Professional Documents
Culture Documents
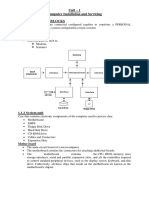
Basic Hardware Configuration of PC
Basic Hardware Configuration of PC
Uploaded by
pubgyouknow1Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Modulex3 Bruchure GBDocument12 pagesModulex3 Bruchure GBmrinal570No ratings yet
- Typical Configuration of Computer SystemDocument90 pagesTypical Configuration of Computer Systemgani100% (1)
- HP Compaq Merger Full ReportDocument31 pagesHP Compaq Merger Full ReportMuhammad Mubasher Rafique86% (7)
- Mainboard Components With Their FunctionsDocument11 pagesMainboard Components With Their FunctionsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- What Is ComputerDocument19 pagesWhat Is ComputerVivek FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3, HardwareDocument3 pagesChapter 3, HardwareRaj Srivastav RJNo ratings yet
- PC BasicsDocument19 pagesPC BasicsPavleŠlehtaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1Document2 pagesExperiment No.1SubiNo ratings yet
- Maxim Nyansa I.T Solution (Nigeria) : Note On Computer RepairsDocument16 pagesMaxim Nyansa I.T Solution (Nigeria) : Note On Computer RepairsOlúwaṣẹ́gunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (The Visible PC)Document9 pagesChapter 3 (The Visible PC)Rifat HassanNo ratings yet
- Parts of PCDocument2 pagesParts of PCAlex -No ratings yet
- Computer InstallationDocument23 pagesComputer Installationkhatib mtumweniNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Computer With Their FunctionsDocument5 pagesParts of A Computer With Their Functionsglenn0805No ratings yet
- Peripherals of A ComputerDocument16 pagesPeripherals of A ComputerAkmal HishamNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware: Personal Computer Operating System SoftwareDocument15 pagesComputer Hardware: Personal Computer Operating System SoftwareallahabadcityNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument37 pagesComputer HardwareTECH REALMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1nashwah mahomedNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer Hardware and TroubleshootingDocument39 pagesBasic Computer Hardware and TroubleshootingR. BorresNo ratings yet
- Personal Computer HardwareDocument16 pagesPersonal Computer HardwareSonu DhangarNo ratings yet
- The 8086 Computer Architectu Re and Hardware Compone NTS: Ronel CortezDocument16 pagesThe 8086 Computer Architectu Re and Hardware Compone NTS: Ronel CortezRonel CortezNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument18 pagesMotherboardRegine ManuelNo ratings yet
- Cew Exp 1 PC Disassembling and AssemblingDocument14 pagesCew Exp 1 PC Disassembling and AssemblingAluri shruthiNo ratings yet
- BASIC COMPONENTS Chapter3Document8 pagesBASIC COMPONENTS Chapter3pldtuyyNo ratings yet
- Systemunitcomponents 110217032152 Phpapp01 PDFDocument12 pagesSystemunitcomponents 110217032152 Phpapp01 PDFStephanie S. Afable-ReyesNo ratings yet
- Types of Computer HardwareDocument3 pagesTypes of Computer HardwareManuel Delfin Jr.No ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument18 pagesMotherboardRegine ManuelNo ratings yet
- ACT ReviewerDocument10 pagesACT ReviewerYnaNo ratings yet
- Computer System ComponentsDocument11 pagesComputer System ComponentsNoone F. moonNo ratings yet
- 1.personal Computer Hardware Architecture: Assignment: Embedded SystemsDocument8 pages1.personal Computer Hardware Architecture: Assignment: Embedded SystemsSATYAPRAKASH DASNo ratings yet
- Personal Computer HardwareDocument22 pagesPersonal Computer HardwareSugandhan AvNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer and Its Applications: Name: Patel Rahi ID: 21IT117 Batch: IT-2 (C2)Document12 pagesIntroduction To Computer and Its Applications: Name: Patel Rahi ID: 21IT117 Batch: IT-2 (C2)21IT117 PATEL RAHI PINKALKUMARNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Prepared byDocument22 pagesProject Report: Prepared byumeshNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware BasicsDocument15 pagesComputer Hardware BasicsDiotima Bhattacharya100% (1)
- Hardware: Computer Hardware Is A Collective Term Used To Describe Any of The Physical Components of AnDocument4 pagesHardware: Computer Hardware Is A Collective Term Used To Describe Any of The Physical Components of AnkalNo ratings yet
- Computer Workshop PSBTEDocument21 pagesComputer Workshop PSBTEShubhanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware ServicingDocument34 pagesComputer Hardware ServicingJhayden BlueNo ratings yet
- Main Parts of Desktop Computer - TarpDocument1 pageMain Parts of Desktop Computer - TarpChristopher Jay GervacioNo ratings yet
- Install and Configure Computer SystemDocument254 pagesInstall and Configure Computer SystemTeraGamingNo ratings yet
- Itws 2Document33 pagesItws 2rg22No ratings yet
- Caring For Network and Computer HardwareDocument18 pagesCaring For Network and Computer Hardwarebiruk mollaNo ratings yet
- Computer ComponentsDocument8 pagesComputer ComponentsbrbioinfoNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1Document9 pagesAssignment No.1asma abbasNo ratings yet
- Computer ScienceDocument22 pagesComputer ScienceHoorain HameedNo ratings yet
- CMT ProjectDocument7 pagesCMT ProjectHet DalwadiNo ratings yet
- Computer Workshop Job 1Document19 pagesComputer Workshop Job 1ayushkumar77447No ratings yet
- System Components 1: Muhamed ShejDocument14 pagesSystem Components 1: Muhamed ShejAdna Islamoska❤️No ratings yet
- Student Handout 1 Hardware Components of A ComputerDocument4 pagesStudent Handout 1 Hardware Components of A ComputerLemuel Condes100% (1)
- It Lab 1 .Document7 pagesIt Lab 1 .carl billNo ratings yet
- Seminar On MotherboardDocument21 pagesSeminar On MotherboardPrathamesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Latest Basic Computer Hardware Interview QuestionsDocument3 pagesLatest Basic Computer Hardware Interview QuestionsSahil ThakurNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument36 pagesChapter TwoyonasNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware BasicDocument17 pagesComputer Hardware Basicvik ramNo ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticsDocument13 pagesNursing InformaticsNursidar Pascual MukattilNo ratings yet
- Lec02 - Components of ComputersDocument17 pagesLec02 - Components of ComputersBilal ImranNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics DefinitonDocument8 pagesComputer Basics DefinitonJeetender nath100% (1)
- Computer HardwareDocument11 pagesComputer HardwareRodriguez NikkoNo ratings yet
- MuntasirDocument1 pageMuntasirabdurahmonzodamuntasirNo ratings yet
- TLEd 204 MT Lesson 1Document46 pagesTLEd 204 MT Lesson 1balanemaryjoy4No ratings yet
- Building A Computer SystemDocument4 pagesBuilding A Computer SystemKay LinnNo ratings yet
- The Major Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesThe Major Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsJosekutty N Joseph75% (4)
- Basic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitDocument35 pagesBasic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitShenny CariscalNo ratings yet
- 24051Document3 pages24051bhuvi2312100% (1)
- DiamondDocument158 pagesDiamondYashodeep KambleNo ratings yet
- Al-Cap Company ProfileDocument10 pagesAl-Cap Company ProfileMadaherAliNo ratings yet
- SIMATICPCS7 STPCS7AO Complete English 2013 WebDocument180 pagesSIMATICPCS7 STPCS7AO Complete English 2013 WebDiana ArredondoNo ratings yet
- BSNL 3G Data Card TrainingDocument47 pagesBSNL 3G Data Card Trainingsandcauli1147No ratings yet
- TRY TRX Datasheet Moore IndustriesDocument8 pagesTRY TRX Datasheet Moore IndustriesHendri HnzNo ratings yet
- A GSM Based Password Protection System Used in AtmDocument53 pagesA GSM Based Password Protection System Used in Atmprince4444No ratings yet
- Rock Link 800 User ManualDocument382 pagesRock Link 800 User ManualJOELSAUCEDONo ratings yet
- The Basic Stamp Ii and LabviewDocument10 pagesThe Basic Stamp Ii and Labviewviernes06No ratings yet
- Universal Weighing Terminal, W&M Approved, For Industrial UseDocument4 pagesUniversal Weighing Terminal, W&M Approved, For Industrial UseDeysi Flores RiveraNo ratings yet
- Flexible Automation: Z Z Z ZDocument12 pagesFlexible Automation: Z Z Z ZMuhammad HafizNo ratings yet
- Exploring wV1 Grader CAPDocument8 pagesExploring wV1 Grader CAPsargeywargeyNo ratings yet
- ETAP 22 - System RequirementsDocument1 pageETAP 22 - System RequirementsMuhammad FarooqNo ratings yet
- Fingerprint Time Attendance ManualDocument72 pagesFingerprint Time Attendance ManualRohit SinghNo ratings yet
- MSM BSM DB Uk 006 PDFDocument16 pagesMSM BSM DB Uk 006 PDFioacymNo ratings yet
- PCAdvisor201401 PDFDocument148 pagesPCAdvisor201401 PDFGeorge RadulescuNo ratings yet
- APC - Xmas 2017 AU PDFDocument116 pagesAPC - Xmas 2017 AU PDFSuman Abir PaulNo ratings yet
- It Workshop Lab ManualDocument144 pagesIt Workshop Lab Manualhanji17No ratings yet
- Sds Operation M Ver6Document106 pagesSds Operation M Ver6Roberto Vertel RomeroNo ratings yet
- Beekey10: Game Solution For China Mobile-Fresh File - RarDocument7 pagesBeekey10: Game Solution For China Mobile-Fresh File - RarAmelyn CanillasNo ratings yet
- Notebook Bangho PDFDocument226 pagesNotebook Bangho PDFrussofranco86No ratings yet
- Assignment#3 (Belleza) BSA1Document5 pagesAssignment#3 (Belleza) BSA1Karl Ethan MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- BED 215 Lecture Note 2024Document35 pagesBED 215 Lecture Note 2024ngozig82No ratings yet
- CAD Flatbed: User's ManualDocument17 pagesCAD Flatbed: User's ManualseppeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information Technology: DR Dharmendra Kumar KanchanDocument83 pagesIntroduction To Information Technology: DR Dharmendra Kumar KanchanSadhika KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Mikroboard For Pic 40-Pin: ManualDocument6 pagesMikroboard For Pic 40-Pin: ManualDaniel Crutan100% (1)
- Trend Open Protocol Server: Data SheetDocument8 pagesTrend Open Protocol Server: Data SheetMOUMENNo ratings yet
- 5 Pen PC Technology Powerpoint PresentationDocument18 pages5 Pen PC Technology Powerpoint PresentationnishiraviNo ratings yet
Basic Hardware Configuration of PC
Basic Hardware Configuration of PC
Uploaded by
pubgyouknow1Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Hardware Configuration of PC
Basic Hardware Configuration of PC
Uploaded by
pubgyouknow1Copyright:
Available Formats
Basic Hardware Configuration of PC:
A PC typically includes:
Central Processing Unit (CPU): The "brain" of the computer that executes instructions.
Motherboard: The main circuit board connecting all components.
RAM (Random Access Memory): Temporary storage for data and programs.
Storage: Hard drives (HDDs) or solid-state drives (SSDs) for data storage.
Power Supply Unit (PSU): Provides electrical power.
Graphics Card (optional): Enhances graphics performance.
Input/Output Ports: USB, HDMI, audio jacks, etc.
Peripherals: Keyboard, mouse, monitor, etc.
Main Characteristics of Monitors:
Screen Size: Measured diagonally in inches.
Resolution: Number of pixels (e.g., 1920x1080).
Refresh Rate: Number of times the screen refreshes per second (e.g., 60Hz).
Panel Type: LCD, OLED, IPS, etc.
Response Time: How quickly pixels change color.
Connectivity: HDMI, DisplayPort, VGA, etc.
Device, Structure, and Operation Principles of the Keyboard:
Device: An input device with keys for typing and controlling the computer.
Structure: Consists of keys arranged in a QWERTY layout.
Operation: When a key is pressed, it completes an electrical circuit, sending a signal to the
computer, which then registers the keypress.
Design and Function of the Mouse:
Design: Hand-held device with buttons and a sensor.
Function: Moves a cursor on the screen and interacts with graphical elements. Left and right
buttons are for clicking, and the scroll wheel is for navigation.
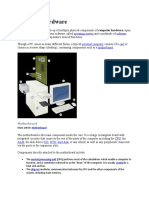
Motherboard Device:
Device: The main circuit board.
Components: Houses CPU, RAM, connectors, and chipsets.
Function: Connects and facilitates communication between all hardware components.
Computer Cards, Sockets, Slots, Jumpers, Connectors, and Cables:
Cards: Expansion cards like graphics cards.
Sockets and Slots: Connectors for attaching cards to the motherboard.
Jumpers: Small connectors used to configure hardware settings.
Connectors and Cables: Used for data transfer and power distribution between components.
Computer Power Supply:
Function: Converts AC power from the wall into DC power for the computer's components.
Wattage: Rated in watts to supply sufficient power to all components.
Hard Drives: Device, Interface, Connection:
Device: Storage devices for data.
Interface: Connection protocol (e.g., SATA, NVMe) for data transfer.
Connection: Physical attachment to the motherboard and PSU for power.
The CD-ROM Drive:
Device: Optical drive used for reading CDs and DVDs.
Function: Reads data from optical discs for software installation, media playback, and data
access.
Video Adapter, Video Modes, and Resolution:
Video Adapter (Graphics Card): Enhances graphics performance and connects to the monitor.
Video Modes: Configuration settings for the display.
Resolution: Determines the number of pixels displayed on the screen (e.g., 1920x1080).
Sound and Network Cards:
Sound Card: Enables audio input and output.
Network Card: Facilitates network connectivity, often integrated into the motherboard.
Main Memory (RAM):
Function: Provides fast, volatile storage for currently running programs and data.
Processors: Buses, Instruction System, Basic Parameters:
Buses: Data pathways for communication between CPU, RAM, and peripherals.
Instruction System: The set of commands (instructions) the CPU can execute.
Basic Parameters: Include clock speed (measured in GHz), number of cores, and cache size
The ROM Chip and the BIOS System:
ROM Chip: Read-Only Memory is a type of memory that stores data permanently and cannot be
easily modified.
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System): Software stored in ROM that initializes hardware
components during the computer's startup process.
The Nonvolatile Memory CMOS:
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor): A type of nonvolatile memory used to
store BIOS settings and system configuration data, including date and time.
Bus Motherboard Interfaces:
Bus Interfaces: These are pathways on the motherboard that allow data transfer between the
CPU, RAM, and peripheral devices. Common bus interfaces include PCIe, USB, SATA, and
more.
The Functions of the Microprocessor Kit (Chipset):
Chipset: The chipset is a set of chips on the motherboard that manages data flow and
communication between the CPU, RAM, and other hardware components. It also provides
support for various interfaces and expansion slots.
19?
20?
21?
Peripheral Devices of Personal Computer:
Peripheral devices include input devices (e.g., keyboard, mouse), output devices (e.g., monitor,
printer), and storage devices (e.g., hard drives, USB drives) that connect to a personal
computer to extend its functionality.
Signed Data Input Devices:
These devices capture input through physical movements and typically include devices like the
mouse, touchpad, and stylus.
Command and Control Devices:
Command and control devices include keyboards and game controllers used for input and
control of software and games.
Graphical Data Input Devices:
Graphical data input devices are used for precise input in graphical applications and include
graphics tablets and touchscreens.
Data Output Devices:
Data output devices include monitors for displaying visual information, printers for producing
hard copies of documents, and speakers for audio output.
Storage Devices:
Storage devices are used to store data and can include hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs),
optical drives (e.g., CD/DVD drives), and external drives.
Data Interchange Devices:
Data interchange devices like USB drives, memory cards, and external hard drives allow for the
transfer of data between computers and other devices.
The Order of Installation and Connection of Hard Drives, Memory Modules, Various Cards, and
Adapters:
The specific order and process of installation can vary depending on the computer's
configuration and components. It's essential to follow manufacturer instructions and guidelines
for proper installation to avoid hardware issues. Generally, the order might be:
Install the CPU and RAM on the motherboard.
Connect power cables and data cables to the motherboard.
Install additional cards (graphics card, sound card, etc.) into expansion slots.
Connect storage devices (hard drives, SSDs) to the motherboard and PSU.
Install peripheral devices (keyboard, mouse, monitor) as needed.
Boot up the computer and install the operating system and drivers.p
You might also like
- Modulex3 Bruchure GBDocument12 pagesModulex3 Bruchure GBmrinal570No ratings yet
- Typical Configuration of Computer SystemDocument90 pagesTypical Configuration of Computer Systemgani100% (1)
- HP Compaq Merger Full ReportDocument31 pagesHP Compaq Merger Full ReportMuhammad Mubasher Rafique86% (7)
- Mainboard Components With Their FunctionsDocument11 pagesMainboard Components With Their FunctionsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- What Is ComputerDocument19 pagesWhat Is ComputerVivek FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3, HardwareDocument3 pagesChapter 3, HardwareRaj Srivastav RJNo ratings yet
- PC BasicsDocument19 pagesPC BasicsPavleŠlehtaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1Document2 pagesExperiment No.1SubiNo ratings yet
- Maxim Nyansa I.T Solution (Nigeria) : Note On Computer RepairsDocument16 pagesMaxim Nyansa I.T Solution (Nigeria) : Note On Computer RepairsOlúwaṣẹ́gunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (The Visible PC)Document9 pagesChapter 3 (The Visible PC)Rifat HassanNo ratings yet
- Parts of PCDocument2 pagesParts of PCAlex -No ratings yet
- Computer InstallationDocument23 pagesComputer Installationkhatib mtumweniNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Computer With Their FunctionsDocument5 pagesParts of A Computer With Their Functionsglenn0805No ratings yet
- Peripherals of A ComputerDocument16 pagesPeripherals of A ComputerAkmal HishamNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware: Personal Computer Operating System SoftwareDocument15 pagesComputer Hardware: Personal Computer Operating System SoftwareallahabadcityNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument37 pagesComputer HardwareTECH REALMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1nashwah mahomedNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer Hardware and TroubleshootingDocument39 pagesBasic Computer Hardware and TroubleshootingR. BorresNo ratings yet
- Personal Computer HardwareDocument16 pagesPersonal Computer HardwareSonu DhangarNo ratings yet
- The 8086 Computer Architectu Re and Hardware Compone NTS: Ronel CortezDocument16 pagesThe 8086 Computer Architectu Re and Hardware Compone NTS: Ronel CortezRonel CortezNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument18 pagesMotherboardRegine ManuelNo ratings yet
- Cew Exp 1 PC Disassembling and AssemblingDocument14 pagesCew Exp 1 PC Disassembling and AssemblingAluri shruthiNo ratings yet
- BASIC COMPONENTS Chapter3Document8 pagesBASIC COMPONENTS Chapter3pldtuyyNo ratings yet
- Systemunitcomponents 110217032152 Phpapp01 PDFDocument12 pagesSystemunitcomponents 110217032152 Phpapp01 PDFStephanie S. Afable-ReyesNo ratings yet
- Types of Computer HardwareDocument3 pagesTypes of Computer HardwareManuel Delfin Jr.No ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument18 pagesMotherboardRegine ManuelNo ratings yet
- ACT ReviewerDocument10 pagesACT ReviewerYnaNo ratings yet
- Computer System ComponentsDocument11 pagesComputer System ComponentsNoone F. moonNo ratings yet
- 1.personal Computer Hardware Architecture: Assignment: Embedded SystemsDocument8 pages1.personal Computer Hardware Architecture: Assignment: Embedded SystemsSATYAPRAKASH DASNo ratings yet
- Personal Computer HardwareDocument22 pagesPersonal Computer HardwareSugandhan AvNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer and Its Applications: Name: Patel Rahi ID: 21IT117 Batch: IT-2 (C2)Document12 pagesIntroduction To Computer and Its Applications: Name: Patel Rahi ID: 21IT117 Batch: IT-2 (C2)21IT117 PATEL RAHI PINKALKUMARNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Prepared byDocument22 pagesProject Report: Prepared byumeshNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware BasicsDocument15 pagesComputer Hardware BasicsDiotima Bhattacharya100% (1)
- Hardware: Computer Hardware Is A Collective Term Used To Describe Any of The Physical Components of AnDocument4 pagesHardware: Computer Hardware Is A Collective Term Used To Describe Any of The Physical Components of AnkalNo ratings yet
- Computer Workshop PSBTEDocument21 pagesComputer Workshop PSBTEShubhanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware ServicingDocument34 pagesComputer Hardware ServicingJhayden BlueNo ratings yet
- Main Parts of Desktop Computer - TarpDocument1 pageMain Parts of Desktop Computer - TarpChristopher Jay GervacioNo ratings yet
- Install and Configure Computer SystemDocument254 pagesInstall and Configure Computer SystemTeraGamingNo ratings yet
- Itws 2Document33 pagesItws 2rg22No ratings yet
- Caring For Network and Computer HardwareDocument18 pagesCaring For Network and Computer Hardwarebiruk mollaNo ratings yet
- Computer ComponentsDocument8 pagesComputer ComponentsbrbioinfoNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1Document9 pagesAssignment No.1asma abbasNo ratings yet
- Computer ScienceDocument22 pagesComputer ScienceHoorain HameedNo ratings yet
- CMT ProjectDocument7 pagesCMT ProjectHet DalwadiNo ratings yet
- Computer Workshop Job 1Document19 pagesComputer Workshop Job 1ayushkumar77447No ratings yet
- System Components 1: Muhamed ShejDocument14 pagesSystem Components 1: Muhamed ShejAdna Islamoska❤️No ratings yet
- Student Handout 1 Hardware Components of A ComputerDocument4 pagesStudent Handout 1 Hardware Components of A ComputerLemuel Condes100% (1)
- It Lab 1 .Document7 pagesIt Lab 1 .carl billNo ratings yet
- Seminar On MotherboardDocument21 pagesSeminar On MotherboardPrathamesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Latest Basic Computer Hardware Interview QuestionsDocument3 pagesLatest Basic Computer Hardware Interview QuestionsSahil ThakurNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument36 pagesChapter TwoyonasNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware BasicDocument17 pagesComputer Hardware Basicvik ramNo ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticsDocument13 pagesNursing InformaticsNursidar Pascual MukattilNo ratings yet
- Lec02 - Components of ComputersDocument17 pagesLec02 - Components of ComputersBilal ImranNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics DefinitonDocument8 pagesComputer Basics DefinitonJeetender nath100% (1)
- Computer HardwareDocument11 pagesComputer HardwareRodriguez NikkoNo ratings yet
- MuntasirDocument1 pageMuntasirabdurahmonzodamuntasirNo ratings yet
- TLEd 204 MT Lesson 1Document46 pagesTLEd 204 MT Lesson 1balanemaryjoy4No ratings yet
- Building A Computer SystemDocument4 pagesBuilding A Computer SystemKay LinnNo ratings yet
- The Major Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesThe Major Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsJosekutty N Joseph75% (4)
- Basic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitDocument35 pagesBasic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitShenny CariscalNo ratings yet
- 24051Document3 pages24051bhuvi2312100% (1)
- DiamondDocument158 pagesDiamondYashodeep KambleNo ratings yet
- Al-Cap Company ProfileDocument10 pagesAl-Cap Company ProfileMadaherAliNo ratings yet
- SIMATICPCS7 STPCS7AO Complete English 2013 WebDocument180 pagesSIMATICPCS7 STPCS7AO Complete English 2013 WebDiana ArredondoNo ratings yet
- BSNL 3G Data Card TrainingDocument47 pagesBSNL 3G Data Card Trainingsandcauli1147No ratings yet
- TRY TRX Datasheet Moore IndustriesDocument8 pagesTRY TRX Datasheet Moore IndustriesHendri HnzNo ratings yet
- A GSM Based Password Protection System Used in AtmDocument53 pagesA GSM Based Password Protection System Used in Atmprince4444No ratings yet
- Rock Link 800 User ManualDocument382 pagesRock Link 800 User ManualJOELSAUCEDONo ratings yet
- The Basic Stamp Ii and LabviewDocument10 pagesThe Basic Stamp Ii and Labviewviernes06No ratings yet
- Universal Weighing Terminal, W&M Approved, For Industrial UseDocument4 pagesUniversal Weighing Terminal, W&M Approved, For Industrial UseDeysi Flores RiveraNo ratings yet
- Flexible Automation: Z Z Z ZDocument12 pagesFlexible Automation: Z Z Z ZMuhammad HafizNo ratings yet
- Exploring wV1 Grader CAPDocument8 pagesExploring wV1 Grader CAPsargeywargeyNo ratings yet
- ETAP 22 - System RequirementsDocument1 pageETAP 22 - System RequirementsMuhammad FarooqNo ratings yet
- Fingerprint Time Attendance ManualDocument72 pagesFingerprint Time Attendance ManualRohit SinghNo ratings yet
- MSM BSM DB Uk 006 PDFDocument16 pagesMSM BSM DB Uk 006 PDFioacymNo ratings yet
- PCAdvisor201401 PDFDocument148 pagesPCAdvisor201401 PDFGeorge RadulescuNo ratings yet
- APC - Xmas 2017 AU PDFDocument116 pagesAPC - Xmas 2017 AU PDFSuman Abir PaulNo ratings yet
- It Workshop Lab ManualDocument144 pagesIt Workshop Lab Manualhanji17No ratings yet
- Sds Operation M Ver6Document106 pagesSds Operation M Ver6Roberto Vertel RomeroNo ratings yet
- Beekey10: Game Solution For China Mobile-Fresh File - RarDocument7 pagesBeekey10: Game Solution For China Mobile-Fresh File - RarAmelyn CanillasNo ratings yet
- Notebook Bangho PDFDocument226 pagesNotebook Bangho PDFrussofranco86No ratings yet
- Assignment#3 (Belleza) BSA1Document5 pagesAssignment#3 (Belleza) BSA1Karl Ethan MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- BED 215 Lecture Note 2024Document35 pagesBED 215 Lecture Note 2024ngozig82No ratings yet
- CAD Flatbed: User's ManualDocument17 pagesCAD Flatbed: User's ManualseppeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information Technology: DR Dharmendra Kumar KanchanDocument83 pagesIntroduction To Information Technology: DR Dharmendra Kumar KanchanSadhika KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Mikroboard For Pic 40-Pin: ManualDocument6 pagesMikroboard For Pic 40-Pin: ManualDaniel Crutan100% (1)
- Trend Open Protocol Server: Data SheetDocument8 pagesTrend Open Protocol Server: Data SheetMOUMENNo ratings yet
- 5 Pen PC Technology Powerpoint PresentationDocument18 pages5 Pen PC Technology Powerpoint PresentationnishiraviNo ratings yet