Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Notes
Bio Notes
Uploaded by
YashiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Notes
Bio Notes
Uploaded by
YashiCopyright:
Available Formats
Sexual reproduction in plants
The plants that have flowers are called flowering plants.
Most of the plants reproduce by the sexual method- there’s an involvement of male and
female gametes
Flowers are the reproducing part of the plant.
The function of a flower is to make male and female gametes and to ensure that
fertilization will take place to make seeds from growing news plants.
It performs reproduction by producing seeds for the plant.
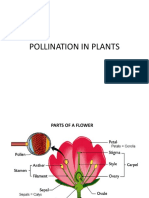
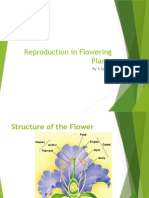
Parts of a flower- Calyx-Sepals , Corolla-Petals , androecium-Stamen(Filament,
Anther) ,gynoecium –Pistil(Stigma ,Style ,Ovary)
The green leaf like parts in the outermost circle of the flower-Sepals
All the sepals are taken as calyx
They cover and protect the inner parts of the flower in the bud stage
Corolla- made of brightly colored petals(lie inside the sepals at the bud stage)
Main function of petals is to attract insects for pollination and to protect reproductive
parts of the flower(i.e at the center)
Androecium-male reproductive part, made up of stamens :- anther(contains pollen grains
in the form of yellowish powdery substance) and filament(long ,slender)
Pollen grains- male gametes
Gynoecium- female reproductive, innermost whorl, consists of- pistil/carpels
Pistil-made up of enlarged OVARY[(it contains OVULES:-contains female gametes that
develop into seeds after fertilization+develops into seeds+covering of the ovule alters and
changes into seed coat )OVARY:-swollen end of style+enlarges and converts into fruit],
long slender STYLE (tube that leads from stigma to ovary and helps in the passage of
pollen from the tip of sigma from ovary), broad STIGMA (sticky in nature basically to
attract pollens dispersed in air)
POLLINATION-transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a stamen to a stigma of a
pistil is known as pollination,
SELF-POLLINATION-transfer of pollen grains from the stamens produced in a
flower to the stigma of the pistil of the same flower or another flower blooming on the
same plant
CROSS-POLLINATION-transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower on a
plant to the stigma of a flower of a different plant of the same species.
POLLINATION BY INSECTS-
When an insect sits on a flower attracted by the bright petals, fragrance and nectar, the
pollen grains stick on its body.
When the same insect sits on another flower, the pollen grains gets brushed off on the
stigma of that flower.
This helps in the transfer of pollen grains from one flower to another and insects help in
carrying out pollination.
CHARACTERISTICS OF INSECT-POLLINATED FLOWERS-
Large, bright ,colorful petals + scented flowers(fragrance) to attract insects
Presence of nectar in these flowers which is food for insects hence causing insects to sit
on flowers to suck nectar.
Production of sticky pollen grains which can easily stick to the bodies of insects
POLLINATION BY WIND-
Blowing wind carries pollen grain from one flower to another causing pollination.
CHARACTERISTICS OF WIND-POLLINATED FLOWERS-
Are not large, not scented, not nectar producing as they do not have to attract insects
Have anthers and stigmas hanging/protruding outside the flower
Light-weight pollen grains
Winged pollen
High no. of pollen grains produced to increase the accuracy of cross-pollination/increase
the probability of fertilization.
POLLINATION BY WATER-
Plants water-pollinated(vallisneria + pond weeds)are usually aquatic but not all aquatic
plants are water-pollinated example Lotus(insect pollinated)
The pollen floats in water and when they come in contact with the stigma of the female
flower(cross-pollination is usually conducted in mono-sexual plants) then fertilization
takes place.
Mostly water-pollinated are monosexual
CHARACTERISTICS OF WATER-POLLINATED FLOWERS-
In water-pollinated plants, male and female flowers are borne on separate plants,
Pollens are produced in large quantities.
Flowers are lighter and smaller so that they can easily float on the surface of water
Pollens are not sticky but are water-resistant
ARTIFICIAL POLLINATION-
Usually carried out to improve the variety of a particular plant.
Crops of DESIRED CHARACTERISTICS called PARENT CROPS are selected
Gynoecium of the flower is kept covered so prevent natural pollination.
Once the stigma of one crop plant is mature, selected pollen grains from the anther are
placed on these stigmas.
The seeds produced in this manner processes characteristics of both the crop parents and
this new variety is called as hybrid.
the hybrid plant produced is of superior quality.
FERTILISATION-
After pollen reaches the stigma of another flower of the same species
It starts to grow by forming a pollen tube
It travels down the style and reaches the ovary
In the ovary, pollen tubes release male gametes which fuses with female gametes(present
in ovules ,ovules are present in ovary)
You might also like
- Angiosperms PPT RevisedDocument55 pagesAngiosperms PPT RevisedJohn Philip Neri Besedillas100% (2)
- Palak SinghDocument19 pagesPalak SinghPalak Singh0% (1)
- Plant PropagationDocument25 pagesPlant Propagationaon poatNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction WebquestDocument5 pagesPlant Reproduction WebquestJenny ThomasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 Review QuestionsDocument9 pagesChapter 09 Review QuestionsRhose Anne DelaPaz LanzagaNo ratings yet
- Pollination NotesDocument6 pagesPollination Notesketki kamatNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AngiospermsDocument19 pagesReproduction in Angiospermstapas kunduNo ratings yet
- HOW Flowering Plants Reproduce: November 4, 2019Document29 pagesHOW Flowering Plants Reproduce: November 4, 2019Ligaya Orozco Bautista-GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Q2 - W5 Science 5Document48 pagesQ2 - W5 Science 5Mac RamNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument20 pagesReproduction in PlantsAndrea AgustinNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project (Class 12)Document14 pagesBiology Investigatory Project (Class 12)MAX Music78% (23)
- Flower Pollination NoteDocument5 pagesFlower Pollination NotejuliaNo ratings yet
- Biology Project (Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants)Document6 pagesBiology Project (Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants)47. Anas SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System in Plants SS2Document7 pagesReproductive System in Plants SS2Ezeh PrincessNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument7 pagesSexual Reproduction in PlantsAshraf ali palhNo ratings yet
- Pollination Notes Grade: 5 Parts of A FlowersDocument2 pagesPollination Notes Grade: 5 Parts of A FlowersSunil Nagar100% (1)
- GR4 Science Plant ReproductionDocument35 pagesGR4 Science Plant ReproductionG09 Janelle Ivana Rose GoNo ratings yet
- PRINTDocument10 pagesPRINT24 Rashi Anand JangdeNo ratings yet
- Pollination Project 12Document37 pagesPollination Project 12PriyanshuNo ratings yet
- How Do Plants ReproduceDocument29 pagesHow Do Plants ReproduceNikki S VergaraNo ratings yet
- Flower Background InfoDocument5 pagesFlower Background Infoahuddle1No ratings yet
- Pollination in PlantsDocument214 pagesPollination in PlantsAbraham SekyiNo ratings yet
- SEXUAL_REPRODUCTION_IN_PLANTSDocument7 pagesSEXUAL_REPRODUCTION_IN_PLANTSOditor MwaangaNo ratings yet
- SS2 3rd Term BiologyDocument16 pagesSS2 3rd Term BiologyabursooterNo ratings yet
- PollinationDocument15 pagesPollinationShinoy SwathyNo ratings yet
- 3RD Grading ScienceDocument16 pages3RD Grading ScienceJohannah Eleiya CalimagNo ratings yet
- PollinationDocument17 pagesPollinationSoumik MahapatroNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument6 pagesReproduction in PlantsjwonpediaNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument15 pagesAsexual Reproductioneugene_970418755No ratings yet
- (Flower Anatomy) : Kurdistan Regional Government-Iraq College of Education/shaqlawa Biology Department Second StageDocument12 pages(Flower Anatomy) : Kurdistan Regional Government-Iraq College of Education/shaqlawa Biology Department Second StageShalaw LatifNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsDocument22 pagesPlant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsLebohang MakhanyaNo ratings yet
- Science Synt II 4Document6 pagesScience Synt II 4lala0483No ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Plant ReproductionDocument45 pagesChapter 23 Plant ReproductionSara SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of A PlantDocument17 pagesLife Cycle of A Plantmarc louise tipayNo ratings yet
- Good Afternoon: CHAPTER NAME: Self IncompatibilityDocument30 pagesGood Afternoon: CHAPTER NAME: Self IncompatibilitylkokodkodNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology Notes - Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument14 pagesForm 5 Biology Notes - Reproduction in Flowering PlantsCashelle ChallengerNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plants: Life-Cycle of A Flowering PlantDocument5 pagesFlowering Plants: Life-Cycle of A Flowering Plantraunak sarafNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument26 pagesReproduction in PlantsaddaestewartNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document10 pagesChapter 8Lebanan Aprille MarieNo ratings yet
- FlowaringDocument21 pagesFlowaringMohamad HattaNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction 4 1Document4 pagesPlant Reproduction 4 1Belen MartinezNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterDocument7 pagesScience 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterHoneylet Alberto Castro ArilloNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument14 pagesReproduction in PlantsLeona KokeraiNo ratings yet
- Partsoftheflower 160715111306Document13 pagesPartsoftheflower 160715111306Ralph Bryan HidalgoNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument6 pagesReproductionChal WijeNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction: in Plants in HumanDocument215 pagesSexual Reproduction: in Plants in HumanOctaviano SimonNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument36 pagesSexual ReproductionMasrat AmirNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument47 pagesAsexual ReproductionMae RicañaNo ratings yet
- EALSDocument4 pagesEALSemarites ronquilloNo ratings yet
- Flowers Fruit and SeedsDocument3 pagesFlowers Fruit and SeedsJoanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Science How Plants ReproduceDocument41 pagesGrade 5 Science How Plants ReproduceJulie Mae Sajulga JacobeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument40 pagesLecture 4 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsEsther Suan-LancitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Plants From SeedsDocument9 pagesChapter 3 Plants From SeedsHend HamedNo ratings yet
- Parts of A FlowerDocument2 pagesParts of A FlowerIrish cambriNo ratings yet
- The Flower and PollinationDocument4 pagesThe Flower and PollinationMichaelNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System of Flowering, Non-Flowering, and Spore-BearingDocument34 pagesReproductive System of Flowering, Non-Flowering, and Spore-BearingJulie BalogoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Flowering Plants Integrated ScienceDocument20 pagesReproduction Flowering Plants Integrated ScienceSharina GeraldNo ratings yet
- Pollination: Flower Specialization and PollinationDocument2 pagesPollination: Flower Specialization and PollinationyosephineikaaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsrichie2885No ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Plant ReproductionDocument45 pagesChapter 23 Plant ReproductionMárk SerfőzőNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chapter 12 Reproduction in PlantsDocument13 pagesNotes - Chapter 12 Reproduction in PlantsAdnan SathikNo ratings yet
- Reproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)Document10 pagesReproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)richelyn navalesNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument62 pagesPlant ReproductionAdonis BesaNo ratings yet
- Flowering vs. Non-Flowering Plants : Knowing the Difference - Biology 3rd Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandFlowering vs. Non-Flowering Plants : Knowing the Difference - Biology 3rd Grade | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Plant Morphology - BungaDocument39 pagesPlant Morphology - BunganprutNo ratings yet
- Silabus 2Document5 pagesSilabus 2Rentika SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Natural System of ClassificationDocument6 pagesNatural System of ClassificationMuhammad Shahab NaranjiNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Pollination and Fertilization: in Vitro Pollination and FertilizationDocument3 pagesIn Vitro Pollination and Fertilization: in Vitro Pollination and FertilizationkashyapakashNo ratings yet
- Arecaceae Family: HabitDocument17 pagesArecaceae Family: HabitAbdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Reproduction 3 - Flowering and Non-FloweringDocument27 pagesReproduction 3 - Flowering and Non-Floweringrenato.minaNo ratings yet
- Science7 Q2 Mod6 AloneorTogetherLetsMulyiplyfortheBetter V2Document28 pagesScience7 Q2 Mod6 AloneorTogetherLetsMulyiplyfortheBetter V2Romeo Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument13 pagesReproductionHuma NazneyNo ratings yet
- PollinationDocument2 pagesPollinationAriel BarcelonaNo ratings yet
- Science Unit 1 - Food (1. Plant Reproduction)Document3 pagesScience Unit 1 - Food (1. Plant Reproduction)Dhiman DeyNo ratings yet
- Desert SongDocument3 pagesDesert SongDiane HuNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants PDFDocument23 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants PDFRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: SectionsDocument6 pagesI. Objectives: SectionsCherry Pink VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Third Summative TestDocument3 pagesQ2 - Third Summative TestMilagros ReyesNo ratings yet
- Learn MarcottingDocument14 pagesLearn MarcottingJOVELYN Y. ALFORQUENo ratings yet
- Reproductive Ecology of Cleome Gynandra and Cleome Viscosa (Capparaceae)Document15 pagesReproductive Ecology of Cleome Gynandra and Cleome Viscosa (Capparaceae)noahNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of Plants - 5 Stages + Fun Facts - Science4FunDocument8 pagesLife Cycle of Plants - 5 Stages + Fun Facts - Science4FunMasthankhan PatanNo ratings yet
- Grafting PP Oregon ExtDocument73 pagesGrafting PP Oregon ExtzhorvatovicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - MorphologyDocument27 pagesChapter 5 - Morphologyavishank584No ratings yet
- Crsci 1100 Exercise No.5Document6 pagesCrsci 1100 Exercise No.5Vera Nadeshna EseoNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jan 09, 2024Document12 pagesAdobe Scan Jan 09, 2024lthakurr124No ratings yet
- PT3 - Plant Propagation and Nursery PracticesDocument8 pagesPT3 - Plant Propagation and Nursery PracticesMARK LOUIE SUGANOBNo ratings yet
- Purok 5, Brgy. Santa, Tumauini, Isabela: Agricultrural Crops Production NC Ii (336 Hours)Document8 pagesPurok 5, Brgy. Santa, Tumauini, Isabela: Agricultrural Crops Production NC Ii (336 Hours)Merly SalvadorNo ratings yet
- A Study On Floral Morphology of Brinjal Genotypes in Gangetic-Alluvial Zone of West Bengal, IndiaDocument9 pagesA Study On Floral Morphology of Brinjal Genotypes in Gangetic-Alluvial Zone of West Bengal, IndiaArindam DasNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument18 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsashketc3No ratings yet
- A CTIVITIESDocument5 pagesA CTIVITIESjellyB RafaelNo ratings yet