Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Linear Electronics Assignment 1
Linear Electronics Assignment 1
Uploaded by
David AmarteyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Linear Electronics Assignment 1
Linear Electronics Assignment 1
Uploaded by
David AmarteyCopyright:
Available Formats
Linear Electronics: Assignment 1
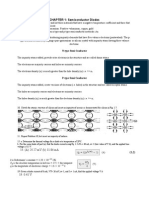
1. Sketch the atomic structure of copper and discuss why it is a good conductor and how its
structure is different from that of germanium, silicon, and gallium arsenide.
a. In your own words, define an intrinsic material, a negative temperature coefficient, and
covalent bonding.
b. Consult your reference library and list three materials that have a negative temperature
coefficient and three that have a positive temperature coefficient.
2. How much energy in joules is required to move a charge of 12 mC through a difference in
potential of 6 V?
a. For part (2), find the energy in electron-volts.
3. If 48 eV of energy is required to move a charge through a potential difference of 3.2 V, determine
the charge involved.
4. Consult your reference library and determine the level of Energy for GaP, ZnS, and GaAsP,
three semiconductor materials of practical value. In addition, determine the written name for each
material.
5. Describe the difference between n-type and p-type semiconductor materials.
a. Describe the difference between donor and acceptor impurities.
6. Describe the difference between majority and minority carriers.
7. Sketch the atomic structure of silicon and insert an impurity of arsenic
8. Consult your reference library and find another explanation of hole versus electron flow.
9. Using both descriptions, describe in your own words the process of hole conduction.
10. Describe in your own words the conditions established by forward- and reverse-bias conditions
on a p–n junction diode and how the resulting current is affected.
11. Describe how you will remember the forward- and reverse-bias states of the p–n junction diode.
That is, how will you remember which potential (positive or negative) is applied to which
terminal?
12. Determine the thermal voltage for a diode at a temperature of 20°C.
13. Given a diode current of 8 mA and n=1, find I s if the applied voltage is 0.5 V and the
temperature is room temperature (25°C).
14. Given a diode current of 6 mA, VT = 26 mV, n = 1, and Is = 1nA, find the applied voltage VD
You might also like
- Problems (Electronics)Document3 pagesProblems (Electronics)AndoryuuBanRaian100% (1)
- ECE1Document9 pagesECE1basiliogarcia36No ratings yet
- 12th SLO Model Paper IIIDocument2 pages12th SLO Model Paper IIIajaz ahmadNo ratings yet
- SHORT ANSWER QUESTION Current Electricity SubjectiveDocument2 pagesSHORT ANSWER QUESTION Current Electricity Subjectivephysicist sharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Review PackageDocument3 pagesPhysics Review Packageapi-310503032No ratings yet
- Semicond Phys Question BankDocument6 pagesSemicond Phys Question Bankvatsalbbk2No ratings yet
- Cbse Paper Leak PDFDocument7 pagesCbse Paper Leak PDFRohan AroraNo ratings yet
- Curr Elec Imp QuestionsDocument2 pagesCurr Elec Imp QuestionsShyamNo ratings yet
- Garhwali SongsDocument4 pagesGarhwali SongsAthul LXNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Galvanic Cells, The Nernst Equation: Chemistry For Engineers LaboratoryDocument8 pagesExperiment 4: Galvanic Cells, The Nernst Equation: Chemistry For Engineers Laboratoryjamila milanoNo ratings yet
- Reduced Syllabus Questions (Physics)Document15 pagesReduced Syllabus Questions (Physics)Saher SaghirNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper-01: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 20Document20 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper-01: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 20ANUP KUMARNo ratings yet
- Sem 3 Question PaperDocument3 pagesSem 3 Question PaperAthul LXNo ratings yet
- 23 ISC Electricity and Electronics 2026Document7 pages23 ISC Electricity and Electronics 2026asNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Frequently Asked Questions in ExaminationsDocument30 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Frequently Asked Questions in ExaminationsArshad KhanNo ratings yet
- QB - FEE - Unit 1, 2 & 3Document8 pagesQB - FEE - Unit 1, 2 & 3shwerghu2003No ratings yet
- Chapterwise Board QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapterwise Board QuestionsMirza SabeelNo ratings yet
- Subjective Questions B2Document2 pagesSubjective Questions B2Vikash PalNo ratings yet
- Important Questions PhysicsDocument12 pagesImportant Questions PhysicsNaziaParveenNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework Class: XII Subject: PhysicsDocument3 pagesHoliday Homework Class: XII Subject: PhysicsAlind GuptaNo ratings yet
- QB FeeDocument12 pagesQB Feeshwerghu2003No ratings yet
- Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument20 pagesFrequently Asked Questionsambujambuj65No ratings yet
- CBSE 12th Physics Sample Paper 2019 Question PaperDocument7 pagesCBSE 12th Physics Sample Paper 2019 Question PapermisostudyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Ncert Practice QuestionsDocument15 pagesChapter-3 Ncert Practice QuestionsRAHIM MDNo ratings yet
- Bee DC Circuit Question Bank-1Document2 pagesBee DC Circuit Question Bank-1Mona PadhyNo ratings yet
- Boards NoteDocument3 pagesBoards NoteShajukk100% (4)
- Session: Important Questions of Xii Year PhysicsDocument6 pagesSession: Important Questions of Xii Year PhysicsAdnanNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Electronics Mock ExamDocument1 pageElectricity and Electronics Mock Examenidtp9No ratings yet
- 2024 03 13-Three Electrode CVDocument10 pages2024 03 13-Three Electrode CVLong BuiNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Class 12 QuestionsDocument6 pagesCurrent Electricity - Class 12 QuestionsBug LordNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentRuprabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Internal ResistanceDocument3 pagesInternal ResistanceClayan MuschetteNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Physics - Ii Regulation 2013Document10 pagesQuestion Bank For Physics - Ii Regulation 2013PRIYA RAJINo ratings yet
- PHYsics Question Bank Chap 3Document7 pagesPHYsics Question Bank Chap 3ChithambaramNo ratings yet
- Xii R Phy Worksheet 29-7-22Document13 pagesXii R Phy Worksheet 29-7-22Rahul GautamNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Worksheet (Rvised ws1)Document2 pagesCurrent Electricity Worksheet (Rvised ws1)3D SAMINo ratings yet
- Miller 1990 Modeling Ferr CapacitorsDocument10 pagesMiller 1990 Modeling Ferr CapacitorsFroy MartinezNo ratings yet
- Supercapacitor Electrodes Based On Graphene MaterialsDocument26 pagesSupercapacitor Electrodes Based On Graphene MaterialselectroternalNo ratings yet
- New Holiday Homework Class XiiDocument5 pagesNew Holiday Homework Class Xiiabhinavshrivastava04No ratings yet
- Important QuestionsDocument26 pagesImportant QuestionsAyush TomarNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument1 pageCurrent ElectricityPratiti samantaNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstractMARIA ELLAH LUBATNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS HOLIDAY HOMEWORK CLASS XII Docx 2023Document3 pagesPHYSICS HOLIDAY HOMEWORK CLASS XII Docx 2023unknownNo ratings yet
- List of Practicals Class XiiDocument3 pagesList of Practicals Class XiiLakshitaNo ratings yet
- Current Ele Pre QDocument2 pagesCurrent Ele Pre QAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Sub: Engg Physics Chapter - I: Modern PhysicsDocument3 pagesSub: Engg Physics Chapter - I: Modern PhysicsReji K DhamanNo ratings yet
- 12th Sept TestDocument4 pages12th Sept TestYogesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Derivation of All ChapterDocument6 pagesDerivation of All Chapterplutouec86% (14)
- Chapter Wise Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter Wise Important QuestionsTechnical Hacks100% (1)
- Important Derivations Type Questions in PhysicsDocument3 pagesImportant Derivations Type Questions in PhysicsJaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- 7-Electrical Properties Practice Problems SolutionsDocument8 pages7-Electrical Properties Practice Problems Solutionsandrescasas850No ratings yet
- Electronic Science SyllabusDocument15 pagesElectronic Science Syllabussudipchatterjee059No ratings yet
- Electricity WorksheetDocument11 pagesElectricity Worksheetsrijankanduri14No ratings yet
- Sample Paper Sample Paper Sample Paper Sample Paper - 2014 2014 2014 2014Document3 pagesSample Paper Sample Paper Sample Paper Sample Paper - 2014 2014 2014 2014manishaNo ratings yet
- Planner For Preparatory Exam.Document3 pagesPlanner For Preparatory Exam.RaonarNo ratings yet
- Total 64Document6 pagesTotal 64Vikram RaoNo ratings yet
- Physics XII 12-10-2017Document49 pagesPhysics XII 12-10-2017Neelkant DubeyNo ratings yet
- XII Physics Important Topic List 2024Document2 pagesXII Physics Important Topic List 2024khaanianasNo ratings yet
- LAS Electronics 10 Q2 Week 1 2 1Document11 pagesLAS Electronics 10 Q2 Week 1 2 1samanthaNo ratings yet
- Solid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonFrom EverandSolid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- MATH 211 Integral Calculus New NewDocument193 pagesMATH 211 Integral Calculus New NewDavid AmarteyNo ratings yet
- Car Tracker Installation BusinessDocument16 pagesCar Tracker Installation BusinessDavid AmarteyNo ratings yet
- Alternating Voltages and CurrentsDocument15 pagesAlternating Voltages and CurrentsDavid AmarteyNo ratings yet
- Intro To Control TheoryDocument15 pagesIntro To Control TheoryDavid AmarteyNo ratings yet