Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Future From The Present
Future From The Present
Uploaded by
Jelena Josijević0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesThe document summarizes options for expressing future tenses in English. It provides tables and examples of constructions using will, be going to, and the present simple tense to indicate predictions, timetables, pre-arranged events, and more. It also discusses using the present progressive instead of be going to for pre-decided actions. Future perfect and future perfect progressive are used to refer to actions completed before some future time point or to emphasize duration.
Original Description:
Original Title
FUTURE FROM THE PRESENT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes options for expressing future tenses in English. It provides tables and examples of constructions using will, be going to, and the present simple tense to indicate predictions, timetables, pre-arranged events, and more. It also discusses using the present progressive instead of be going to for pre-decided actions. Future perfect and future perfect progressive are used to refer to actions completed before some future time point or to emphasize duration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesFuture From The Present
Future From The Present
Uploaded by
Jelena JosijevićThe document summarizes options for expressing future tenses in English. It provides tables and examples of constructions using will, be going to, and the present simple tense to indicate predictions, timetables, pre-arranged events, and more. It also discusses using the present progressive instead of be going to for pre-decided actions. Future perfect and future perfect progressive are used to refer to actions completed before some future time point or to emphasize duration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
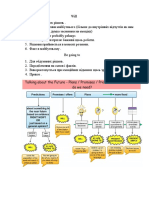
FUTURE FROM THE PRESENT-TIME PERSPECTIVE
In English, we use different constructions for expressing future. The following
table summarizes the options for simple future.
will be going to present simple
Predictions Timetables
with no evidence with visible evidence bus, train, flight, movie
timetables; working hours,
etc.
I think she will win Look at those clouds. It is Hurry up! Our train leaves in
Wimbledon. going to rain. fifteen minutes.
The weather will be perfect Watch out! The tree is going The classes start at 8, so we
all weekend. to fall. need to hurry up.
I’m sure she will call you.
Pre-arranged and planned Scheduled/repeated events
events (present progressive)
We are going to get married It is my birthday tomorrow.
th
on June 24 . It is Christmas next week!
We are going to have a coffee I have a German class next
tomorrow. week.
He has a job interview in a
fortnight.
Decisions Conditional clauses
Spontaneous on-spot Pre-decided actions; Zero: If you cool water to 0
decisions intentions (present degrees Celsius, it freezes.
progressive)
Yes, I will marry you. We are going to get married, 1st conditional: If she cools
I will help you. but we haven’t set a date. water to 0 degrees, it will
freeze.
Offers and promises Time clauses
Don’t worry! I will help you When you see him, tell him to
with that. come.
Instead of using be going to for pre-arranged and pre-decided events and actions, we
can use present progressive:
We are getting married on June 24th.
We are having coffee tomorrow.
In time clauses, we can use both present simple and present perfect. Present
simple is used when the completion of the event is not emphasized: When we get there, we
will have dinner first. Present perfect is used when the completion of the event is
highlighted: When we’ve had a rest, we’ll go out.
Future progressive is used to (1) describe an event which will be happening at a
future point in time: Come round in the morning. I’ll be baking a pie. (this time tomorrow, this
time next week, etc.) It can also be used for (2) fixed arrangements and plan to emphasize
duration; plus that they will be on-going, in progress, etc.: The band will be performing live
across Europe this summer.
Future perfect simple and progressive refer to time we look back at from a
future point. In simpler terms, it is used for actions and events that are to take place before
some future moment: In four years, I will have graduated. By the time you graduate, you will
have mastered English tenses.
If we additionally put emphasis on duration, we need future perfect progressive
tense: By the time you graduate, you will have been learning English for sixteen years. All
progressive tenses temporally correspond to their simple counterparts. However, they either
emphasize that actions were ongoing at the given moment, or they emphasize their duration:
You might also like
- FUTURE Tenses - PPTDocument37 pagesFUTURE Tenses - PPTi.diana100% (1)
- (AC-S03) Week 03 - Pre-Task - Quiz - Weekly Quiz - INGLES IV (10962)Document4 pages(AC-S03) Week 03 - Pre-Task - Quiz - Weekly Quiz - INGLES IV (10962)Elio Mamani Ticona100% (1)
- YLE Practice Tests Plus Movers TB 2nd EdDocument153 pagesYLE Practice Tests Plus Movers TB 2nd EdTrang Le88% (8)
- A Dictionary of Grammatical Analysis in Color From The Holy KoranDocument701 pagesA Dictionary of Grammatical Analysis in Color From The Holy Koranhaathabaitun302100% (1)
- Future TensesDocument21 pagesFuture TensesValeria MEDINANo ratings yet
- Simple Future - Usage and ExercisesDocument3 pagesSimple Future - Usage and ExercisesMiguel RojasNo ratings yet
- Future Will, May & Might1)Document2 pagesFuture Will, May & Might1)Aldo Jei IronyNo ratings yet
- G8 - Future TimeDocument4 pagesG8 - Future Timethu hien nguyenNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Session 1Document10 pagesUnit 5 Session 1Rocio GomezNo ratings yet
- Future Tense - THEORYDocument7 pagesFuture Tense - THEORYRoxana Caia GheboianuNo ratings yet
- Future TimeDocument18 pagesFuture Timeapi-252190418No ratings yet
- Futuro Con WillDocument5 pagesFuturo Con Willfernanda muñoz rengifoNo ratings yet
- Libro de Ingles (Tercer Nivel)Document75 pagesLibro de Ingles (Tercer Nivel)Mig EngelNo ratings yet
- Basic Future ExercisesDocument2 pagesBasic Future ExercisesRadosław SłowińskiNo ratings yet
- The FutureDocument7 pagesThe FutureMelisa SanchezNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses: Ins Olivar GranDocument20 pagesFuture Tenses: Ins Olivar GranOmar Herrera RodríguezNo ratings yet
- G8 - Future TimeDocument4 pagesG8 - Future Timenickclone217No ratings yet
- Future FormsDocument5 pagesFuture FormsIulia OstafiNo ratings yet
- Future Forms Week 13Document2 pagesFuture Forms Week 13LuNa AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Lesson StudentDocument3 pagesLesson StudentCynthiaNo ratings yet
- The Future - Infinitive of PurposeDocument24 pagesThe Future - Infinitive of PurposeSusaku KururugiNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses: Shall I / We Will He / She / It / You / TheyDocument25 pagesFuture Tenses: Shall I / We Will He / She / It / You / TheyТетяна КовтунNo ratings yet
- Going To Present Cont WillDocument2 pagesGoing To Present Cont WillanaNo ratings yet
- Future Forms CompleteDocument4 pagesFuture Forms CompleteNikeninoNo ratings yet
- Guía Examen Inglés INTERMEDIO 1Document4 pagesGuía Examen Inglés INTERMEDIO 1Jennifer AcevedoNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument20 pagesFutureAli AteeqNo ratings yet
- English III - Student - S TextbookDocument76 pagesEnglish III - Student - S TextbookGabriela Delgado SepúlvedaNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH Language I - Topic 5 - Future TensesDocument31 pagesENGLISH Language I - Topic 5 - Future TensesSandra VNo ratings yet
- Future FormsDocument4 pagesFuture Formsniks1999aNo ratings yet
- The Future (Predictions, Decisions and Intentions, Arrangements, Other Future MeaningsDocument12 pagesThe Future (Predictions, Decisions and Intentions, Arrangements, Other Future MeaningsYulia SidelnykNo ratings yet
- The Future TenseDocument8 pagesThe Future Tenseazeen.zanzoonNo ratings yet
- Furure ContinuousDocument2 pagesFurure ContinuousAnna JanczewskaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Microsoft WordDocument18 pagesEnglish Grammar Microsoft WordMarysia AndrunyszynNo ratings yet
- Future FormsDocument19 pagesFuture FormsFEDERICO JOSE BENLLOCH MARTINo ratings yet
- How To Express The Future in English?Document29 pagesHow To Express The Future in English?July RojasNo ratings yet
- Upper-Intermediate GW 03aDocument2 pagesUpper-Intermediate GW 03aJose AlbertoNo ratings yet
- The Future Tenses: Subject + Auxiliary Verb + Main Verb (Present Part.)Document6 pagesThe Future Tenses: Subject + Auxiliary Verb + Main Verb (Present Part.)Чарли ЖутиNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Future TenseDocument28 pagesUnit 1 - Future Tenseerick onofreNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses: Class 106 / B1Document42 pagesFuture Tenses: Class 106 / B1Yiğit Kaan ÜnalNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses UpperDocument9 pagesFuture Tenses UpperMacaNo ratings yet
- Talking About FutureDocument21 pagesTalking About FutureAnuradha SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- PPT. Expressing The FutureDocument53 pagesPPT. Expressing The FutureHanizar Rachman100% (1)
- Semana 06 - PPT Sesión Presencial English IVDocument34 pagesSemana 06 - PPT Sesión Presencial English IVIvan CotrinaNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument3 pagesFuture Tensessabina juiNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument18 pagesGrammarAnandan GunasekaranNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument16 pagesFutureAnnaSmith100% (1)
- Future TensesDocument56 pagesFuture TensesThảo LyNo ratings yet
- Materi Will Vs Going ToDocument5 pagesMateri Will Vs Going Tohanum lulukNo ratings yet
- CGM - Will Vs Be Going To (Week 1) (Student Copy)Document3 pagesCGM - Will Vs Be Going To (Week 1) (Student Copy)Yusuf Can SözerNo ratings yet
- English III - Student - S TextbookDocument82 pagesEnglish III - Student - S TextbookEdier BravoNo ratings yet
- Future Time 1Document16 pagesFuture Time 1taniaanglinawatiNo ratings yet
- S Will Come 'LL Leave See Will Give: Come and Go I'm Coming /i'm GoingDocument2 pagesS Will Come 'LL Leave See Will Give: Come and Go I'm Coming /i'm GoingdsadsaNo ratings yet
- Be Going ToDocument5 pagesBe Going TofilipabarbosaNo ratings yet
- Expressing FutureDocument1 pageExpressing FutureKrisEnglNo ratings yet
- Future EmlDocument5 pagesFuture EmlElvira MateoNo ratings yet
- XauqueDocument25 pagesXauqueLindsey StokesNo ratings yet
- Intermediate GW 04b PDFDocument2 pagesIntermediate GW 04b PDFMarie NayukyNo ratings yet
- Future ContinuousDocument1 pageFuture ContinuousWaldo GostNo ratings yet
- Grammar Revision - FutureDocument6 pagesGrammar Revision - FutureSara SmithNo ratings yet
- Engleski (Future Forms)Document12 pagesEngleski (Future Forms)Kozmetika Amina-Mirnesa SubašićNo ratings yet
- Futures AdvancedDocument14 pagesFutures AdvancedJorge RoseroNo ratings yet
- Be Going To BE GOING TO For IntentionsDocument5 pagesBe Going To BE GOING TO For IntentionsAamir KhanNo ratings yet
- Tense FormationDocument3 pagesTense FormationJelena JosijevićNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 GrammarDocument2 pagesHandout 1 GrammarJelena JosijevićNo ratings yet
- Met A Linguistic ComparativeDocument13 pagesMet A Linguistic ComparativeJelena JosijevićNo ratings yet
- Phonological Features of Slogans in English Mirna VidakovicDocument14 pagesPhonological Features of Slogans in English Mirna VidakovicJelena JosijevićNo ratings yet
- G Comparison of AdjectivesDocument3 pagesG Comparison of AdjectivesJelena JosijevićNo ratings yet
- Past Modals: What Do You Think Happened Here?Document14 pagesPast Modals: What Do You Think Happened Here?Jelena JosijevićNo ratings yet
- Past Modals: What Do You Think Happened Here?Document14 pagesPast Modals: What Do You Think Happened Here?Jelena JosijevićNo ratings yet
- EF4e Intplus AK Filetest 3bDocument3 pagesEF4e Intplus AK Filetest 3bjeanneramazanovaNo ratings yet
- Chat GPTDocument8 pagesChat GPTFayçal SinaceurNo ratings yet
- Permutation & Combination 6 DPP 59Document2 pagesPermutation & Combination 6 DPP 59Ashwani SinghNo ratings yet
- Get Ready For IELTS SBDocument228 pagesGet Ready For IELTS SBTuan Dung HoNo ratings yet
- Critical Book Review English For PhysicsDocument19 pagesCritical Book Review English For PhysicsElfrida TurnipNo ratings yet
- Number and Letter SeriesDocument3 pagesNumber and Letter SeriesDEVENDER KASHYAVNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent ContinuousNguyễn HảiNo ratings yet
- Grammar TH.1 - Đáp ÁnDocument2 pagesGrammar TH.1 - Đáp ÁnAnh Hào Võ VănNo ratings yet
- 1 The Challenge of Teaching Kids Part 1 HandbookDocument198 pages1 The Challenge of Teaching Kids Part 1 HandbookMonica GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Recerencing, CitationsDocument4 pagesRecerencing, CitationsLiana HoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1ADocument2 pagesWorksheet 1AMilton Vincent LibajanNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Tense (Geniş Zaman) : 1. Facts, Truths, GeneralizationsDocument7 pagesPresent Simple Tense (Geniş Zaman) : 1. Facts, Truths, Generalizationsmehmet fatih kılıçNo ratings yet
- With Time ExpressionsDocument7 pagesWith Time ExpressionsMartaNo ratings yet
- Bae 8Document22 pagesBae 8KintokoNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument2 pagesTranscriptionAbril LeivaNo ratings yet
- BC Chap-3 PPT NewDocument31 pagesBC Chap-3 PPT NewEalshady HoneyBee Work ForceNo ratings yet
- Deal or No Deal ModalsDocument23 pagesDeal or No Deal ModalsCris FedericoNo ratings yet
- Writing A News Report - Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesWriting A News Report - Lesson PlanAnita Jankovic100% (1)
- SO2ndEd Elem Unit Test 8Document1 pageSO2ndEd Elem Unit Test 8Vase PetrovNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary For Academic IELTS Writing Task 1Document45 pagesVocabulary For Academic IELTS Writing Task 1Farah BahrouniNo ratings yet
- ملخص شامل في اللغة الإنجليزية للشعب العلمية1649968630Document80 pagesملخص شامل في اللغة الإنجليزية للشعب العلمية1649968630SabrinaNo ratings yet
- Iex 3e Intermediate Tests U6Document5 pagesIex 3e Intermediate Tests U6Martyna CegiełkaNo ratings yet
- ENG014 CanaresDocument2 pagesENG014 CanaresFearless CnrsNo ratings yet
- The Semitic Languages (2nd - (Z-Library) - 240501 - 223407Document773 pagesThe Semitic Languages (2nd - (Z-Library) - 240501 - 223407Mimi ScreminNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - MacroskillsDocument8 pagesMODULE 1 - MacroskillsIze PentecostesNo ratings yet
- 2 Cutting 2002 P. 1-7 PDFDocument8 pages2 Cutting 2002 P. 1-7 PDFAilénVillalbaNo ratings yet
- Describing Your Hometown - EngooDocument12 pagesDescribing Your Hometown - EngooSandra SorianoNo ratings yet