Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geology - UCLA Notes
Geology - UCLA Notes
Uploaded by
Dana HakimiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Grade 10 Plate TectonicsDocument30 pagesGrade 10 Plate TectonicsJhen Bon82% (17)
- 01 Mineral Resources and GeologyDocument25 pages01 Mineral Resources and GeologyAnonymous VoidNo ratings yet
- Plates Tectonics 2Document57 pagesPlates Tectonics 2Mark LourenceNo ratings yet
- Tectonofisik 8Document78 pagesTectonofisik 8Harlen MuntheNo ratings yet
- Rezim TektonikDocument42 pagesRezim TektonikSari Fitria RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Presentation #1 Structure of The EarthDocument42 pagesPresentation #1 Structure of The EarthNathan McintoshNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsgildeddivaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (Grade 10)Document3 pagesScience Reviewer (Grade 10)Dove Mendelieve100% (7)
- Geog!!Document11 pagesGeog!!diandra.yanuar2017No ratings yet
- Continental and Oceanic CrustDocument38 pagesContinental and Oceanic CrustEvelyn MayorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Tectonic and Structural GeomorphologyDocument32 pagesLecture 5 Tectonic and Structural GeomorphologyJoseph ZotooNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument38 pagesPlate TectonicsKhanett DagohoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10 - Notes Local Local LocalDocument7 pagesChapter - 10 - Notes Local Local LocalBryan YasgilNo ratings yet
- Deformation of The CrustDocument27 pagesDeformation of The CrustxerseiNo ratings yet
- Theory of Global Plate TectonicsDocument11 pagesTheory of Global Plate TectonicsHannylet OcateNo ratings yet
- NAT ReviewerDocument4 pagesNAT ReviewerAllen Aquino PradoNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Plate TectonicsDocument74 pagesWeek 3 Plate TectonicsmuhammadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document33 pagesLecture 1Ahmad AshourNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesJohn BenedictNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesvinod pNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument35 pagesPlate Tectonicslightningpj1234No ratings yet
- Tectonics and BasinsDocument43 pagesTectonics and Basinsalbert mwairwaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Layers of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument33 pages2016 Layers of The Earth and Plate TectonicsKen Verona Ferrera100% (2)
- PlatesDocument33 pagesPlatesJhana MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics and The Ocean FloorDocument34 pagesChapter 2: Plate Tectonics and The Ocean FloorCarol GirottoNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument36 pagesPlate TectonicsliopNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Mr.K.Naveen KumarDocument6 pagesPlate Tectonics: Mr.K.Naveen Kumar7praveenNo ratings yet
- G10 Q1 L7 Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument18 pagesG10 Q1 L7 Plate Tectonic TheoryMark GalangNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3ADocument5 pagesPlate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3AMark Rienzo HingpisNo ratings yet
- Continental DriftDocument5 pagesContinental DriftEllan MainitNo ratings yet
- Bahan UAS BatuanDocument49 pagesBahan UAS BatuanbarangdenNo ratings yet
- ISNS 4359 Earthquakes and Volcanoes (Aka Shake and Bake) : Lecture 4: Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesISNS 4359 Earthquakes and Volcanoes (Aka Shake and Bake) : Lecture 4: Plate TectonicsAgeologistNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument43 pagesPlatesMerrie Anne BagsicNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Plate TectonicsDocument9 pagesClass 8 Plate TectonicsDarkerNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - TectonicsDocument21 pagesLab 1 - TectonicsPatrick TiernanNo ratings yet
- 5 - Plate Tectonics Part 2 - Ch03 04Document37 pages5 - Plate Tectonics Part 2 - Ch03 04Jordan RixNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsnoelNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Plate TectonicsDocument76 pagesTopic 1 Plate TectonicsYogiNo ratings yet
- Plate TechtonicsDocument37 pagesPlate Techtonicsapi-294510653No ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesMagistrado DrewNo ratings yet
- Plates Volcanoes EarthquakesDocument45 pagesPlates Volcanoes EarthquakesAbigail HernandezNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic BasicsDocument12 pagesPlate Tectonic BasicsnayemNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument38 pagesPlate TectonicsAlfVera RectoNo ratings yet
- TectonicsDocument32 pagesTectonicsFlavyus06No ratings yet
- Plates SSE Grade 11Document26 pagesPlates SSE Grade 11Noor AlDiniNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics2Document90 pagesPlate Tectonics2MariahNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument1 pagePlate TectonicsSai SubuNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics NotesDocument20 pagesPlate Tectonics NotesRaj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sea Floor Spreading and Plate TectonicsDocument26 pagesSea Floor Spreading and Plate Tectonicsbking bbNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics: Mountains at Plate BoundariesDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Plate Tectonics: Mountains at Plate BoundariesMohamedNo ratings yet
- GG101 Lecture11Document31 pagesGG101 Lecture11Jhon Manuel PorcinculaNo ratings yet
- 11mss Earth Chapter09Document86 pages11mss Earth Chapter09igyanchandaniNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument36 pagesPlate TectonicsJoHan Xyth RizaldoNo ratings yet
- m1 Plate BoundariesDocument30 pagesm1 Plate BoundariesAnn Formalejo Paredes LptNo ratings yet
- Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesPlate Boundariesgods5173No ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument52 pagesPlate TectonicsTrembletonNo ratings yet
- Earth Internal HeatDocument66 pagesEarth Internal HeatKRISTINE GRACE PANOPIONo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument98 pagesPlate TectonicsNaynuzka JaniceNo ratings yet
- Why Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
Geology - UCLA Notes
Geology - UCLA Notes
Uploaded by
Dana HakimiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geology - UCLA Notes
Geology - UCLA Notes
Uploaded by
Dana HakimiCopyright:
Available Formats
Title: Plate Tectonics and Earth’s Dynamic Crust
Introduction:
• Plate tectonics is the fundamental theory that explains the movement and
interactions of Earth’s lithospheric plates.
Key Concepts:
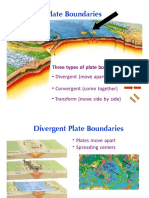
1. Plate Boundaries:
• Divergent Boundaries: Plates move away from each other, creating mid-ocean
ridges.
• Convergent Boundaries: Plates collide, leading to subduction zones, mountain
ranges, and earthquakes.
• Transform Boundaries: Plates slide past each other, causing lateral motion and
faulting.
2. Driving Forces:
• Mantle Convection: Heat from Earth’s interior drives the circulation of material in
the mantle, in uencing plate movement.
• Ridge Push and Slab Pull: Mechanisms that contribute to plate motion at
divergent and convergent boundaries.
3. Plate Interactions:
• Oceanic-Continental Convergence: Forms volcanic arcs and deep-sea trenches.
• Continental-Continental Convergence: Leads to the uplift of mountain ranges.
• Oceanic-Oceanic Convergence: Results in island arcs and deep-sea trenches.
4. Earthquakes and Volcanoes:
• Earthquakes often occur along plate boundaries due to stress accumulation and
release.
• Volcanic activity is associated with subduction zones and divergent boundaries.
5. Evidence for Plate Tectonics:
• Fossil and paleoclimatic evidence.
• Matching coastlines and geologic features.
• Sea oor spreading and magnetic striping.
Conclusion:
• Plate tectonics revolutionized our understanding
fl
fl
You might also like
- Grade 10 Plate TectonicsDocument30 pagesGrade 10 Plate TectonicsJhen Bon82% (17)
- 01 Mineral Resources and GeologyDocument25 pages01 Mineral Resources and GeologyAnonymous VoidNo ratings yet
- Plates Tectonics 2Document57 pagesPlates Tectonics 2Mark LourenceNo ratings yet
- Tectonofisik 8Document78 pagesTectonofisik 8Harlen MuntheNo ratings yet
- Rezim TektonikDocument42 pagesRezim TektonikSari Fitria RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Presentation #1 Structure of The EarthDocument42 pagesPresentation #1 Structure of The EarthNathan McintoshNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsgildeddivaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (Grade 10)Document3 pagesScience Reviewer (Grade 10)Dove Mendelieve100% (7)
- Geog!!Document11 pagesGeog!!diandra.yanuar2017No ratings yet
- Continental and Oceanic CrustDocument38 pagesContinental and Oceanic CrustEvelyn MayorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Tectonic and Structural GeomorphologyDocument32 pagesLecture 5 Tectonic and Structural GeomorphologyJoseph ZotooNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument38 pagesPlate TectonicsKhanett DagohoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10 - Notes Local Local LocalDocument7 pagesChapter - 10 - Notes Local Local LocalBryan YasgilNo ratings yet
- Deformation of The CrustDocument27 pagesDeformation of The CrustxerseiNo ratings yet
- Theory of Global Plate TectonicsDocument11 pagesTheory of Global Plate TectonicsHannylet OcateNo ratings yet
- NAT ReviewerDocument4 pagesNAT ReviewerAllen Aquino PradoNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Plate TectonicsDocument74 pagesWeek 3 Plate TectonicsmuhammadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document33 pagesLecture 1Ahmad AshourNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesJohn BenedictNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesvinod pNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument35 pagesPlate Tectonicslightningpj1234No ratings yet
- Tectonics and BasinsDocument43 pagesTectonics and Basinsalbert mwairwaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Layers of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument33 pages2016 Layers of The Earth and Plate TectonicsKen Verona Ferrera100% (2)
- PlatesDocument33 pagesPlatesJhana MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics and The Ocean FloorDocument34 pagesChapter 2: Plate Tectonics and The Ocean FloorCarol GirottoNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument36 pagesPlate TectonicsliopNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Mr.K.Naveen KumarDocument6 pagesPlate Tectonics: Mr.K.Naveen Kumar7praveenNo ratings yet
- G10 Q1 L7 Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument18 pagesG10 Q1 L7 Plate Tectonic TheoryMark GalangNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3ADocument5 pagesPlate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3AMark Rienzo HingpisNo ratings yet
- Continental DriftDocument5 pagesContinental DriftEllan MainitNo ratings yet
- Bahan UAS BatuanDocument49 pagesBahan UAS BatuanbarangdenNo ratings yet
- ISNS 4359 Earthquakes and Volcanoes (Aka Shake and Bake) : Lecture 4: Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesISNS 4359 Earthquakes and Volcanoes (Aka Shake and Bake) : Lecture 4: Plate TectonicsAgeologistNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument43 pagesPlatesMerrie Anne BagsicNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Plate TectonicsDocument9 pagesClass 8 Plate TectonicsDarkerNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - TectonicsDocument21 pagesLab 1 - TectonicsPatrick TiernanNo ratings yet
- 5 - Plate Tectonics Part 2 - Ch03 04Document37 pages5 - Plate Tectonics Part 2 - Ch03 04Jordan RixNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsnoelNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Plate TectonicsDocument76 pagesTopic 1 Plate TectonicsYogiNo ratings yet
- Plate TechtonicsDocument37 pagesPlate Techtonicsapi-294510653No ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesMagistrado DrewNo ratings yet
- Plates Volcanoes EarthquakesDocument45 pagesPlates Volcanoes EarthquakesAbigail HernandezNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic BasicsDocument12 pagesPlate Tectonic BasicsnayemNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument38 pagesPlate TectonicsAlfVera RectoNo ratings yet
- TectonicsDocument32 pagesTectonicsFlavyus06No ratings yet
- Plates SSE Grade 11Document26 pagesPlates SSE Grade 11Noor AlDiniNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics2Document90 pagesPlate Tectonics2MariahNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument1 pagePlate TectonicsSai SubuNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics NotesDocument20 pagesPlate Tectonics NotesRaj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sea Floor Spreading and Plate TectonicsDocument26 pagesSea Floor Spreading and Plate Tectonicsbking bbNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics: Mountains at Plate BoundariesDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Plate Tectonics: Mountains at Plate BoundariesMohamedNo ratings yet
- GG101 Lecture11Document31 pagesGG101 Lecture11Jhon Manuel PorcinculaNo ratings yet
- 11mss Earth Chapter09Document86 pages11mss Earth Chapter09igyanchandaniNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument36 pagesPlate TectonicsJoHan Xyth RizaldoNo ratings yet
- m1 Plate BoundariesDocument30 pagesm1 Plate BoundariesAnn Formalejo Paredes LptNo ratings yet
- Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesPlate Boundariesgods5173No ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument52 pagesPlate TectonicsTrembletonNo ratings yet
- Earth Internal HeatDocument66 pagesEarth Internal HeatKRISTINE GRACE PANOPIONo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument98 pagesPlate TectonicsNaynuzka JaniceNo ratings yet
- Why Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet