Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 viewsBio Reviewer
Bio Reviewer
Uploaded by
A - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonThe cell cycle consists of interphase and cell division. Interphase includes G1, S, and G2 phases where the cell grows and prepares for division. The cell undergoes DNA replication in S phase. Cell division includes karyokinesis, where DNA is replicated, and cytokinesis, where the cell cytoplasm divides. Mitosis produces two daughter cells with identical DNA to the parent cell. Cells divide to grow, repair tissues, and prevent becoming too large to function properly.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Feasibility Study of Banana Peels and Coconut Husks As An Alternative Raw Materials For Paper MakingDocument45 pagesFeasibility Study of Banana Peels and Coconut Husks As An Alternative Raw Materials For Paper MakingA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Histology Question Bank-1Document55 pagesHistology Question Bank-1Abd El-Rahman Salah100% (5)
- Cell Cycle, Apoptosis, and CancerDocument13 pagesCell Cycle, Apoptosis, and Cancermiguel cuevas100% (1)
- Word CycleDocument3 pagesWord CycleNday GwapaKUNONo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument9 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Divisionjmd5qbmt4kNo ratings yet
- Notes-Cell Cycle and Cell Division NewDocument6 pagesNotes-Cell Cycle and Cell Division NewKisna guptaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell DivisionKaith Ashlee De LeonNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis PresentationDocument53 pagesCell Cycle and Mitosis Presentationbisma nadeemNo ratings yet
- Bio LectureDocument4 pagesBio LectureAbegail TaarNo ratings yet
- Control Points in The Cell CycleDocument3 pagesControl Points in The Cell CyclelibbyNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell DivisionMEDRANO, Hana Jhiemyka O.No ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument2 pagesCell CycleGlenda ArajaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Lecture ReviewerDocument2 pagesCell Cycle Lecture ReviewerIgnacio, Moira Jomille K.No ratings yet
- Cont CytoDocument7 pagesCont CytoVeronica AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Biology of Cell DivisionDocument34 pagesBiology of Cell DivisionWai KikiNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument81 pagesCell CycleHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3-Cell Cycle and CheckpointsDocument53 pagesLesson 3-Cell Cycle and CheckpointsHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle NCERTDocument12 pagesCell Cycle NCERTskindustrieshelplineNo ratings yet
- Bio11 Campbell Chapter 12Document4 pagesBio11 Campbell Chapter 12ChristineNo ratings yet
- 1 ScanDocument11 pages1 ScanAsadNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Mitosis DividionDocument24 pagesCell Cycle Mitosis DividionAshley Nicole VillegasNo ratings yet
- Cell Growth and DivisionDocument13 pagesCell Growth and DivisionmunozayshiaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Cell Reproduction TIDARATDocument102 pagesCell Division and Cell Reproduction TIDARATPanyapat SrisawatNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - Study ModuleDocument31 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division - Study ModuleRitun KumarNo ratings yet
- 3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisDocument4 pages3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument3 pagesCell Cycle and MitosisalxndrasenalesNo ratings yet
- 3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisDocument4 pages3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Important Take AwaysDocument12 pagesBiotechnology Important Take AwaysRexel BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Gen Bio 1 - MidtermDocument7 pagesModule 3 - Gen Bio 1 - MidtermAngel Cuacko GacmatanNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Trans 1st SemDocument62 pagesCytogenetics Trans 1st SemMhizzy ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Cell Division: Interphase M (Mitosis) PhaseDocument2 pagesCell Cycle Cell Division: Interphase M (Mitosis) Phasesridevikamaraj16No ratings yet
- 4th Module 2 Cel ReproductionDocument57 pages4th Module 2 Cel ReproductionLocal ClownNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle: Histology Lab Mitosis and Meiosis 02/10/2021Document8 pagesCell Cycle: Histology Lab Mitosis and Meiosis 02/10/2021Danielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa LambanNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer 2Document9 pagesBiology Reviewer 2John Arnel BunquinNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For General Biology (Mitosis, Meiosis, Etc.) : Grade 11 STEMDocument20 pagesReviewer For General Biology (Mitosis, Meiosis, Etc.) : Grade 11 STEMYanni SerenoNo ratings yet
- General Biology (2nd Quarter Reviewer)Document18 pagesGeneral Biology (2nd Quarter Reviewer)Kimberly DalagNo ratings yet
- Cell-Cycle ReviewerDocument6 pagesCell-Cycle ReviewerRoan James OcampoNo ratings yet
- Bio 1S The Cell CycleDocument92 pagesBio 1S The Cell Cyclestem.patinosamcharrieNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument33 pagesCell CycleA- CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument46 pagesCell Cyclehobiforlife 22No ratings yet
- Week 10 - GenBio1 CELL CYCLE 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document3 pagesWeek 10 - GenBio1 CELL CYCLE 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- General-Biology Notes PerezDocument4 pagesGeneral-Biology Notes PerezAshley PerezNo ratings yet
- 2ND Year CytogeneticsDocument11 pages2ND Year Cytogenetics뷸한연No ratings yet
- L1 Mitosis NEWDocument39 pagesL1 Mitosis NEWloaiNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Cell ReproductionDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology - Cell Reproductionlol okNo ratings yet
- 종양Document22 pages종양wiwaxia1911No ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument17 pagesGeneral BiologyZyra Mae PaguintoNo ratings yet
- Chromosome: - To Efficiently Package DNA Into Smaller Volumes ToDocument10 pagesChromosome: - To Efficiently Package DNA Into Smaller Volumes ToCarmela Cordon FelixNo ratings yet
- The Phase of Growth and DNADocument4 pagesThe Phase of Growth and DNARedNo ratings yet
- Week 3 BiologyDocument9 pagesWeek 3 BiologyKadelyn GomezNo ratings yet
- Cell Growth and Division PrintDocument3 pagesCell Growth and Division PrintArif HakimiNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument10 pagesCell CycleChad LabradorNo ratings yet
- State Phase Abbrevia Tion DescriptionDocument5 pagesState Phase Abbrevia Tion DescriptionMae Matias100% (1)
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument3 pagesGen Bio ReviewerJustin JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument7 pagesCell DivisionLujinelle FusinganNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Divisionchar montejeroNo ratings yet
- Biotech 3 Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesBiotech 3 Cell DivisionClinton YmbongNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument100 pagesCell CycleAriane NicoleNo ratings yet
- Biology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Solutions Manual DownloadDocument11 pagesBiology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Solutions Manual DownloadJamie Hayes100% (26)
- Union of Egg and Sperm Cell in The Fallopian Tube, Producing A Zygote (The First Cell of The New Offspring)Document2 pagesUnion of Egg and Sperm Cell in The Fallopian Tube, Producing A Zygote (The First Cell of The New Offspring)AIMEE MARGARET FLORESNo ratings yet
- Topical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2From EverandTopical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chapter Iii MethodologyDocument14 pagesChapter Iii MethodologyA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Stem6 Lesson 5 Final TermDocument26 pagesStem6 Lesson 5 Final TermA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Potential of Various AgrDocument13 pagesAnalysis of The Potential of Various AgrA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Amylum and Citrus Aurantium L Peeling Utilizing inDocument16 pagesAmylum and Citrus Aurantium L Peeling Utilizing inA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- JPSP 2022 613Document6 pagesJPSP 2022 613A - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Pulp and Paper Making From Grass FibreDocument3 pagesPulp and Paper Making From Grass FibreA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Feasibility of Dried Leaves in The Production of PaperDocument14 pagesFeasibility of Dried Leaves in The Production of PaperA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - Hermon100% (2)
- NorMazlanaetal 2014suitabilitycoiraspulpandpaperDocument9 pagesNorMazlanaetal 2014suitabilitycoiraspulpandpaperA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3-Group 5Document14 pagesChapter-3-Group 5A - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- REVISED RESEARCH PAPER Algae Paper An Innovation of Algae Based PDFDocument50 pagesREVISED RESEARCH PAPER Algae Paper An Innovation of Algae Based PDFA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Romblon Pandanusutilis Leaves Mixedwith Causticsodaasan Alternativein Making PaperfinalDocument37 pagesRomblon Pandanusutilis Leaves Mixedwith Causticsodaasan Alternativein Making PaperfinalA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Design in Art Crafts .Document4 pagesContemporary Design in Art Crafts .A - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Sample Business Plan Mi Faburrito Part 2 3Document3 pagesSample Business Plan Mi Faburrito Part 2 3A - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 - Group 5Document13 pagesChapter-2 - Group 5A - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- CV OutputDocument1 pageCV OutputA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- CV OutputDocument1 pageCV OutputA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Atom Araullo BiographyDocument3 pagesAtom Araullo BiographyA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- ENG 9 Movie ReviewDocument2 pagesENG 9 Movie ReviewA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- English Output WKWKWKDocument1 pageEnglish Output WKWKWKA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Bots 4th Paragraph FINALDocument1 pageBots 4th Paragraph FINALA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Individual Title Form - STEMDocument2 pagesIndividual Title Form - STEMA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Arts ReviewerDocument4 pagesContemporary Arts ReviewerA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Happ Lab Week 3Document36 pagesHapp Lab Week 3A - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Examination Room Assignment SHS 1st Sem MIDTERMDocument29 pagesExamination Room Assignment SHS 1st Sem MIDTERMA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Chapter TestDocument4 pagesEndocrine Chapter TestPrince K. TaileyNo ratings yet
- Mushroom Production and TechnologyDocument36 pagesMushroom Production and Technologymozhi74826207No ratings yet
- Foods That Cause Acne: SUNDAY, APRIL 8, 2012Document3 pagesFoods That Cause Acne: SUNDAY, APRIL 8, 2012FitriAndriyaniNo ratings yet
- Test Rev AnswersDocument17 pagesTest Rev AnswersViea Pacaco SivaNo ratings yet
- Kidney Problems and DialysisDocument3 pagesKidney Problems and DialysismarymakinNo ratings yet
- Resources - Fat Embolism Syndrome (FES)Document19 pagesResources - Fat Embolism Syndrome (FES)Hareen Reddy100% (1)
- 1.1 Introduction To Human Anatomy - 2018-2019 PDFDocument11 pages1.1 Introduction To Human Anatomy - 2018-2019 PDFسيف محمود شاكر حسنNo ratings yet
- Food and Feeding Habits of The African Big Barb Labeobarbus Intermedius (Rüppell, 1836) in Ethiopian Water Bodies: A ReviewDocument6 pagesFood and Feeding Habits of The African Big Barb Labeobarbus Intermedius (Rüppell, 1836) in Ethiopian Water Bodies: A ReviewAgumassie TesfahunNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Air Sinus Oral SurgeryDocument49 pagesMaxillary Air Sinus Oral SurgeryDentist Dina SamyNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology - Physical & Chemical Injuries of Oral CavityDocument44 pagesOral Pathology - Physical & Chemical Injuries of Oral CavityRachit Srivastava83% (18)
- Aha Acsm Risk Screening AdaDocument1 pageAha Acsm Risk Screening AdawalterNo ratings yet
- Biceps WorkoutDocument11 pagesBiceps WorkoutBhuvanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of RespirationDocument19 pagesPhysiology of RespirationRafiqo hafidNo ratings yet
- 243 FullDocument8 pages243 FullbiologiaufbaNo ratings yet
- 2020 - 06 - 25 NEJM Salicylate ToxicityDocument12 pages2020 - 06 - 25 NEJM Salicylate ToxicityVishwaCrNo ratings yet
- X ICSE Endocrine System-1 PDFDocument9 pagesX ICSE Endocrine System-1 PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Toxicologic Emergencies, 11th Goldfrank's 2019Document10 pagesToxicologic Emergencies, 11th Goldfrank's 2019RenéNo ratings yet
- Niraamaya Spa MenuDocument35 pagesNiraamaya Spa MenuSanjeev HariharanNo ratings yet
- Cervical Plexua, Phrenic NerveDocument15 pagesCervical Plexua, Phrenic NervetuhinsinghNo ratings yet
- Oina SummaryDocument37 pagesOina SummaryC1 - RAZALAN NICKA JOYNo ratings yet
- Food NutritionDocument19 pagesFood NutritionLaeeq R MalikNo ratings yet
- Embracing Changes: Managing Anxiety, Returning To "A Norm" With Vivian ZhangDocument2 pagesEmbracing Changes: Managing Anxiety, Returning To "A Norm" With Vivian ZhangGrad MindsNo ratings yet
- IBO 2001 Theory Part B - CCLDocument28 pagesIBO 2001 Theory Part B - CCLBrayan GallardoNo ratings yet
- Stimuli & Responses 1.3 & 1.4Document5 pagesStimuli & Responses 1.3 & 1.4Yusrahanis NadilahNo ratings yet
- Performance of PRISM III and PELOD-2 Score in A PICUDocument6 pagesPerformance of PRISM III and PELOD-2 Score in A PICUAnantaBenvenutoNo ratings yet
- 11 - Head & Neck (Blood Vessels) (FF) - Part 1Document20 pages11 - Head & Neck (Blood Vessels) (FF) - Part 1checkmate100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Aids and NecessitiesDocument6 pagesPharmaceutical Aids and NecessitiestriciapascualMD100% (1)
- Evaluation of Compliance With Standard Criteria For Postero-Anterior (Pa) Chest Radiographs in Parklane Hospital EnuguDocument37 pagesEvaluation of Compliance With Standard Criteria For Postero-Anterior (Pa) Chest Radiographs in Parklane Hospital EnuguLavinia VictorNo ratings yet
- Staar g3 2016test Read FDocument33 pagesStaar g3 2016test Read FsatishNo ratings yet
Bio Reviewer
Bio Reviewer
Uploaded by
A - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - Hermon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesThe cell cycle consists of interphase and cell division. Interphase includes G1, S, and G2 phases where the cell grows and prepares for division. The cell undergoes DNA replication in S phase. Cell division includes karyokinesis, where DNA is replicated, and cytokinesis, where the cell cytoplasm divides. Mitosis produces two daughter cells with identical DNA to the parent cell. Cells divide to grow, repair tissues, and prevent becoming too large to function properly.
Original Description:
Original Title
bio reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe cell cycle consists of interphase and cell division. Interphase includes G1, S, and G2 phases where the cell grows and prepares for division. The cell undergoes DNA replication in S phase. Cell division includes karyokinesis, where DNA is replicated, and cytokinesis, where the cell cytoplasm divides. Mitosis produces two daughter cells with identical DNA to the parent cell. Cells divide to grow, repair tissues, and prevent becoming too large to function properly.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesBio Reviewer
Bio Reviewer
Uploaded by
A - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonThe cell cycle consists of interphase and cell division. Interphase includes G1, S, and G2 phases where the cell grows and prepares for division. The cell undergoes DNA replication in S phase. Cell division includes karyokinesis, where DNA is replicated, and cytokinesis, where the cell cytoplasm divides. Mitosis produces two daughter cells with identical DNA to the parent cell. Cells divide to grow, repair tissues, and prevent becoming too large to function properly.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
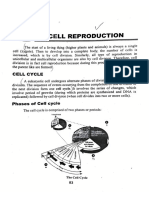
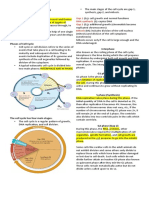
LESSON 3.
1: CELL CYCLE - Production of spindle fibers
(microtubules) in the centrioles (part of
CELL CYCLE – life cycle of cell which it grows and
the centrosome) occurs.
divides
CHECKPOINT IN G2 PHASE
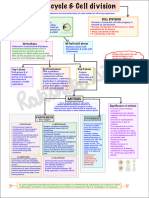
TWO STAGE OF CELL CYCLE
- DNA made in S phase working correctly
INTERPHASE – preparation of cell before it
- Is it growing well enough?
undergoes cellular division
- Does it have the enough resource to
- Composed of 90% of cell cycle continue to cell division
- Growing
CHECKPOINT – monitor if cells are capable to
- DNA replicating
divide
- Doing their functions
- Preparation before cell division APOPTOSIS – Cell death, self-destruct, happens
when problems cannot be fixed
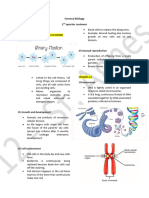
CELL DIVISON DEPENDS ON TYPE OF ORGANISM
CELL REST – cell will rest if the problem can still
EUKARYOTES – multicellular organism, cell
be fixed
division: Mitosis and Meiosis
Some cells don’t go to the phases that we
PROKARYOTES – unicellular organism, cell
mention instead they remain to G0 (GAP 0)
division: binary fission (asexual)
G0 is a RESTING PHASE
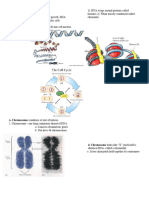
INTERPHASE CONSIST OF 3 STAGES
Cells are still performing functions but
G1 (GAP1) PHASE
they are not preparing to divide
- Cell decides whether to enter cell cycle Some cells go here temporarily
- Characterized by increase cell mass due Some cells stay here permanently (brain
to absorption of nutrients and nerve cells)
- Organelles are highly active on this stag
IMPORTANT NOTE
CHECKPOINT IN G1 PHASE
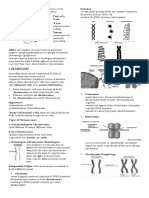
- During interphase DNA is in it loose
- Is the cell growing well enough? form called chromatin fiber
- Is its DNA damaged? - During mitosis DNA is in its condensed
- Does it have resources to continue? form called chromosomes
S (SYNTHESIS) PHASE CELL DIVISION – process by which a cell, called
the parent cell, divides into two or more cells,
- Stage where DNA replication occurs
called daughter cells
- Doubling for genetic content for each
daughter cells - Both eukaryotes and prokaryotes
- Synthesis of histones and other nuclear undergo cell division
requirements
TWO TYPE OF CELL DIVISION
G2 (GAP2) PHASE
- Mitosis (somatic cell division)
- Cell is ready enter mitosis - Meiosis (reproductive cell division)
TWO MAIN EVENTS OF CELL DIVISION
Karyokinesis
- Also known as mitosis or nuclear cell
division
- Doubling of genetic information for
each daughter cells (DNA replication)
Cytokinesis
- Also known as cytoplasmic division
- Division of cytoplasm and its
components
Mitosis
- Produce daughter cell that have the
same number of chromosomes as their
parent (diploid)
- In mitosis if the parent cell has 46
chromosomes the daughter cells will
both have 46 chromosomes
WHY DO CELLS NEED TO DIVIDE?
- Living things grow by producing cells
- Repair of damaged tissues
- If cell gets too big, it cannot get enough
nutrients into the cell and wastes out
of the cell
- Original cell is called parent cell; 2 new
cells are called daughter cells
- Before cell division, cell replicates all of
its DNA, so each daughter cell gets
complete set of genetic information
You might also like
- Feasibility Study of Banana Peels and Coconut Husks As An Alternative Raw Materials For Paper MakingDocument45 pagesFeasibility Study of Banana Peels and Coconut Husks As An Alternative Raw Materials For Paper MakingA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Histology Question Bank-1Document55 pagesHistology Question Bank-1Abd El-Rahman Salah100% (5)
- Cell Cycle, Apoptosis, and CancerDocument13 pagesCell Cycle, Apoptosis, and Cancermiguel cuevas100% (1)
- Word CycleDocument3 pagesWord CycleNday GwapaKUNONo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument9 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Divisionjmd5qbmt4kNo ratings yet
- Notes-Cell Cycle and Cell Division NewDocument6 pagesNotes-Cell Cycle and Cell Division NewKisna guptaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell DivisionKaith Ashlee De LeonNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis PresentationDocument53 pagesCell Cycle and Mitosis Presentationbisma nadeemNo ratings yet
- Bio LectureDocument4 pagesBio LectureAbegail TaarNo ratings yet
- Control Points in The Cell CycleDocument3 pagesControl Points in The Cell CyclelibbyNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell DivisionMEDRANO, Hana Jhiemyka O.No ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument2 pagesCell CycleGlenda ArajaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Lecture ReviewerDocument2 pagesCell Cycle Lecture ReviewerIgnacio, Moira Jomille K.No ratings yet
- Cont CytoDocument7 pagesCont CytoVeronica AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Biology of Cell DivisionDocument34 pagesBiology of Cell DivisionWai KikiNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument81 pagesCell CycleHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3-Cell Cycle and CheckpointsDocument53 pagesLesson 3-Cell Cycle and CheckpointsHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle NCERTDocument12 pagesCell Cycle NCERTskindustrieshelplineNo ratings yet
- Bio11 Campbell Chapter 12Document4 pagesBio11 Campbell Chapter 12ChristineNo ratings yet
- 1 ScanDocument11 pages1 ScanAsadNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Mitosis DividionDocument24 pagesCell Cycle Mitosis DividionAshley Nicole VillegasNo ratings yet
- Cell Growth and DivisionDocument13 pagesCell Growth and DivisionmunozayshiaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Cell Reproduction TIDARATDocument102 pagesCell Division and Cell Reproduction TIDARATPanyapat SrisawatNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - Study ModuleDocument31 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division - Study ModuleRitun KumarNo ratings yet
- 3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisDocument4 pages3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument3 pagesCell Cycle and MitosisalxndrasenalesNo ratings yet
- 3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisDocument4 pages3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Important Take AwaysDocument12 pagesBiotechnology Important Take AwaysRexel BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Gen Bio 1 - MidtermDocument7 pagesModule 3 - Gen Bio 1 - MidtermAngel Cuacko GacmatanNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Trans 1st SemDocument62 pagesCytogenetics Trans 1st SemMhizzy ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Cell Division: Interphase M (Mitosis) PhaseDocument2 pagesCell Cycle Cell Division: Interphase M (Mitosis) Phasesridevikamaraj16No ratings yet
- 4th Module 2 Cel ReproductionDocument57 pages4th Module 2 Cel ReproductionLocal ClownNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle: Histology Lab Mitosis and Meiosis 02/10/2021Document8 pagesCell Cycle: Histology Lab Mitosis and Meiosis 02/10/2021Danielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa LambanNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer 2Document9 pagesBiology Reviewer 2John Arnel BunquinNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For General Biology (Mitosis, Meiosis, Etc.) : Grade 11 STEMDocument20 pagesReviewer For General Biology (Mitosis, Meiosis, Etc.) : Grade 11 STEMYanni SerenoNo ratings yet
- General Biology (2nd Quarter Reviewer)Document18 pagesGeneral Biology (2nd Quarter Reviewer)Kimberly DalagNo ratings yet
- Cell-Cycle ReviewerDocument6 pagesCell-Cycle ReviewerRoan James OcampoNo ratings yet
- Bio 1S The Cell CycleDocument92 pagesBio 1S The Cell Cyclestem.patinosamcharrieNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument33 pagesCell CycleA- CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument46 pagesCell Cyclehobiforlife 22No ratings yet
- Week 10 - GenBio1 CELL CYCLE 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document3 pagesWeek 10 - GenBio1 CELL CYCLE 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- General-Biology Notes PerezDocument4 pagesGeneral-Biology Notes PerezAshley PerezNo ratings yet
- 2ND Year CytogeneticsDocument11 pages2ND Year Cytogenetics뷸한연No ratings yet
- L1 Mitosis NEWDocument39 pagesL1 Mitosis NEWloaiNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Cell ReproductionDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology - Cell Reproductionlol okNo ratings yet
- 종양Document22 pages종양wiwaxia1911No ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument17 pagesGeneral BiologyZyra Mae PaguintoNo ratings yet
- Chromosome: - To Efficiently Package DNA Into Smaller Volumes ToDocument10 pagesChromosome: - To Efficiently Package DNA Into Smaller Volumes ToCarmela Cordon FelixNo ratings yet
- The Phase of Growth and DNADocument4 pagesThe Phase of Growth and DNARedNo ratings yet
- Week 3 BiologyDocument9 pagesWeek 3 BiologyKadelyn GomezNo ratings yet
- Cell Growth and Division PrintDocument3 pagesCell Growth and Division PrintArif HakimiNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument10 pagesCell CycleChad LabradorNo ratings yet
- State Phase Abbrevia Tion DescriptionDocument5 pagesState Phase Abbrevia Tion DescriptionMae Matias100% (1)
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument3 pagesGen Bio ReviewerJustin JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument7 pagesCell DivisionLujinelle FusinganNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Divisionchar montejeroNo ratings yet
- Biotech 3 Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesBiotech 3 Cell DivisionClinton YmbongNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument100 pagesCell CycleAriane NicoleNo ratings yet
- Biology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Solutions Manual DownloadDocument11 pagesBiology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Solutions Manual DownloadJamie Hayes100% (26)
- Union of Egg and Sperm Cell in The Fallopian Tube, Producing A Zygote (The First Cell of The New Offspring)Document2 pagesUnion of Egg and Sperm Cell in The Fallopian Tube, Producing A Zygote (The First Cell of The New Offspring)AIMEE MARGARET FLORESNo ratings yet
- Topical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2From EverandTopical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chapter Iii MethodologyDocument14 pagesChapter Iii MethodologyA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Stem6 Lesson 5 Final TermDocument26 pagesStem6 Lesson 5 Final TermA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Potential of Various AgrDocument13 pagesAnalysis of The Potential of Various AgrA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Amylum and Citrus Aurantium L Peeling Utilizing inDocument16 pagesAmylum and Citrus Aurantium L Peeling Utilizing inA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- JPSP 2022 613Document6 pagesJPSP 2022 613A - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Pulp and Paper Making From Grass FibreDocument3 pagesPulp and Paper Making From Grass FibreA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Feasibility of Dried Leaves in The Production of PaperDocument14 pagesFeasibility of Dried Leaves in The Production of PaperA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - Hermon100% (2)
- NorMazlanaetal 2014suitabilitycoiraspulpandpaperDocument9 pagesNorMazlanaetal 2014suitabilitycoiraspulpandpaperA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3-Group 5Document14 pagesChapter-3-Group 5A - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- REVISED RESEARCH PAPER Algae Paper An Innovation of Algae Based PDFDocument50 pagesREVISED RESEARCH PAPER Algae Paper An Innovation of Algae Based PDFA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Romblon Pandanusutilis Leaves Mixedwith Causticsodaasan Alternativein Making PaperfinalDocument37 pagesRomblon Pandanusutilis Leaves Mixedwith Causticsodaasan Alternativein Making PaperfinalA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Design in Art Crafts .Document4 pagesContemporary Design in Art Crafts .A - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Sample Business Plan Mi Faburrito Part 2 3Document3 pagesSample Business Plan Mi Faburrito Part 2 3A - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 - Group 5Document13 pagesChapter-2 - Group 5A - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- CV OutputDocument1 pageCV OutputA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- CV OutputDocument1 pageCV OutputA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Atom Araullo BiographyDocument3 pagesAtom Araullo BiographyA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- ENG 9 Movie ReviewDocument2 pagesENG 9 Movie ReviewA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- English Output WKWKWKDocument1 pageEnglish Output WKWKWKA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Bots 4th Paragraph FINALDocument1 pageBots 4th Paragraph FINALA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Individual Title Form - STEMDocument2 pagesIndividual Title Form - STEMA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Arts ReviewerDocument4 pagesContemporary Arts ReviewerA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Happ Lab Week 3Document36 pagesHapp Lab Week 3A - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Examination Room Assignment SHS 1st Sem MIDTERMDocument29 pagesExamination Room Assignment SHS 1st Sem MIDTERMA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Chapter TestDocument4 pagesEndocrine Chapter TestPrince K. TaileyNo ratings yet
- Mushroom Production and TechnologyDocument36 pagesMushroom Production and Technologymozhi74826207No ratings yet
- Foods That Cause Acne: SUNDAY, APRIL 8, 2012Document3 pagesFoods That Cause Acne: SUNDAY, APRIL 8, 2012FitriAndriyaniNo ratings yet
- Test Rev AnswersDocument17 pagesTest Rev AnswersViea Pacaco SivaNo ratings yet
- Kidney Problems and DialysisDocument3 pagesKidney Problems and DialysismarymakinNo ratings yet
- Resources - Fat Embolism Syndrome (FES)Document19 pagesResources - Fat Embolism Syndrome (FES)Hareen Reddy100% (1)
- 1.1 Introduction To Human Anatomy - 2018-2019 PDFDocument11 pages1.1 Introduction To Human Anatomy - 2018-2019 PDFسيف محمود شاكر حسنNo ratings yet
- Food and Feeding Habits of The African Big Barb Labeobarbus Intermedius (Rüppell, 1836) in Ethiopian Water Bodies: A ReviewDocument6 pagesFood and Feeding Habits of The African Big Barb Labeobarbus Intermedius (Rüppell, 1836) in Ethiopian Water Bodies: A ReviewAgumassie TesfahunNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Air Sinus Oral SurgeryDocument49 pagesMaxillary Air Sinus Oral SurgeryDentist Dina SamyNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology - Physical & Chemical Injuries of Oral CavityDocument44 pagesOral Pathology - Physical & Chemical Injuries of Oral CavityRachit Srivastava83% (18)
- Aha Acsm Risk Screening AdaDocument1 pageAha Acsm Risk Screening AdawalterNo ratings yet
- Biceps WorkoutDocument11 pagesBiceps WorkoutBhuvanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of RespirationDocument19 pagesPhysiology of RespirationRafiqo hafidNo ratings yet
- 243 FullDocument8 pages243 FullbiologiaufbaNo ratings yet
- 2020 - 06 - 25 NEJM Salicylate ToxicityDocument12 pages2020 - 06 - 25 NEJM Salicylate ToxicityVishwaCrNo ratings yet
- X ICSE Endocrine System-1 PDFDocument9 pagesX ICSE Endocrine System-1 PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Toxicologic Emergencies, 11th Goldfrank's 2019Document10 pagesToxicologic Emergencies, 11th Goldfrank's 2019RenéNo ratings yet
- Niraamaya Spa MenuDocument35 pagesNiraamaya Spa MenuSanjeev HariharanNo ratings yet
- Cervical Plexua, Phrenic NerveDocument15 pagesCervical Plexua, Phrenic NervetuhinsinghNo ratings yet
- Oina SummaryDocument37 pagesOina SummaryC1 - RAZALAN NICKA JOYNo ratings yet
- Food NutritionDocument19 pagesFood NutritionLaeeq R MalikNo ratings yet
- Embracing Changes: Managing Anxiety, Returning To "A Norm" With Vivian ZhangDocument2 pagesEmbracing Changes: Managing Anxiety, Returning To "A Norm" With Vivian ZhangGrad MindsNo ratings yet
- IBO 2001 Theory Part B - CCLDocument28 pagesIBO 2001 Theory Part B - CCLBrayan GallardoNo ratings yet
- Stimuli & Responses 1.3 & 1.4Document5 pagesStimuli & Responses 1.3 & 1.4Yusrahanis NadilahNo ratings yet
- Performance of PRISM III and PELOD-2 Score in A PICUDocument6 pagesPerformance of PRISM III and PELOD-2 Score in A PICUAnantaBenvenutoNo ratings yet
- 11 - Head & Neck (Blood Vessels) (FF) - Part 1Document20 pages11 - Head & Neck (Blood Vessels) (FF) - Part 1checkmate100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Aids and NecessitiesDocument6 pagesPharmaceutical Aids and NecessitiestriciapascualMD100% (1)
- Evaluation of Compliance With Standard Criteria For Postero-Anterior (Pa) Chest Radiographs in Parklane Hospital EnuguDocument37 pagesEvaluation of Compliance With Standard Criteria For Postero-Anterior (Pa) Chest Radiographs in Parklane Hospital EnuguLavinia VictorNo ratings yet
- Staar g3 2016test Read FDocument33 pagesStaar g3 2016test Read FsatishNo ratings yet