Professional Documents
Culture Documents
21st Century Literature
21st Century Literature
Uploaded by
Mark PalomarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Quiz 1 PDFDocument8 pagesQuiz 1 PDFKurt Vendane VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Literature and Its CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesLiterature and Its CharacteristicsRicxz Xedric63% (8)
- Breaking Into Japanese LiteratureDocument195 pagesBreaking Into Japanese Literaturechucketti2100% (16)
- 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The World REVIEWERDocument6 pages21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The World REVIEWERYolanda Morales100% (1)
- HUMBOLDT, Alexander Von. Cosmos Vol.2Document417 pagesHUMBOLDT, Alexander Von. Cosmos Vol.2Diego Montenegro100% (1)
- English Reviewer: ST ND TH RD THDocument6 pagesEnglish Reviewer: ST ND TH RD THMelissa PasoquinNo ratings yet
- 21st CENTURY LIT 2ND SEM REVIEWERDocument5 pages21st CENTURY LIT 2ND SEM REVIEWERYsa ToledoNo ratings yet
- Lit ReviewerDocument11 pagesLit Reviewerljarcangel0324No ratings yet
- The Literary Forms in Philippine LiteratureDocument6 pagesThe Literary Forms in Philippine LiteratureRonalyn Cabana BlanceNo ratings yet
- C GELIT02 PrelimsDocument9 pagesC GELIT02 PrelimsKarl LintanNo ratings yet
- 12 - 21ST Century Literature (1-5)Document5 pages12 - 21ST Century Literature (1-5)Blessy Myl MagrataNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LiteratureDocument8 pagesIntroduction To LiteratureMerlyn Len AytonaNo ratings yet
- CNF Reviewer W1 2Document4 pagesCNF Reviewer W1 2ZairaNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature Reviewer 1st QuarterDocument6 pages21st Century Literature Reviewer 1st QuarterRiseson Peñas100% (4)
- 21st Century From The Philippines and The WorldDocument3 pages21st Century From The Philippines and The WorldZhemxie KimNo ratings yet
- 21st Century From The Philippines and The World 3Document4 pages21st Century From The Philippines and The World 3Alexandrea WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Green Monochromatic Simple The Minimalist Presentation TemplateDocument21 pagesGreen Monochromatic Simple The Minimalist Presentation TemplateTimmmyyy 27No ratings yet
- 21ST First Quarter Lesson CompilationDocument7 pages21ST First Quarter Lesson CompilationDenise Nicole T. LopezNo ratings yet
- LAS 1-Intro To LitDocument2 pagesLAS 1-Intro To Litannamarieabegael.lomaNo ratings yet
- Literature: General Types of LiteratureDocument1 pageLiterature: General Types of LiteratureJune Philip AtilledoNo ratings yet
- LIT101Document20 pagesLIT101luxasuhiNo ratings yet
- NON-FICTION - A Prose Writing That: Prose Is Derived From The Latin Prosa Which LiterallyDocument4 pagesNON-FICTION - A Prose Writing That: Prose Is Derived From The Latin Prosa Which LiterallyJomir Kimberly DomingoNo ratings yet
- Prose Poetry Hand OutDocument2 pagesProse Poetry Hand OutIyah Xyza VenturaNo ratings yet
- PhilitDocument4 pagesPhilitIrish AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Literary Genres: Kinds of Poetry 1. NARRATIVE POETRY-tells A Story Through Creative LinesDocument2 pagesLiterary Genres: Kinds of Poetry 1. NARRATIVE POETRY-tells A Story Through Creative LinesXIUBBI SNOWIENo ratings yet
- 21st CLPW First Quarter ReviewerDocument3 pages21st CLPW First Quarter ReviewerSagee Ann AgOrNo ratings yet
- Notes Phil Lit...Document2 pagesNotes Phil Lit...Lannie Mae SamayangNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature 3rd Q NayyesaDocument8 pages21st Century Literature 3rd Q NayyesaJenrich MarceloNo ratings yet
- Phil Lit - Introduction IIDocument3 pagesPhil Lit - Introduction IIJessica AbuqueNo ratings yet
- Eng 4 NotesDocument7 pagesEng 4 NotesKESHIA FAITH RIZONNo ratings yet
- World Lit Prelim Exam ReviewerDocument20 pagesWorld Lit Prelim Exam ReviewerBES BEBENo ratings yet
- A Poem Which Tells A Story.: LiteratureDocument2 pagesA Poem Which Tells A Story.: LiteratureVienne AxlNo ratings yet
- English 2nd TestDocument1 pageEnglish 2nd TestWildred LamintaoNo ratings yet
- 21st Century From The Philippines and The World 3Document2 pages21st Century From The Philippines and The World 3Assiah AndreaNo ratings yet
- Lit Midterm RevDocument2 pagesLit Midterm RevNorolhaya UsmanNo ratings yet
- Phil Lit ReviewewrDocument11 pagesPhil Lit ReviewewrJessaNo ratings yet
- Edelt 104 Lesson 1 4 CompilationDocument14 pagesEdelt 104 Lesson 1 4 CompilationRhea BermejoNo ratings yet
- 21 Lit Nat ReviewerDocument5 pages21 Lit Nat ReviewerApricus BenciNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Nature and Meaning of Literature: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocument8 pagesLesson 1: Nature and Meaning of Literature: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldGillian Caingat LicuananNo ratings yet
- 21clpw ReviewerDocument8 pages21clpw ReviewerpatNo ratings yet
- Gned 15 ReviewerDocument6 pagesGned 15 ReviewerKarylle Anne Montoya100% (1)
- 21stCenturyLiterature Reviewer (FINAL)Document15 pages21stCenturyLiterature Reviewer (FINAL)Gian CPANo ratings yet
- LITERATUREDocument2 pagesLITERATUREPamela MarieNo ratings yet
- Philippine Literature in EnglishDocument3 pagesPhilippine Literature in EnglishSofia SJ Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- LITDocument4 pagesLITMarivica DagunaNo ratings yet
- See19 ReviewerDocument6 pagesSee19 ReviewerHazel Ann Sto TomasNo ratings yet
- Damasco Michelle Ann LIT 2 MID YEAR CLASS Activity 1Document4 pagesDamasco Michelle Ann LIT 2 MID YEAR CLASS Activity 1Mimi DamascoNo ratings yet
- 21 StrevDocument8 pages21 StrevJohn Carl SalavarriaNo ratings yet
- Definition of LiteratureDocument5 pagesDefinition of LiteratureHenry BascuguinNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature From The Philippines To The WorldDocument11 pages21st Century Literature From The Philippines To The WorldMelmar RiveraNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewerDocument7 pagesLiterature ReviewerLovelle Pirante OyzonNo ratings yet
- Asean Lit ReviewerDocument3 pagesAsean Lit ReviewerJENNIFER DOMINGONo ratings yet
- Lit ReviewerDocument13 pagesLit ReviewernellielumanglasNo ratings yet
- 1-20 Definition and Divisions of Literature Divisions of LiteratureDocument43 pages1-20 Definition and Divisions of Literature Divisions of LiteratureEll VNo ratings yet
- ST Lesson PoetryDocument2 pagesST Lesson PoetryharukincaidNo ratings yet
- PL PrelimDocument3 pagesPL PrelimMika CatimbangNo ratings yet
- Prose: Literatura/litteratura "Writing Formed With Letters", Although Some Definitions IncludeDocument3 pagesProse: Literatura/litteratura "Writing Formed With Letters", Although Some Definitions IncludeAj GomezNo ratings yet
- Nature, Essence, and Significance of LiteratureDocument3 pagesNature, Essence, and Significance of LiteratureJanelle Marcayda BritoNo ratings yet
- CNF Reviewer: 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesCNF Reviewer: 3rd QuarterKYZEIR JOVER JAVIERNo ratings yet
- Hum Notes 1Document7 pagesHum Notes 1SZAREHNA KEITH URRONo ratings yet
- Soclit Prelims: Do You Know About Its OriginDocument35 pagesSoclit Prelims: Do You Know About Its OriginGwy RubisNo ratings yet
- Philippine Literature 101Document8 pagesPhilippine Literature 101MarkAlcazar100% (1)
- 816-Article Text-3055-1-10-20220625Document10 pages816-Article Text-3055-1-10-20220625Mark PalomarNo ratings yet
- 2F and 2H Lecture 9Document57 pages2F and 2H Lecture 9Mark PalomarNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Contemporary Philippine ArtsDocument2 pagesReviewer in Contemporary Philippine ArtsMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument14 pagesEconomicsMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Disciplines and Ideas in Social ScienceDocument2 pagesReviewer in Disciplines and Ideas in Social ScienceMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- 2F and 2H Lecture 10Document50 pages2F and 2H Lecture 10Mark PalomarNo ratings yet
- English 10Document6 pagesEnglish 10Mark PalomarNo ratings yet
- 1 UTS IntroductionDocument15 pages1 UTS IntroductionMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Computer 9thDocument6 pagesReviewer For Computer 9thMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument46 pagesNSTPMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- Pathfit PresentationDocument8 pagesPathfit PresentationMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- 2 Philosophical PerspectivesDocument32 pages2 Philosophical PerspectivesMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Poetry SnakeDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 10 Poetry SnakerathnaNo ratings yet
- Villegasjerome Floyd SDocument2 pagesVillegasjerome Floyd Sapi-587944514No ratings yet
- Poetry Book ProjectDocument12 pagesPoetry Book ProjectHoài PhạmNo ratings yet
- Romeo and Juliet 5Document4 pagesRomeo and Juliet 5api-482261520No ratings yet
- 8th Action Plan ENGDocument9 pages8th Action Plan ENGsanthoshNo ratings yet
- Mary Jane RamosDocument6 pagesMary Jane RamosMasubay Arron Lance P.No ratings yet
- What Elements Will You Find in Epics and Myths?Document27 pagesWhat Elements Will You Find in Epics and Myths?Rocket Fire0% (1)
- ENGLISH - PROJECT - 2023-24 (1) SonuDocument18 pagesENGLISH - PROJECT - 2023-24 (1) Sonuprince3606.sharmaNo ratings yet
- BOW MTB REVISED v1Document29 pagesBOW MTB REVISED v1Jeseril HumamoyNo ratings yet
- Syllabus MAEnglish2017Document46 pagesSyllabus MAEnglish2017harideb733No ratings yet
- 21 STreportDocument18 pages21 STreportlalizegouNo ratings yet
- Poem AnalysisDocument2 pagesPoem Analysislakesiderunner100% (2)
- Emily 20 Bronte 20 BiographyDocument3 pagesEmily 20 Bronte 20 BiographyhrahamansanNo ratings yet
- The Witches of Durer and Hans Baldung GrienDocument37 pagesThe Witches of Durer and Hans Baldung GrienDanys ArtNo ratings yet
- Summer Vacation Homework in UrduDocument7 pagesSummer Vacation Homework in Urduafnaborlnaaiea100% (1)
- HAST SAMPLE Questions For Year 7 - 2Document3 pagesHAST SAMPLE Questions For Year 7 - 2liuqiong1011No ratings yet
- Reducing Test-Taking AnxietyDocument44 pagesReducing Test-Taking AnxietyEdessaMarieTiwanakNo ratings yet
- SRLIP Line DiagramDocument1 pageSRLIP Line Diagramvaranasirk1No ratings yet
- Mirror (Sylvia Plath) - Class NotesDocument23 pagesMirror (Sylvia Plath) - Class NotesDhruthi YanduriNo ratings yet
- Sonnet 116: William ShakespeareDocument10 pagesSonnet 116: William ShakespeareShah FarjanaNo ratings yet
- Essay - DONE - Owen - Anthem For Dommed YouthDocument2 pagesEssay - DONE - Owen - Anthem For Dommed YouthPranvera KameriNo ratings yet
- The Shakespearean Sonnet: WorksheetDocument3 pagesThe Shakespearean Sonnet: WorksheetJ M McRaeNo ratings yet
- Literary Terms: Example: and Sings A Solitary Song That Whistles in The Wind. - Wordsworth, Lucy Gray (Poem)Document8 pagesLiterary Terms: Example: and Sings A Solitary Song That Whistles in The Wind. - Wordsworth, Lucy Gray (Poem)M MNo ratings yet
- A New England Girlhood, Outlined From Memory (Beverly, MA) by Larcom, Lucy, 1824-1893Document127 pagesA New England Girlhood, Outlined From Memory (Beverly, MA) by Larcom, Lucy, 1824-1893Gutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- Song - George SzirtesDocument5 pagesSong - George Szirtesnef100% (2)
- English 9 Type of Text WritingDocument23 pagesEnglish 9 Type of Text WritingAizel Nova Fermilan ArañezNo ratings yet
- King Lear LanguageDocument3 pagesKing Lear LanguageMay ChanNo ratings yet
21st Century Literature
21st Century Literature
Uploaded by
Mark PalomarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
21st Century Literature
21st Century Literature
Uploaded by
Mark PalomarCopyright:
Available Formats
21st Century Literature (Reviewer) 9.
Flash Fiction – no beginning, middle, or end,
but tells the entire story.
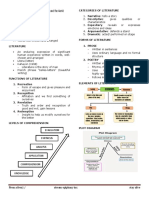
Forms of Literature
Oral – pre-Spanish colonization (verbally)
Written – published in books. (printed form)
Visual – presented in front of an audience.
Division of Literature
Prose – Most typographical form of language. Natural
flow of speech (i.e short stories)
Poems – uses aesthetic qualities of language to evoke
meaning. Rhythmic (i.e poems)
Types of Non-Fiction
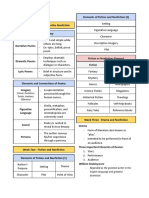
Differences of Prose and Poetry
Autobiography – life story of a person written by
Language himself
Prose – Straight - forward Biography – written by another person
Poetry - Expressive or Decorated Newspaper – Collection of news articles
Magazine – collection of articles regarding the lifestyle
Nature of man
Prose – Pragmatic Journal – daily record of personal events
Poetry – Imaginative Planner – daily record of business commitments
Anecdote – a brief revealing of an individual person
Essence
Prose – Information Classification of Poetry
Poetry – Experience Narrative – which tells a story, written in a
metered verse
Purpose Lyric – expresses personal and emotional
Prose – Convey a message feelings, were sung
Poetry – Delight or Amuse Drama – specific mode of fiction represented
in performance. Comes from a Greek word that
Paraphrasing means action
Prose – Possible
Poetry – Not Possible Types of Narrative
Epic – abt supernatural powers
Ideas Ballad – w/ harmony and rhythm
Prose – Found in sentences arranged in paragraphs Metrical Romance – dealing with emotions or
Poetry – Found in lines arranged In stanzas. phases of life. Simple straightforward, realistic.
Classification of Prose Types of Lyric
1. Fiction 2. Non-Fiction Song – Lyric Poem
Sonnet – 14 Iambic parameter lines
Types of Fiction Ode – praising or glorifying of an event
1. Fairytale Elegy – Lament for the dead.
2. Mythology (gods and goddesses)
3. Fable Types of Drama
4. Legend Historical – theatrical play with historic plot
5. Parable (abt religion) Comedy – w/ a happy ending
6. Allegory (symbolism to present an idea) Tragedy – with the death of some major
7. Novel – usually 500 pages characters
8. Short Story – max of 300 pages
Literary Devices
1. Allusion – can be used to paint a clear picture
or to connect with readers
2. Diction – choice of words or style used by the
writer to convey their message
- Formal, Informal (Conversational), and
Slang Diction (younger audience)
3. Alliteration – using the same letters or sounds
4. Euphemism – any terms that refer to
something impolite or unpleasant.
5. Flashbacks – goes back in time for a specific
6. Foreshadowing – clues about what will happen
in the future of the story.
7. Imagery – visually descriptive or figurative
language
8. Personification – gives human-like qualities to
non-human elements.
9. Juxtaposition – placing contras-ting elements
next to one another.
10. Onomatopoeia – sound something makes.
11. Symbolism – a larger message.
Metafiction
Reader is conscious of the craft
Author makes the reader more aware
“Hey, these characters are not true”
Historiographical Metafiction
Something that came from the author’s
imagination
Also tells the reader that a particular historical
event can be also made up as much as fiction
Historical Revisionism
Jose Protacio Rizal Mercado y Alonso Realonda
You might also like
- Quiz 1 PDFDocument8 pagesQuiz 1 PDFKurt Vendane VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Literature and Its CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesLiterature and Its CharacteristicsRicxz Xedric63% (8)
- Breaking Into Japanese LiteratureDocument195 pagesBreaking Into Japanese Literaturechucketti2100% (16)
- 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The World REVIEWERDocument6 pages21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The World REVIEWERYolanda Morales100% (1)
- HUMBOLDT, Alexander Von. Cosmos Vol.2Document417 pagesHUMBOLDT, Alexander Von. Cosmos Vol.2Diego Montenegro100% (1)
- English Reviewer: ST ND TH RD THDocument6 pagesEnglish Reviewer: ST ND TH RD THMelissa PasoquinNo ratings yet
- 21st CENTURY LIT 2ND SEM REVIEWERDocument5 pages21st CENTURY LIT 2ND SEM REVIEWERYsa ToledoNo ratings yet
- Lit ReviewerDocument11 pagesLit Reviewerljarcangel0324No ratings yet
- The Literary Forms in Philippine LiteratureDocument6 pagesThe Literary Forms in Philippine LiteratureRonalyn Cabana BlanceNo ratings yet
- C GELIT02 PrelimsDocument9 pagesC GELIT02 PrelimsKarl LintanNo ratings yet
- 12 - 21ST Century Literature (1-5)Document5 pages12 - 21ST Century Literature (1-5)Blessy Myl MagrataNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LiteratureDocument8 pagesIntroduction To LiteratureMerlyn Len AytonaNo ratings yet
- CNF Reviewer W1 2Document4 pagesCNF Reviewer W1 2ZairaNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature Reviewer 1st QuarterDocument6 pages21st Century Literature Reviewer 1st QuarterRiseson Peñas100% (4)
- 21st Century From The Philippines and The WorldDocument3 pages21st Century From The Philippines and The WorldZhemxie KimNo ratings yet
- 21st Century From The Philippines and The World 3Document4 pages21st Century From The Philippines and The World 3Alexandrea WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Green Monochromatic Simple The Minimalist Presentation TemplateDocument21 pagesGreen Monochromatic Simple The Minimalist Presentation TemplateTimmmyyy 27No ratings yet
- 21ST First Quarter Lesson CompilationDocument7 pages21ST First Quarter Lesson CompilationDenise Nicole T. LopezNo ratings yet
- LAS 1-Intro To LitDocument2 pagesLAS 1-Intro To Litannamarieabegael.lomaNo ratings yet
- Literature: General Types of LiteratureDocument1 pageLiterature: General Types of LiteratureJune Philip AtilledoNo ratings yet
- LIT101Document20 pagesLIT101luxasuhiNo ratings yet
- NON-FICTION - A Prose Writing That: Prose Is Derived From The Latin Prosa Which LiterallyDocument4 pagesNON-FICTION - A Prose Writing That: Prose Is Derived From The Latin Prosa Which LiterallyJomir Kimberly DomingoNo ratings yet
- Prose Poetry Hand OutDocument2 pagesProse Poetry Hand OutIyah Xyza VenturaNo ratings yet
- PhilitDocument4 pagesPhilitIrish AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Literary Genres: Kinds of Poetry 1. NARRATIVE POETRY-tells A Story Through Creative LinesDocument2 pagesLiterary Genres: Kinds of Poetry 1. NARRATIVE POETRY-tells A Story Through Creative LinesXIUBBI SNOWIENo ratings yet
- 21st CLPW First Quarter ReviewerDocument3 pages21st CLPW First Quarter ReviewerSagee Ann AgOrNo ratings yet
- Notes Phil Lit...Document2 pagesNotes Phil Lit...Lannie Mae SamayangNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature 3rd Q NayyesaDocument8 pages21st Century Literature 3rd Q NayyesaJenrich MarceloNo ratings yet
- Phil Lit - Introduction IIDocument3 pagesPhil Lit - Introduction IIJessica AbuqueNo ratings yet
- Eng 4 NotesDocument7 pagesEng 4 NotesKESHIA FAITH RIZONNo ratings yet
- World Lit Prelim Exam ReviewerDocument20 pagesWorld Lit Prelim Exam ReviewerBES BEBENo ratings yet
- A Poem Which Tells A Story.: LiteratureDocument2 pagesA Poem Which Tells A Story.: LiteratureVienne AxlNo ratings yet
- English 2nd TestDocument1 pageEnglish 2nd TestWildred LamintaoNo ratings yet
- 21st Century From The Philippines and The World 3Document2 pages21st Century From The Philippines and The World 3Assiah AndreaNo ratings yet
- Lit Midterm RevDocument2 pagesLit Midterm RevNorolhaya UsmanNo ratings yet
- Phil Lit ReviewewrDocument11 pagesPhil Lit ReviewewrJessaNo ratings yet
- Edelt 104 Lesson 1 4 CompilationDocument14 pagesEdelt 104 Lesson 1 4 CompilationRhea BermejoNo ratings yet
- 21 Lit Nat ReviewerDocument5 pages21 Lit Nat ReviewerApricus BenciNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Nature and Meaning of Literature: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocument8 pagesLesson 1: Nature and Meaning of Literature: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldGillian Caingat LicuananNo ratings yet
- 21clpw ReviewerDocument8 pages21clpw ReviewerpatNo ratings yet
- Gned 15 ReviewerDocument6 pagesGned 15 ReviewerKarylle Anne Montoya100% (1)
- 21stCenturyLiterature Reviewer (FINAL)Document15 pages21stCenturyLiterature Reviewer (FINAL)Gian CPANo ratings yet
- LITERATUREDocument2 pagesLITERATUREPamela MarieNo ratings yet
- Philippine Literature in EnglishDocument3 pagesPhilippine Literature in EnglishSofia SJ Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- LITDocument4 pagesLITMarivica DagunaNo ratings yet
- See19 ReviewerDocument6 pagesSee19 ReviewerHazel Ann Sto TomasNo ratings yet
- Damasco Michelle Ann LIT 2 MID YEAR CLASS Activity 1Document4 pagesDamasco Michelle Ann LIT 2 MID YEAR CLASS Activity 1Mimi DamascoNo ratings yet
- 21 StrevDocument8 pages21 StrevJohn Carl SalavarriaNo ratings yet
- Definition of LiteratureDocument5 pagesDefinition of LiteratureHenry BascuguinNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature From The Philippines To The WorldDocument11 pages21st Century Literature From The Philippines To The WorldMelmar RiveraNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewerDocument7 pagesLiterature ReviewerLovelle Pirante OyzonNo ratings yet
- Asean Lit ReviewerDocument3 pagesAsean Lit ReviewerJENNIFER DOMINGONo ratings yet
- Lit ReviewerDocument13 pagesLit ReviewernellielumanglasNo ratings yet
- 1-20 Definition and Divisions of Literature Divisions of LiteratureDocument43 pages1-20 Definition and Divisions of Literature Divisions of LiteratureEll VNo ratings yet
- ST Lesson PoetryDocument2 pagesST Lesson PoetryharukincaidNo ratings yet
- PL PrelimDocument3 pagesPL PrelimMika CatimbangNo ratings yet
- Prose: Literatura/litteratura "Writing Formed With Letters", Although Some Definitions IncludeDocument3 pagesProse: Literatura/litteratura "Writing Formed With Letters", Although Some Definitions IncludeAj GomezNo ratings yet
- Nature, Essence, and Significance of LiteratureDocument3 pagesNature, Essence, and Significance of LiteratureJanelle Marcayda BritoNo ratings yet
- CNF Reviewer: 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesCNF Reviewer: 3rd QuarterKYZEIR JOVER JAVIERNo ratings yet
- Hum Notes 1Document7 pagesHum Notes 1SZAREHNA KEITH URRONo ratings yet
- Soclit Prelims: Do You Know About Its OriginDocument35 pagesSoclit Prelims: Do You Know About Its OriginGwy RubisNo ratings yet
- Philippine Literature 101Document8 pagesPhilippine Literature 101MarkAlcazar100% (1)
- 816-Article Text-3055-1-10-20220625Document10 pages816-Article Text-3055-1-10-20220625Mark PalomarNo ratings yet
- 2F and 2H Lecture 9Document57 pages2F and 2H Lecture 9Mark PalomarNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Contemporary Philippine ArtsDocument2 pagesReviewer in Contemporary Philippine ArtsMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument14 pagesEconomicsMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Disciplines and Ideas in Social ScienceDocument2 pagesReviewer in Disciplines and Ideas in Social ScienceMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- 2F and 2H Lecture 10Document50 pages2F and 2H Lecture 10Mark PalomarNo ratings yet
- English 10Document6 pagesEnglish 10Mark PalomarNo ratings yet
- 1 UTS IntroductionDocument15 pages1 UTS IntroductionMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Computer 9thDocument6 pagesReviewer For Computer 9thMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument46 pagesNSTPMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- Pathfit PresentationDocument8 pagesPathfit PresentationMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- 2 Philosophical PerspectivesDocument32 pages2 Philosophical PerspectivesMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Poetry SnakeDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 10 Poetry SnakerathnaNo ratings yet
- Villegasjerome Floyd SDocument2 pagesVillegasjerome Floyd Sapi-587944514No ratings yet
- Poetry Book ProjectDocument12 pagesPoetry Book ProjectHoài PhạmNo ratings yet
- Romeo and Juliet 5Document4 pagesRomeo and Juliet 5api-482261520No ratings yet
- 8th Action Plan ENGDocument9 pages8th Action Plan ENGsanthoshNo ratings yet
- Mary Jane RamosDocument6 pagesMary Jane RamosMasubay Arron Lance P.No ratings yet
- What Elements Will You Find in Epics and Myths?Document27 pagesWhat Elements Will You Find in Epics and Myths?Rocket Fire0% (1)
- ENGLISH - PROJECT - 2023-24 (1) SonuDocument18 pagesENGLISH - PROJECT - 2023-24 (1) Sonuprince3606.sharmaNo ratings yet
- BOW MTB REVISED v1Document29 pagesBOW MTB REVISED v1Jeseril HumamoyNo ratings yet
- Syllabus MAEnglish2017Document46 pagesSyllabus MAEnglish2017harideb733No ratings yet
- 21 STreportDocument18 pages21 STreportlalizegouNo ratings yet
- Poem AnalysisDocument2 pagesPoem Analysislakesiderunner100% (2)
- Emily 20 Bronte 20 BiographyDocument3 pagesEmily 20 Bronte 20 BiographyhrahamansanNo ratings yet
- The Witches of Durer and Hans Baldung GrienDocument37 pagesThe Witches of Durer and Hans Baldung GrienDanys ArtNo ratings yet
- Summer Vacation Homework in UrduDocument7 pagesSummer Vacation Homework in Urduafnaborlnaaiea100% (1)
- HAST SAMPLE Questions For Year 7 - 2Document3 pagesHAST SAMPLE Questions For Year 7 - 2liuqiong1011No ratings yet
- Reducing Test-Taking AnxietyDocument44 pagesReducing Test-Taking AnxietyEdessaMarieTiwanakNo ratings yet
- SRLIP Line DiagramDocument1 pageSRLIP Line Diagramvaranasirk1No ratings yet
- Mirror (Sylvia Plath) - Class NotesDocument23 pagesMirror (Sylvia Plath) - Class NotesDhruthi YanduriNo ratings yet
- Sonnet 116: William ShakespeareDocument10 pagesSonnet 116: William ShakespeareShah FarjanaNo ratings yet
- Essay - DONE - Owen - Anthem For Dommed YouthDocument2 pagesEssay - DONE - Owen - Anthem For Dommed YouthPranvera KameriNo ratings yet
- The Shakespearean Sonnet: WorksheetDocument3 pagesThe Shakespearean Sonnet: WorksheetJ M McRaeNo ratings yet
- Literary Terms: Example: and Sings A Solitary Song That Whistles in The Wind. - Wordsworth, Lucy Gray (Poem)Document8 pagesLiterary Terms: Example: and Sings A Solitary Song That Whistles in The Wind. - Wordsworth, Lucy Gray (Poem)M MNo ratings yet
- A New England Girlhood, Outlined From Memory (Beverly, MA) by Larcom, Lucy, 1824-1893Document127 pagesA New England Girlhood, Outlined From Memory (Beverly, MA) by Larcom, Lucy, 1824-1893Gutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- Song - George SzirtesDocument5 pagesSong - George Szirtesnef100% (2)
- English 9 Type of Text WritingDocument23 pagesEnglish 9 Type of Text WritingAizel Nova Fermilan ArañezNo ratings yet
- King Lear LanguageDocument3 pagesKing Lear LanguageMay ChanNo ratings yet