Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sulfonamides, Cotrimoxazole and Quinolones
Sulfonamides, Cotrimoxazole and Quinolones
Uploaded by
NtettOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sulfonamides, Cotrimoxazole and Quinolones
Sulfonamides, Cotrimoxazole and Quinolones
Uploaded by
NtettCopyright:
Available Formats
Sulfonamides, Cotrimoxazole and Quinolones
Thursday, June 1, 2023 20:23
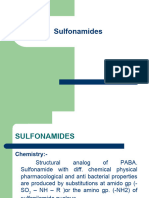
Sulfonamides
Sulfonamides are primarily bacteriostatic against many gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Mechanism of action
• being structural analogues of PABA, inhibit bacterial folate synthase, so that FA is not formed
• competitively inhibit the union of PABA with pteridine residue to form dihydropteroic acid which
conjugates with glutamic acid to produce dihydrofolic acid.
Uses
• Sulfametoxazole + trimethoprim used for many bacterial infections, P. jiroveci and nocardiosis
• Sulfonamides + Pyrimethamine used for malaria and toxoplasmosis
• Ocular sulfacetamide sod. (10–30% alternative in trachoma/inclusion conjunctivitis
• Topical silver sulfadiazine used for preventing infectionon burn surfaces
Resistance
Prominent among these are gonococci, pneumococci, S. aureus, meningococci, E. coli, Shigella, Strep. pyogenes
The resistant mutants either:
(a) produce increased amounts of PABA, or
(b) their folate synthase enzyme has low affinity for sulfonamides, or
(c) adopt an alternative pathway in folate metabolism.
because of rapid emergence of bacterial resistance, they are currently used only in combination with
trimethoprim (as cotrimoxazole) or with pyrimethamine (for malaria)
Pharmakokinetics
Absorbtion : rapidly and nearly completely absorbed from g.i.t
Distribution : widely distributed in the body, cross placenta freely
Metabolism : primarily in liver, acetylated derivative less soluble in acidic urine, may cause crystalluria
Excretion : mainly by the kidney through glomerular filtration
Sulfamethoxazole
slower oral absorption and urinary excretion, preferred compound for combining with trimethoprim because
the t½ of both is similar
Sulfadoxine, Sulfamethopyrazine
High plasma protein binding and slow renal excretion (t½ 5–9days), can caused serious cutaneous reactions
Silver sulfadiazine
Used topically as 1% cream against a large number of bacteria and fungi, even those resistant to other
sulfonamides, considered to be one of the most effective drugs for preventing infection of burnt surfaces
and chronic ulcers
Adverse Effect
• Hypersensitivity, mostly in the form of rashes, urticaria and drug fever, serious: SJS
• Nausea, vomiting and epigastric pain.
• Crystalluria, can be minimized by taking plenty of fluids and by alkalinizing the urine
Cotrimoxazole
The fixed dose combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole is called cotrimoxazole
both sulfonamide and trimethoprim are bacteriostatic, but the combination becomes cidal against many
organisms.
Cotrimoxazole should not be given during pregnancy, dose should be reduced in moderately severe renal
impairment, The elderly are also at greater risk of bone marrow toxicity
Dose : 80 mg T + 400 mg tab S: 2 BD for 2 days; 40 mg + 200 mg per 5 ml susp
New Section 1 Page 1
New Section 1 Page 2
You might also like
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookFrom EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Psychopharmacology 2 AntidepressantsDocument7 pagesPsychopharmacology 2 AntidepressantsBea Samonte100% (2)
- Bfad Circular NoDocument3 pagesBfad Circular NoKoreen Torio Mangalao-Baculi100% (1)
- Pregabalin Drug by IvanDocument3 pagesPregabalin Drug by IvanRoseben Somido100% (1)
- SulfonamideDocument2 pagesSulfonamideAbo DowiaNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides: Miss Preeti Verma Assistant Professor Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Rama University, Kanpur, U.PDocument17 pagesSulfonamides: Miss Preeti Verma Assistant Professor Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Rama University, Kanpur, U.PYash SinghNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamidesandcotrimoxazole 130910115011 Phpapp02Document20 pagesSulfonamidesandcotrimoxazole 130910115011 Phpapp02SanketNandaniNo ratings yet
- Folic Acid Synthesis InhibitorsDocument30 pagesFolic Acid Synthesis InhibitorsPROF DR SHAHMURADNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of SulfonamidesDocument37 pagesPharmacology of SulfonamidesDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHM100% (1)
- SulfonamidesDocument40 pagesSulfonamidesMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Antifolate Drugs 17970Document19 pagesAntifolate Drugs 17970TES SENNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides and Sulfonamide Combinations : Continued On Next PageDocument4 pagesSulfonamides and Sulfonamide Combinations : Continued On Next PageIfan ZulfantriNo ratings yet
- Paparella: Volume I: Basic Sciences and Related Disciplines Section 6: Pharmacology Chapter 28: Antibiotics Leonard P. RybakDocument16 pagesPaparella: Volume I: Basic Sciences and Related Disciplines Section 6: Pharmacology Chapter 28: Antibiotics Leonard P. RybakDiana Mihaela BadescuNo ratings yet
- Biseptol & IsoniazidDocument61 pagesBiseptol & IsoniazidYeshaa MiraniNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides: Wednesday, 1 October 2014 10 Am - 12 PMDocument9 pagesSulfonamides: Wednesday, 1 October 2014 10 Am - 12 PMecc bafNo ratings yet
- Dr. Raghu Prasada M S: MBBS, MD Assistant Professor Dept. of Pharmacology Ssims & RCDocument23 pagesDr. Raghu Prasada M S: MBBS, MD Assistant Professor Dept. of Pharmacology Ssims & RCRaman KumarNo ratings yet
- Sulphonamides KSRpaiDocument31 pagesSulphonamides KSRpaiwolverine12309No ratings yet
- Folic Acid Synthesis InhibitorsDocument24 pagesFolic Acid Synthesis Inhibitorsalihyderabro166No ratings yet
- DRUG SUMMARY TABLE: CHAPTER 33 Principles of Antimicrobial and Antineoplastic PharmacologyDocument3 pagesDRUG SUMMARY TABLE: CHAPTER 33 Principles of Antimicrobial and Antineoplastic PharmacologyNiki NourNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of SulphonamidesDocument21 pagesPharmacology of SulphonamidesGANESH KUMAR JELLA100% (1)
- Sulfonamides Mechanism of Action & Antimicrobial ActivityDocument9 pagesSulfonamides Mechanism of Action & Antimicrobial ActivityMuhammad L RusydiNo ratings yet
- SulphonamidesDocument13 pagesSulphonamidesSantosh Bhandari100% (1)
- Antimicrobials 1Document3 pagesAntimicrobials 1anupama menonNo ratings yet
- SULFONAMIDES Dr. NeenuDocument37 pagesSULFONAMIDES Dr. Neenuneenu csNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 Sulfonamides, Trimethoprim and FlouroquinolonesDocument24 pagesLecture 15 Sulfonamides, Trimethoprim and FlouroquinoloneshamzabhayatNo ratings yet
- Quinolones, Folic Acid Antagonist, and Urinary Tract AntisepticsDocument29 pagesQuinolones, Folic Acid Antagonist, and Urinary Tract AntisepticsAliImadAlKhasakiNo ratings yet
- SULFONAMIDESDocument25 pagesSULFONAMIDESanaya khan StudentNo ratings yet
- Anti-Folates and QuinolonesDocument19 pagesAnti-Folates and QuinolonestaongachikunyuNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides: BY Jagir R. Patel Assistant ProfessorDocument23 pagesSulfonamides: BY Jagir R. Patel Assistant ProfessorJagirNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides: Tejal Khade Assistant Professor KGRDCP & RiDocument42 pagesSulfonamides: Tejal Khade Assistant Professor KGRDCP & RiAkshada bhangreNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides Trimethoprim and QuinolonesDocument25 pagesSulfonamides Trimethoprim and Quinolonespopat78No ratings yet
- Antifolate Drugs: Sulfonamides: Pharmacology IvDocument22 pagesAntifolate Drugs: Sulfonamides: Pharmacology IvShashidharan MenonNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Agents-Sulfonamides 032305Document139 pagesAntibacterial Agents-Sulfonamides 032305Odiit StephenNo ratings yet
- Theme 22. Synthetic Chemotherapeutic Drugs: General Structure of Streptocides Paraaminobenzoic AcidDocument12 pagesTheme 22. Synthetic Chemotherapeutic Drugs: General Structure of Streptocides Paraaminobenzoic Acidfatima ALArrayedhNo ratings yet
- Sulphonamides & TrimethoprimDocument32 pagesSulphonamides & TrimethoprimShiva KarthikNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument3 pagesGeneric NamepachichoyNo ratings yet
- Sulphonamides 180312174623Document27 pagesSulphonamides 180312174623madeha goharNo ratings yet
- SulfonamidesDocument3 pagesSulfonamidesMahdi DiabNo ratings yet
- Sulphonamides: DR - Amal Belaid 3Document34 pagesSulphonamides: DR - Amal Belaid 3Mustafa RihanNo ratings yet
- Drugs I N Der Mato Lo GyDocument85 pagesDrugs I N Der Mato Lo GySilviuNo ratings yet
- Nursing NotesDocument6 pagesNursing NotesLinguumNo ratings yet
- Sulphonamides & Co - Trimoxazole BamsDocument46 pagesSulphonamides & Co - Trimoxazole BamsKasturiRangan SrivatsaNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides: BY Jagir R. Patel Anand Pharmacy CollegeDocument27 pagesSulfonamides: BY Jagir R. Patel Anand Pharmacy CollegeJagirNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Dr. Mazhar-Ul-Haq Submitted By: Khadija Salka Arid No.: 18-Arid-4479 Morning - ADocument2 pagesSubmitted To: Dr. Mazhar-Ul-Haq Submitted By: Khadija Salka Arid No.: 18-Arid-4479 Morning - AKhadija SalkaNo ratings yet
- SULFONAMIDES and FluroquinolonesDocument23 pagesSULFONAMIDES and FluroquinolonesRabi ShahNo ratings yet
- StandartDocument14 pagesStandartEder AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyKirtia Mae CapuloNo ratings yet
- Dapsone PIDocument7 pagesDapsone PInsucopyNo ratings yet
- SulfonamidesDocument9 pagesSulfonamidestabletvoda100% (1)
- Tetracyclines and ChloramphenicolDocument19 pagesTetracyclines and ChloramphenicolNikita ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleDocument1 pageTrimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleRenmico Aquino0% (1)
- 8 SulphonamidesDocument33 pages8 SulphonamidesMuhammad Shahid BilalNo ratings yet
- SulfonamidesDocument12 pagesSulfonamidesKoppaka JayakanthNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Bactrim Generic Name: Sulfamethoxazole, Trimethoprim, Co-Trimoxazole Drug ClassificationDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Bactrim Generic Name: Sulfamethoxazole, Trimethoprim, Co-Trimoxazole Drug Classificationianecunar100% (2)
- Anti-Folate DrugsDocument4 pagesAnti-Folate Drugssarguss14100% (2)
- PHARM Yoshimura SulfonamidesAndDHFRInhibitor 2 PDFDocument23 pagesPHARM Yoshimura SulfonamidesAndDHFRInhibitor 2 PDFDhaif dhaifNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycosides and SulfonamidesDocument35 pagesAminoglycosides and SulfonamidesPhoenixNo ratings yet
- Cology PageDocument4 pagesCology PageAbdulhakim ZekeriyaNo ratings yet
- SulfonamidesDocument22 pagesSulfonamidesFaizan Tariq100% (1)
- Al-Bayan University Pharmacy College 3 Stage: Metabolism Inhibitors Antibacterial DrugsDocument8 pagesAl-Bayan University Pharmacy College 3 Stage: Metabolism Inhibitors Antibacterial DrugsAhmed HadeerNo ratings yet
- 8 SulphonamidesDocument33 pages8 SulphonamidesMuhammad Shahid BilalNo ratings yet
- Folic Acid Antag BPTDocument12 pagesFolic Acid Antag BPTfoziiiiiNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Inhibitors (Lecture 5) PDFDocument24 pagesNucleic Acid Inhibitors (Lecture 5) PDFhnanaly77No ratings yet
- Marijuana in The United StatesDocument4 pagesMarijuana in The United StatesParas khuranaNo ratings yet
- 12 - AmitriptylineDocument6 pages12 - Amitriptylinekoko100% (1)
- Bourgoin Biologics MarketDocument29 pagesBourgoin Biologics Marketkohinoordas2007No ratings yet
- TgaDocument33 pagesTgavarun rajNo ratings yet
- Master - Schunk - Carina - 2019 OINDPDocument88 pagesMaster - Schunk - Carina - 2019 OINDPJaya AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Sedative Effect of Citronella (Cymbopogon Nardus (L.) Rendle) Towards Male Mice (Mus Musculus)Document8 pagesSedative Effect of Citronella (Cymbopogon Nardus (L.) Rendle) Towards Male Mice (Mus Musculus)aprizaNo ratings yet
- Data Expired DateDocument8 pagesData Expired DateFARMASI PRIMA HUSADA SUKOREJONo ratings yet
- How To Use KetoconazoleDocument4 pagesHow To Use KetoconazoleTadilakshmikiranNo ratings yet
- Week 8.2Document74 pagesWeek 8.2ginny.mycookiecanNo ratings yet
- 2020 03 19 Wright-Patterson Medical Center Pharmacy FlyerDocument1 page2020 03 19 Wright-Patterson Medical Center Pharmacy FlyerNevin SmithNo ratings yet
- Clinical PharmacokineticsDocument36 pagesClinical PharmacokineticsWalaa YousefNo ratings yet
- Seminar Obgyn Chemotheraphy in GynaecologyDocument38 pagesSeminar Obgyn Chemotheraphy in GynaecologyRoshandiep GillNo ratings yet
- Pharma Pellets Manufacturers in India - SainorDocument2 pagesPharma Pellets Manufacturers in India - Sainorsainor labNo ratings yet
- Patient Database Form, DTPW, PCPDocument7 pagesPatient Database Form, DTPW, PCPClarence100% (1)
- Buku Farmasi Apoteker Di IlmufarmasisDocument6 pagesBuku Farmasi Apoteker Di IlmufarmasisdinitarijayantiNo ratings yet
- CARBOPLATINDocument3 pagesCARBOPLATINErza GenatrikaNo ratings yet
- 4 2a Bcs BasedBWDocument52 pages4 2a Bcs BasedBWJai KumarNo ratings yet
- Attachment E Substance Abuse Encounter Rpting HCPCS and Revenue Codes Chart FY10 287030 7Document10 pagesAttachment E Substance Abuse Encounter Rpting HCPCS and Revenue Codes Chart FY10 287030 7Mia JacksonNo ratings yet
- Basic ManagementsDocument10 pagesBasic ManagementsSARKAR JAVED AKHTARNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 (Clerkship)Document11 pagesAssignment 3 (Clerkship)Ataur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous MelanomaDocument199 pagesCutaneous MelanomahapzanimNo ratings yet
- Antihistamine MedicationsDocument1 pageAntihistamine MedicationsCora GougeNo ratings yet
- Receptors and PharmacodynamicsDocument78 pagesReceptors and PharmacodynamicsMuhammad Bilal Bin Amir100% (1)
- Diltiazem - ProfileDocument14 pagesDiltiazem - Profileumamaheswararao4No ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesLiterature Reviewapi-302507520No ratings yet
- Price List Feb 2022Document10 pagesPrice List Feb 2022My VideosNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Notes DRADocument22 pagesUnit 3 Notes DRAOyshi RaoNo ratings yet