Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHEM E6100 Exercise 2 2021
CHEM E6100 Exercise 2 2021
Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEM E6100 Exercise 2 2021
CHEM E6100 Exercise 2 2021
Copyright:
Available Formats
CHEM-E6100 Fundamentals of Chemical Thermodynamics
Exercise 2, Energy & entropy
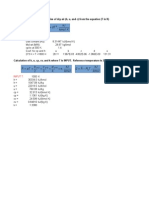
One mole of N2 gas is contained at 273 K and a pressure of 1 atm. The addition of 3000 J of
heat to the gas at constant pressure causes 832 J of work to be done during the expansion.
Calculate:
a. The final state of the gas
b. The values of ΔU and ΔH for the change of state
c. The values of cv and cp for N2
Assume that nitrogen behaves as an ideal gas, and that the change of state is reversible.
(ANSWERS: Final state V2 = 30.61 dm3, T2 = 373 K, U = 2168 J, H = 3000 J,
cv = 21.7 J mol-1 K-1, cp = 30 J mol-1 K-1)
The heat capacity for iron oxide Fe2O3 is given by the Kelley equation
Cp(Fe2O3) = 98.28 + 77.82·10-3·T + -14.85·105·T-2 J mol-1 K-1
What is the value of the heat capacity at 900 K?
How much energy is required when 100 kg of iron oxide Fe2O3 is heated from 500 K to 900 K?
(ANSWERS: 166.48 J mol-1 K-1, 37.4 MJ)
A steel gear weighing 45 kg and at T = 450°C is quenched in 200 kg of oil at 20°C. Heat
capacity of steel is Cp,St = 0.49 kJ kg-1 K-1 and of oil Cp,oil = 2.5 kJ kg-1 K-1. If there are no heat
losses, what are the entropy changes of gear, oil, and both considered together?
(ANSWERS: gear -18.58 kJ/K, oil 30.06 kJ/K, together 11.47 kJ/K)
Some statistical thermodynamics: Calculate the molar configurational entropy of lead. The
isotopic composition in atomic percent is as follows:
Atomic Weight Atomic Percent
204 1.5
206 23.6
207 22.6
208 52.3
To calculate the number of states, use Stirlings approximation: ln(n!) = n * ln(n) and then use
Boltzmann equation.
(ANSWER: 8.97 J/K)
You might also like
- Pipe Solved ProbsetDocument115 pagesPipe Solved ProbsetRemae Garci100% (1)
- PROBLEMS of Energy BallanceDocument35 pagesPROBLEMS of Energy BallanceDiah Wulan AyuningtiasNo ratings yet
- BB101 Engineering Science Chapter 6 Temperature and HeatDocument7 pagesBB101 Engineering Science Chapter 6 Temperature and HeatAh Tiang100% (4)
- 80 81,84 86,87 88,95 97Document5 pages80 81,84 86,87 88,95 97Ivy Joy Ubina100% (1)
- Worksheet 686Document2 pagesWorksheet 686Viswa DexterNo ratings yet
- Property Calculations: Virial Equation of StateDocument9 pagesProperty Calculations: Virial Equation of Statesalman hussainNo ratings yet
- PHYSCHEM4Document2 pagesPHYSCHEM4Nikki ByrneNo ratings yet
- Homework in Physical ChemistryDocument1 pageHomework in Physical ChemistryiyarashanazNo ratings yet
- CHEM 103 TutorialDocument17 pagesCHEM 103 TutorialUjjWal MahAjan0% (1)
- Thermo Tutorial 04 - Prof. SSinhaDocument1 pageThermo Tutorial 04 - Prof. SSinhakajal mishrsNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentSaurabh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29 Heat Energy and Transfer: EXERCISE 134, Page 295Document6 pagesChapter 29 Heat Energy and Transfer: EXERCISE 134, Page 295JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics & Thermochemistry: Chapter Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesThermodynamics & Thermochemistry: Chapter Practice ProblemsAyush Chouhan100% (1)
- Ideal Gas Processes ExampleDocument14 pagesIdeal Gas Processes ExampleMary Joy AlmerenoNo ratings yet
- CY101 Chemistry For Engineers Worksheet-3: P - 5 3 P P F - 1 - 1 - 1Document2 pagesCY101 Chemistry For Engineers Worksheet-3: P - 5 3 P P F - 1 - 1 - 1Hemant MeenaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics ProbDocument7 pagesThermodynamics ProbJan Mae Beja AdolfoNo ratings yet
- Air PropDocument4 pagesAir PropWrya SaeedNo ratings yet
- Ambedkar Nagar: Prime Classes For IIT-JEE/PMT, Ambedkar NagarDocument2 pagesAmbedkar Nagar: Prime Classes For IIT-JEE/PMT, Ambedkar NagarUday Prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- THERMO AssignmentDocument2 pagesTHERMO Assignmentaleena'No ratings yet
- Section-1: Material-Independent Property Relations: AnswersDocument20 pagesSection-1: Material-Independent Property Relations: Answersnkosana2No ratings yet
- 2300 HW 13 SolDocument4 pages2300 HW 13 SolFrederick DugayNo ratings yet
- Unit Nine Homework Solutions, November 9, 2010: V V R T T C S S Const C If V V R T DT C S SDocument5 pagesUnit Nine Homework Solutions, November 9, 2010: V V R T T C S S Const C If V V R T DT C S SAbubakar AdeniNo ratings yet
- ME3140Assignment 2Document2 pagesME3140Assignment 2me20btech11034No ratings yet
- FUELS & THERMOCHEMISTRY Practice Q'sDocument15 pagesFUELS & THERMOCHEMISTRY Practice Q'sIshu PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2-With AnswersDocument11 pagesTutorial 2-With AnswersHayicNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - 14-09-2021Document2 pagesAssignment 1 - 14-09-2021Abhishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 The Second Law - HomeworkDocument2 pagesChapter 03 The Second Law - HomeworkrottymarsellaNo ratings yet
- Che 501 - TutorialsDocument7 pagesChe 501 - TutorialsIgnatius Setiadi PrabowoNo ratings yet
- HW8 SolutionDocument4 pagesHW8 SolutionchrisNo ratings yet
- CH 19Document42 pagesCH 19danvc@hotmail.comNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document23 pagesCH 5Ahmed GadNo ratings yet
- THERMODYNAMICS RevisionDocument2 pagesTHERMODYNAMICS Revisionsuri rayNo ratings yet
- E2SEM1MT2TD06102012Document3 pagesE2SEM1MT2TD06102012anmol6237No ratings yet
- Air PropDocument4 pagesAir Propanup_nairNo ratings yet
- AssignmentII With AnswersDocument7 pagesAssignmentII With AnswersChetan SoamNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemical Engineering, NITKDocument4 pagesDepartment of Chemical Engineering, NITKDechenPemaNo ratings yet
- Problems - 4Document1 pageProblems - 4jamesgNo ratings yet
- 1 PEAB ZC311 Assignment IDocument2 pages1 PEAB ZC311 Assignment IDedy Mustafa0% (1)
- Thermodynamics (Solved Prob)Document22 pagesThermodynamics (Solved Prob)Jubert Perez100% (1)
- Thermochemistry 13thDocument16 pagesThermochemistry 13thRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Exercises: o A. e emDocument2 pagesThermodynamics Exercises: o A. e emAnnisa Sylvia SimbolonNo ratings yet
- Thermo ChemistryDocument15 pagesThermo ChemistrySachin Kumar50% (2)
- Solutions ProblemSet8 Sem22007Document7 pagesSolutions ProblemSet8 Sem22007clearcastingNo ratings yet
- ME REVIEW ThermodynamicsDocument65 pagesME REVIEW ThermodynamicsKhate ÜüNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Set 3Document1 pageTutorial Set 3warithabousaidNo ratings yet
- ME 231 Montazami Whharris 10-2-18 Class Work SolutionDocument15 pagesME 231 Montazami Whharris 10-2-18 Class Work SolutionJoana ArielaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test Class 11Document2 pagesChemistry Test Class 11faisalneyaziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Thermochemistry (Write The Thermochemical Equations)Document6 pagesChapter 9: Thermochemistry (Write The Thermochemical Equations)cikgu_aminNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 6 - EntropyDocument7 pagesTutorial - 6 - EntropyanotherdeobiNo ratings yet
- Adamson UniversityDocument3 pagesAdamson UniversityVanessa Elaine CaoNo ratings yet
- Question One:: Thermodynamic 2 Test (1) Time 1:30Document2 pagesQuestion One:: Thermodynamic 2 Test (1) Time 1:30Nihad S ZainNo ratings yet
- Phys 73 1st Ps 1say14-15Document15 pagesPhys 73 1st Ps 1say14-15Marco ConopioNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap17 P096Document19 pagesThermo 5th Chap17 P096UTA - Std - Elvin ChantreNo ratings yet
- BT Hóa Chapter 9Document2 pagesBT Hóa Chapter 9Giang TrươngNo ratings yet
- Technology Engineering and Environment Division of Engineering Design and Manufacturing Systems Applied Thermodynamics Gas ProcessesDocument2 pagesTechnology Engineering and Environment Division of Engineering Design and Manufacturing Systems Applied Thermodynamics Gas Processespilas_nikolaNo ratings yet
- Class Xi (Ac-03)Document4 pagesClass Xi (Ac-03)Aastha ThakurNo ratings yet
- Unit Four Homework Solutions, September 23. 2010: Mechanical Engineering 370 ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesUnit Four Homework Solutions, September 23. 2010: Mechanical Engineering 370 ThermodynamicsRengganis Putri ParmudyaNo ratings yet
- Patriarca - Lesson 04unit 01Document3 pagesPatriarca - Lesson 04unit 01Erich D. PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)