate Cellular Parasites Composed of Nucleic AcidhadeelNo ratings yet
- 5thsem - Abj - Rabies - Study MaterialDocument9 pages5thsem - Abj - Rabies - Study Materialsouvikmaity2024No ratings yet
- Viral Disease Handout 2007Document10 pagesViral Disease Handout 2007anon-19857No ratings yet
- Slide - K-27 - Farmakologi AntivirusDocument36 pagesSlide - K-27 - Farmakologi AntivirusFaisal AlhasNo ratings yet
- Viruses (B) PDFDocument4 pagesViruses (B) PDFLyka MahrNo ratings yet
- Antiviral Agents and Infection ControlDocument94 pagesAntiviral Agents and Infection ControlKimberly GeorgeNo ratings yet
- USMLE Flashcards: Pharmacology - Side by SideDocument178 pagesUSMLE Flashcards: Pharmacology - Side by SideMedSchoolStuff67% (3)
- 104 AntiviralsDocument9 pages104 AntiviralsMuhammad HaseebNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument5 pagesAntiviral DrugsSajid AliNo ratings yet
- 17anti-Viral DrugsDocument5 pages17anti-Viral DrugsbhadraiahNo ratings yet
- Anti ViralsDocument14 pagesAnti ViralsparinitaNo ratings yet
- PALMK-IV - 6 - Obat Antivirus Ganjil 2122Document34 pagesPALMK-IV - 6 - Obat Antivirus Ganjil 2122Oktavia Marintan ManullangNo ratings yet
- AntiviralDocument15 pagesAntiviralIvann EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Pharm78 Antiviral 1Document55 pagesPharm78 Antiviral 1MANORANJAN NAIKNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy - 2Document90 pagesChemotherapy - 2shNo ratings yet
- Fluoroquinolones: QuinolonesDocument7 pagesFluoroquinolones: QuinolonesGhubaya CopNo ratings yet
- Anti Viral Drugs: Dr. Yani Mulyani, M.Si, AptDocument47 pagesAnti Viral Drugs: Dr. Yani Mulyani, M.Si, AptYani MulyaniNo ratings yet
- Part2 OncologyDocument39 pagesPart2 OncologySamah AlshamiNo ratings yet
- 64bf6c9aa2629f0019094132 - ## - Human Health and Diseases Handwritten Notes (Of Lecture 09)Document4 pages64bf6c9aa2629f0019094132 - ## - Human Health and Diseases Handwritten Notes (Of Lecture 09)sourajeetsahoo2610No ratings yet
- Pharma NotesDocument9 pagesPharma NotesMayya FirdousNo ratings yet
- Anti-Viral DrugsDocument53 pagesAnti-Viral DrugsClaudia SunshieNo ratings yet
- The Mechanism of Resistance To Favipiravir in Influenza: SignificanceDocument6 pagesThe Mechanism of Resistance To Favipiravir in Influenza: SignificancedeviNo ratings yet
- DrugstusymicroparaDocument13 pagesDrugstusymicroparaJuliana ViteNo ratings yet
- AVMA Vaccination Recommendations F or CatsDocument2 pagesAVMA Vaccination Recommendations F or CatsHazim Azmi Al-QadryNo ratings yet
- Antiviral HIVDocument60 pagesAntiviral HIVyewollolijfikreNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument12 pagesAntiviral DrugsAmelia RumiNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument25 pagesAntiviral Drugss.k. kubraNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: OrthomyxovirusDocument3 pagesMicrobiology: OrthomyxovirusJustin TayabanNo ratings yet
- Antiviral AgentsDocument14 pagesAntiviral AgentsKate MendozaNo ratings yet
- Cns - Infections f2022 Slow Virus and Prion DiseasesDocument14 pagesCns - Infections f2022 Slow Virus and Prion DiseasesMadison MillwoodNo ratings yet
- 4517anti Viral DrugsDocument45 pages4517anti Viral DrugsBOsch VakilNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument44 pagesAntiviral DrugsMohammed WasimNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument44 pagesAntiviral DrugsMohammed WasimNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument12 pagesAntiviral DrugsRisal DidinNo ratings yet
- Antiviral: Prepared By: Jameel Alazraq Submitted To: DR - Ahmad AltarifiDocument41 pagesAntiviral: Prepared By: Jameel Alazraq Submitted To: DR - Ahmad AltarifiAdham MansiNo ratings yet
- Antiviral Drugs: Ana Khusnul Faizah Farmasi FK Uht 2020Document24 pagesAntiviral Drugs: Ana Khusnul Faizah Farmasi FK Uht 2020Muhammad Iqbal DarmansyahNo ratings yet
- Antiviral and Antifungal Drugs: "An Ounce of Prevention Worth Pound of Cure"Document21 pagesAntiviral and Antifungal Drugs: "An Ounce of Prevention Worth Pound of Cure"Jayendiran JaiNo ratings yet
- Tratament ARV NouDocument237 pagesTratament ARV NouMirelaNo ratings yet
- Depart. of Farmacology, Medical Faculty, Moslem University: WisudawanDocument12 pagesDepart. of Farmacology, Medical Faculty, Moslem University: Wisudawansuyudi kimikoNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument14 pagesAntiviral DrugsSunil100% (4)
- Virology ReviewDocument21 pagesVirology ReviewfrabziNo ratings yet
- Corona VirusesDocument42 pagesCorona VirusesstudymedicNo ratings yet
- 5 Antiviral1Document34 pages5 Antiviral1Amr KhayyalNo ratings yet
- Anti Viral and Antiretroviral Drugs: Presented byDocument36 pagesAnti Viral and Antiretroviral Drugs: Presented byshree devNo ratings yet
- Biology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseFrom EverandBiology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Immunology: A Case-Based Collection with MCQs, Volume 2From EverandPediatric Immunology: A Case-Based Collection with MCQs, Volume 2No ratings yet
- Planned Births, Unplanned Persons Class NotesDocument11 pagesPlanned Births, Unplanned Persons Class NotesLilyNo ratings yet
- Connelly 2008 Fatal Misconception - Chapter 6Document22 pagesConnelly 2008 Fatal Misconception - Chapter 6LilyNo ratings yet
- Financing Health Care Week 1 NotesDocument4 pagesFinancing Health Care Week 1 NotesLilyNo ratings yet
- Red Blood CellsDocument5 pagesRed Blood CellsLilyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Complement SystemDocument9 pagesLecture Complement SystemLilyNo ratings yet
- V1 ELISA TestsDocument1 pageV1 ELISA TestsLilyNo ratings yet
- Room Checksums: 01F-Phong Khach&Bep Heating Coil Peak CLG Space Peak Cooling Coil Peak TemperaturesDocument6 pagesRoom Checksums: 01F-Phong Khach&Bep Heating Coil Peak CLG Space Peak Cooling Coil Peak TemperaturesSieuNhanNo ratings yet
- Body of Research Paper 2Document5 pagesBody of Research Paper 2uxy lolNo ratings yet
- Eportfolio Resume 20190325Document3 pagesEportfolio Resume 20190325api-452776602No ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds and Mixtures: Gen. ScienceDocument31 pagesElements, Compounds and Mixtures: Gen. ScienceMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportsDocument18 pagesLab ReportsLana RaedNo ratings yet
- Notified Vide SRO No. 575 Dated 22 May 2019Document3 pagesNotified Vide SRO No. 575 Dated 22 May 2019Hussain RahibNo ratings yet
- BASKS2Document7 pagesBASKS2NGUYEN EthanNo ratings yet
- TAD 1630 GE: Genset Engine - Gen PacDocument2 pagesTAD 1630 GE: Genset Engine - Gen PacselfyNo ratings yet
- Astm A325Document8 pagesAstm A325Nacer KisyNo ratings yet
- Process Plant Layout - 1Document30 pagesProcess Plant Layout - 1Kahlaoui Taha eladnaneNo ratings yet
- Bgcse Sda Paper 1 2015Document24 pagesBgcse Sda Paper 1 2015anne0% (1)
- SR710 Tunnel Systems ReportDocument138 pagesSR710 Tunnel Systems ReportseriouscallerzonlyNo ratings yet
- Legal and Ethical Aspects OfstDocument4 pagesLegal and Ethical Aspects OfstЕлена ВасиленкоNo ratings yet
- Phacoemulsification: Departemen Ilmu Kesehatan Mata Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas HasanuddinDocument28 pagesPhacoemulsification: Departemen Ilmu Kesehatan Mata Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas HasanuddinHerin NataliaNo ratings yet
- Geography Chapter 7 Land SupplyDocument9 pagesGeography Chapter 7 Land SupplydenrabyNo ratings yet
- 10-12si Brush Holder ReplacementDocument1 page10-12si Brush Holder Replacementrogerc1894No ratings yet
- Wax Pattern: Type 1 (Medium Direct IntraoralDocument11 pagesWax Pattern: Type 1 (Medium Direct IntraoralMustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Jacob Wolfe - Native American Land Use WebquestDocument3 pagesJacob Wolfe - Native American Land Use Webquestapi-550219419No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Stacker - Model No. Mn397: Operating Instructions and Parts ListDocument9 pagesHydraulic Stacker - Model No. Mn397: Operating Instructions and Parts ListAJ MusicNo ratings yet
- Latihan Autocad KIMI-A2 - PlanDocument1 pageLatihan Autocad KIMI-A2 - PlanMuhd HakimieNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Exam 1Document3 pagesDay 1 Exam 1Cheng PasionNo ratings yet
- Indigo Cadet Programme Course PriceDocument5 pagesIndigo Cadet Programme Course PriceSNo ratings yet
- January 2020Document64 pagesJanuary 2020Eric Santiago100% (1)
- Injuries Diseases & Disorders of The Muscular SystemDocument22 pagesInjuries Diseases & Disorders of The Muscular SystemAngeli LozanoNo ratings yet
- Building ServicesDocument108 pagesBuilding ServicesSilvinus Clisson Pragash50% (2)
- Medical Ethics and Professional Practice Yr III and IV - Lecture IIIDocument11 pagesMedical Ethics and Professional Practice Yr III and IV - Lecture IIIMwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet: Hanson Construction AggregatesDocument9 pagesTechnical Data Sheet: Hanson Construction AggregatesShaiful ZamriNo ratings yet
- QM 34 - TanksDocument10 pagesQM 34 - Tanksmohamed elmasryNo ratings yet