Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsYear 8 Organisms Retrieval Quiz
Year 8 Organisms Retrieval Quiz
Uploaded by
Sayed ShohelThis document contains questions from two tests about organism processes. It asks about the digestion process, including the enzymes that break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Questions also cover gas exchange in the lungs, including the roles of the diaphragm and ribs during inhalation and exhalation. Scores are provided for each test.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Year 8 Breathing and RespirationDocument4 pagesYear 8 Breathing and RespirationRodaina MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Science Unit 1 7TH JDocument2 pagesScience Unit 1 7TH JHafiz Danish Rehman RanaNo ratings yet
- Class X LN - 6 Life Processes Work Sheet 20-21Document2 pagesClass X LN - 6 Life Processes Work Sheet 20-21Saraswathi GopalNo ratings yet
- Respiration Sample Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesRespiration Sample Multiple Choice QuestionsMaogageoffreyNo ratings yet
- Gulf Indian School: Life ProcessesDocument3 pagesGulf Indian School: Life ProcessesshalomNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Imp Ch6 2Document10 pages10 Science Imp Ch6 2Kamya SyalNo ratings yet
- LP AnsDocument16 pagesLP AnsGayatri MishraNo ratings yet
- Ch-6 Life Processes (QA - Nutrition & Respiration)Document3 pagesCh-6 Life Processes (QA - Nutrition & Respiration)sudhitdcm12No ratings yet
- Grade: VII Worksheet: Key Respiration in OrganismDocument6 pagesGrade: VII Worksheet: Key Respiration in OrganismnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Digestion Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesDigestion Worksheet AnswersMelodina AcainNo ratings yet
- LIFE PROCESSES - Question BankDocument15 pagesLIFE PROCESSES - Question BankMISHKA KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document37 pagesCH 6Aditya YadavNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 4 On Transportation (Circulatory System)Document2 pagesWorksheet 4 On Transportation (Circulatory System)Naruto UzumakiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Solutions Ncert Class 10Document12 pagesChapter 6 Solutions Ncert Class 10senthil2003kasNo ratings yet
- What Are The Grapelike Structures Found in The Lungs?Document7 pagesWhat Are The Grapelike Structures Found in The Lungs?RachelNo ratings yet
- CH.5 LIFE PROCESSES NOTES ANSKEY CompleteDocument25 pagesCH.5 LIFE PROCESSES NOTES ANSKEY Completemananahuja0987No ratings yet
- Class 10 Life Processes WKSHTDocument8 pagesClass 10 Life Processes WKSHTVihaan S BishtNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument11 pagesRespiration in PlantsIMTIYAZ ALINo ratings yet
- Life Process Revision WorksheetDocument6 pagesLife Process Revision WorksheetAdithya VinodNo ratings yet
- Answers To Revision Questions For HomeworkDocument1 pageAnswers To Revision Questions For HomeworkechozvoiceNo ratings yet
- 10bio AssignmentDocument4 pages10bio AssignmentKrishna GovilNo ratings yet
- Science Class 7thDocument10 pagesScience Class 7thAfifashoukatNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document15 pagesLab 5InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Second Summative Test Science 6 2018-2019Document6 pagesSecond Summative Test Science 6 2018-2019LeeMcQ_78No ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument27 pagesLife Processesyogeshjngid41No ratings yet
- Life Processes NotesDocument7 pagesLife Processes NotesTalented ShivaanshNo ratings yet
- 03 Life Processes Chapter Wise Important QuestionsDocument17 pages03 Life Processes Chapter Wise Important Questionsmm8871100% (4)
- cf4e305a9efd1f5697aab8fc67ca426bDocument6 pagescf4e305a9efd1f5697aab8fc67ca426bmrittikaNo ratings yet
- LIFEPROCESSDocument8 pagesLIFEPROCESSKumar AbhishantNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessDocument8 pagesLife ProcessKumar AbhishantNo ratings yet
- Kerala Class 9 Biology - Unit2 (Eng Med) - Simplified Coloured Notes 2024 - Rasheed OdakkalDocument6 pagesKerala Class 9 Biology - Unit2 (Eng Med) - Simplified Coloured Notes 2024 - Rasheed Odakkalnazila alzamNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Biology RevisionDocument13 pagesYear 8 Biology RevisionKHAUSALYA A/P VERAKUMAR100% (1)
- Sean P - Science Review Exam ExerciseDocument4 pagesSean P - Science Review Exam ExerciseSubatomoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science q2 l5Document37 pagesEarth and Life Science q2 l5Adrian Paul Sto DomingoNo ratings yet
- Seth P D Hinduja Sindhi Model Senior Secondary School Kellys, Chennai 600 010Document12 pagesSeth P D Hinduja Sindhi Model Senior Secondary School Kellys, Chennai 600 010budesasaiaw.v.re32.90No ratings yet
- Cbse LP RevisionDocument18 pagesCbse LP RevisionKanak ChhajerNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Science - Life ProcessesDocument14 pagesClass 10 - Science - Life ProcessesNaitik sethiaNo ratings yet
- HSB SummaryDocument19 pagesHSB SummarybessaryanneNo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument265 pagesHuman AnatomynicevenuNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Imp ch6 Mix2Document5 pages10 Science Imp ch6 Mix2Anush ShettigarNo ratings yet
- Exchange Surfaces: Bio NotesDocument6 pagesExchange Surfaces: Bio NotesSingh GurleenNo ratings yet
- Digestive System WorksheetDocument12 pagesDigestive System WorksheetBenjamin Rosenblatt100% (2)
- Dps - Mis, Doha-Qatar: C REVISION ASSIGNMENT (June, 2015-16) Class-7Document6 pagesDps - Mis, Doha-Qatar: C REVISION ASSIGNMENT (June, 2015-16) Class-7Venkatesan RamalingamNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Semester Exam - Part I - Study Guide JANUARY 2007Document6 pagesSkeletal System: Semester Exam - Part I - Study Guide JANUARY 2007api-3698353No ratings yet
- Notices - Human Body Class 6 RevisedDocument10 pagesNotices - Human Body Class 6 RevisedKaustubh GayadhankarNo ratings yet
- X Life Processes Nutrition WSDocument1 pageX Life Processes Nutrition WSStudyNo ratings yet
- Zoology Second Term ExamDocument8 pagesZoology Second Term ExamAmy BalicagNo ratings yet
- Life Processes NotesDocument10 pagesLife Processes NotesKarishmm KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Life Processes (Important Questions)Document26 pagesLife Processes (Important Questions)ASTRO MANAVNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument7 pagesRespiration in Organismschristopher thomasNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument3 pagesDigestivePrishaNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - NCERT Exercises (Prashant Kirad)Document31 pagesLife Processes - NCERT Exercises (Prashant Kirad)kirtiravindradusaneNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument7 pagesLife ProcesseskrithicktcrNo ratings yet
- Histo FinalDocument298 pagesHisto Finalsanullah123khan.13No ratings yet
- Chapter-6-Life ProcessesDocument13 pagesChapter-6-Life Processesapi-400692183No ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Life Process NotesDocument9 pagesClass 10 Science Life Process Notestomarsimran55No ratings yet
- Lifeprocesses CaseDocument3 pagesLifeprocesses Casekrishavsurya259No ratings yet
- Digestion: Dartos MusclesDocument3 pagesDigestion: Dartos MusclesDaniella TabuenaNo ratings yet
- revision wk class 10Document3 pagesrevision wk class 10rajniyd2No ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
Year 8 Organisms Retrieval Quiz
Year 8 Organisms Retrieval Quiz
Uploaded by
Sayed Shohel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThis document contains questions from two tests about organism processes. It asks about the digestion process, including the enzymes that break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Questions also cover gas exchange in the lungs, including the roles of the diaphragm and ribs during inhalation and exhalation. Scores are provided for each test.
Original Description:
hi
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains questions from two tests about organism processes. It asks about the digestion process, including the enzymes that break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Questions also cover gas exchange in the lungs, including the roles of the diaphragm and ribs during inhalation and exhalation. Scores are provided for each test.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesYear 8 Organisms Retrieval Quiz
Year 8 Organisms Retrieval Quiz
Uploaded by
Sayed ShohelThis document contains questions from two tests about organism processes. It asks about the digestion process, including the enzymes that break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Questions also cover gas exchange in the lungs, including the roles of the diaphragm and ribs during inhalation and exhalation. Scores are provided for each test.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
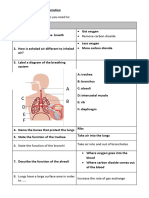
Y8 Organisms Question Test 2 Test 1
Name the 7 food groups.
Which enzyme helps us to digest carbohydrates?
Which enzyme helps us to digest proteins?
Which enzyme helps us to digest fats?
Where is amylase produced?
What is absorbed from the small intestine?
What is absorbed from the large intestine?
Which nutrients do not need to be digested?
Where is most food digested?
What is produced when proteins are digested?
Where does digestion start?
What gives alveoli a large surface area?
State one other adaptation of the lungs for
efficient gas exchange.
What is the scientific name for the windpipe?
Why is it important for the lungs to have a rich
blood supply?
What is ventilation?
Which gas diffuses from the alveoli (lungs) into
the blood?
Which gas diffuses from the blood into the alveoli
(lungs)?
What happens to the diaphragm, ribs and lungs
Ribs = diaphragm = lungs = Ribs = diaphragm = lungs =
during inhalation? (3)
What happens to the diaphragm, ribs and lungs
Ribs = diaphragm = lungs = Ribs = diaphragm = lungs =
during exhalation? (3)
Score /24 /24
Y8 Organisms Question Answer
1. Name the 7 food groups Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, fibre, vitamins, minerals, water
2. Which enzyme helps us to digest carbohydrates? Amylase
3. Which enzyme helps us to digest proteins? Protease
4. Which enzyme helps us to digest fats? Lipase
5. Where is amylase produced? Salivary glands and small intestine
6. What is absorbed from the small intestine? Nutrients
7. What is absorbed from the large intestine? Water
8. Which nutrients do not need to be digested? Minerals, vitamins and water
9. Where is most food digested? Small intestine
10.What is produced when proteins are digested? Amino acids
11.Where does digestion start? The mouth
12.What gives the small intestine a large surface ares? Villi
Lots of alveoli to increase surface area; Rich blood
13.State one adaptation of the lungs for efficient gas exchange.
supply/Extensive capillary network; Thin walls (one cell thick)
14.What is the scientific name for the windpipe? Trachea
15.Why is it important for the lungs to have a rich blood
Maintain steep concentration gradient for efficient diffusion
supply?
16.What is ventilation? Breathing
17.Which gas diffuses from the alveoli (lungs) into the blood? Oxygen
18.Which gas diffuses from the blood into the alveoli (lungs)? Carbon dioxide
19.What happens to the diaphragm, ribs and lungs during
Ribs = expand, diaphragm = contract, lungs = inflate
inhalation?
20.What happens to the diaphragm, ribs and lungs during
Ribs = contract, diaphragm = relaxes, lungs = deflate
exhalation?
You might also like
- Year 8 Breathing and RespirationDocument4 pagesYear 8 Breathing and RespirationRodaina MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Science Unit 1 7TH JDocument2 pagesScience Unit 1 7TH JHafiz Danish Rehman RanaNo ratings yet
- Class X LN - 6 Life Processes Work Sheet 20-21Document2 pagesClass X LN - 6 Life Processes Work Sheet 20-21Saraswathi GopalNo ratings yet
- Respiration Sample Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesRespiration Sample Multiple Choice QuestionsMaogageoffreyNo ratings yet
- Gulf Indian School: Life ProcessesDocument3 pagesGulf Indian School: Life ProcessesshalomNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Imp Ch6 2Document10 pages10 Science Imp Ch6 2Kamya SyalNo ratings yet
- LP AnsDocument16 pagesLP AnsGayatri MishraNo ratings yet
- Ch-6 Life Processes (QA - Nutrition & Respiration)Document3 pagesCh-6 Life Processes (QA - Nutrition & Respiration)sudhitdcm12No ratings yet
- Grade: VII Worksheet: Key Respiration in OrganismDocument6 pagesGrade: VII Worksheet: Key Respiration in OrganismnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Digestion Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesDigestion Worksheet AnswersMelodina AcainNo ratings yet
- LIFE PROCESSES - Question BankDocument15 pagesLIFE PROCESSES - Question BankMISHKA KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document37 pagesCH 6Aditya YadavNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 4 On Transportation (Circulatory System)Document2 pagesWorksheet 4 On Transportation (Circulatory System)Naruto UzumakiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Solutions Ncert Class 10Document12 pagesChapter 6 Solutions Ncert Class 10senthil2003kasNo ratings yet
- What Are The Grapelike Structures Found in The Lungs?Document7 pagesWhat Are The Grapelike Structures Found in The Lungs?RachelNo ratings yet
- CH.5 LIFE PROCESSES NOTES ANSKEY CompleteDocument25 pagesCH.5 LIFE PROCESSES NOTES ANSKEY Completemananahuja0987No ratings yet
- Class 10 Life Processes WKSHTDocument8 pagesClass 10 Life Processes WKSHTVihaan S BishtNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument11 pagesRespiration in PlantsIMTIYAZ ALINo ratings yet
- Life Process Revision WorksheetDocument6 pagesLife Process Revision WorksheetAdithya VinodNo ratings yet
- Answers To Revision Questions For HomeworkDocument1 pageAnswers To Revision Questions For HomeworkechozvoiceNo ratings yet
- 10bio AssignmentDocument4 pages10bio AssignmentKrishna GovilNo ratings yet
- Science Class 7thDocument10 pagesScience Class 7thAfifashoukatNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document15 pagesLab 5InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Second Summative Test Science 6 2018-2019Document6 pagesSecond Summative Test Science 6 2018-2019LeeMcQ_78No ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument27 pagesLife Processesyogeshjngid41No ratings yet
- Life Processes NotesDocument7 pagesLife Processes NotesTalented ShivaanshNo ratings yet
- 03 Life Processes Chapter Wise Important QuestionsDocument17 pages03 Life Processes Chapter Wise Important Questionsmm8871100% (4)
- cf4e305a9efd1f5697aab8fc67ca426bDocument6 pagescf4e305a9efd1f5697aab8fc67ca426bmrittikaNo ratings yet
- LIFEPROCESSDocument8 pagesLIFEPROCESSKumar AbhishantNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessDocument8 pagesLife ProcessKumar AbhishantNo ratings yet
- Kerala Class 9 Biology - Unit2 (Eng Med) - Simplified Coloured Notes 2024 - Rasheed OdakkalDocument6 pagesKerala Class 9 Biology - Unit2 (Eng Med) - Simplified Coloured Notes 2024 - Rasheed Odakkalnazila alzamNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Biology RevisionDocument13 pagesYear 8 Biology RevisionKHAUSALYA A/P VERAKUMAR100% (1)
- Sean P - Science Review Exam ExerciseDocument4 pagesSean P - Science Review Exam ExerciseSubatomoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science q2 l5Document37 pagesEarth and Life Science q2 l5Adrian Paul Sto DomingoNo ratings yet
- Seth P D Hinduja Sindhi Model Senior Secondary School Kellys, Chennai 600 010Document12 pagesSeth P D Hinduja Sindhi Model Senior Secondary School Kellys, Chennai 600 010budesasaiaw.v.re32.90No ratings yet
- Cbse LP RevisionDocument18 pagesCbse LP RevisionKanak ChhajerNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Science - Life ProcessesDocument14 pagesClass 10 - Science - Life ProcessesNaitik sethiaNo ratings yet
- HSB SummaryDocument19 pagesHSB SummarybessaryanneNo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument265 pagesHuman AnatomynicevenuNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Imp ch6 Mix2Document5 pages10 Science Imp ch6 Mix2Anush ShettigarNo ratings yet
- Exchange Surfaces: Bio NotesDocument6 pagesExchange Surfaces: Bio NotesSingh GurleenNo ratings yet
- Digestive System WorksheetDocument12 pagesDigestive System WorksheetBenjamin Rosenblatt100% (2)
- Dps - Mis, Doha-Qatar: C REVISION ASSIGNMENT (June, 2015-16) Class-7Document6 pagesDps - Mis, Doha-Qatar: C REVISION ASSIGNMENT (June, 2015-16) Class-7Venkatesan RamalingamNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Semester Exam - Part I - Study Guide JANUARY 2007Document6 pagesSkeletal System: Semester Exam - Part I - Study Guide JANUARY 2007api-3698353No ratings yet
- Notices - Human Body Class 6 RevisedDocument10 pagesNotices - Human Body Class 6 RevisedKaustubh GayadhankarNo ratings yet
- X Life Processes Nutrition WSDocument1 pageX Life Processes Nutrition WSStudyNo ratings yet
- Zoology Second Term ExamDocument8 pagesZoology Second Term ExamAmy BalicagNo ratings yet
- Life Processes NotesDocument10 pagesLife Processes NotesKarishmm KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Life Processes (Important Questions)Document26 pagesLife Processes (Important Questions)ASTRO MANAVNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument7 pagesRespiration in Organismschristopher thomasNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument3 pagesDigestivePrishaNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - NCERT Exercises (Prashant Kirad)Document31 pagesLife Processes - NCERT Exercises (Prashant Kirad)kirtiravindradusaneNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument7 pagesLife ProcesseskrithicktcrNo ratings yet
- Histo FinalDocument298 pagesHisto Finalsanullah123khan.13No ratings yet
- Chapter-6-Life ProcessesDocument13 pagesChapter-6-Life Processesapi-400692183No ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Life Process NotesDocument9 pagesClass 10 Science Life Process Notestomarsimran55No ratings yet
- Lifeprocesses CaseDocument3 pagesLifeprocesses Casekrishavsurya259No ratings yet
- Digestion: Dartos MusclesDocument3 pagesDigestion: Dartos MusclesDaniella TabuenaNo ratings yet
- revision wk class 10Document3 pagesrevision wk class 10rajniyd2No ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)