Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dice 2
Dice 2
Uploaded by
dharmrajchaudhary1998cOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dice 2
Dice 2
Uploaded by
dharmrajchaudhary1998cCopyright:
Available Formats
ww
w.
yo
ur
sm
08
ah
bo
ob
CHAPTER
.w
DICE
or
dp
re
ss
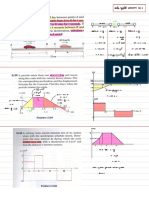
Dice has a shape of cube or cuboid. CASE I dice is general or if sum of 7
.c
om
It have six faces but at a time only When only one position is Given are not seen then the dice is
three faces are visible when as When only one position is given in standard.
three faces are hidden. a question then we will check our ;fn nks lyaXu lrg dk ;ksx
7 gSA rc iklk
iklk ?ku ;k ?kukHk dh vkd`fr dk gksrk
bldh N%
gSAdice is standard or general. lkekU; fLFkfr esa gS ;k ;fn mudk7 ;ksx
lrg gksrh gSA ysfdu ,d le; esa dsoy rhu lrgtc dsoy ,d fLFkfr nh gksA fn[kkbZ ugha nsrk gS rc bls ge ekud iklk
r
gh fn[kkbZ nsrh gSA tcfd rhu lrg fNih gqbZtcgksrh gSA
iz'u esa dsoy ,d fLFkfr nh gks rc ge ikals dks dgrs gSA
Si
E H ekud ;k lkekU; esa tkap djrs gSaA Examples
A D Standard Dice 4 2 6 4
1. 5 3 1 2
G If every opposite surfaces sum is 3 1 5 5
F
equal to 7 then the dice is called
av
B C standard dice. Which of the following is a stan-
(i) ABCD –– Front surface (visible) Opposite ekud iklk dard dice.
(ii) EFGH –– Back surface (hidden)
;fn izR;sd foijhr lrg ij ;ksx7 ds cjkcj gS rc fuEufyf[kr esa ls dkSu lk ekud iklk gSa
(iii) ADHE –– Top surface (visible)
(iv) BCGF –– bottom surface (hidden)
Opposite
2
d
bls ge ekud iklk dgrs gSA
5 (opposite)
4 2 6 4
Ya
5 3 1 2
(v) DCGH – Right surface (visible) 4 Sol. 3 1 5 5
Opposite
(vi) ABFE – Left surface (hidden) 6 4 3 (opposite)
7 7 7 7
2 6 1 (opposite)
(i) ABCD lkeus dh lrg (fn[kkbZ nsus okyh) 2. Opposite to 5 = ?
foijhr
(ii) EFGH ihNs dh lrg (fn[kkbZ ugha nsus okyh) 5 ds foijhr = ?
sh
(iii) ADHE Åijh lrg (fn[kkbZ nsus okyh) General Dice: 2
foijhr
(iv) BCGF fupyh lrg (fn[kkbZ ugha nsus okyh) If any two adjacent surfaces have 3
1
sum 7 then the dice is called gen-
(v) DCGH nk;ha lrg (fn[kkbZ nsus okyh)
foijhr eral dice.
ke
sol:- 7×
(vi) ABFE ck;ha lrg (fn[kkbZ ugha nsus okyh)
lkekU; iklk It is a standard dice
There are 4 cases to ask a question
;fn nks leku lrg dk ;ksx7 gSA rc bls ge ;g ekud iklk gSA
in any exam. 5 2 (Ans.)
lkekU; iklk dgrs gSA
Ra
fdlh ijh{kk esa pkj izdkj ds iz'u iwNs tkrs gSA 3. 6 5
4
Case I 5 2 1
3 3 4
when only one position is
given.
3 + 4 = 7 it is a general dice./ opposite to 6 = ?
Case II
lkekU; iklk gSA Sol. There is no two adjacent sur-
When only two position faces have sum 7
are given In general dice visible no are
opposite to hidden numbers it is a standard dice.
Case III
When more than two po-
lkekU; iklk fn[kkbZ nsrk gS ijaUrq blds foijhr
Opposite to 6 is 1 Ans.
sition are given. lrg fn[kkbZ ugha nsrh gSA nks LkyaXu lrg ds iklksa esa lrg7dkgSa
;ksx
;ksxI lkekU; ;k ekud ikls dh tkap dSls djrs gS& ;g ekud iklk gSA
tc dsoy ,d fLFkfr nh gksA 3/4/5/ 1/6/2 6 ds foijhr 1 gSA
;ksxII How to identify whether it is 4.
4 6
standard or General
tc dsoy nks fLFkfr nh gksA 3
5
1
2
If sum of any two adjacent
;ksxIII surfaces is 7 (7 visible) then the
tc nks ls T;knk fLFkfr nh gksA (i) (ii)
214 Rakesh Yadav Readers Publication Pvt. Ltd
ww
w.
yo
opposite to 4 = ? (in Clock wise direction) Which option is correct?
ur
4 ds foijhr dkSu (?kM+h dh lqbZ dh fn'kk esa] fuEufyf[kr esa ls dkSu lk fodYi lgh gSA
sm
=? )
ah
(hidden) 6 3 2
bo
Sol. 4 opposite opposite
ob
5 6 2
Sol.
.w
5 opposite 6 1
3 4 1 4
or
1. 3 1
dp
6 1
re
7
(i) (ii)
ss
5 3
It is a general dice 2 5
.c
1 3 6
;g lkekU; iklk gSA
om
(I) (ii) 5
4 1 / 6 / 2 Ans.
Opposite to 3 = ? 1 4
2
5. 4 opposite to 6 = ? foijhr 3 = ?
Note: Two opposite number can
5 Sol. never be seen at a time.
3
r
6 1 uksV
: nks foijhr lrg ,d lkFk dHkh fn[kkbZ ugha
Si
2
5
5
3 ns ldrh gSa
Sol. 4 General 3 3
5 (i) (ii)
3 5 4
5 2 6 1 2
av
4
7
5 1 3 (A) (B)
3/ 4 / 5 1/ 2 / 6 3 6 (Ans.) (Can never be
2. to gether)
opposite to 6 is 3 / 4 / 5 6 3
CASE –II. 3
d 1
4
2
6
3
4
6
Ya
5 2
When only two position are given
(i) (ii)
tc nks fLFkfr;ka nh xbZ gks& (C) (D)
What is the no at bottom surface of
(a) No common 4.
figure (i) B D
fp=k(i) esa fupyh lrg ij dkSu lh la[;k
gS&
sh
2 5 C F
A C
3 6 Sol. 6 3
1 4
1 2
3 4
D D
ke
(I) (ii)
(i) (ii)
E E
If there is nothing common in (3) 6 1 C A
figure (i) and figure (ii) then we (3) 2 4
Ra
will check dice is standard or (A) (B)
Top = 6
general.
Bottom = 2 B D
;fn fn;s gq, iklksa esa dqN Hkh leku ugha gS
rc ge lkekU; ;k ekud iklsa dh tkap fupyh lrg = 2 E
A
B
F
djsxsaA Ans. (opposite to 6)
(b) Only one common (6 ds foijhr) (C) (D)
buesa dsoy ,d lrg leku gSA 3.
6 2
1 4 Sol. D D
3 1
3 6 E E
C A
2 4 (i) (ii)
6 1
3 3
(A) (B)
5 4
(i) (ii) 1 2
Only one number (6) is common
(A) (B) B D
dsoy ,d la[;k (6) leku gSA
6 4 A F
3 6 E B
3 6
5 2
2 4
6 1 (C) (D)
(C) (D)
Rakesh Yadav Readers Publication Pvt. Ltd 215
ww
w.
yo
E B/C 3 1 2
ur
B D
sm
A
C
C
F Opption C is correct. 6
ah
foDYiC lgh gSA 3 5 4
bo
2.
ob
C A B 5 3 Examples
.w
E 3 4 B E E
2 2
or
C F C D F
dp
D 1. A A D
re
(i) (ii)
5.
ss
2 4 1 5 3 opposite to D = ?
.c
3 6 ? 6 1 foijhr D ds = ?
om
1 2 5 4 2
Sol.
(i) (ii) (iii) B E E
(A) (B)
(A)1 (B)6 C D F
A A D
6 3
(C)2 (D)3
2 6 (i) (ii) (iii)
r
Sol. 1 4
2 4 From (i) & (ii)
Si
1
3
2
6 (C) (D) (i) vkSj(ii) ls]
Sol.
A B C
2 3 1 5 3
F
5 3 4
2 2
av
A E D
24 6
4 5 Opposite to D is C Ans.
(c) Two Common
2/3 1/6 D ds foijhr C gSA
nks lkeku la[;k;s
3 6
3
d
Note:- Two opposite no. can never
be seen together or can never be
3. $
#
C
#
C
Ya
5 hidden together. @ % %
1 1
485 can never be seen (option A) (i) (ii) (iii)
(i) (ii) and can never be hidden (B,C) opposite to $ –––?
Remaining number are oppo- Since option D is correct,
site to each other. Sol. From (i) & (iii)
uksV:- nks foi
jhr la[;k ,d lkFk fn[kkbZ ugha ns ldrh (i) vkSj(iii) ls
sh
cph gqbZ la[;k izR;sd ds foijhr gksrh;kgSA
fNih gqbZ la[;k ,d lkFk ugha gks ldrh gSA
5 6 $ #
fodYi (A) esa485 dks dHkh ns[k ugha ldrs
Hidden number are opposite to vis- # C
gSA vkSj fNih gqbZ
C) dHkh fn[kkbZ ugha ns @
ke
(B, %
ible no.
ldrh gSA
fNih gqbZ la[;k fn[kkbZ nsus okyh la[;k ds foijhr (i) (iii)
fodYi D lgh gSA
gksrh gSA $ % Ans.
Ra
1/3 2/4. CASE III
CASE IV
Ex. More than two positions are Given
Opening of a Dice,
1. B F nks ls vf/d fLFkfr nh x;h gS&
Each alternate surface are opposite
C C 2 5 3
A B to each other.
3 6 5
1 4 4
ikls dks [kksyus ij] izR;sd oSdfYid lrg ,d nwljs
(I ) (ii)
(A) (B) (C) ds lkeus gksrh gSA
opposite to E = ?
Solve the Question by taking any two
E ds foijhr = ? position of only one common. 2
(A)A (B)F fdlh nks inks dks ysdj iz'u dks gy djus ij mudh
(C)B (D)D fLFkfr leku gksrh gSA 1 3 4 5
Sol. 3
B F From A & C. 6
C C
A B 2 3 (A)
3 5
A F 1 4 1–––– 4
B/C D/E (A) (C) 3––––5
216 Rakesh Yadav Readers Publication Pvt. Ltd
ww
w.
yo
2––––6 A–––– E 2–––– 4
ur
sm
C–––– F 3–––– 5
D
ah
D–––– B 1–––– 6
bo
ob
C 1 2
.w
or
A B E 3
dp
re
4
ss
F
.c
6
om
(B) 5
EXERCISE-1
r
1. Four forms of a dice are shown 4. Four forms of a dice are shown ,d ikls dh pkj fLFkfr;ksa dks fn[kk;k x;k gS
Si
below. In this dice which word below in this dice which digit bl ikls esa nks
fcanq ds foijhr fdrus fcanq gksxsa\
will be on the surface opposite will be on the surface opposite
.. ..
to the word D? ... ...... .... ...... .. .... .. .....
to the digit 4 ?
,d ikls dh pkj fLFkfr;ksa dks n'kkZ;k x;k gS .
,d ikls dh pkj fLFkfr;ka n'kkZ;h xbZ gSA bl .
av
D lrg ds foijhr dkSu&lk 'kCn gS& rks bl ikls esa
iklsa esa 4 ds foijhr dkSu lh lrg (a) 1 (b) 4
vk;sxh\ (c) 5 (d) 6
B E C D
2 1 4 2
C A A C D E C B 8. Four forms of a dice are shown
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
5
(i)
1
d 5
(ii)
6 5 6
(iii)
4
(iv)
3
below. In this dice which figure
will be on the surface opposite
Ya
(a) D (b) A (a) 6 (b) 3
to the figure ?
(c) B (d) C (c) 1 (d) 5
5. Four forms of a dice are shown
,d ikls dh pkj fLFkfr;ksa dks n'kkZ;k x;k gS
2. If a dice thrown four times and bu iklksa esa fp=k
ds foijhr D;k gksxk\
different forms of dice are below in this dice which digit
shown below. I n this dice will be on the surface opposite + – ÷ ÷
to the digit 3?
sh
which digit will be on the sur- 0 × × 0 + + 0
face opposite to the digit 2? ,d ikls dh pkj fLFkfr;ksa dks n'kkZ;k x;k gS (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
;fn ,d ikls dks pkj ckj iQsdk tkrk gS vkSj rks bl ikls esa3 ds foijhr dkSu lh la[;k (a) × (b) +
vk;sxh\
izR;sd fLFkfr eas vyx la[;k,sa fn[kkbZ nsrh gS bl
ke
(c) 0 (d) ÷
izdkj iklsa 2esa
ds foijhr dkSu lh la[;k gSA 5 3 2 4
9. Four forms of a dice are shown
4 6 5 6 1 4 1 6
6 2 3 1
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
below. In this dice which colour
2 4 3 4 5 4 3 2 will be on the surface opposite
Ra
(a) 5 (b) 4
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
to the yellow colour?
(c) 2 (d) 6
(a) 6 (b) 3
6. Four forms of a dice are shown
,d ikls dh pkj fLFkfr;ksa dks n'kkZ;k x;k gS bl
(c) 5 (d) 4 below. In this dice is addition ikls esa ihys jax ds foijhr dkSu lk jax gksxk\
3. 1,2,3,4,5 and 6 have written on of it's two opposite surface is 7. Yellow Orange Blue Red
surface of dice. Four forms of Which will be the right form of
w
w
O
Pi
oi
llo
llo
ra
Blue Blue
ed
nk
le
ng
dice shown below. In this dice
Ye
Ye
t
this dice in given forms?
e
which digit will be on the sur-
,d ikls dh pkj fLFkfr;ksa dks n'kkZ;k x;k gS (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
face opposite to the digit 3? (a) Red/yky
bl ikls esa nks foijhr lrg ftuds ;ksx 7 gS
,d ikls dh lrg ij 1,2,3,4,5 vkSj6
feyk fn;k tkrk gS rks bl iklksa esa lgh dks(b) Blue/uhyk
fy[kk tkrk gS uhps ikls dh pkj fLFkfr (c) Pink/xqykch
crkb,s\
n'kkZ;h xbZ bl gS
ikls eas3 ds foijhr dkSu ..
..... .. .... .. ...... ..... ...... .
(d) Voilet/cSaxuh
lh la[;k gS& 10. Four forms of a dice are shown
2 1 3 6
.. . .. .. below. In this dice which digit
(a) (b) (c) (d)
3 4 3 2 5 4 2 4 will be on the surface opposite
7. Four forms of a dice are shown to the digit 1?
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) below. In this dice which digit
(a) 4 (b) 5
,d ikls dh pkj fLFkfr;ksa dks n'kkZ;k x;k gS bl
will be on the surface opposite
(c) 6 (d) 1 to the digit 2? ikls esa ,d fcanq ds foijhr fdrus fcanq vk;sxk\
Rakesh Yadav Readers Publication Pvt. Ltd 217
ww
w.
yo
.. ..
.. ... ........ ......... .......
which digit will on the surface la[;k gksxh\
ur
. opposite to the digit 1?
sm
,d ikls dh rhu fLFkfr;ksa dks n'kkZ;k x;k gS 4 4 4
ah
bo
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
bl ikls esa ,d fcanq ds foijhr fcUnqvksa dh 3 6 2 3 1 2
ob
(a) 2 (b) 3
la[;k Kkr djksa
.w
(c) 4 (d) 6 (iii)
.. (i) (ii)
or
. .
........
11. Four forms of a dice are shown
.. .. .. ..... .
dp
(a) 5 (b) 1
below. In this dice which digit
re
(c) 2 (d) 3
ss
will be on the surface opposite
Directions/funsZ'k
.c
to the digit 4? (i) (ii) (iii) (16-18)
om
,d ikls dks pkj fLFkfr;ksa esa n'kkZ;k x;k gS(a)
bl 2
ikls esa
4 ds foijhr dkSu lh la[;k vk;sxh\
(b) 3
.
2 1 4 2
(c) 4 (d) 6
14. Three forms of a dice are
shown below. I n this side
* + + . . *
5 1 5 6 6 5 3 4 which digit will be on the sur-
r
(i) (ii) (iii)
face opposite to the digit 3?
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
,d ikls dh rhu fLFkfr;ksa dks n'kkZ;k x;k16.
gS blWhich figure will be opposite
Si
(a) 1 (b) 2 of (•)?
(c) 3 (d) 5
ikls esa
3 ds foijhr dkSu lh la[;k vk;sxh\
fn;s x;s fp=k (•)
esads foijhr D;k gksxk\
12. If in a dice it's two opposite sur- 2 3 4 (a) + (b) *
face addition is 7. Which is the 1 3 1 5 2 3
(c) (d) 5
av
right form of this dice shown
below? (i) (ii) (iii) 17. Which figure will be opposite of (+)?
(a) 1 (b) 6 fn;s x;s fp=k (+)
esads foijhr D;k gksxk\
;fn ,d ikls esa nks foijhr lrg ftudk ;ksx
7 gS fn;s
(a) * (b) •
x;s ikls esa dkSu lh fLFkfr lgh ikls dks n'kkZrh(c)
gS\4 (d) 5
...
..... ...
...
..... ...
...
..... ..
.....
.. d
15. Three forms of a dice are
shown below. I n this dice
(c) (d)
Ya
18. In given from (iii) which will be
. ... .. which digit will be on the sur- opposite of ( )?
face opposite to the digit 4 ? fn;s x;s fp=k
(iii) esa
( ) ds foijhr D;k gksxk\
(a) (b) (c) (d)
,d ikls dh rhu fLFkfr;ksa dks uhps n'kkZ;k
(a) * (b)
13. Three forms of a dice are
shown below. I n this dice x;k gS bl iklsa esa
4 ds foijhr dkSu lh (c) • (d) +
sh
ANSWER KEYS
ke
(Exercise-1)
1. (b) 3. (c) 5. (b) 7. (d) 9. (d) 11. (a) 13. (d) 15. (a) 17. (c)
Ra
2. (c) 4. (c) 6. (a) 8. (c) 10. (d) 12. (c) 14. (b) 16. (d) 18. (d)
By The Team of Best Faculties of Mukherjee Nagar
Batches for
SSC
SSC CGL/CPO
G.S. Spl.
218 Rakesh Yadav Readers Publication Pvt. Ltd
ww
w.
yo
ur
SOLUTION
sm
ah
bo
1.(b) In figure (ii) and (iii) C and E 5. (b) 12. (c)
ob
are common so A is opposite of
.w
5 3 2 4
or
D 13. (d)
dp
4 6 5 6 1 4 1 6
fp=k(ii) o (iii) esaC vkSjE leku gS vr%
re
A ds foijhr D gksxk\ 2 3 4
ss
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
.c
2. (c) 6. (a) 1 3 1 5 2 3
14. (b)
om
6 2 3 1 7. (d)
.. . . .. ..
2 4 3 4 5 4 3 2 ... ...... ..... ...... . ... . .... (i) (ii) (iii)
. 15. (a)
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) 4 4 4
3.(c) From figure (ii) and (iii) because addition of two adja- 3 6 2 3 1 2
r
cent surface is not equal to 7
1 3 in a standard dice. (i) (ii) (iii)
Si
8. (c) From (i) (ii) and (iii)
3 2 5 4
+ – ÷ ÷ 3 will be opposite of 1
0 × × 0 + + 0 6 will be opposite of 2
1 will be opposite of 4
4 will be opposite of 5
av
2 will be opposite of 5 (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
3 will be opposite of 6 missing 9. (d) 3 ds foijhr 1 gksxkA
number 10. (d) 6 ds foijhr 2 gksxkA
.. ... ........ .. ..
1 ds foijhr 4 gksxkA
2 ds foijhr 5 gksxkA . d ......... ....... 4 ds foijhr 5 gksxkA
Ya
3 ds foijhr 6 gksxk tks fn;k ugha x;k gSA (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
Solution (16-18)
4. (c) 11. (a)
2 1 4 2 16. (d)
2 1 4 2
5 1 5 6 6 5 3 4
5 1 5 6 5 6 4 3
sh
17. (c)
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) 18. (d)
ke
EXERCISE-II
Ra
1. Which figure we can make the A E D A 4. In a given figure of open dice.
given figure C E D F B A B C Which dice we can make?
fn;s x;s fp=k esa ge dkSu lk fp=k cuk ldrs gS\ (a) (b) (c) (d) [kqyk iklk fn;k x;k gS blesa dkSu lk iklk
F F will be opposite of B
(a) only a cuk ldrs gS&
A E (b) only b
E will be opposite of C
B (c) only a and c
A will be opposite of D A
C D
(d) only b and d A will be opposite of D
Answer figure C
3. Question figure B will be opposite of F
D B
F F E D
2 2 will be opposite of 4 E
B E E D B C E A C will be opposite of E
5 1
1 will be opposite of 6 F
(a) (b) (c) (d) 4
2. Question figure 6 3 5 will be opposite of 3
Answer figure
C C will be opposite of F Answer figure
A B A B C C
B will be opposite of D 3 1 2 3
F C B F A E D E A
A will be opposite of E 6 1 3 5 6 4 1 4
D E
Answer figure (a) (b) (c) (d) (a) (b) (c) (d)
Rakesh Yadav Readers Publication Pvt. Ltd 219
ww
w.
yo
5. Question figure 6. Question figure 7. Questions figure
ur
sm
×
ah
C + ÷
bo
A B
×
ob
D
.w
=
or
F E Answer Figure
dp
×
re
Answer figure ÷ ÷ ×
ss
Answer figure
.c
A C A A (a) (b) (c) (d)
om
(a) Only (a) and (b)
E F D F D B D C × = + + (b) Only (d)
(a) (b) (c) (d) + = (c) Only (b) and (d)
(d) Only (c) and (d)
(a) Only (a) and (c) (a) (b) (c ) (d) 8. Which is the opposite surface
of 1.
(b) Only (b) and (d) (a) Only (a)
r
1
(c) Only (c) (b) Only (a) and (d) 2 3
Si
(d) Only (a) and (d) (c) Only (b) and (c)
4
5
(d) Only (a) and (d) (a) 1 (b) 3
(c) 4 (d) 5
ANSWER KEYS
av
(Exercise-II)
1.
2.
(b)
(d)
3.
4.
(d)
(a)
d 5.
6.
(c)
(a)
7.
8.
(d)
(c)
Ya
sh
SOLUTION
ke
7. (d)
Ra
1. (b) F A C A A ×
5. (c) E F D F D B D C
÷ ÷ ×
E D (a) (b) (c) (d)
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(b)
C will be opposite of D
A E D A
2. (d) B will be opposite of F
C E D F B A B C
(a) (b) (c) (d)
A will be opposite of E × will be opposite of
6. (a) × = + + will be opposite of
3 1 2 3 + =
3. (d) 6 1 3 5 6 4 1 4
(a) (b) (c ) (d) ÷ will be opposite of
(a) (b) (c) (d)
8. (c)
+ will be opposite of = 1
A B C C
4. (a) C B F A E D E A will be opposite of 2 3
(a) (b) (c) (d) 4
will be opposite of × 5
220 Rakesh Yadav Readers Publication Pvt. Ltd
ww
w.
yo
ur
EXERCISE-III
sm
ah
bo
1. Form the following two different f=kHkqtksa dh la[;k crkb,s\
ob
8. Three positions of a dice are
.w
appearances of dice find out the given below. Identify the number
or
number which is opposite to '5' on the face opposite to 6.
dp
nks vyx&vyx izdkj ds ikls mifLFkr gS bu ,d ikls ds rhu fLFkfr;ksa dks n'kkZ;k x;k gS
re
ikls esa
5 ds foijhr dkSu lh la[;k vk;sxh\ rks6 ds foijhr lrg dh la[;k crkb,s\
ss
.c
2 (a) 4 (b) 3
2
om
3 3 4
3 3 (c) 2 (d) 5 2 6 3
5 6 6 5 5
5. Choose from the four answer
(a) 2 (b) 3 figures, the figure that will be (a) 1 (b) 4
(c) 4 (d) 6 formed when the question figure
(c) 5 (d) 6
2. Little wooden cubes each with a is folded into a box.
r
9. A solid cube of 4 inches has been
side of one inch are put together fn;s x;s fp=k esa pkj fodYi fn;s x;s gS tc painted Red, Green, and Black
fn;s x, fp=k dks cUn fd;k tkrk gS rks buesaon pair of opposite faces. It has
Si
to form a solid cube with a side
of three inches. This big cube is ls dkSu&lk ?ku cusxk\ been cut into one inch cubes.
then painted red all over on the How many cubes have only one
outside. When the big cube is face painted that too only red?
,d pkj bap dk Bksl ?ku yky] gjk vkSj dkys
av
broken up into the original little
ones, how many cubes will have jax ls gS foijhr lrgksa ij jaxk tkrk gS ;fn
paint on two sides? Answer Figures blesa ls1 bap dk ?ku dkV fy;k tkrk gS rc
ydM+h dk ,d NksVk ?ku ftldh izR;sd Hkqtk dsoy yky jax ls jaxs lrg okys ?kuksa dh
1 bap gS dks
3 bap ds ?ku ds lkFk j[kk tkrk
gS bl izdkj cM+s ?ku dh izR;sd ckgjh lrg
d la[;k crkb,s\
Ya
(a) 4 (b) 8
dks yky jax ls jaxk tkrk gS tc cM+s ?ku dks (a) (b) (c) (d) (c) 16 (d) 24
okLrfod NksVs Hkkxksa esa rksM+ fn;k tkrk gS rc 10. A solid cube of 4 inches has been
6. In a solid cube which is made painted red, green and black on
?kuksa dh la[;k ftlds nks lrg jaxs gq;s gS\ up of 27 small cubes, two
pair of opposite faces. It has
sh
(a) 4 (b) 8 opposite sides are painted red, been cut into one inch cubes.
(c) 12 (d) 0 two painted yellow and the other How many cubes have only one
two with white. How many cubes face painted?
3. Two positions of a cube are
have two colours? ,d 4 bap dk Bksl ?ku yky] gjk vkSj dkys
ke
given. Based on them find out
which number is found opposite ,d Bksl ?ku dks NksV&NksVs
27 ?kuksa ls cuk;k jax ls foijhr lrg ij jaxk tkrk gS blesa
1 ls
number 1 in the given cube. tkrk gS nks foijhr lrg yky jax ls jaxh tkrh bap dk ?ku dkV fy;k tkrk gS rks ,d lrg
gS] nks ihys jax ls vkSj nwljh nks liQsn ls ijjaxh
jaxs gq, ?kuksa dh la[;k crkb,s\
,d ?ku dh nks fLFkfr;ka n'kkZ;h
muij xbZ
vk/kfjr
gS
Ra
tkrh gS nks jaxksa ls jaxs ?kuksa dh la[;k crkb,\
(a) 4 (b) 8
?kudh 1 ds foijhr la[;k D;k gksxh\
(a) 8 (b) 12 (c) 16 (d) 24
6 6 11. Position of Dices is given below:
2 3 (c) 16 (d) 24
1 2 Identify the number when top is
7. In a solid cube made up of 27
(a) 1 (b) 2 small cubes, two opposite sides 5 what will be at bottom?
(c) 3 (d) 4 are painted red, two opposite ,d ikls dh fLFkfr;k¡ uhps nh xbZ gS ,d iklk
4. Two positions of a cubical block
sides yellow and two other sides ftldh Åijh lrg ij 5 gS rks bldh fupyh
are given below, each face having
white. How many small cubes lrg ij dkSu lh la[;k gksxh\
have the colours yellow and
a number of small triangles. In 4 3 1 2
white alone in them? 3 2 1 5 4 6 3 5
another position of the cube, it
there is one triangle at the ,d Bksl ?ku dks NksVs&NksVs
27 ?kuksa ls feydj
(a) 6 (b) 3
bottom, how many triangle will cuk;k tkrk gSA nks foijhr Hkqtk,sa yky jax ls
(c) 4 (d) 2
be there on the top face? jaxh gqbZ gS] vkSj nks foijhr Hkqtk,s ihys ls vkSj
12. Which number appear in the
,d ?ku dh nks fLFkfr;ka uhps n'kkZ;h xbZnksgSnwljh rjiQ liQsn ls jaxh tkrh gS ihys rFkkface opposite to the face with
izR;sd lrg ij NksVs&NksVs f=kHkqt fn;sliQsn
x;s gSlrg ds jaxksa okys ?kuksa dh la[;k crkb;sa\
number 4?
?ku dh nwljh fLFkfr esa ?ku ds fupyh lrg (a) 4 (b) 8 fn;s x;s iklksa4esa
ds foijhr la[;k dk irk
ij ,d f=kHkqt gS ?ku dh Åijh lrg ij (c) 12 (d) 16 yxkb,s\
Rakesh Yadav Readers Publication Pvt. Ltd 221
ww
w.
yo
6 2 18. A solid red coloured cube is (a) 6 (b) 5
ur
3 3 painted yellow on all sides. The
sm
4 1 (c) 3 (d) 1
cube is cut into 125 equal
ah
(a) 1 (b) 2 23. Two positions of a dice are
bo
cubes. How many sides will
given. Which number would be
ob
(c) 3 (d) 5 have 3 sides yellow?
at the top when bottom is 2?
.w
13. Study the following figures and ,d Bksl yky jax ds ?ku dh lHkh lrg dks
,d lrg dh nks fLFkfr;ka n'kkZ;h x;h gS ;fn
or
find out the number opposite to ihys jax esa jaxk tkrk gS ;fn blesa
125 ls
dp
3. fupyh lrg ij 2 gS rks ikls ds Åijh lrg
leku ?ku dkVs tkrs gS rc rhu ihyh lrgksa
re
fn;s x, fp=k dks fujh{k.k djrs3 gq,
ds ij la[;k crkb,sa\
ss
okys ?kuksa dh la[;k crkb,s\
foijhr la[;k crkb,s\
.c
(a) 10 (b) 4
om
3 4 2
3 3
1 2 5 6 1 5 (c) 8 (d) 12 2 5 6 1
19. How many cubes are there in
(a) 6 (b) 4 this figure? (a) (b)
(c) 5 (d) 2 fn;s x;s fp=k esa ?kuksa dh la[;k crkb,s\ (a) 4 (b) 1
14. Study the following figures and
r
find out the number opposite to (c) 5 (d) 6
Si
2. 24. Four different positions of a
fn;s x, fp=k dks fujh{k.k djrs2 gq,
ds dice are as shown below. What
number is opposite to face 3?
foijhr la[;k crkb,s\
(a) 69 (b) 180 ,d ikls dh pkj fLFkfr;ksa dks uhps n'kkZ;k x;k
3 3 4
gS rks
3 ds foijhr lrg dh la[;k crkb,s\
av
2 6 3 (c) 144 (d) 84
6 5 5
20. How many cubes are unseen
(a) 1 (b) 4 2 5 6 3
in the figure?
(c) 5 (d) 6 3 6 2 4 3 1 5 1
fn;s x;s fp=k esa Nqis gq,s ?kuksa dh la[;k
15. A dice is thrown four times and
its four different positions are
crkb,s\
d (a) 4
(c) 2
(b) 3
(d) 6
Ya
given below. Find the number
on the face opposite the face 25. A cube which is painted red on
showing 2. the outer surface is of 2 inches
,d ikls dks pkj ckj iQsdk tkrk gS vkSj pkjksa height, 2 inches wide and 2
fLFkfr;ka vyx&vyx vkrh gS tks uhps nh xbZ inches across. If it is cut into
gS rc 2 ds foijhr la[;k crkb,s\
sh
one-inch cubes as shown by
(a) 5 (b) 6 dotted lines, indicate the
2 1 3 6 number of cubes which are red
(c) 10 (d) 15
3 4 2 3 5 4 2 4
21. Four positions of dice are given on two sides only?
ke
(a) 4 (b) 5 below. Which letter will be ,d ?ku dks ftldh ckgjh lrg 2 bap Åaph]
(c) 6 (d) 3 opposite to D? 2 bap pkSM+h rFkk nks bap lkeus dh vksj mls
16. Form the following two different ,d ?ku dh pkj fLFkfr;ksa dks n'kkZ;k x;k gSyky jax ls jaxk tkrk gSA ;fn blesa
1 bap
ls
Ra
appearance of a dice, which fn;s x;s iklksaDesa
ds foijhr v{kj D;k gksxk\ ds ?ku dks dkVk tkrk gS ftls MkaV ykbu esa
number lies to the opposite of 2? Questions Figures: n'kkZ;k x;k gS rc nksuksa rjiQ yky jax ls jaxs
,d ikls dh nks fLFkfr;ka n'kkZ;h x;h gS rks gq, ?ku dh la[;k crkb,A
buesa2 ds foijhr dh la[;k crkb,s\
C D B E
D E C B C A A C
5 5 (a) (b) (c) (d)
4 1
1 2
(a) B (b) C
(a) 1 (b) 4 (c) D (d) A
(c) 6 (d) 5 22. Three positions of a dice are (a) 4 (b) 6
17. How many cubes are there in given. Find out which number
(c) 8 (d) 0
this diagram? is found opposite the number 2
26. Three views of the same cube
fn;s x;s fp=k esa fdrus ?ku gS\ in the given cube. are given. All the faces of the
,d ?ku dh rhu fLFkfr;ka n'kkZ;h x;h gS fn;scube are numbered from 1 to
x;s ?ku esa
2 ds foijhr la[;k dks crkb,s\ 6. Select one figure which will
result when the cube is
6 5 4 unfolded.
(a) 10 (b) 8
1 4 3 6 1 2 ,d ?ku dh rhu fLFkfr;ka nh xbZ gS ?ku dh
(c) 16 (d) 12 (a) (b) (c)
lHkh lrg dks1 ls 6 rd ds la[;k,sa n'kkZ;h
222 Rakesh Yadav Readers Publication Pvt. Ltd
ww
w.
yo
x;h gS ?ku dks [kksyus ij fuEu esa ls dkSu&lk3 35. Two positions of a dice are
ur
3 4
?ku cusxkA shown below. When the heart
sm
2 6 3
6 5 5
Questions Figures: shape is at the top what will
ah
bo
(a) 4 (b) 5 be at the bottom?
ob
3 3 4
5 5 2 ? (c) 3 (d) 1 ,d ikls dh nks fLFkfr;ksa dks uhps n'kkZ;k x;k
.w
2 1 3
31. If the difference between the gS ;fn ikls esa fny ds izdkj Åijh lrg ij
or
no. of dots on the opposite faces gks rks fupyh lrg ij D;k gksxk\
dp
re
4 5 6 4
5 6 3 6 4 5 1 6 is 3. Find out the figure which Question Figures:
ss
1
3 2
4
2 1
3
2 1
5
3 2
is correct?
.c
;fn foijhr iQydksa ds fcUnqvksa dk vUrj rhu
om
(a) (b) (c) (d)
27. Which of the following cubes gS rks lgh mÙkj vkÑfr crkb,\
can be created by folding the Answer Figures: Answer Figures:
given figure?
(a) (b)
fn;s x, fp=k dks eksM+dj fuEu esa ls dkSu lk
?ku cuk;k tk ldrk gS\
r
(c) (d)
Questions Figure: (a) (b) (c) (d)
Si
36. Choose the cube which will be
32. Four positions of a dice are formed on folding the given
E given below. I dentify the
AF question figure.
B number at the bottom when top
CD is 6. fn;s x, fp=k esa tyk gqvk ?ku n'kkZ;k x;k
;fn ,d ?ku dh pkj fLFkfr;ksa dks uhps gS bls cUn djus ds ckn cuk ?ku crkb,s\
av
Answer Figures:
n'kkZ;k x;k gS ;fn Åijh lrg 6ij gS rks Questions Figure:
F E E D
B
E
F
D
B
C
E
A blds fupys lrg dh la[;k crkb,s\
(a) (b) (c) (d)
2
d
Questions Figures
4 6 5
Ya
28. From the given blocks when 10
1 3 1 2 4 2 4 6 Answer Figures:
is at the bottom, which number
will be at the top? (a) 1 (b) 3
fn, x, CykWd ij tc fupyh lrg 10 gS rks (c) 4 (d) 5
Åijh lrg ij dkSu&lh la[;k gksxh\ 33. Four positions of a dice are
sh
(a) (b) (c) (d)
given below. I dentify the 37. Few cubes are arranged as
10 12
4 8 number at the bottom when the shown in the figure. How many
2 6
number on the top is 2. cubes are unseen?
ke
(a) 8 (b) 12 ;fn ,d ikls dh pkj fLFkfr;ksa dks uhps dqN ?ku dks fp=k esa O;ofLFkr fd;k x;k gS rks
(c) 6 (d) 4 n'kkZ;k x;k gS ;fn ikls dh Åijh lrg ij Nqis gq, ?kuksa dh la[;k crkb,s\
29. How many cubes are there in the 2 gks rks fupyh lrg ij la[;k crkb,s\
group?
Ra
fn;s x;s xzqi esa ?kuksa dh la[;k crkb,\ 4 5 6 3
6 5 1 4 2 3 1 5
(a) 3 (b) 5
(a) 8 (b) 10
(c) 4 (d) 6
(c) 12 (d) 14
34. Four positions of a dice are
38. The sides of a cube show the
given below. I dentify the
colours of rainbow. Two
number at the bottom when the
positions of the cube are shown
number on the top is 2.
below. Which of the colours of
;fn ,d ikls dh pkj fLFkfr;ksa dks uhps rainbow is left out?
(a) 20 (b) 10 n'kkZ;k x;k gS ;fn ikls dh Åijh lrg ij ,d ?ku dh lrg dks bUn/uq"k ds jxksa esa
(c) 16 (d) 18 2 gS rks fupyh lrg ij la[;k crkb,s\ n'kkZ;k tkrk gS ftlls nks fLFkfr;ka uhps n'kkZ;h
30. Study the 3 different positions
3 5 3 6
x;h gS rks ck;sa dh ckgjh lrg ij bUnz/uq"k ds
of a cube given below and
answer what number comes 6 5 4 1 1 2 3 2 fdrus jax gS\
opposite to 2? I B
(a) 6 (b) 3
,d ?ku dh rhu fLFkfr;ksa dks uhps n'kkZ;k x;k G
Y
R
O
gSA rks 2 ds foifjr dkSu&lh la[;k vk;asxh\(c) 4 (d) 5
Rakesh Yadav Readers Publication Pvt. Ltd 223
ww
w.
yo
(a) Yellow/ihyk form a block. Which symbol will
ur
(b) Green/ gjk appear on the oppsite of triangle
sm
,d ?ku dks [kksyus ij uhps nh xbZ fLFkfr
ah
(c) Violet/cSaxuh
bo
izkIr gksrh gS
rks
f=kHkqt ds foijhr dkSu lk
ob
(d) Indigo/vklekuh
izkIr gksxhA
.w
39. Based on the diagrams which
or
letter is opposite to A?
dp
fp=k ij vk/kfjrA ds foijhr v{kj dks
re
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
ss
crkb,s\
.c
om
B E (a) (ii) and (iii) only
C B
A D (b) (i), (iii) and (iv) only
(a) B (b) C (c) (ii) and (iv) only (a) (b)
(c) D (d) E (d) (i) and (iv) only (c) (d)
40. Which colour is opposite to 43. If a paper is folded as shown in 2017
r
purple? figure to form a cube, then the 46. Three positions of a cube are
pairs of opposite faces are:
Si
cSaxuh jax ds foijhr dkSu lk jax gS\ shown below. What will come
;nfi ,d dkxt dks eksM+dj ?ku vkÑfr ds opposite to the face containing
Questions Figures:
:i esa n'kkZ;k tkrk gS rks muds foijhr lewg'$'?
Purple Yellow Green Blue
D;k gksxk\ uhps ,d ?ku dh rhu fLFkfr;ka n'kkZb xbZ gSaA
Purple
Purple
Green
Green
e
w
ng
izrhd fpÉ'$' ds foijhr iQyd ij dkSu&lk
llo
av
Blue Red Question Figure:
ra
Ye
(a) Blue/uhyk (b) Orange izrhd fpÉ vk;sxk\
/ukjaxh
% +
(c) Red/yky (d) Green/ gjk + ÷
41. Choose the cube that will be
d $ * + * & *
Ya
formed by folding the sheet a Answer Figures:
paper shown in the problem + AND + AND AND + AND ÷ (a) % (b) &
figure. ÷ AND ÷ AND + AND ÷ AND
(c) ^ (d) +
AND AND AND AND
,d dkxt dks eksM+dj cuk;h x;h iz'u (a) (b) (c) (d)
47. Three position of a cube are
vkÑfr ls ,d lgh ?ku vkÑfr pqusA shown below. What will come
sh
opposite to face containing '5'?
Question Figure: 44.
uhps ,d ?ku dh rhu fLFkfr;ka n'kkZb xbZ gSaA
the solid so formed by joining vad '5' ds foijhr iQyd ij dkSu&lk vad
ke
unit cubes is rotated to obtain vk;sxk\
different positions, which of
these cannot be the shape after 3 5 1
Answer Figures: it has turned? 6 2 3
5
Ra
4 2
fofHkUu ?kuks dks feykdj ,d Bksl vkdkj dks
cuk;k tkrk gS bls ?kqekus ij vyx&vyx (a) 1 (b) 3
(c) 4 (d) 6
fLFkfr;ka izkIr gksrh gS rks ml fLFkfr dks
crkb,s tks ml Bksl vkdkj ls ugha cuk;k48.
tk Position of Dices is given below:
(a) (b) (c) (d)
Identify the number when top
42. The figure given on the left ldrk gSA
is 5 what will be at bottom?
hand side is folded to form a
uhps ,d ?ku dh fofHkUUk fLFkfr;ka n'kkZb xbZ
both choose from the
alternatives (1), (2), (3) and (4) (a) (b) gSaA ;fn vad
'5' mQij dh iQyd ij gks] rks
the boxes that similar to the
fupyh iQyd ij dkSu&lk vad vk;sxk\
box formed. 4 3 1 2
3 2 1 5 4 6 3 5
uhps fn, x, fp=k esa ckbZ rjiQ ls nksuksa
vkÑfr dks eksM+k tkrk gS] rks pkj ?ku vkÑfr (a) 6 (b) 3
curh gS] rks muesa ls fdrus leku vkÑfr (c) (d) (c) 4 (d) 2
cusaxs\ 49. Four positions of a dice are
given below. I dentify the
45. The following figure is folded to number at the bottom when top
is 6.
224 Rakesh Yadav Readers Publication Pvt. Ltd
ww
w.
yo
uhps ,d ?ku dh fofHkUUk fLFkfr;ka n'kkZb
(a) xbZ
q and d (b) a and b
ur
gSaA ;fn vad
'6' mQij dh iQyd ij gks] rks
sm
(c) q and b (d) q and g 1 6
fupyh iQyd ij dkSu&lk vad vk;sxk\
ah
bo
52. Three positions of a cube are 2
ob
2 4 6 5 shown below. What will come
.w
1 3 1 2 4 2 4 6 opposite to face containing 'N'? 3 5
or
(a) 1 (b) 3 uhps ,d ?ku dh nks fLFkfr;ka n'kkZb xbZ gSaA
dp
v{kj 'N' ds foijhr iQyd ij dkSu&lk 4
re
(c) 4 (d) 5
ss
50. Three positions of a cube are v{kj vk;sxk\
.c
shown below. What will come
om
opposite to the face containing
'a '? (a) (b)
uhps ,d ?ku dh rhu fLFkfr;ka n'kkZb xbZ gSaA
izrhd fpÉ'a ' ds foijhr iQyd ij dkSu&lk (a) P (b) Q
izrhd fpÉ vk;sxk\ (c) S (d) Z
r
(c) (d)
53. Two positions of a cube are
Si
shown below. what will come 55.
Which of the following cube in
opposite to face containing
'' ? the answer figure cannot be
uhps ,d ?ku dh nks fLFkfr;ka n'kkZb xbZ made
gSaA based on the unfolded
cube in the question figure?
(a) b (b) d izrhd fpÉ
'' ds foijhr iQyd ij dkSu&lk fuEufyf[kr mÙkj vkd`fr esa ls dkSu lk ?ku
av
(c) h (d) q v{kj vk;sxk\ fn, x, iz'u vkd`fr esa [kqys ?ku ls cuk;k
51. Three positions of a cube are
shown below. Which symbol will ugha tk ldrk\
come on two faces marked '1 • •
and 2' ?
uhps ,d ikls dh rhu fLFkfr;ka n'kkZb xbZ gSaA
d •
• •
Ya
(a) (b)
dkSu&ls izrhd fpÉ '1' rFkk'2' vafdr
iQydksa ds LFkku ij vk;saxs\ (c) or (d)
54. From the given options, which
figure can be formed by folding
sh
the figure in the question? (a) • •
(b)
•
fuEufyf[kr fodYiksa esa ls dkSu&lh mÙkj
• •
vkÑfr iz'u esa nh xbZ vkÑfr dks eksM+dj
ke
cukbZ tk ldrh gS\ (c) (d)
Ra
ANSWER KEYS
(Exercise-III)
1. (d) 7. (a) 13. (c) 19. (c) 25. (d) 31. (d) 37. (b) 43. (c) 49. (a) 54. (a)
2. (c) 8. (b) 14. (c) 20. (a) 26. (d) 32. (a) 38. (c) 44. (c) 50. (b) 55. (b)
3. (c) 9. (b) 15. (b) 21. (d) 27. (b) 33. (b) 39. (d) 45. (c) 51. (c)
4. (b) 10. (d) 16. (b) 22. (a) 28. (b) 34. (d) 40. (b) 46. (b) 52. (*)
5. (b) 11. (c) 17. (d) 23. (d) 29. (a) 35. (c) 41. (a) 47. (a) 53. (d)
6. (b) 12. (a) 18. (c) 24. (a) 30. (b) 36. (b) 42. (b) 48. (b)
Rakesh Yadav Readers Publication Pvt. Ltd 225
ww
w.
yo
ur
SOLUTION
sm
ah
bo
1. (d) From the two different views 6. (b) Number of cubes having two yky jax ls dsoy8 ?ku gh jaxs gksxsaA
ob
.w
of the dice it is clear that '6' colours
or
lies opposite to '5'. = 4×3 = 12 Red
dp
nks vyx&2 fLFkfr;ksa ls ;g vFkZ fudyrk nks jxksa ds ?kuksa =dh4×3
la[;k
re
= 12
gS fd5 ds foijhr 6 gksxkA
ss
7. (a)
.c
Layer-1
2. (b)
om
d
Re
Layer-2
First Layer Yellow
Layer-3
Second Layer
te
Layer-4
hi
W
Third Layer Black
Green
The cubes of middle row will have
r
no red colour 9 cubes 10. (d)
Si
The number of cubes which The Central cube will have no
are painted on 2 sides: colour
Layer-1
12 (n – 2). Now, out of 8 cubes, 4 cubes have Layer-2
n = length of bigger cube ÷ either yellow or white colour. Layer-3
av
length of smaller cube
,d ?ku ds chp dh ykbu esa fcuk yky jax ds ?kuksa Layer-4
So, 12 (3 – 2)
dh la[;k 9 ?ku 11. (c) The numbers 1, 2, 4 and 5 lie
12 × 1 = 12
dsUnz ds ?ku esa dksbZ jax ugha gksxkA on the faces adjacent to 3.
,sls ?kuksa dh la[;k ftldh nks lrg jaxh
gqbZ gSa% 8 ?ku esa ls pkj ?ku ;k
d
rks ihyh ;k liQsn jax ds Therefore, the number 6
Ya
12 (n – 2). gSA lies opposite 3.
n = cM+s ?ku dh Hkqtk dh yEckbZ ÷ 8. (b) The numbers 2, 4, 5 and 6 The numbers 3, 4, 5 and 6 lie
NksVs ?ku dh Hkqtk dh yEckbZ cannot be on the face on the faces adjacent to 1.
vr% 12 (3 – 2) opposite to 3. Therefore, the number 2
The numbers 1, 3, 4 and 6 lies opposite 1.
sh
12 × 1 = 12
cannot be on the face Now, the number 4 lies
3. (c) From the two views of cube it opposite 5.
opposite to 5.
is clear the '3' lies opposite to
'1' Therefore, 2 lies opposite 5. lrg la[;k 3, la[;k,sa
1, 2, 4 vkSj5
ke
,d ?ku dh nks fLFkfr;ksa ls ;g lkiQ gksrk Clearly, 4 lies opposite 6. ij lyaXu djrh gSA
gS fd3, 1 ds foijhr gSA fn;s x;s ?kuksa2, esa
4, 5 vkSj6, 3 ds ;|fi la[;k 6, 3 ds foijhr fLFkr gSA
foijhr ugha gks ldrs gS
Ra
6 la[;k 1, la[;k 3, 4, 5 vkSj6 ij
2 rFkk1, 3, 4 vkSj6, 5 ds foijhr ugha lyaXu djrh gSA
1 gks ldrk gSA
;|fi la[;k 2, 1 ds foijhr fLFkr gSA
blfy, , 5 ds foijhr 2 gksxk rFkk
6 ds
vc la[;k 4, 5 ds foijhr gSA
4. (b) If there is one triangle at foijhr 4 gksxkA
12. (a) From the two views of dice.
the bottom. there would be 9. (b) There are four cubes in
it is clear that number '1'
three triangle on the top. Layer-I and four cubes in
lies opposite to number '4'.
;fn ?ku dh fupyh lrg ij ,d f=kHkqt gS Layer IV which have only
one face painted red and all ,d ?ku dh pkj fLFkfr;ksa ls ;g irk
rks mldh Åijh lrg ij 3 f=kHkqt gksus
other faces not painted at pyrk gS fd4 ds foijhr 1 gksxkA
pkfg,A all. Thus there are eight 13. (c) The numbers 1, 2, 3 and 6
such cubes. are on adjacent faces of the
5. (b)
,d ?ku ds ijr& I esa4 ?ku gS rFkk number 5. Therefore, the
ijr& IV esa Hkh pkj ?ku gS ftlls dsoy number 3 lies opposite to 5.
lrg dks yky jax ls jaxk tkrk gS rks lHkh blesa5 dh lyaXu la[;k,sa
1, 2, 3 vkSj
nwljh lrg dks ugh jaxk tkrk gS blfy, 6 gS blfy, 5 ds foijhr 3 gksxkA
226 Rakesh Yadav Readers Publication Pvt. Ltd
ww
w.
yo
14. (c) The number 2, 4, 5 and 6 are each of the Layer-II, III and IV, the lrg 6 dh lyaXu la[;k,sa
1, 3, 4 vkSj
ur
5 gS blfy, 2, 6 ds foijhr fLFkr gSA
sm
on adjacent faces of the nine central cubes have no face
ah
number 3, Therefore, painted, the four cubes at the
23. (d) The numbers 1, 2, 5 and 6
bo
number 1 lies opposite to 3. corner have two faces painted and
ob
are on the adjacent faces of
The numbers 2, 3 and 5 are the remaining
.w
number 3. Therefore, the
or
on adjacent faces of the 12 cubes have one face painted. number 4 lies opposite 3.
dp
number 6, Therefore, the In Layer-V, the nine central The numbers 3, 4 and 6
re
number 4 lies opposite to 6. cubes have only one face painted,
ss
cannot be on the faces
Now, the number 5 lies the four cubes at the corner have
.c
opposite to 1.
om
opposite to 2, three faces painted and the
Therefore, 5 lies opposite 1.
la[;k 3, la[;k 2, 4, 5 vkSj6 ij remaining 12 cubes have two faces
painted. Now, 2 lies opposite 6.
lyaXu djrh gSA ;|fi la[;k1, 3 ds
Thus, the number of cubes having la[;k 3 ds lyaXu lrg dh la[;k,sa
1,
foijhr gSA
three faces painted is 8 2, 5 vkSj6 gS ;|fi la[;k 4, 3 ds
la[;k 6, la[;k 2, 3 vkSj5 lyaXu djrh
r
lrg -I esa] ,d lrg jaxs gq, 9 ?kuksa ds chp foijhr gSA
gSA ;|fi la[;k4, 6 ds foijhr gSA esa fLFkr4gS ?ku3 lrg jaxksa okys ?ku gS vkSj cps la[;k 3, 4 vkSj6 la[;k 1 ds foijhr
Si
vc la[;k 5, 2 ds foijhr gSA gq, 12 ?ku dh2 lrg jaxh gqbZ gSA-II, lrgIII ugha gks ldrh gSA
15. (b) The number 1, 3, 4 and 6 lie vkSjIV esa9 ?ku fcuk jxas gq, gSA rFkk4dksus ij
;|fi la[;k 5, 1 ds foijhr gSA
on the faces adjacent to the ?ku dh2 lrg jaxh gqbZ gS vkSj cps 12 ?kuksa
gq, dh
vc , 2, 6 ds foijhr gSA
av
number 2. Therefore, the
,d lrg jaxh gqbZ gSA
number 5 lies on the face 24. (a) The numbers 1, 2, 5 and 6
opposite to the number 2. lrg & V esa
] chp ds 9 ?ku ftuesa budh dsoy are on the adjacent faces of
;fn la[;k 2 dh lyaXu la[;k,sa 1, 3,
,d lrg gqbZ gS rFkk dksus
4 ?kuksa
ij dh rhu lrg the number 3. So, the
4 vkSj6 gSA ;fn la[;k
foijhr fLFkr gSA
5 la[;k 2 dfs
jaxh
gSA
gqbZ
rc]
gS
rhu
d vkSj
lrg ls
cps
12
jaxs
?kuksa
gq,
gq,
2 esa
lrg
?kuksa
jaxh
dh
gqbZ
8la[;k
gSA
number 4 lies opposite 3.
la[;k 3 dh lyaXu la[;k,s1, 2, 5
Ya
16. (b) Clearly, the number 4 lies
19. (c) Total number of cubes vkSj6 gS blfy, 4, 3 ds foijhr fLFkr
to the opposite of 2. = 6×6×4 = 144 gSA
iwjh lrg ls4, 2 ds foijhr fLFkr gSA ?kuksa dh lEiw.kZ la[;k = 144 25. (d) No Cube is there with two
= 6×6×4
20. (a) Altogether there are 15 red faces only. All the eight
sh
cubes. 10 cubes are seen in cubes have three red faces.
5
the figure. So, five cubes are nks yky lrg dk dksbZ Hkh ?ku ugha
8 lHkh
4 unseen in the figure. ?ku dh rhu lrg yky jaxks ls jaxh xbZ gSA
ke
1
;|fi blesa15 ?ku gS ftlesa 10
ls ?ku 26. (d) If we fold the option (a) the
fn[kkbZ ns jgs gS tcfd5 cps
?ku Nqis gq, number 2 will the opposite 5.
gSA If we fold the option (b) the
Ra
17. (d) There are 12 cubes.
21. (d) The letters A, B, D and E are number
blesa12 ?ku gSaA
on the adjacent faces of face 1 will lie opposite 3.
C. Therefore, some other If we fold the option (c) the
letter lies opposite 'C'. The number 2 will lie opposite 5.
letters B. C and E are on the Therefore, Answer Figure
adjacent faces of face D. (d) is correct.
Layer-I Therefore, A lies opposite D.
Layer-II ;fn ge fodYi (a) dks [kksysaxs
2 5,rks
18. (c) Layer-III lrg C dh lyaXu v{kjA, B, D vkSj ds foijhr gksxk ;fn ge fodYi
(b) dks
E gS ;|fi dqN nwljs v{kj
C ds foijhr
Layer-IV [kksyrs gS1,rks
3 ds foijhr gksxkA
fLFkr gS
D lrg dh lyaXu ds v{kjB,
Layer-V ;fn ge fodYi (c) dks [kksyrs gS rks
C vkSjE gSA blfy,A, D ds foijhr
la[;k 2, 5 ds foijhr gksxkA
In Layer-I, the nine central cubes fLFkr gSA
blfy, mÙkj vkd`fr (d) lgh gSA
have only one face painted, four 22. (a) The numbers 1, 3, 4 and 5
cubes at the corner have three are on the adjacent faces of 27. (b) From the two views of blocks
faces painted and the remaining 12 number 6. Therefore, 2 lies it is clear that 'F' is adjacent
cubes have two faces painted. In oppsite 6. to 'B', 'E' appears opposite 'C'
Rakesh Yadav Readers Publication Pvt. Ltd 227
ww
w.
yo
and 'A' appears opposite 31. (d) Answer Figure (4) shows the would be at the bottom, when
ur
sm
'D'. number of dots on its faces the heart shape is at the top.
ah
In option (1) 'F' ia adjacent to 'B' like a standard dice. So, in ikls dh nh xbZ fLFkfr ls irk pyrk gS fd
bo
this dice the difference
In option (3) 'E' is adjacent to 'C' o`Ùk fupyh lrg ij gksuk pkfg, tc fny
ob
between the numbers of
.w
In option (4) 'D' is adjacent to
dots on opposite faces may
ds vkdkj dk Åijh lrg ij gSA
or
'A'
dp
be 3. 36. (b)
nks fLFkfr;ksa ls ;g irk pyrkFgS
dhfd
re
mÙkj fp=k
4 ;g fn[kkrk gSA
ss
lyaXu v{kjB gSaA E, C ds foijhr gS
.c
32. (a) The number 1, 2, 5 and 6 are
vkSjA, D ds foijhr gSA
om
on the faces adjacent to the
fodYi (1) esa'F' ds lyaXu'B' gSA number 4. So, the number 37. (b) Three cubes each in the
column I and column II from
fodYi (3) esa'E' ds lyaXu'C' gSA 3 lies opposite 4.
the left are not seen.
The numbers 1, 3, 4 and 6
fodYi (4) esa'D' ds lyaXu'A' gSA Similarly two cubes each in
lies on the face adjacent to
r
28. (b) From the two views of blocks column III and IV are not
the number 2. So, the
it is clear that when 10 is seen
Si
number 5 lies opposite 2.
at the bottom. number 12 Total number of unseen
Now, the number 1 lies
will be at the top. cubes = 3+3+2+2 = 10
opposite 6.
nks fLFkfr;ksa ls irk pyrk gS fd fupyh izR;sd dkWye- I esa]3 ?ku gS vkSj
la[;k 4, la[;k 1, 2, 5 vkSj6 ij
lrg ij 10 gS12 gksxkA dkWye&II esa] ftlls ?ku fn[kkbZ ugha nsrs
av
layXu gS] blfy,3, 4 ds foijhr gSA
29. (a) 10 cubes are visible and 10 gS2 ?ku dkWye -III rFkkIV nksuksa esa
cubes are hidden. Clearly, la[;k 2, la[;k 1, 3, 4 vkSj6 ij fn[kkbZ ugha nsrs gSA
there is one column having layXu gS
blfy, 5, 2 ds foijhr gSA
vc
fcuk ns[ksa ?kuksa dh dqy la[;k
four cubes.
There are two columns each
d
1, 6 ds foijhr gSA
33. (b) The numbers 1, 3, 4 and 6
= 3 + 3 + 2 + 2 = 10
Ya
38. (c) The seven colours of a
having three cubes. are on faces adjacent to Rainbow are : Violet, Indigo.
There are three columns. number 5. Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange
each having two cubes. Therefore, 5 lies opposite 2. and Red. Thus, Violet colour
There are four columns. la[;k 5 dh layXu la[;k,s1, 3, 4 of rainbow is left out.
sh
each having only one cube. vkSj6 gSA bUnz/uq"k7 ds
jax bl izdkj gS& cSaxuh]
Thus, total number of cubes
vc 1, 6 ds foijhr gSA vklekuh] uhyk] gjk] ihyk] yky ukajxh
= 4+6+6+4 = 20 cubes. 39. (d) From the two views of the
34. (d) The numbers, 1, 2, 3 and 6
ke
20 ?kuksa esa
10 ls
?ku fn[kkbZ nsxs tcfd are on the faces adjacent to same dice it is clear that. B,
10 ?ku fn[kkbZ ugha nsxsa blls ;g lkiQ the number 3. Therefore, 4 C and E are on the faces
adjacent to A. so, E lies
gksrk fd ,d dkWye4ls?ku izkIr gksxsaA lies opposite 3.
Ra
opposite to A.
nks dkWye
3 ?ku fLFkr gSA The numbers 2, 3, 4 and 5
,d ikls ds rhu fLFkfr;ksa ls ;g Li"V
are on the faces adjacent to
rhu dkWye4 ?ku fLFkr gSA
the number gksrk gSAfdds lyaXuB, C vkSjE gS]
pkj dkWye esa dsoy ,d ?ku fLFkr gSA 1 . Th e r e f or e , 6 lies E, A ds foijhr gSA
= 4 + 6 + 6 + 4 = 20 ?ku opposite 1. 40. (b) Yellow, Green, Red and Blue
30. (b) The numbers 2, 4, 5 and 6 Now, the number 5 lies colours are on the faces
are on the adjacent faces of opposite 2. adjacent to Purple. So,
Orange colour is opposite to
number 3, So, number 1 lies la[;k 3 dh lyaXu la[;k,sa
1, 2, 3 v kSj
opposite 3. The number 5 is Purple.
6 gS blfy, 4, 3 ds foijhr fLFkr gSA
on the adjacent faces of cSaxuh jax ds layXu jax ihyk] gjk] yky
numbers 4 and 6. So, la[;k 3, la[;k 1, 2, 3 vkSj6 ij vkSj uhyk gSA blfy,] cSaxuh jax ds foijhr
number 5 lies opposite 2. l yaXu gS blfy, la[;k
4, 3 ds foijhr gSA ukjaxh gksxkA
la[;k 3 ds lyaXu la[;k,s2, 4, 5 vkSj 1. blfy, 6, 1 ds foijhr fLFkr gSA41. (a) After folding the sheet of
6 gS blfy, 1, 3 ds foijhr fLFkr;fn
gS vc la[;k 5, 2 ds foijhr fLFkr gSA paper in the form of a cube
la[;k 5 dh lYkaXu la[;k,sa
4 vkSj6 gS 35. (c) From the given positions of will lie opposite
blfy, 5, 2 ds foijhr fLFkr gSA a dice, it is clear that circle
will lie opposite
228 Rakesh Yadav Readers Publication Pvt. Ltd
You might also like
- Harry Lorayne - Rim ShotsDocument156 pagesHarry Lorayne - Rim ShotsDavid magician100% (5)
- All in The CardsDocument5 pagesAll in The CardsJohn Bertrum Ford100% (4)
- MTG: QL Magic Turn StructureDocument1 pageMTG: QL Magic Turn StructurecianopanzaNo ratings yet
- MUET Model Paper ReadingDocument8 pagesMUET Model Paper ReadingNicholson Nicholson0% (1)
- Permuting CardsDocument5 pagesPermuting CardsTerryNo ratings yet
- Blackjack FlowchartDocument1 pageBlackjack FlowchartJose ArmazaNo ratings yet
- Hoyle Card Games HelpDocument146 pagesHoyle Card Games HelpPandexaNo ratings yet
- Coding DecodingDocument56 pagesCoding DecodingdddfeNo ratings yet
- 16-Clay Bricklaying Made EasyDocument4 pages16-Clay Bricklaying Made EasymahnoorimranNo ratings yet
- Reykjavic Arctic Oct 2022Document92 pagesReykjavic Arctic Oct 2022gabriel_leccasNo ratings yet
- V Si R: Number SeriesDocument11 pagesV Si R: Number SeriesdddfeNo ratings yet
- DGCA Module 08 AUGUST 2017 HANDWRITTEN SET 2 PDFDocument4 pagesDGCA Module 08 AUGUST 2017 HANDWRITTEN SET 2 PDFShiva JeevaNo ratings yet
- 08 August 2017Document4 pages08 August 2017Rakesh BhoraNo ratings yet
- Easter EggsDocument2 pagesEaster EggshappyNo ratings yet
- DW Ard S: Swing 48 - Rocky GressetDocument5 pagesDW Ard S: Swing 48 - Rocky GressetHikaru HashimotoNo ratings yet
- DW Ard S: Swing 48 - Rocky GressetDocument5 pagesDW Ard S: Swing 48 - Rocky GressetHikaru HashimotoNo ratings yet
- Healthy PlateDocument4 pagesHealthy PlateJessica ArvizuNo ratings yet
- DGCA Module 08 MARCH 2017 HANDWRITTEN SET 1 & 2 PDFDocument5 pagesDGCA Module 08 MARCH 2017 HANDWRITTEN SET 1 & 2 PDFShiva JeevaNo ratings yet
- 08 March 2017Document5 pages08 March 2017Rakesh BhoraNo ratings yet
- Dgca ModuleDocument2 pagesDgca ModulejanhaviNo ratings yet
- La Psicologia de Los GruposDocument9 pagesLa Psicologia de Los Gruposgadramon69No ratings yet
- ILR - 113 - HTW Elephant? - Sanskrit - VK - 100922Document9 pagesILR - 113 - HTW Elephant? - Sanskrit - VK - 100922Rajesh SoundararajanNo ratings yet
- Class Test No.7Document8 pagesClass Test No.7NIRMALANo ratings yet
- SM 13Document983 pagesSM 13gustavo holikNo ratings yet
- General Catalog: Butterfly Valves Knife Gate Valves Pinch ValvesDocument30 pagesGeneral Catalog: Butterfly Valves Knife Gate Valves Pinch ValvesNikhil JaiswalNo ratings yet
- DoorCylinders2011 AbloyDocument20 pagesDoorCylinders2011 AbloyCecília PerdigãoNo ratings yet
- Vpam and 04 2017 enDocument2 pagesVpam and 04 2017 endemirmustafa7777No ratings yet
- V Si R: Blood RelationDocument27 pagesV Si R: Blood RelationdddfeNo ratings yet
- Catalog Wire Rope Permaloc SlingsDocument22 pagesCatalog Wire Rope Permaloc Slingsramakrishna3333No ratings yet
- Party ChartDocument2 pagesParty Chartapi-379368506No ratings yet
- Vocabulary: Common ObjectsDocument2 pagesVocabulary: Common ObjectsEdith ChambillaNo ratings yet
- RPV Unit 2Document2 pagesRPV Unit 2Rodrigo Miranda NascimentoNo ratings yet
- My Heart Will Go On Vyacheslav ShuvalovDocument6 pagesMy Heart Will Go On Vyacheslav ShuvalovXael IgnisNo ratings yet
- 5 6332280742185271392Document884 pages5 6332280742185271392Dayanandhi ElangovanNo ratings yet
- SM 43Document486 pagesSM 43Salud y Cuidado AutomotrizNo ratings yet
- Em Am B D G: Standard TuningDocument3 pagesEm Am B D G: Standard TuningОлександр РешетухаNo ratings yet
- La Tarde Slvia Prez Cruz LaTardeDocument6 pagesLa Tarde Slvia Prez Cruz LaTardeSergi Zaragoza GarciaNo ratings yet
- dhmh113 PDFDocument13 pagesdhmh113 PDFDayakar RanaNo ratings yet
- Love of Crochet - Fall 2015Document100 pagesLove of Crochet - Fall 2015Nami Sanz100% (5)
- T T 5537 Healthy Eating Divided Plate Sorting Activity Ver 2Document4 pagesT T 5537 Healthy Eating Divided Plate Sorting Activity Ver 2abiodun ilesanmiNo ratings yet
- Map Showing The Fireline OF Brgy. Panggao Munai, Lanao Del NorteDocument1 pageMap Showing The Fireline OF Brgy. Panggao Munai, Lanao Del NorteAlga Zalli Datu-daculaNo ratings yet
- Andy Wood 12 Bar ImprovisationDocument2 pagesAndy Wood 12 Bar ImprovisationJames Gale100% (1)
- Refrigeration Systems Product MatrixDocument3 pagesRefrigeration Systems Product MatrixDaniel MachadoNo ratings yet
- Liesing: Montag-Freitag (Schule) Montag-Freitag (Ferien) Samstag Sonn-Und FeiertagDocument28 pagesLiesing: Montag-Freitag (Schule) Montag-Freitag (Ferien) Samstag Sonn-Und FeiertagSamuel PuławskiNo ratings yet
- User Manual Xiaomi Mi Robot Vacuum-Mop Essential (English - 327 Pages)Document1 pageUser Manual Xiaomi Mi Robot Vacuum-Mop Essential (English - 327 Pages)jjmfjtmnj8No ratings yet
- Get The R: Esult S You Want!Document28 pagesGet The R: Esult S You Want!Mannan WayneNo ratings yet
- Compound Interest PDFDocument2 pagesCompound Interest PDFPrem KumarNo ratings yet
- General w300Document30 pagesGeneral w300Felipe SalvatierraNo ratings yet
- India Top CountriesDocument1 pageIndia Top CountriesMayank SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lightning Strike Counter: Lightning Protection Equipment CatalogDocument1 pageLightning Strike Counter: Lightning Protection Equipment CatalogComsip400No ratings yet
- The Punisher (Guitar Tab)Document2 pagesThe Punisher (Guitar Tab)Doğukan KıyıklıkNo ratings yet
- K Lic MjI1MC00ODYzLTM5OTA K SCH Y2hyaXN0aW5lLmRvbm9odWVAZmNwcy5vcmc Kami Export - Ucm 4519Document2 pagesK Lic MjI1MC00ODYzLTM5OTA K SCH Y2hyaXN0aW5lLmRvbm9odWVAZmNwcy5vcmc Kami Export - Ucm 4519Hannah NessNo ratings yet
- 500 Miles High: IntroDocument2 pages500 Miles High: IntroSéraphin SacavinNo ratings yet
- 2013 Ucc ResultsDocument2 pages2013 Ucc ResultsJane PollyNo ratings yet
- Wellness WheelDocument2 pagesWellness WheelpinalNo ratings yet
- vdSchans2011_Urban agriculture in developed economiesDocument16 pagesvdSchans2011_Urban agriculture in developed economiesAbel CrawfordNo ratings yet
- Fahrplan Citybus 62aDocument30 pagesFahrplan Citybus 62aMilicaVristalicaNo ratings yet
- Cityringen Metro Project: Referenza Tecnica - Technical ReferenceDocument8 pagesCityringen Metro Project: Referenza Tecnica - Technical ReferenceSalvatore MirandaNo ratings yet
- Master Chart On 20 11 22 NewDocument334 pagesMaster Chart On 20 11 22 NewBabu SumanNo ratings yet
- 003 6410501471 1 5ข้อ PDFDocument2 pages003 6410501471 1 5ข้อ PDFTawan BOONMANGMEENo ratings yet
- 2021-04-01 CosmopolitanDocument116 pages2021-04-01 CosmopolitanslavcoqNo ratings yet
- EGM2 Issue 40 (October 1997)Document150 pagesEGM2 Issue 40 (October 1997)cocranNo ratings yet
- Castlegar/Slocan Valley Pennywise June 27, 2017Document48 pagesCastlegar/Slocan Valley Pennywise June 27, 2017Pennywise PublishingNo ratings yet
- The Crown's Game GameDocument1 pageThe Crown's Game GameEpicReads100% (1)
- In Bed with the Word: Reading, Spirituality, and Cultural PoliticsFrom EverandIn Bed with the Word: Reading, Spirituality, and Cultural PoliticsNo ratings yet
- Section 4.4 SolutionsDocument4 pagesSection 4.4 SolutionsmojarramanNo ratings yet
- The First Tarot DeckDocument5 pagesThe First Tarot DeckchauNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Aptitude - Vol 2Document93 pagesQuantitative Aptitude - Vol 2Ian MckenzyNo ratings yet
- Regicide - RuleBook - RTPDocument2 pagesRegicide - RuleBook - RTPIacopoMariaFilippoBarniNo ratings yet
- En Manual Gwent ONLINEDocument6 pagesEn Manual Gwent ONLINEdagushNo ratings yet
- Catalog 048 WEBDocument103 pagesCatalog 048 WEBNaveSilva100% (1)
- Intermediate Course No Trump Slam Bidding 1Document19 pagesIntermediate Course No Trump Slam Bidding 1Mario RubanathanNo ratings yet
- E-Book - The Ultimate Card Magic TricksDocument7 pagesE-Book - The Ultimate Card Magic TricksMitch86% (7)
- Cardistry Tricks TutorialsDocument6 pagesCardistry Tricks TutorialsCarlos Mc5No ratings yet
- 7 WONDERS SOLITAIRE VARIANT Version 1.0 PDFDocument1 page7 WONDERS SOLITAIRE VARIANT Version 1.0 PDFGreg NiederNo ratings yet
- The Art of Card Magic Box #1 Books Finished USE Stand Up 1Document1 pageThe Art of Card Magic Box #1 Books Finished USE Stand Up 1MagicManNo ratings yet
- Game of Trains Rules en WebDocument1 pageGame of Trains Rules en Webges176No ratings yet
- Instrucciones Del BoomoDocument2 pagesInstrucciones Del BoomoksabinaNo ratings yet
- Verflixxt Hoch 2Document2 pagesVerflixxt Hoch 2Brian MooreNo ratings yet
- Hanamikoji Rule EN RGB PDFDocument2 pagesHanamikoji Rule EN RGB PDFAnonymous HbUc1qQcNo ratings yet
- UNO Rules PDFDocument3 pagesUNO Rules PDFankuramity50% (2)
- The Perfect Acaan Theory PDFDocument1 pageThe Perfect Acaan Theory PDFjaylen gardnerNo ratings yet
- 6 EZ To Do Card MiraclesDocument22 pages6 EZ To Do Card MiraclesChuck100% (2)
- En GARDE - Advanced Rules ReferenceDocument2 pagesEn GARDE - Advanced Rules Referencesch21No ratings yet
- Lennart Green Magic Card TricksDocument6 pagesLennart Green Magic Card Tricksmagi0170% (2)
- 3 Effects From Careys Way PDFDocument9 pages3 Effects From Careys Way PDFEvan Hamilton0% (1)
- KELTIS RulebookDocument3 pagesKELTIS RulebookIsa R. AkbarNo ratings yet
- INDEX OF: Jean Hugard & Frederick Braue - Expert Card TechniqueDocument7 pagesINDEX OF: Jean Hugard & Frederick Braue - Expert Card TechniqueMadsStrangeNo ratings yet
- Isaludo - Beta 1.0 20210125Document54 pagesIsaludo - Beta 1.0 20210125desmontesNo ratings yet