Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12 7 (A) Define Potential Difference (P.D.) .: 0625/42/F/M/23 © UCLES 2023
12 7 (A) Define Potential Difference (P.D.) .: 0625/42/F/M/23 © UCLES 2023
Uploaded by
Daniel CannywoodOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12 7 (A) Define Potential Difference (P.D.) .: 0625/42/F/M/23 © UCLES 2023
12 7 (A) Define Potential Difference (P.D.) .: 0625/42/F/M/23 © UCLES 2023
Uploaded by
Daniel CannywoodCopyright:
Available Formats
12
7 (a) Define potential difference (p.d.).
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [2]
(b) (i) State the equation which defines electromotive force (e.m.f.) E.
[1]
(ii) The e.m.f. of a battery is 9.0 V. The battery is in a circuit.
Calculate the work done by the battery when it moves a charge of 30 C around a complete
circuit.
work done = ......................................................... [2]
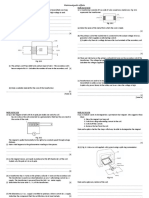
(c) A circuit consists of a d.c. power supply, a lamp and a thermistor.
(i) Draw a circuit diagram of these components connected in series.
[2]
© UCLES 2023 0625/42/F/M/23
13
(ii) Explain what happens in the circuit you have drawn in (c)(i) when the temperature of the
thermistor is increased.
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [2]
[Total: 9]
© UCLES 2023 0625/42/F/M/23 [Turn over
14
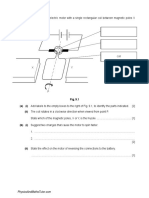
8 Fig. 8.1 shows a horizontal, flat coil in a magnetic field
coil
axis
B
N A
Fig. 8.1
The coil is connected to a cell. The coil rotates.
(a) Determine the direction of movement of the side AB relative to the plane of the coil.
direction of movement = ......................................................... [1]
(b) Explain how you determined the direction in (a).
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [2]
(c) State and explain what happens to the coil as it reaches the vertical position.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [2]
(d) To operate as a motor, a split‑ring commutator and brushes are added to the parts shown in
Fig. 8.1.
Explain the effects of the split‑ring commutator and the brushes on the action of the motor.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [3]
[Total: 8]
© UCLES 2023 0625/42/F/M/23
You might also like
- Electrical Quantities WorksheetDocument10 pagesElectrical Quantities WorksheetMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- 46.2-Electromagnetic Effects-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-QpDocument13 pages46.2-Electromagnetic Effects-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-QpNurul FadhilahNo ratings yet
- UNIT TEST CHAPTER 11 IMMUNITY - Jamal XI69069Document8 pagesUNIT TEST CHAPTER 11 IMMUNITY - Jamal XI69069Muhammad NaufalNo ratings yet
- Set 61 - Chapter 1Document25 pagesSet 61 - Chapter 1lelon81No ratings yet
- Physics 1Document4 pagesPhysics 1syedaaliha13No ratings yet
- FT 12 Gr10 P4 Qs (Electricity)Document8 pagesFT 12 Gr10 P4 Qs (Electricity)Kiron SheiqNo ratings yet
- Astronomy & CosmologyDocument53 pagesAstronomy & CosmologyGulwarina SaleemNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Effects 2 QPDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic Effects 2 QPValerine Victoria100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Effects 2 QPDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic Effects 2 QPVyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-03 at 9.41.01 PMDocument100 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-03 at 9.41.01 PM8f7cbjgh6vNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/43Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/43Krisha ElangovanNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism 6 - 5 MarkerDocument35 pagesElectricity and Magnetism 6 - 5 MarkerLalit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 13 7 Fig. 7.1 Shows A Circuit That Contains A Battery, A Switch, A Voltmeter and Three 40 Resistors, RDocument2 pages13 7 Fig. 7.1 Shows A Circuit That Contains A Battery, A Switch, A Voltmeter and Three 40 Resistors, RDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- 46.2-Electromagnetic EffectsDocument14 pages46.2-Electromagnetic Effectskatise1794No ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 MergedDocument15 pages1 2 3 4 5 6 Mergedbhattmaneet6No ratings yet
- Electric Circuits 7 QPDocument16 pagesElectric Circuits 7 QPChong Xue ErNo ratings yet
- Astronomy & Cosmology QuestionsDocument34 pagesAstronomy & Cosmology QuestionsShakeel MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Set 99Document25 pagesSet 99lelon81No ratings yet
- A2 TPM-7 QP (2020) PDFDocument9 pagesA2 TPM-7 QP (2020) PDFANo ratings yet
- Safari PDFDocument13 pagesSafari PDFHussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity 5 QPDocument7 pagesRadioactivity 5 QPceline.the988No ratings yet
- Electricity WS2Document3 pagesElectricity WS2visit.rgNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions PDFDocument9 pagesRevision Questions PDFmwagweNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w22 - QP - 22 - Q8 - Chapter 4Document3 pagesPages From 5054 - w22 - QP - 22 - Q8 - Chapter 4lelon81No ratings yet
- Electrical Quantities 5 QPDocument8 pagesElectrical Quantities 5 QPSaad RehmanNo ratings yet
- With Air.: Set 63 - Page 1 Compiled by Mr. Lelon 012-6556593Document11 pagesWith Air.: Set 63 - Page 1 Compiled by Mr. Lelon 012-6556593lelon81No ratings yet
- New Electric Fields - ProtectedDocument26 pagesNew Electric Fields - ProtectedMahnoor AliNo ratings yet
- P2 3 Higher QuestionsDocument93 pagesP2 3 Higher QuestionsjesudassajNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Effect (Motor Generator Transformer)Document6 pagesElectromagnetic Effect (Motor Generator Transformer)FN LowNo ratings yet
- 46.4 Electromagnetic EffectsDocument11 pages46.4 Electromagnetic Effectskatise1794No ratings yet
- Electronics QDocument4 pagesElectronics QallqnryanNo ratings yet
- Physics 5054 P2 Complete Electricity Topical Past Paper (Only Questions)Document183 pagesPhysics 5054 P2 Complete Electricity Topical Past Paper (Only Questions)Manthan Chakraborty100% (1)
- Y11 Revision QuestionsDocument13 pagesY11 Revision QuestionsKwang yuan HiiNo ratings yet
- 2023 Specimen Paper 4Document16 pages2023 Specimen Paper 4Olanibi GratitudeNo ratings yet
- Igcse Physics c9 Prac Questions MSDocument6 pagesIgcse Physics c9 Prac Questions MShuxxiNo ratings yet
- Physics-0625-Paper-4 2023Document16 pagesPhysics-0625-Paper-4 2023Kasumi Sato60% (5)
- 1 (A) Two Straight, Vertical Wires X and Y Pass Through Holes in A Horizontal CardDocument12 pages1 (A) Two Straight, Vertical Wires X and Y Pass Through Holes in A Horizontal CardhuxxiNo ratings yet
- Space QuestionsDocument7 pagesSpace Questionsar3n82No ratings yet
- G481 Module 3 Work and Energy QuestionsDocument14 pagesG481 Module 3 Work and Energy QuestionsAmberNo ratings yet
- Magnets Test 1Document4 pagesMagnets Test 1sniperpandabNo ratings yet
- Test Chem 1,2Document7 pagesTest Chem 1,2Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- As Electricity Part IIDocument86 pagesAs Electricity Part IIhello helloNo ratings yet
- Electrical QuantitiesDocument9 pagesElectrical Quantitieswitness vurayayiNo ratings yet
- Electromotive Force & Internal Resistance QPDocument10 pagesElectromotive Force & Internal Resistance QPcrochetbyellaa4No ratings yet
- ST 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Introductory Electronics) PDFDocument10 pagesST 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Introductory Electronics) PDFSaleem ShahidNo ratings yet
- Tsokos LSN 5-6 To 5-8 Test ReviewDocument11 pagesTsokos LSN 5-6 To 5-8 Test ReviewRaunak PrasadNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/41Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/41Rituja PawarNo ratings yet
- 2 1 There Is No Atmosphere On The Moon.: 0625/43/M/J/18 © UCLES 2018Document4 pages2 1 There Is No Atmosphere On The Moon.: 0625/43/M/J/18 © UCLES 2018Yakshrajsinh JadejaNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power P2Document69 pagesWork, Energy and Power P2carbohemoglobinNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - TestDocument5 pagesUnit 2 - Testevioktavianti260619No ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 2 - PhysicsDocument25 pagesActivity Sheet 2 - PhysicsRida AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Environmental Management 5014/12Document20 pagesCambridge O Level: Environmental Management 5014/12Ayesha Ijaz - 49434/TCHR/BLDCNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/22Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/22Ved P4h PratapNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - TestDocument7 pagesUnit 4 - Testevioktavianti260619No ratings yet
- 4 7 3InducedPotentialTransformersandtheNatGrid PDFDocument69 pages4 7 3InducedPotentialTransformersandtheNatGrid PDFlNo ratings yet
- PphhyyDocument6 pagesPphhyysangita bediyaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Physics c9 Prac QuesDocument6 pagesIgcse Physics c9 Prac QueshuxxiNo ratings yet
- SP TheoryDocument41 pagesSP Theoryaliyameen2006No ratings yet
- Mock Exam 11Document19 pagesMock Exam 11walyatNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Daniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Question 1d Separate: Chemistry and Extended Only: Head To For More Awesome ResourcesDocument1 pageQuestion 1d Separate: Chemistry and Extended Only: Head To For More Awesome ResourcesDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Physics 5Document5 pagesPhysics 5Daniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- S3 MidyearDocument13 pagesS3 MidyearDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Physics 3Document5 pagesPhysics 3Daniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- 12 8 (A) (I) State What Is Meant by A Magnetic Field.: 0625/42/M/J/23 © UCLES 2023Document2 pages12 8 (A) (I) State What Is Meant by A Magnetic Field.: 0625/42/M/J/23 © UCLES 2023Daniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- What Is One Method by Which Thermal Energy Is Transferred in The Copper Rod?Document3 pagesWhat Is One Method by Which Thermal Energy Is Transferred in The Copper Rod?Daniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Longman Physics 11 14 For O LevelDocument182 pagesLongman Physics 11 14 For O LevelDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- 8 16 The Diagram Shows A Pan Used For Cooking FoodDocument4 pages8 16 The Diagram Shows A Pan Used For Cooking FoodDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Sayar Daniel 09-404660506: ElectricityDocument1 pageSayar Daniel 09-404660506: ElectricityDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Physics New NotesDocument8 pagesPhysics New NotesDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Speed Y: © UCLES 2023 0625/22/F/M/23Document3 pagesSpeed Y: © UCLES 2023 0625/22/F/M/23Daniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Which Measuring Devices Are Most Suitable To Determine The Volume of About 200Document4 pages2 1 Which Measuring Devices Are Most Suitable To Determine The Volume of About 200Daniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Chemistry New NotesDocument5 pagesChemistry New NotesDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- © Ucles 2022 0625/22/F/M/22Document3 pages© Ucles 2022 0625/22/F/M/22Daniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Essential Chemistry Coursebook PDFDocument286 pagesEssential Chemistry Coursebook PDFDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Physics PaperDocument16 pagesCambridge Physics PaperDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Collapse of The World Trade CenterDocument2 pagesCollapse of The World Trade CenterDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Metal ExtractionDocument37 pagesMetal ExtractionDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Essential Chemistry Coursebook PDFDocument286 pagesEssential Chemistry Coursebook PDFDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- 4MB0 01R Rms 20170824 PDFDocument22 pages4MB0 01R Rms 20170824 PDFDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- 2-C Airplane Systems - Flight Instruments Flashcards - QuizletDocument2 pages2-C Airplane Systems - Flight Instruments Flashcards - QuizletJay GalangNo ratings yet
- Studying The Flight of A Paper Airplane Using Manual Simulation and Dimensional AnalysisDocument12 pagesStudying The Flight of A Paper Airplane Using Manual Simulation and Dimensional Analysisarya ladhaniNo ratings yet
- Copy of Momentum Practice Questions LV 5-9 With AnswersDocument7 pagesCopy of Momentum Practice Questions LV 5-9 With AnswersIgnacioNo ratings yet
- 1 Assignment 1 - FIC1502 - 2021Document10 pages1 Assignment 1 - FIC1502 - 2021Tshepiso MaileNo ratings yet
- Adetunji Timilehin Eee191334Document4 pagesAdetunji Timilehin Eee191334somoyetobi8No ratings yet
- TSMH4MD1 H4 01 TG T 31 TG0 002003213391Document39 pagesTSMH4MD1 H4 01 TG T 31 TG0 002003213391hamidrezaNo ratings yet
- Class 2 - Active & Passive ElementsDocument25 pagesClass 2 - Active & Passive ElementsSwayam Tejas PadhyNo ratings yet
- 4286 04Document18 pages4286 04carlos ricardo herrera castilloNo ratings yet
- Carlos Sierra - Mine Ventilation - A Concise Guide For Students-Springer International Publishing - Springer (2020)Document372 pagesCarlos Sierra - Mine Ventilation - A Concise Guide For Students-Springer International Publishing - Springer (2020)George GomezNo ratings yet
- Kickstart Physics - Depth Study - Fields and Transformers v1.0Document15 pagesKickstart Physics - Depth Study - Fields and Transformers v1.0Kaavya JoshiNo ratings yet
- Dissolution Study CaseDocument42 pagesDissolution Study CaseBayu Indra PermanaNo ratings yet
- Schedule "WP-01" Technical Data Wood Poles, Length 16 M Stout GradeDocument24 pagesSchedule "WP-01" Technical Data Wood Poles, Length 16 M Stout GradeHosam AlzubairyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Aasign Set 2 For 2020-24 BatchDocument2 pagesUnit 1 Aasign Set 2 For 2020-24 BatchHARSHNI R 24EENo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Basic Measurement in SurveyingDocument33 pagesUnit 3 Basic Measurement in SurveyingJulius EtukeNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS I RECTILINEAR MOTION StudentsDocument13 pagesPHYSICS I RECTILINEAR MOTION StudentsNathan QuintuanNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit Withstand of Power CablesDocument42 pagesShort Circuit Withstand of Power CablesDheeraj Yadav100% (1)
- Y9 November 2019 (Non-Calc)Document8 pagesY9 November 2019 (Non-Calc)John LeeNo ratings yet
- 5SU93041KK16 Datasheet enDocument3 pages5SU93041KK16 Datasheet enJp DepartmentNo ratings yet
- VR: Vaccuum Room PM1: PM1 Spare AreaDocument44 pagesVR: Vaccuum Room PM1: PM1 Spare AreaMohd A IshakNo ratings yet
- Al Ayen University College of Engineering Petroleum DepartmentDocument5 pagesAl Ayen University College of Engineering Petroleum DepartmentMohammedalwaelyNo ratings yet
- Phyc121 Week 5 9Document26 pagesPhyc121 Week 5 9Leycoline Almren100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Lecture 3 - Chapter - 3Document15 pagesFluid Mechanics Lecture 3 - Chapter - 3Benjamin BageyaNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument9 pagesDefinitionsshirley wangNo ratings yet
- Oven Calibration StatusDocument3 pagesOven Calibration StatusKarthikNo ratings yet
- VASP计算细节Document14 pagesVASP计算细节Nostalgia BlueNo ratings yet
- 0601 Enthusiast Phase-S, TRAS, I (A) & I Score-I Paper-1 (E) JMDocument19 pages0601 Enthusiast Phase-S, TRAS, I (A) & I Score-I Paper-1 (E) JMalokNo ratings yet
- Electrical Submersible Pump (ESP) : Operation & Trouble Shooting PTP-6.2Document11 pagesElectrical Submersible Pump (ESP) : Operation & Trouble Shooting PTP-6.2JayNo ratings yet
- Category GeodesyDocument3 pagesCategory GeodesyMileaCøsmin100% (1)
- SUN2000-3KTL-10KTL-M1 Datasheet - 17.05.2023Document2 pagesSUN2000-3KTL-10KTL-M1 Datasheet - 17.05.2023Nelson PalenciaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Terms and DefinitionsDocument15 pagesBasic Electrical Terms and Definitionsilango palaniNo ratings yet