Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 viewsHoa 4 Kodigs
Hoa 4 Kodigs
Uploaded by
Sean DigmanThis document summarizes early Philippine shelters such as rock-shelters and caves used during the Pleistocene period. It then describes various traditional house types from different ethnic groups in the Philippines like the Ifugao house, Ivatan house, Bahay Kubo, and Badjao boat-house. It also discusses interior spaces, features of vernacular architecture, and architectural structures introduced during the Spanish colonial period such as churches, fortresses, and institutional buildings following the Laws of the Indies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Pre-Colonial Architecture LectureDocument16 pagesPre-Colonial Architecture LectureAshley Winchester100% (1)
- MasaiDocument22 pagesMasaiSiddhi Vashi100% (3)
- Hexcrawl Adventures: A Basic Fantasy Role-Playing SupplementDocument16 pagesHexcrawl Adventures: A Basic Fantasy Role-Playing SupplementManashwi KishoreNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture 4 Lecture 1 PDFDocument43 pagesHistory of Architecture 4 Lecture 1 PDFNino Ylagan100% (1)
- Pre ColonialDocument42 pagesPre ColonialShula Rizz Lavaro GalupeNo ratings yet
- DR - Safaa Hameed Faisal Heat Transfer LectureDocument1 pageDR - Safaa Hameed Faisal Heat Transfer LectureSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Neoset Catalog 2012Document173 pagesNeoset Catalog 2012nguyễn thăng vănNo ratings yet
- HOA MODULE 1 - Courtesy of Ar. DianneDocument27 pagesHOA MODULE 1 - Courtesy of Ar. DianneTimothy SeseNo ratings yet
- E1 E2 Hand NotesDocument55 pagesE1 E2 Hand NotesKINT ADRIAN TESORIONo ratings yet
- HOA 4prelimsDocument10 pagesHOA 4prelimsSEAN ELVIN DIGMANNo ratings yet
- Hoa Module 4 P1Document94 pagesHoa Module 4 P1cyril delfin100% (2)
- Early Shelter To Spanish ColonialDocument96 pagesEarly Shelter To Spanish ColonialTricia Infante100% (1)
- 2 Pre Colonial Luzon PDFDocument58 pages2 Pre Colonial Luzon PDFAbigail Palmones100% (1)
- History of Architecture 4 Week 2 3 2Document40 pagesHistory of Architecture 4 Week 2 3 2vt8dth8vzyNo ratings yet
- 02 Vernacular ArchitectureDocument68 pages02 Vernacular ArchitectureAnn Margaret TanNo ratings yet
- AI Midterm ReviewerDocument29 pagesAI Midterm ReviewerIra CruzNo ratings yet
- Hoa NotesDocument6 pagesHoa NotesAfanie Mae Romero EstepaNo ratings yet
- Week No. 1: Rizal Technological UniversityDocument12 pagesWeek No. 1: Rizal Technological UniversityStephany JulaoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Spanish PeriodDocument27 pagesPre-Spanish PeriodJr VelosNo ratings yet
- HOA4 Reviewer 1Document36 pagesHOA4 Reviewer 1Angelic BasiyaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of The HouseDocument4 pagesEvolution of The HouseJha Jha CaLvezNo ratings yet
- Pre-Spanish PeriodDocument27 pagesPre-Spanish PeriodMai MaiNo ratings yet
- Hoa-4 1Document30 pagesHoa-4 1CarmsNo ratings yet
- Folk Arts in The PhilippinesDocument26 pagesFolk Arts in The PhilippinesRosalie CustodioNo ratings yet
- Samal House in BookDocument12 pagesSamal House in BookYen DaNo ratings yet
- Buitre 1Document18 pagesBuitre 1Alfred TabaresNo ratings yet
- Project in HOA 4Document28 pagesProject in HOA 4_iamarcanthony07No ratings yet
- Quizlet Table 8Document6 pagesQuizlet Table 8JosielynNo ratings yet
- Ethnic Groups in The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesEthnic Groups in The Philippines2019989266No ratings yet
- Pre-Spanish PeriodDocument27 pagesPre-Spanish PeriodJr VelosNo ratings yet
- Ethnic Houses in The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesEthnic Houses in The PhilippinesLəonardo SasingNo ratings yet
- Aa11 12Document11 pagesAa11 12Angela BrioboNo ratings yet
- RSW 2 - RawDocument21 pagesRSW 2 - RawJerico JulianNo ratings yet
- Early Societies in The PhilippinesDocument83 pagesEarly Societies in The PhilippinesasolisNo ratings yet
- A. Kalinga House: - Building Character - Similarities - Building Parts - Construction Materials - Building AreasDocument41 pagesA. Kalinga House: - Building Character - Similarities - Building Parts - Construction Materials - Building AreasArriane Aya BaylonNo ratings yet
- Re 1 - Cultural Heritage VillageDocument13 pagesRe 1 - Cultural Heritage Villageelijah jirah binadayNo ratings yet
- Official Notes HOA Midterm HispanicDocument4 pagesOfficial Notes HOA Midterm HispanicredeemedshaaaNo ratings yet
- 01 - Introduction - Philippine Architecture 02aDocument29 pages01 - Introduction - Philippine Architecture 02aJohn Nichole Hernandez DacanayNo ratings yet
- IpsDocument19 pagesIpsCj ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- Arts in The WorldDocument13 pagesArts in The WorldAbojalil CaminNo ratings yet
- MaranaoDocument40 pagesMaranaoJuan Miguel BernardoNo ratings yet
- Vernacul Ar Period 1521: Yakan Traditional HousesDocument13 pagesVernacul Ar Period 1521: Yakan Traditional HousesAlmira AsimNo ratings yet
- 01 - Introduction - Philippine Architecture 02bDocument22 pages01 - Introduction - Philippine Architecture 02bJohn Nichole Hernandez DacanayNo ratings yet
- Cultural Beliefs IN Housing: (Regional Characrteristics)Document9 pagesCultural Beliefs IN Housing: (Regional Characrteristics)Doroty CastroNo ratings yet
- Philippine Architecture Pre Spanish Era PDFDocument63 pagesPhilippine Architecture Pre Spanish Era PDFDeanne Guinto100% (1)
- Intro To PH and Early Philippine SheltersDocument7 pagesIntro To PH and Early Philippine SheltersCharmie Cabeltera CuelloNo ratings yet
- Folk Architecture in The PhilippinesDocument12 pagesFolk Architecture in The PhilippinesMark60% (5)
- NU HOA4 1d PHILIPPINE ARCHITECTURE (COPYRIGHTED)Document38 pagesNU HOA4 1d PHILIPPINE ARCHITECTURE (COPYRIGHTED)formaranvicky88No ratings yet
- Arts and Crafts of MindanaoDocument2 pagesArts and Crafts of MindanaoChester Rey VillordonNo ratings yet
- PH Folk Arts and Maritime Transpo 1Document30 pagesPH Folk Arts and Maritime Transpo 1Kevin San50% (2)
- Arts in Cordillera RegionDocument71 pagesArts in Cordillera RegionCrisela V. TalabaNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture NotesDocument2 pagesHistory of Architecture NotesMaureen AlboresNo ratings yet
- Vernacular Architecture of NagalandDocument16 pagesVernacular Architecture of NagalandNaitik Jaiswal100% (1)
- A135 PDFDocument37 pagesA135 PDFDM AndradeNo ratings yet
- Official Notes HOA Midterm IslamicDocument4 pagesOfficial Notes HOA Midterm IslamicredeemedshaaaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Laos & ChinaDocument53 pagesGroup 2 - Laos & Chinachengliii.luluNo ratings yet
- TOROGAN HOUSE (Lanao Del Sur) : LOCATION: Hills, Along The River, Road, or Lakeshore of Mindanao HistoryDocument12 pagesTOROGAN HOUSE (Lanao Del Sur) : LOCATION: Hills, Along The River, Road, or Lakeshore of Mindanao HistoryCharles Dominic Reyes TapnioNo ratings yet
- Japanese Architecture ExamplesDocument64 pagesJapanese Architecture ExamplesPurchiaNo ratings yet
- Early Shelters of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesEarly Shelters of The PhilippinesdenesonsNo ratings yet
- FailureDocument13 pagesFailureSamNo ratings yet
- Isolated Col or Pad FoundationDocument8 pagesIsolated Col or Pad FoundationLeroy LifestyleNo ratings yet
- Design of Buildings For Earthquake Resistance According To Eurocode 8 - Part 1Document53 pagesDesign of Buildings For Earthquake Resistance According To Eurocode 8 - Part 1babuliuNo ratings yet
- BSD Floor Plan Na TalagaDocument1 pageBSD Floor Plan Na TalagaHelen CastilloNo ratings yet
- Abts - Industry Case Study PDFDocument2 pagesAbts - Industry Case Study PDFNimse ManavNo ratings yet
- Ozone Parc PDFDocument40 pagesOzone Parc PDFachopra14No ratings yet
- LTE CSFB Call Flows - Referred From Ericsson & HuaweiDocument27 pagesLTE CSFB Call Flows - Referred From Ericsson & HuaweiAlthaf HussainNo ratings yet
- EnsoWoods GamudaCove SummaryDocument24 pagesEnsoWoods GamudaCove SummaryMike MikeNo ratings yet
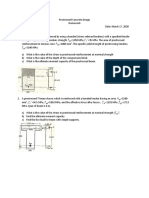
- PCD HomeworkDocument3 pagesPCD Homeworknikko reloxNo ratings yet
- History of Urban MorphologyDocument9 pagesHistory of Urban MorphologyChan Siew ChongNo ratings yet
- Alfredo LuzDocument15 pagesAlfredo LuzKIM ADRIAN MAGTIBAYNo ratings yet
- Core Comparisons: Fire PerformanceDocument2 pagesCore Comparisons: Fire PerformanceGarryNo ratings yet
- Rudofsky Bernard Architecture Without Architects A Short Introduction To Non-Pedigreed ArchitectureDocument63 pagesRudofsky Bernard Architecture Without Architects A Short Introduction To Non-Pedigreed ArchitecturepeeobeeNo ratings yet
- Steel: Built To Last: Case Study No 3Document4 pagesSteel: Built To Last: Case Study No 3clam2014No ratings yet
- Beam To Column'S Flange Fixed Connection Type Bcff-1: 1-Design DataDocument5 pagesBeam To Column'S Flange Fixed Connection Type Bcff-1: 1-Design DataAchmad RifaiNo ratings yet
- SHEETSDocument40 pagesSHEETSHETVI PATELNo ratings yet
- DX Split Unit - YorkDocument200 pagesDX Split Unit - YorkFaiyaz Bin Mazid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Firestop Application Handbook (Macau) - Part-1Document21 pagesFirestop Application Handbook (Macau) - Part-1Sharoon S raoNo ratings yet
- Mockito ExampleDocument11 pagesMockito ExampleSourabh JainNo ratings yet
- City Planning and Realities - : A Case Study of ChandigarhDocument31 pagesCity Planning and Realities - : A Case Study of Chandigarhzakkaullah Bader0% (1)
- FSF Forcible EntryDocument31 pagesFSF Forcible EntryIgnacio NicolásNo ratings yet
- Gera's World of Joy - Phase II-60Document1 pageGera's World of Joy - Phase II-60Primon KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Switzer - Genset PlanDocument1 pageSwitzer - Genset PlanArun MohanNo ratings yet
- Insulation - EIL STD PDFDocument4 pagesInsulation - EIL STD PDFchaiya sonwongNo ratings yet
- P-02 - Ground - Second Floor Water Layout-P-02 - Ground - Second Floor Water LayoutDocument1 pageP-02 - Ground - Second Floor Water Layout-P-02 - Ground - Second Floor Water LayoutX XNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Rate For Kota Stone Steps 25mm 2Document3 pagesAnalysis of Rate For Kota Stone Steps 25mm 2yashomita sharma100% (2)
- Link Dahsyat Mei 2021Document2 pagesLink Dahsyat Mei 2021Hadi SuagungNo ratings yet
Hoa 4 Kodigs
Hoa 4 Kodigs
Uploaded by
Sean Digman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views3 pagesThis document summarizes early Philippine shelters such as rock-shelters and caves used during the Pleistocene period. It then describes various traditional house types from different ethnic groups in the Philippines like the Ifugao house, Ivatan house, Bahay Kubo, and Badjao boat-house. It also discusses interior spaces, features of vernacular architecture, and architectural structures introduced during the Spanish colonial period such as churches, fortresses, and institutional buildings following the Laws of the Indies.
Original Description:
Original Title
HOA 4 KODIGS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes early Philippine shelters such as rock-shelters and caves used during the Pleistocene period. It then describes various traditional house types from different ethnic groups in the Philippines like the Ifugao house, Ivatan house, Bahay Kubo, and Badjao boat-house. It also discusses interior spaces, features of vernacular architecture, and architectural structures introduced during the Spanish colonial period such as churches, fortresses, and institutional buildings following the Laws of the Indies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views3 pagesHoa 4 Kodigs
Hoa 4 Kodigs
Uploaded by
Sean DigmanThis document summarizes early Philippine shelters such as rock-shelters and caves used during the Pleistocene period. It then describes various traditional house types from different ethnic groups in the Philippines like the Ifugao house, Ivatan house, Bahay Kubo, and Badjao boat-house. It also discusses interior spaces, features of vernacular architecture, and architectural structures introduced during the Spanish colonial period such as churches, fortresses, and institutional buildings following the Laws of the Indies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
EARLY PHILIPPINE ▪ Ulog or olog, female ■ Harun, stairs where women
SHELTERS dormitory. often wash clothes and kitchen
TABON CAVE COMPLEX ▪ Al-kang, storage for food, utensils.
-first establish the presence of jewelry and wine jars.
humans in the Philippines ▪ Akhamang, rice granary. BAHAY SINUG
during ▪ Falinto-og, pig pens. TAUSOG HOUSE
BALE ■ House building can be
the Pleistocene.
IFUGAO HOUSE construed as corresponding to
TAU’T BATU
■ Abong, dwelling for the poor. the birth of a human.
-still continue the primeval
■ Support system: four posts, ■ Tadjuk pasung finials.
practice of living in caves
two girders, three joists or TOROGAN
IDJANG
beams. MARANAO HOUSE
-ROCK-HEWN
■ Halipan, rat guard. ■ Mala-a-walai, traditional
PINANAHANG
■ “The house as a womb.” large house.
-LEAN TO
BINANGIYAN ■ Lawig, small house.
KALINGA TREE HOUSE
KANKANAI HOUSE ■ The panolong (decorative
■ Apa or inapa, for poorer beam
PRE-COLONIAL VERN.
families; temporary abode. ends) are often with pako
ARCH.
■ Allao, more temporary. rabong
tropical characteristics of
RAKUH and naga carvings.
Southeast Asian
IVATAN HOUSE ■ Lamin, lady’s dormitory
domestic architecture:
■ Thick thatch, walls mortared tower.
▪ An elevated living floors
with stone or plastered with
▪ Buoyant rectangular volume
white lime. Features of Vernacular
▪ Raised pile foundation
■ Wooden post and lintel Architecture
▪ Voluminous thatched roof
framework is implanted in the ▪ The builders are non-
walls. professional architects or
BINURON
BAHAY KUBO engineers.
ISNEG HOUSE
LOWLAND DWELLING ▪ There is constant adaptation,
Roof suggests an inverted
■ “The passively-cooled using natural materials, to the
hull.
house.” geographical environment.
■ Exposed floor joists outside
■ Porous surfaces ▪ The actual process of
suggest the profile of a boat.
■ Horizontality of windows construction involves intuitive
■ Datag or Xassaran, main
■ Roof and window overhangs thinking and is open to later
section.
■ Surrounding gardens modifications.
■ Tamuyon, slightly raised
▪ There is balance between
platform on three sides.
Interior Spaces social/economic functionality
BINAYON
Primary spaces and aesthetic features.
KALINGA HOUSE
▪ Living room ▪ Styles are subject to the
Octagonal in plan; exterior
▪ Kitchen and service area evolution of traditional patterns
features are not strongly
(dapogan, banggerahan, and specific to an ethnic domain.
defined.
batalan)
■ Dataggon, central section.
Secondary spaces SPANISH COLONIAL ARCH’L
■ Sipi, slightly elevated side
▪ Dining Reducción
sections.
▪ Silong and balkon The formerly scattered barangays
FAY-U
▪ Bedrooms were brought together and
BONTOC HOUSE
Katyufong, dwelling for the reduced in number and made
LEPA into compact and larger
poor.
BADJAO BOAT-HOUSE
■ Kol-lob, residence of widows communities to facilitate
■ No outriggers, roofed, loose
or unmarried old women; can religious conversion and cultural
and detachable structure.
also be called katyufong. change. Bajo de las campana,
■ Djenging, has outriggers,
INAGAMANG under the sound of the bells
roofed, walled in on all sides
BONTOC IN SAGADA
by wooden boards.
Agamang, upper level granary.
■ Dapang or Vinta, not roofed,
Other building types
only used for fishing and short
▪ Afong, family residence.
trips.
▪ Ato, council house and
LUMA
dormitory of the young and old
BADJAO LANDHOUSE
unmarried males.
Encomienda Colonial Infrastructures ■ The facade epitomizes the
The colony was divided into New building typologies and Filipino transfiguration of
parcels assigned to a Spanish construction technology western decorative elements
colonist (encomendero) who was was introduced
mandated to “allocate, allot or Santa Maria Church
distribute” the resources of the CHURCHES Santa Maria, Ilocos Sur.
domain PARTS OF A CHURCH: ■ Church of Nuestra Señora de la
▪ Altar mayor, main altar. Asunción.
System of Cities and Towns ▪ Sagrario, tabernacle. ■ Situated on a hill surrounded
The institution of a hierarchal ▪ Pulpito, pulpit. by a defensive wall.
settlement system. Cabecera ▪ Retablo, elaborately ■ Separate pagoda-like bell tower
(city) or poblacion (town), core of ornamented altar screen. at the midpoint of the nave wall.
the municipality. Barrios, ▪ Sacristia, where the priest and ■ The brick walls are devoid of
adjacent barangays. his assistants put on ornament but have delicately
their robes before the mass. carved side entrances and strong
Intramuros ▪ Coro, choir loft. buttresses
■ Patterned after the walled ▪ Tribunas, screened gallery.
fortresses of Europe CONSERVATION
■ Reserved for the nobility and Church Complex ▪ RA 10066 (National Heritage
the clergy. ▪ Church Law)
▪ Convento, parish house or ▪ RA 10086 (National Historical
Extramuros rectory. Commission of the Philippines
Living beyond the walls. ▪ Campanarios, bell towers. Law)
▪ Pueblos, villages outside the
walls. San Agustin Church FORTRESSES
▪ Parian, a separate urban Intramuros, Manila. Parts of a Fort
quarter designated to the ■ The Church of the Immaculate ▪ Cortinas, thick perimeter walls.
Chinese community . Conception of San Agustín. ▪ Bastiones or baluartes, four-
▪ Dilao, Japanese community. ■ First church to be built in sided bulwarks skirting the
Luzon. cortinas on both ends.
Cuadricula ■ Only structure in Intramuros to ▪ Foso, moat.
A system of streets and blocks survive WWII. ▪ Casamatas, stone embrasures
laid out in a grid pattern, with ■ High Baroque style retablo. where artilleries were propped
uniform precision. ■ Ceiling paintings in the trompe up.
l’oeil style.
The Laws of the Indies, 1573 ■ Chinese fu dogs at the entrance INSTITUTIONAL BUILDINGS
▪ Characteristics: Ayuntamiento
▪ elevated location Paoay Church Intramuros, Manila.
▪ an orderly grid of streets Paoay, Ilocos Norte. ■ Also known as Casa del
▪ a central plaza, a defensive wall, ■ Saint Augustine Church. Ayuntamiento, Casa del Cabildo,
and zones for churches, shops, ■ Most outstanding example in Casa Consistorial, or Casa Real.
government buildings, hospitals, the Philippines of 'Earthquake ■ As a seat of colonial
and slaughterhouses. Baroque'. governance, it housed several
▪ Encapsulates the classicist ■ Volutes of contrafuertes administrative offices and
theories of urban design (buttresses) and in the pyramidal archives
proposed by Vitruvius and finials of wall facades.
Alberti. ■ Massive coral stone belltower Palacio Real
Intramuros, Manila.
Plaza Complex Miag-ao Church ■ Also known as Palacio del
Grid pattern of streets with the Miag-ao, Iloilo. Gobernador General.
main plaza at the center ■ Sto. Tomas de Villanueva ■ Residence of the highest official
surrounded by the church, the Church of the land.
tribunal, other government ■ Stands on the highest point of ■ Malacañang Palace, the
buildings, and the marketplace. Miag-ao, its towers serving as summer residence of the
lookouts against Muslim raids. Governor General.
■ It is the finest surviving
example of 'Fortress Baroque'.
Other civic buildings COMMERCIAL BUILDINGS Characteristics of a Bahay na bato
▪ Real Audiencia, or Tribunal, trial Shops ▪ Generally has two storeys, at
court. ■ Alcaiceria de San Fernando, times three.
▪ Aduana, customs house. very first large commercial ▪ The ground floor is made of cut
▪ Hacienda Publica, treasury. structure; silk market in Binondo; stone or brick, the
▪ Municipio, Casa de Municipal, housed stores for Chinese upper of wood.
or Casa Real, a smaller merchants and government ▪ Windows: ground floor,
version of the Ayuntamiento in offices. grillworks; second floor, sliding
the provincial towns. ■ Tabacaleras, tobacco and cigar shutters with capiz shells or glass
▪ Casa Hacienda, expansive factories; Cigarreras, female panels.
structures housing spaces workers. ▪ Capped by a high hip roof with a
for the administrators and his ■ The bahay na bato was later 45-degree-angle pitch
workers on a landed estate retrofitted to have room for
commercial function. Parts Ground floor
Educational and Scientific ■ Sari-sari store and carinderias. ■ Cochera, driveway or garage.
Buildings Hotels ■ Zaguan, vestibule or storage;
Schools ■ Hotel la Palma de Mallorca, usually for the caroza.
University of Sto. Tomas, Manila. Hotel de Paris, and Hotel de ■ Entresuelo, mezzanine area, for
Oldest established university in Espana, foremost hotels in offices or servants’ quarters.
Asia. Intramuros. ■ Cuadra, horse stables.
■ Colegio or universidad, found ■ Casas de huespedes, boarding ■ Cocina, kitchen
in the urban areas. houses; less expensive lodgings. ■ Escalera, wooden staircase.
■ Escuela primaria, found in Banks
different pueblos. ■ Banco Español-Filipino de Parts Second floor
Isabel II, first bank built; initially ■ Caida or ante-sala, interior
Hospitals housed in the Aduana overhanging veranda; most
▪ Hospital Real, first hospital; immediate room from the stairs.
built by the Franciscans; DOMESTIC STRUCTURES ■ Sala, living room.
catered only to the Spaniards. Accesorias ■ Baño, bathroom.
▪ Hospital de San Gabriel, for the ■ Apartment dwellings ■ Latrina, toilet.
Chinese in Binondo. ■ Evolved from the need of ■ Cocina, kitchen.
▪ Hospital de San Lazaro, for the migrant laborers for cheap ■ Comedor, dining area.
lepers housing in commercial and ■ Azotea, outdoor terrace,
industrial areas. located beside a balon or over an
Observatories ■ Vivienda, each unit; has a aljibe(water cistern).
▪ Observatorio Astronomico y zaguan, sala and sleeping ■ Cuarto, bedroom.
Meteorologico de Manila, quarters
or the Manila Observatory; ■ Galeria volada or corredor,
established by the Jesuits to BAHAY NA BATO flying wooden gallery.
assist in forecasting typhoons A housing prototype which ■ Oratorio, praying area.
combined elements of the ■ Callado, wooden fretwork on
INDUSTRIAL BUILDINGS indigenous and Hispanic building top of partitions.
Bridges traditions to prevent the dangers ■ Pasamano, window sill.
■ Puente de España posed by fire, earthquakes and ■ Ventanillas, vents beneath the
Train Stations cyclones window sill which reach to the
■ The Tutuban Station of the Arquitectura Mestiza floor.
ManilaDagupan railway line ▪ A new hybrid-type of ■ Barandillas, wooden balusters
Lighthouses construction, coined by Jesuit
■ The Pasig Farola, the oldest Francisco Ignacio Alcina, which
lighthouse in the Philippines refers to structures built partly of
Water System wood and partly of stone.
■ The Carriedo Waterworks
installed the piped-in water
system
You might also like
- Pre-Colonial Architecture LectureDocument16 pagesPre-Colonial Architecture LectureAshley Winchester100% (1)
- MasaiDocument22 pagesMasaiSiddhi Vashi100% (3)
- Hexcrawl Adventures: A Basic Fantasy Role-Playing SupplementDocument16 pagesHexcrawl Adventures: A Basic Fantasy Role-Playing SupplementManashwi KishoreNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture 4 Lecture 1 PDFDocument43 pagesHistory of Architecture 4 Lecture 1 PDFNino Ylagan100% (1)
- Pre ColonialDocument42 pagesPre ColonialShula Rizz Lavaro GalupeNo ratings yet
- DR - Safaa Hameed Faisal Heat Transfer LectureDocument1 pageDR - Safaa Hameed Faisal Heat Transfer LectureSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Neoset Catalog 2012Document173 pagesNeoset Catalog 2012nguyễn thăng vănNo ratings yet
- HOA MODULE 1 - Courtesy of Ar. DianneDocument27 pagesHOA MODULE 1 - Courtesy of Ar. DianneTimothy SeseNo ratings yet
- E1 E2 Hand NotesDocument55 pagesE1 E2 Hand NotesKINT ADRIAN TESORIONo ratings yet
- HOA 4prelimsDocument10 pagesHOA 4prelimsSEAN ELVIN DIGMANNo ratings yet
- Hoa Module 4 P1Document94 pagesHoa Module 4 P1cyril delfin100% (2)
- Early Shelter To Spanish ColonialDocument96 pagesEarly Shelter To Spanish ColonialTricia Infante100% (1)
- 2 Pre Colonial Luzon PDFDocument58 pages2 Pre Colonial Luzon PDFAbigail Palmones100% (1)
- History of Architecture 4 Week 2 3 2Document40 pagesHistory of Architecture 4 Week 2 3 2vt8dth8vzyNo ratings yet
- 02 Vernacular ArchitectureDocument68 pages02 Vernacular ArchitectureAnn Margaret TanNo ratings yet
- AI Midterm ReviewerDocument29 pagesAI Midterm ReviewerIra CruzNo ratings yet
- Hoa NotesDocument6 pagesHoa NotesAfanie Mae Romero EstepaNo ratings yet
- Week No. 1: Rizal Technological UniversityDocument12 pagesWeek No. 1: Rizal Technological UniversityStephany JulaoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Spanish PeriodDocument27 pagesPre-Spanish PeriodJr VelosNo ratings yet
- HOA4 Reviewer 1Document36 pagesHOA4 Reviewer 1Angelic BasiyaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of The HouseDocument4 pagesEvolution of The HouseJha Jha CaLvezNo ratings yet
- Pre-Spanish PeriodDocument27 pagesPre-Spanish PeriodMai MaiNo ratings yet
- Hoa-4 1Document30 pagesHoa-4 1CarmsNo ratings yet
- Folk Arts in The PhilippinesDocument26 pagesFolk Arts in The PhilippinesRosalie CustodioNo ratings yet
- Samal House in BookDocument12 pagesSamal House in BookYen DaNo ratings yet
- Buitre 1Document18 pagesBuitre 1Alfred TabaresNo ratings yet
- Project in HOA 4Document28 pagesProject in HOA 4_iamarcanthony07No ratings yet
- Quizlet Table 8Document6 pagesQuizlet Table 8JosielynNo ratings yet
- Ethnic Groups in The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesEthnic Groups in The Philippines2019989266No ratings yet
- Pre-Spanish PeriodDocument27 pagesPre-Spanish PeriodJr VelosNo ratings yet
- Ethnic Houses in The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesEthnic Houses in The PhilippinesLəonardo SasingNo ratings yet
- Aa11 12Document11 pagesAa11 12Angela BrioboNo ratings yet
- RSW 2 - RawDocument21 pagesRSW 2 - RawJerico JulianNo ratings yet
- Early Societies in The PhilippinesDocument83 pagesEarly Societies in The PhilippinesasolisNo ratings yet
- A. Kalinga House: - Building Character - Similarities - Building Parts - Construction Materials - Building AreasDocument41 pagesA. Kalinga House: - Building Character - Similarities - Building Parts - Construction Materials - Building AreasArriane Aya BaylonNo ratings yet
- Re 1 - Cultural Heritage VillageDocument13 pagesRe 1 - Cultural Heritage Villageelijah jirah binadayNo ratings yet
- Official Notes HOA Midterm HispanicDocument4 pagesOfficial Notes HOA Midterm HispanicredeemedshaaaNo ratings yet
- 01 - Introduction - Philippine Architecture 02aDocument29 pages01 - Introduction - Philippine Architecture 02aJohn Nichole Hernandez DacanayNo ratings yet
- IpsDocument19 pagesIpsCj ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- Arts in The WorldDocument13 pagesArts in The WorldAbojalil CaminNo ratings yet
- MaranaoDocument40 pagesMaranaoJuan Miguel BernardoNo ratings yet
- Vernacul Ar Period 1521: Yakan Traditional HousesDocument13 pagesVernacul Ar Period 1521: Yakan Traditional HousesAlmira AsimNo ratings yet
- 01 - Introduction - Philippine Architecture 02bDocument22 pages01 - Introduction - Philippine Architecture 02bJohn Nichole Hernandez DacanayNo ratings yet
- Cultural Beliefs IN Housing: (Regional Characrteristics)Document9 pagesCultural Beliefs IN Housing: (Regional Characrteristics)Doroty CastroNo ratings yet
- Philippine Architecture Pre Spanish Era PDFDocument63 pagesPhilippine Architecture Pre Spanish Era PDFDeanne Guinto100% (1)
- Intro To PH and Early Philippine SheltersDocument7 pagesIntro To PH and Early Philippine SheltersCharmie Cabeltera CuelloNo ratings yet
- Folk Architecture in The PhilippinesDocument12 pagesFolk Architecture in The PhilippinesMark60% (5)
- NU HOA4 1d PHILIPPINE ARCHITECTURE (COPYRIGHTED)Document38 pagesNU HOA4 1d PHILIPPINE ARCHITECTURE (COPYRIGHTED)formaranvicky88No ratings yet
- Arts and Crafts of MindanaoDocument2 pagesArts and Crafts of MindanaoChester Rey VillordonNo ratings yet
- PH Folk Arts and Maritime Transpo 1Document30 pagesPH Folk Arts and Maritime Transpo 1Kevin San50% (2)
- Arts in Cordillera RegionDocument71 pagesArts in Cordillera RegionCrisela V. TalabaNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture NotesDocument2 pagesHistory of Architecture NotesMaureen AlboresNo ratings yet
- Vernacular Architecture of NagalandDocument16 pagesVernacular Architecture of NagalandNaitik Jaiswal100% (1)
- A135 PDFDocument37 pagesA135 PDFDM AndradeNo ratings yet
- Official Notes HOA Midterm IslamicDocument4 pagesOfficial Notes HOA Midterm IslamicredeemedshaaaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Laos & ChinaDocument53 pagesGroup 2 - Laos & Chinachengliii.luluNo ratings yet
- TOROGAN HOUSE (Lanao Del Sur) : LOCATION: Hills, Along The River, Road, or Lakeshore of Mindanao HistoryDocument12 pagesTOROGAN HOUSE (Lanao Del Sur) : LOCATION: Hills, Along The River, Road, or Lakeshore of Mindanao HistoryCharles Dominic Reyes TapnioNo ratings yet
- Japanese Architecture ExamplesDocument64 pagesJapanese Architecture ExamplesPurchiaNo ratings yet
- Early Shelters of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesEarly Shelters of The PhilippinesdenesonsNo ratings yet
- FailureDocument13 pagesFailureSamNo ratings yet
- Isolated Col or Pad FoundationDocument8 pagesIsolated Col or Pad FoundationLeroy LifestyleNo ratings yet
- Design of Buildings For Earthquake Resistance According To Eurocode 8 - Part 1Document53 pagesDesign of Buildings For Earthquake Resistance According To Eurocode 8 - Part 1babuliuNo ratings yet
- BSD Floor Plan Na TalagaDocument1 pageBSD Floor Plan Na TalagaHelen CastilloNo ratings yet
- Abts - Industry Case Study PDFDocument2 pagesAbts - Industry Case Study PDFNimse ManavNo ratings yet
- Ozone Parc PDFDocument40 pagesOzone Parc PDFachopra14No ratings yet
- LTE CSFB Call Flows - Referred From Ericsson & HuaweiDocument27 pagesLTE CSFB Call Flows - Referred From Ericsson & HuaweiAlthaf HussainNo ratings yet
- EnsoWoods GamudaCove SummaryDocument24 pagesEnsoWoods GamudaCove SummaryMike MikeNo ratings yet
- PCD HomeworkDocument3 pagesPCD Homeworknikko reloxNo ratings yet
- History of Urban MorphologyDocument9 pagesHistory of Urban MorphologyChan Siew ChongNo ratings yet
- Alfredo LuzDocument15 pagesAlfredo LuzKIM ADRIAN MAGTIBAYNo ratings yet
- Core Comparisons: Fire PerformanceDocument2 pagesCore Comparisons: Fire PerformanceGarryNo ratings yet
- Rudofsky Bernard Architecture Without Architects A Short Introduction To Non-Pedigreed ArchitectureDocument63 pagesRudofsky Bernard Architecture Without Architects A Short Introduction To Non-Pedigreed ArchitecturepeeobeeNo ratings yet
- Steel: Built To Last: Case Study No 3Document4 pagesSteel: Built To Last: Case Study No 3clam2014No ratings yet
- Beam To Column'S Flange Fixed Connection Type Bcff-1: 1-Design DataDocument5 pagesBeam To Column'S Flange Fixed Connection Type Bcff-1: 1-Design DataAchmad RifaiNo ratings yet
- SHEETSDocument40 pagesSHEETSHETVI PATELNo ratings yet
- DX Split Unit - YorkDocument200 pagesDX Split Unit - YorkFaiyaz Bin Mazid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Firestop Application Handbook (Macau) - Part-1Document21 pagesFirestop Application Handbook (Macau) - Part-1Sharoon S raoNo ratings yet
- Mockito ExampleDocument11 pagesMockito ExampleSourabh JainNo ratings yet
- City Planning and Realities - : A Case Study of ChandigarhDocument31 pagesCity Planning and Realities - : A Case Study of Chandigarhzakkaullah Bader0% (1)
- FSF Forcible EntryDocument31 pagesFSF Forcible EntryIgnacio NicolásNo ratings yet
- Gera's World of Joy - Phase II-60Document1 pageGera's World of Joy - Phase II-60Primon KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Switzer - Genset PlanDocument1 pageSwitzer - Genset PlanArun MohanNo ratings yet
- Insulation - EIL STD PDFDocument4 pagesInsulation - EIL STD PDFchaiya sonwongNo ratings yet
- P-02 - Ground - Second Floor Water Layout-P-02 - Ground - Second Floor Water LayoutDocument1 pageP-02 - Ground - Second Floor Water Layout-P-02 - Ground - Second Floor Water LayoutX XNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Rate For Kota Stone Steps 25mm 2Document3 pagesAnalysis of Rate For Kota Stone Steps 25mm 2yashomita sharma100% (2)
- Link Dahsyat Mei 2021Document2 pagesLink Dahsyat Mei 2021Hadi SuagungNo ratings yet