Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CP2 Revision Mat
CP2 Revision Mat
Uploaded by
Jaskirat Mann0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views1 page1) The document discusses Newton's laws of motion and concepts related to forces, mass, weight, momentum, and acceleration.
2) Key points include Newton's first law that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted on by a net external force, and his second law that force equals mass times acceleration.
3) Formulas are given linking concepts such as momentum, weight, mass, gravitational field strength, and relationships between forces during collisions or acceleration.
Original Description:
Original Title
CP2-Revision-Mat
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The document discusses Newton's laws of motion and concepts related to forces, mass, weight, momentum, and acceleration.
2) Key points include Newton's first law that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted on by a net external force, and his second law that force equals mass times acceleration.
3) Formulas are given linking concepts such as momentum, weight, mass, gravitational field strength, and relationships between forces during collisions or acceleration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views1 pageCP2 Revision Mat
CP2 Revision Mat
Uploaded by
Jaskirat Mann1) The document discusses Newton's laws of motion and concepts related to forces, mass, weight, momentum, and acceleration.
2) Key points include Newton's first law that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted on by a net external force, and his second law that force equals mass times acceleration.
3) Formulas are given linking concepts such as momentum, weight, mass, gravitational field strength, and relationships between forces during collisions or acceleration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
CP2 Revision Mat Newton’s First Law Mass and Weight cont.
Resultant Forces Newton’sThird
Newton’s SecondLaw Law: Calculate
Momentumtheand
weight of an object on Earth
collisions
What are the two possible outcomes if an
(10N/kg) if the mass is 1000g
object
Higher: has a resultant force of 0 N? What is meant by the term conservation of
Calculating resultant forces: What equation links mass, acceleration and force.
1) forget
Explain
Don’t ………………………………………………………………….
why inthe
a collision
units. between a footballer’s …………………………………………………………………………………..
momentum?
If the forces are in the same direction 2)and
head ………………………………………………………………….
the ball the action-reaction forces are ……………………………………………………………………………………………
you need to …………………………………………….... the same size but the effects are different. Forces on falling bodies:
……………………………………………………………………………………………
If the forces are in opposite ……………………………………………………………………………………………
Higher:
Draw a triangle to help you change the subject.
directions you need to …………………………… 1) Label the forces in each diagram
What is the force labelled Fc in the diagram?
Stopping distances
2) Explain what happens in each diagram
………………………………………………………………………………….
Momentum
Add arrows to the diagram to show the What can be said about the forces needed to Stopping distance =
following forces accelerate
What a lorry
equation linksand a car
mass, by 5m/s2and
momentum ? velocity?
1000N of upthrust ……………………………………………………………………………………………
Don’t forget the units
1000N of weight …………………………………………………………………………………………… Name factors that affect the thinking distance
700N thrust ……………………………………………………………………………………………
300N water resistance A car accelerates at 2m/s2. The resultant force is ……………………………………………………………………………………………
100N air resistance 3000N.
Draw Calculate
a triangle to the
helpmass of the the
you change car. subject ……………………………………………………………………………………………
How can an object moving in a circle have
……………………………………………………………………………………………
different velocities but travel at the same
speed?
Define inertial mass. Name factors that increase braking distance and
……………………………………………………………………………………
A……………………………………………………………………………………………
car has a mass of 1000kg and travels at 4m/s. explain why
………………………………………………………………………………
Calculate the momentum. Diagram 1:
Describe how you could measure the acceleration ……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
of a toy car (Practical Skills) ………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
Mass and Weight
…………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
Calculate the resultant force and state the ……………………………………………………………………………………………
What equation links change in momentum, force Diagram 2:
……………………………………………………………………………………………
direction. What
and equation links weight, mass and
time? …………………………………………………………………………………
gravitational
Newton’s Third field
Lawstrength? ……………………………………………………………………………………
Crash Hazards
………………………………………………………………………………….. Don’t forget the units ………………………………………………………………………………
What is the difference between action reaction
Aforces
2000kg
Diagram 3:
What safety features in cars reduce the large
andcar accelerates
balanced from 10m/s to 25m/s in
forces?
What forces on the boat are balanced? ……………………………………………………………………………………
deceleration in crashes?
10 seconds. What force is needed to produce this
……………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………….. Draw a triangle to help you change the subject. 1)
…………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………
acceleration?
2)
……………………………………………………………………………………
3)
………………………………………………………………………………
Action reaction forces act in ………………………………
directions and are the ……………….. size
You might also like
- Density and Pressure KS5 QuestionsDocument4 pagesDensity and Pressure KS5 QuestionsKaiswan GanNo ratings yet
- CP1 Revision MatDocument3 pagesCP1 Revision MatAryaan I SeekNDstryNo ratings yet
- Density and Pressure KS5 QuestionsDocument4 pagesDensity and Pressure KS5 Questionsprodigypls33% (3)
- Dynamics AssignmentDocument6 pagesDynamics Assignmentsaed cabdiNo ratings yet
- G10 Test ForceDocument4 pagesG10 Test ForceSomali YOS online FadityareNo ratings yet
- Energy Work Power Efficiency Assessed Prep QsDocument5 pagesEnergy Work Power Efficiency Assessed Prep Qsbold bananaNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument3 pagesQuestionsRajani NairNo ratings yet
- Work and Power Worksheet-1452167538Document5 pagesWork and Power Worksheet-1452167538juan jaraNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Examination Trials PhysicsDocument15 pagesForm 2 Examination Trials PhysicsBoaz BravoNo ratings yet
- S.3 Term One Examinations 2023 PhysicsDocument11 pagesS.3 Term One Examinations 2023 PhysicsOwani Jimmy100% (2)
- Yuet Wah College - Form Five Physics - Homework 3 OptionalDocument6 pagesYuet Wah College - Form Five Physics - Homework 3 OptionalWebNo ratings yet
- f2 Newtons Holiday Assigment 1Document3 pagesf2 Newtons Holiday Assigment 1cecilialaventineNo ratings yet
- 2.2 ForcesDocument7 pages2.2 ForcesGeorge TongNo ratings yet
- CLASS 7 - Physics - Foces-TEST PAPER 3Document15 pagesCLASS 7 - Physics - Foces-TEST PAPER 3lokapavani_senthilNo ratings yet
- Momentum 1 QPDocument18 pagesMomentum 1 QPtechnical videosNo ratings yet
- Momentum 23 24Document12 pagesMomentum 23 24Kavishka TrimanneNo ratings yet
- End of Term-PhyDocument5 pagesEnd of Term-PhyDalitso Howard Zulu.No ratings yet
- 2.2 ForcesDocument14 pages2.2 ForcesOshan ChathurangaNo ratings yet
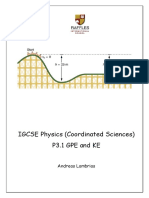
- P3.1 GPE and KE QuestionsDocument8 pagesP3.1 GPE and KE QuestionsAndreas LambriasNo ratings yet
- 16+ PhysicsDocument11 pages16+ PhysicsDarren ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Physics f2t2 QsDocument12 pagesPhysics f2t2 QsBenjamin mwanikiNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 1 Form ThreeDocument12 pagesPhysics Paper 1 Form ThreeelvischerwenyiNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Forces TestDocument17 pagesYear 9 Forces Testaysha kamar halabiNo ratings yet
- P2 Resultant Forces Higher and IntermediateDocument16 pagesP2 Resultant Forces Higher and IntermediatedownendscienceNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document 12Document5 pagesUntitled Document 12mhammouri2006No ratings yet
- Mechanics 3 - Momentum and EnergyDocument13 pagesMechanics 3 - Momentum and Energypoocooloocoo172No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Forces and Motion Exam Pack and MarkschemeDocument86 pagesChapter 10 - Forces and Motion Exam Pack and MarkschemeCraftyZaidNo ratings yet
- Physics F2 QSDocument4 pagesPhysics F2 QSLawrence NyakangoNo ratings yet
- Form 3 PhysicsDocument11 pagesForm 3 PhysicsKisaka G100% (1)
- 06 Forces COMB H HW GridDocument13 pages06 Forces COMB H HW GridRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Answer The Following Question Model (A)Document9 pagesAnswer The Following Question Model (A)Ahmed HassanNo ratings yet
- Contrsurf trc4s1 Prof - AraibachDocument3 pagesContrsurf trc4s1 Prof - Araibachmedhoul13No ratings yet
- Physics F3 QSDocument13 pagesPhysics F3 QSTom O'KebiraNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document 13Document6 pagesUntitled Document 13mhammouri2006No ratings yet
- Lecon Phy 5Document5 pagesLecon Phy 5dressoubellaNo ratings yet
- Kcse Prediction Physics Paper 2 2020Document10 pagesKcse Prediction Physics Paper 2 2020brucewaweru276No ratings yet
- Practice Test - Forces and Motion - Triple Science Year 10Document9 pagesPractice Test - Forces and Motion - Triple Science Year 10Gd Acceler8No ratings yet
- Year 9 EOY Physics WorksheetDocument6 pagesYear 9 EOY Physics Worksheetdiyadipu1No ratings yet
- Physics 1Document7 pagesPhysics 1amisikelvine4No ratings yet
- Young Modulus N ElasticityDocument4 pagesYoung Modulus N ElasticitykamrunnisaNo ratings yet
- Force and Movement 1 WorksheetDocument11 pagesForce and Movement 1 WorksheetNguyen Thi NgaNo ratings yet
- S.2 PhysicsDocument8 pagesS.2 PhysicsNob BoscoNo ratings yet
- 27 Jan 2024 CJMADocument8 pages27 Jan 2024 CJMAtourayadam419No ratings yet
- Rev1. G7 PhyDocument4 pagesRev1. G7 Phymr. mohNo ratings yet
- Noar'S Ark Secondary School Name . Stream: Date: . Form 2 End of Term One Exams Physics Grand TotalDocument8 pagesNoar'S Ark Secondary School Name . Stream: Date: . Form 2 End of Term One Exams Physics Grand Totalhope33061No ratings yet
- Momentum 2 QPDocument11 pagesMomentum 2 QPZayna’s DiariesNo ratings yet
- 04 - Work Done NotesDocument6 pages04 - Work Done NotesUmair LatifNo ratings yet
- S.2 PhyDocument6 pagesS.2 PhyEMMANUEL BIRUNGI100% (1)
- Dec 2021 Lanjet Home Physics PP1 QNDocument12 pagesDec 2021 Lanjet Home Physics PP1 QNonokaanne9No ratings yet
- Work, Energy and PowerDocument44 pagesWork, Energy and Powercaramelrobin17No ratings yet
- S.2 PhysicsDocument4 pagesS.2 Physicsshaficbbaale96No ratings yet
- Mid - Exammination 2020Document9 pagesMid - Exammination 2020Siciid Jaamac DalmarNo ratings yet
- Changes in Energy 1 QPDocument6 pagesChanges in Energy 1 QPMiniNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument5 pagesPHYSICStrady.lewisNo ratings yet
- Pp2 Phy ChampionsDocument13 pagesPp2 Phy Championsrassoah65No ratings yet
- End of Term RevisionDocument127 pagesEnd of Term RevisionEsa FarhanNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Mock Pp1 2023Document13 pagesPhysics Form 4 Mock Pp1 2023brightstarhometuitionNo ratings yet
- S.3 Phy E.O.Y 2023Document6 pagesS.3 Phy E.O.Y 2023DENIS AKOLNo ratings yet
- Viva Physics' Programme 2014: Episode 1Document19 pagesViva Physics' Programme 2014: Episode 1leelee1127No ratings yet
- 22 Photosynthesis 1Document44 pages22 Photosynthesis 1黄心怡No ratings yet
- 1231 Water For Pharmaceutical Purposes Usp35Document22 pages1231 Water For Pharmaceutical Purposes Usp35argbsas100% (2)
- Copernican and DarwinianDocument2 pagesCopernican and Darwinianmastery90210No ratings yet
- Remember The Three-Step Process:: ExampleDocument1 pageRemember The Three-Step Process:: ExampleMăndița BaiasNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 (EARTH SCI)Document5 pagesLab 1 (EARTH SCI)Alyssa Jhoy Yacapin BracerosNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Electrochemistry - REVISION 2024Document28 pagesUnit 1 Electrochemistry - REVISION 2024handungeselmaNo ratings yet
- jsc11 01 Que 20220520Document32 pagesjsc11 01 Que 20220520foreverblinks89No ratings yet
- Topic 18 TestDocument10 pagesTopic 18 TestumerNo ratings yet
- Astm B680 PDFDocument2 pagesAstm B680 PDFAdán Vera Go100% (1)
- Cambridge International Examinations: Physics 9702/43 May/June 2017Document12 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Physics 9702/43 May/June 2017Muhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Assignment QuestionsDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer Assignment QuestionsMurali KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Pendulum LabDocument5 pagesPendulum LabdanahansenNo ratings yet
- RAGJR Lecture Notes: Assiduous Review Institute Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument19 pagesRAGJR Lecture Notes: Assiduous Review Institute Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationJoemar LucasNo ratings yet
- ULO2a - Basic Concepts of Crystal StructureDocument14 pagesULO2a - Basic Concepts of Crystal StructureCHARLIE AMOGUIS JRNo ratings yet
- 1 Homogenization PDFDocument9 pages1 Homogenization PDFLê Hoàng Anh TuấnNo ratings yet
- 1967 - EQUILIBRIA BETWEEN BORATE and Poliol PDFDocument9 pages1967 - EQUILIBRIA BETWEEN BORATE and Poliol PDFLaura PerdomoNo ratings yet
- HCL LabDocument15 pagesHCL LabArash BayatNo ratings yet
- The Rock CycleDocument31 pagesThe Rock CycleRoan Eam TanNo ratings yet
- PharmAnal 8Document50 pagesPharmAnal 8Aaron Jhulian SimbitNo ratings yet
- Dmitri Sorokin - Introduction To The Classical Theory of Higher SpinsDocument33 pagesDmitri Sorokin - Introduction To The Classical Theory of Higher SpinsKlim00No ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Introduction of BiochemistryDocument36 pagesChapter 1. Introduction of BiochemistryshintaNo ratings yet
- Modelling Questionnaires-Biomass CombustionDocument72 pagesModelling Questionnaires-Biomass CombustionsebascianNo ratings yet
- SDS Simoniz Flush AwayDocument5 pagesSDS Simoniz Flush AwaySean VicenteNo ratings yet
- 6.1b Cementing TechnologyDocument69 pages6.1b Cementing TechnologySamuel Okezie100% (2)
- Pump Stroke Counters - Digital Mud Pump Counters CROWDDocument5 pagesPump Stroke Counters - Digital Mud Pump Counters CROWDGallego CarlosNo ratings yet
- Infrared Spectroscopy:: I-Coupling Interactions Due To Stretching VibrationsDocument3 pagesInfrared Spectroscopy:: I-Coupling Interactions Due To Stretching VibrationsAbdel Rahman Mohamed100% (2)
- Conceptual Design I Project I: Prepared byDocument27 pagesConceptual Design I Project I: Prepared byAinulDiliansyah100% (2)
- R&D Outline ProjectDocument3 pagesR&D Outline ProjectDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry Answers S1Document16 pagesIb Chemistry Answers S1anya sNo ratings yet