Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mitosis Infographic in Green Blue Hand Drawn Style
Mitosis Infographic in Green Blue Hand Drawn Style
Uploaded by
Gemay DanglayOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mitosis Infographic in Green Blue Hand Drawn Style
Mitosis Infographic in Green Blue Hand Drawn Style
Uploaded by
Gemay DanglayCopyright:
Available Formats
THE PROCESS OF
MITOSIS
Mitosis is the process by which a single parent cell
divides to make two identical daughter cells.
Unicellular organisms undergo mitosis to reproduce asexually.
Multicellular organisms undergo mitosis to create new cells for
growth and repair old cells.
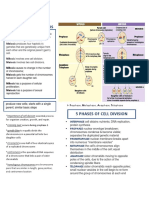
INTERPHASE
The cell grows, replicates its
DNA to prepare for cell
division. This stage occurs
before mitosis commences.
PROPHASE
The chromosomes (genetic
material) condense (coil
tightly) and the nucleolus
disappears.
METAPHASE
The chromosomes align in the
centre of the cell and attach
to microtubules in preparation
to split apart.
ANAPHASE
Chromatids separate and
move to opposite ends of the
cell. This stage ensures that
each cell contains identical
chromosomes after splitting.
TELOPHASE
Two new nuclei form around
each set of chromosomes.
Chromosomes decondense
and the cells begin to split
from each other.
CYTOKINESIS
The cytoplasm of the parent
cell splits to form two identical
daughter cells.
You might also like
- The Puzzle of Mitosis and MeiosisDocument21 pagesThe Puzzle of Mitosis and MeiosisDaniel LopesNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Infographic in Green Blue Hand Drawn StyleDocument1 pageMitosis Infographic in Green Blue Hand Drawn StyleDaisy Rizza AgnesNo ratings yet
- MayetoesisDocument2 pagesMayetoesisaniqa0825No ratings yet
- LSPU BSBIO - ZOO1 - SLM4 ExerciseDocument11 pagesLSPU BSBIO - ZOO1 - SLM4 ExerciseJohn ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument3 pagesMitosis WorksheetHipster48No ratings yet
- MitosisDocument56 pagesMitosisAlexine CartinNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Genral Biology 1Document3 pagesWeek 4 Genral Biology 1Spade ObusaNo ratings yet
- MEIOSISDocument2 pagesMEIOSISKim BeatrizNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument34 pagesCell CycleDesiree AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis InfographDocument1 pageMitosis and Meiosis InfographPatricia BonganayNo ratings yet
- Name - Odango, Clint Xavier F. BSN 1B Score - MCC 1 Seatwork The Cells Date 02/04/2021 A. Draw The Animal Cell and Label The Following PartsDocument3 pagesName - Odango, Clint Xavier F. BSN 1B Score - MCC 1 Seatwork The Cells Date 02/04/2021 A. Draw The Animal Cell and Label The Following Partsclint xavier odangoNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument22 pagesCell CycleVanda MargrafNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Wks ANSWERSDocument2 pagesCell Cycle Wks ANSWERSDimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Module 22 Q4Document11 pagesScience 8 Module 22 Q4domafecaluyoNo ratings yet
- By Mariam HassanDocument14 pagesBy Mariam Hassanmaruamlari40No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument67 pagesCell DivisionRylle SimonNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 - Cell DivisionDocument17 pagesGen Bio 1 - Cell DivisionsalihuddinalkaizarNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs Meiosis: 5 Phases of Cell DivisionDocument1 pageMitosis Vs Meiosis: 5 Phases of Cell DivisionJaninaEhyamNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument2 pagesMitosisKimberly DalagNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument3 pagesMeiosis and MitosisHaileyNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument35 pagesCell DivisionRosalina Bautista RamosNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Infographic in Green Blue Hand DrawnDocument1 pageMitosis Infographic in Green Blue Hand DrawnDaisy Rizza AgnesNo ratings yet
- KODIGODocument64 pagesKODIGOcainglesgaeaNo ratings yet
- From A Single Parent Cell. Growth and Tissue RepairDocument3 pagesFrom A Single Parent Cell. Growth and Tissue RepairafnafnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.64Document3 pagesChapter 3.64afnafnNo ratings yet
- Biology Assessment Task 2Document8 pagesBiology Assessment Task 2akshishree23No ratings yet
- Cell Biology MITOSISDocument15 pagesCell Biology MITOSISwebearning2069No ratings yet
- Phase Process: Reference: GoogleDocument2 pagesPhase Process: Reference: GoogleYuanna I.No ratings yet
- Cell Division ReviewerDocument26 pagesCell Division ReviewerGerald SorianoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants and Animals Notes - Form 3 - BiologyDocument55 pagesReproduction in Plants and Animals Notes - Form 3 - BiologyMUNGE CYBERNo ratings yet
- Most Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GDocument8 pagesMost Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GfredNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Discussion - Cell Cycle and Mitosis OnlyDocument56 pagesCell Division Discussion - Cell Cycle and Mitosis Onlymarimay.lumabanNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell Divisionfefaw93458No ratings yet
- Exercise 4Document4 pagesExercise 4BARRIENTOS, MARIE NICOLENo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Cell DivisionDocument21 pagesMeiosis: Cell DivisionAthena AretaNo ratings yet
- GB2 Asexual ReproductionDocument23 pagesGB2 Asexual Reproductionsja254677No ratings yet
- MitosisDocument8 pagesMitosisMilongy JavierNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument12 pagesMitosisCrystal Janelle TabsingNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle-INTERPHASE-CELL DIVISIONDocument57 pagesCell Cycle-INTERPHASE-CELL DIVISIONcabilesrobilyn479No ratings yet
- Biology (Mitosis Cell Division)Document3 pagesBiology (Mitosis Cell Division)Harry ParconNo ratings yet
- Biology (Mitosis Cell Division)Document3 pagesBiology (Mitosis Cell Division)Harry ParconNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - MitosisDocument27 pagesLesson 6 - MitosisArvin Jay LamberteNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis ExamDocument6 pagesMitosis and Meiosis ExamAishley BerdinNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Mitosis and MeiosisDocument46 pages3.2 Mitosis and MeiosisAhmed AimanNo ratings yet
- Cell Reproduction: How Does It Happen?Document63 pagesCell Reproduction: How Does It Happen?Gabriel NonanNo ratings yet
- STM007 1ST Sem at RevDocument9 pagesSTM007 1ST Sem at Revlujilleb11No ratings yet
- Cells and Control Part 1 Pixl RevisionDocument2 pagesCells and Control Part 1 Pixl Revisionaminaha4444No ratings yet
- Interphase Prophase: ChromoDocument12 pagesInterphase Prophase: ChromoNkosi JupiterNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 MitosisDocument5 pagesGrade 8 MitosisJay r DomingoNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Growth: General Biology IDocument17 pagesCell Division and Growth: General Biology IJhana DanoNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Growth: General Biology IDocument17 pagesCell Division and Growth: General Biology IJhana DanoNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Growth: General Biology IDocument17 pagesCell Division and Growth: General Biology IJhana DanoNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle-Mitosis - Meiosis SlidesDocument19 pagesCell Cycle-Mitosis - Meiosis SlideslkjosNo ratings yet
- Stages of Meiosis - 20240108 - 205848 - 0000Document30 pagesStages of Meiosis - 20240108 - 205848 - 0000Oviya.RNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument5 pagesUntitled Documentpbanaag00No ratings yet
- Agric QuizDocument3 pagesAgric QuizKelsy SalazarNo ratings yet
- Pepaña (A3a78) Apk1Document4 pagesPepaña (A3a78) Apk1Ruth Stephanie P. PepañaNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Cell Division - DifferentiationDocument8 pagesLesson - Cell Division - DifferentiationramyaNo ratings yet
- The Cell CycleDocument2 pagesThe Cell CycleMazon, Dinah Melisse P.No ratings yet
- General Morphology of MicroorganismsDocument43 pagesGeneral Morphology of MicroorganismsGemay DanglayNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument26 pagesMitosisGemay DanglayNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument58 pagesIntroductionGemay DanglayNo ratings yet
- Yukot, LittGDocument14 pagesYukot, LittGGemay DanglayNo ratings yet