Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Moles
Moles
Uploaded by
Muhammad Asghar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageMoles
Moles
Uploaded by
Muhammad AsgharCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Mole Concept and Chemical Calculations by Waqar Ahmad (03349543124)
Relative Atomic Mass
Definition:
The relative atomic mass, Ar, of an element is defined as the average mass of the
isotopes an atom of the element compared with 1 th of the mass of an atom of carbon-
12. 12
Note: * Symbol for the relative atomic mass is Ar and Ar has no unit.
The values of the Ar of atoms of the elements are given in the Periodic Table and is written
on the top of element in the periodic table.
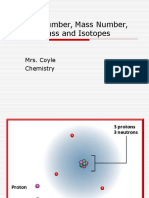
Atomic Number
• It is the number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom. It is also known as the
Proton Number.
Mass Number/ Nucleon Number
• It is the sum of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom.
Relationship between Nucleon number and Relative atomic mass, Ar
• The mass of an atom is due mainly to the total number of protons and neutrons in its
nucleus (Nucleon number). Thus, we would expect the Ar of the element to be the same
as its nucleon number. This is true for elements which have no isotopes.
• For most elements, the nucleon number and the Ar are not the same due to the
existence of isotopes.
• The nucleon number is always a whole number (since we can’t have fractions of protons
or neutrons in the nucleus), but the Ar values may not be whole numbers. If the Ar is not
a whole number and is different from nucleon number, we can conclude that the element
has naturally occurring isotopes.
Relative Molecular Mass
• Many elements and compounds exist as molecules.
• The mass of a molecule is measured in terms of its relative molecular mass, Mr
Definition: The relative molecular mass, Mr, of a substance is defined as the average
mass of a molecule of the substance compared with 1 th of the mass of
Carbon -12 atom 12
• Relative molecular mass is often abbreviated to molecular mass.
• Symbol is Mr and Mr has no units.
• It is calculated as the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in the formula.
You might also like
- 1C Atomic StructureDocument24 pages1C Atomic Structurejustme.azma.meNo ratings yet
- Atomic Number and Atomic MassDocument9 pagesAtomic Number and Atomic MassAnonymous DKxeQVEevNo ratings yet
- Comparing Masses of Substances - Set A Power PointDocument14 pagesComparing Masses of Substances - Set A Power PointMuyatwa LiksNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument5 pagesAtomic StructureAyesha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Atomic Mass - NCUKDocument27 pagesAtomic Structure and Atomic Mass - NCUKphonepyaehtut2006No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument20 pagesChemistryrida ikramNo ratings yet
- ISOTOPO BOM 2 C Atomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass and Isotopes-1Document21 pagesISOTOPO BOM 2 C Atomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass and Isotopes-1idalia helenaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass and IsotopesDocument21 pagesAtomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass and IsotopesKenny James CuberoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure CRGDocument14 pagesAtomic Structure CRGCharlotte GoodeNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsDocument28 pagesAtoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsCandyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- ElementsDocument6 pagesElementsAbdullah SalmanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Isotopes NotesDocument5 pagesAtomic Structure and Isotopes Notesyanny280906No ratings yet
- Chem ModuleDocument20 pagesChem Modulekeeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Atoms, Atomic Number and IsotopesDocument19 pages2.3 Atoms, Atomic Number and IsotopesReena NasriNo ratings yet
- 01 Atomic Structure and IstopesDocument10 pages01 Atomic Structure and IstopesDiyaNo ratings yet
- Science Notes - 2024-05-08T125417.607Document2 pagesScience Notes - 2024-05-08T125417.607ASHNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document41 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1Rufus TsaiNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument13 pagesChemMj CaraanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Mass and NumberDocument15 pagesAtomic Mass and NumberKalaisan KalaichelvanNo ratings yet
- Elements and MoleculesDocument26 pagesElements and MoleculesTrevor NamalawaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Atomic Mass Atomic Number and Isotopes PDFDocument23 pages1.3 Atomic Mass Atomic Number and Isotopes PDFMARVIN DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules 2Document50 pagesAtoms and Molecules 2Bank Yossy WoluslaweNo ratings yet
- 1.1. A Simple Model of The Atom, Symbols, Relative Atomic Mass, Electronic Charge and Isotopes PDFDocument4 pages1.1. A Simple Model of The Atom, Symbols, Relative Atomic Mass, Electronic Charge and Isotopes PDFUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- 01 Atomic StructureDocument49 pages01 Atomic StructurePranav PrasadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Notes-1Document3 pagesChapter 2 Notes-1ARISHA REHMANNo ratings yet
- Atomic Mass: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument15 pagesAtomic Mass: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchJennie KimNo ratings yet
- Atom, Molecule and StoichiometryDocument97 pagesAtom, Molecule and StoichiometryZareen KidwaiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons & ElectronsDocument2 pagesAtomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons & ElectronsAdam JensenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Periodic TableDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Periodic TableMa. Oliva Diana CastroNo ratings yet
- Science 8 13.3 Atomic Number and Mass NumberDocument28 pagesScience 8 13.3 Atomic Number and Mass NumberAna Pearl ColegadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Atomic Structure: Atoms MoleculesDocument2 pagesChapter 3: Atomic Structure: Atoms Moleculesonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Principles of Chemistry: Atomic StructureDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Principles of Chemistry: Atomic StructureKhin Yadanar KyawNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements and Molecules & Compounds and MixturesDocument32 pagesAtoms, Elements and Molecules & Compounds and MixturesTshanna RobertsNo ratings yet
- Atomic Mass: Wiki Loves Monuments: Photograph A Monument, Help Wikipedia and Win!Document13 pagesAtomic Mass: Wiki Loves Monuments: Photograph A Monument, Help Wikipedia and Win!Jennie KimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Atomic Structure Snr1Document50 pagesChapter 5 Atomic Structure Snr1Abdul HaseebNo ratings yet
- Chemie2023 Erdem Gerel UchralDocument21 pagesChemie2023 Erdem Gerel UchralUchral ErkhembayarNo ratings yet
- Structure of Substance - Lesson - 2Document10 pagesStructure of Substance - Lesson - 2samsonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Strand Notes 3Document1 pageChemistry Strand Notes 3Mazuba ChibbelaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FactsheetsDocument415 pagesChemistry FactsheetsAmbrose Aaron DavidNo ratings yet
- 2.atoms, Elements & CompoundDocument6 pages2.atoms, Elements & CompoundhenryNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Atomic Structure and IsotopesDocument43 pages1.1 Atomic Structure and IsotopesDAVID ESCALANTE GILNo ratings yet
- Atoms & ElementsDocument14 pagesAtoms & ElementsMy Cambridge IGCSENo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Notes - LectureDocument19 pagesAtomic Structure Notes - LecturealexandremoutonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document27 pagesChapter 1Imperial PlayzNo ratings yet
- Atoms ch1 Sec 2Document30 pagesAtoms ch1 Sec 2api-294483847100% (1)
- SSC Mts Ex: Studymaterialfor GenralawarenessDocument8 pagesSSC Mts Ex: Studymaterialfor GenralawarenessAmrit SinghNo ratings yet
- Module As Level ChemistryDocument407 pagesModule As Level ChemistryBank Yossy WoluslaweNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atoms and IonsDocument34 pagesStructure of Atoms and IonsChristineNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: The Structure of The Atom Mass Spectrometry Electronic Structure Ionisation EnergiesDocument22 pagesAtomic Structure: The Structure of The Atom Mass Spectrometry Electronic Structure Ionisation EnergiesVijithaNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Atomic StructureDocument13 pagesCh3 Atomic StructurehahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Notes-2Document3 pagesChapter 2 Notes-2ARISHA REHMANNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and StoichometryDocument28 pagesAtoms, Molecules and StoichometryMuhammad KalimNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Atom - PortalDocument50 pagesThe Structure of The Atom - Portaldhruvini100% (1)
- ATOMIC STRUCTUReeDocument20 pagesATOMIC STRUCTUReeCahayaniFanihuNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument19 pagesAtomic Structuregoh benNo ratings yet
- File 2657Document6 pagesFile 2657Alexandra LupuNo ratings yet
- In All Its GloryDocument10 pagesIn All Its GloryKeren HZNo ratings yet
- Cat 1Document2 pagesCat 1Roshan RajNo ratings yet
- 2 C Atomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass and IsotopesDocument21 pages2 C Atomic Number, Mass Number, Atomic Mass and IsotopesKhusnul KhuluqNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1From EverandConcepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2021-03-24 at 12.06.39 PMDocument12 pagesScreenshot 2021-03-24 at 12.06.39 PMMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Nearpod - Year 11 - Production 3Document1 pageNearpod - Year 11 - Production 3Muhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions 2Document5 pagesPractice Questions 2Muhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2021-01-29 at 7.19.04 PMDocument9 pagesScreenshot 2021-01-29 at 7.19.04 PMMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Moles 5Document1 pageMoles 5Muhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- LoopsDocument6 pagesLoopsMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Higher Exam SolutionsDocument15 pagesHigher Exam SolutionsMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Moles 6Document1 pageMoles 6Muhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Moles 3Document1 pageMoles 3Muhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Ajwa Superposition of Sound Waves - Extended ReponseDocument1 pageAjwa Superposition of Sound Waves - Extended ReponseMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions-2Document5 pagesPractice Questions-2Muhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument1 pageBiologyMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Moles 2Document1 pageMoles 2Muhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistryMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- ImageDocument1 pageImageMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Topical Past Papers Biology P4 C1 - C7Document1 pageIGCSE Topical Past Papers Biology P4 C1 - C7Muhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- YouTubeDocument1 pageYouTubeMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument1 pageUntitled NotebookMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Topical Past Papers Biology P4 C1 - C7Document1 pageIGCSE Topical Past Papers Biology P4 C1 - C7Muhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistryMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument1 pageBiologyMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Chem 2Document1 pageChem 2Muhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-05-02 at 8.02.19 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-05-02 at 8.02.19 PMMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument1 pageUntitled NotebookMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument5 pagesUntitled NotebookMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet