Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fundamentals of Programming - Lab 6
Fundamentals of Programming - Lab 6
Uploaded by
urielCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Arrays in C#Document8 pagesArrays in C#Manish PushkarNo ratings yet
- EshanDocument19 pagesEshancebex22655No ratings yet
- ArrayDocument27 pagesArrayapexg786No ratings yet
- Java Assignment 2Document18 pagesJava Assignment 2PSNo ratings yet
- JAVA - CodingDocument22 pagesJAVA - CodingManjula OJNo ratings yet
- Computer Project - FinalDocument98 pagesComputer Project - FinalJasmine BhattNo ratings yet
- Java Practical FileDocument44 pagesJava Practical FileKarandeep Singh54% (13)
- Arrays in JavaDocument13 pagesArrays in Javalaxmi bagadeNo ratings yet
- An Array of Arrays Is Known As Double Dimensional ArrayDocument15 pagesAn Array of Arrays Is Known As Double Dimensional ArrayRISHABH YADAVNo ratings yet
- Ood - Lab ManualDocument50 pagesOod - Lab ManualAswin P TNo ratings yet
- 18bce0074 VL2020210504679 Ast01Document26 pages18bce0074 VL2020210504679 Ast01Lakshya SadanaNo ratings yet
- Code To Solve Set of ProblemsDocument17 pagesCode To Solve Set of ProblemsMamta DoliyaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 C# Fundamentals: The Objective of This Lab Is To Understand The Following Concepts: 3 1 ArraysDocument14 pagesLab 3 C# Fundamentals: The Objective of This Lab Is To Understand The Following Concepts: 3 1 Arraysnisrine omriNo ratings yet
- Package Import Public Class Public Static Void: // Auto-Generated Method StubDocument5 pagesPackage Import Public Class Public Static Void: // Auto-Generated Method Stubmaitrayee karNo ratings yet
- Ce127 JT Lab 1Document9 pagesCe127 JT Lab 1CE127 MEET SHAHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Arrays & StringsDocument36 pagesChapter 4 Arrays & Stringsmekuriameku99No ratings yet
- Array, String and VectorDocument39 pagesArray, String and Vectorkaminisarode1507No ratings yet
- Aqsa Lab ManualDocument161 pagesAqsa Lab ManualAqsa TabassumNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument426 pagesJavaBima maulanaNo ratings yet
- Practical Part OneDocument14 pagesPractical Part OneSrijana ShetNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-Applying The Concepts of ArraysDocument43 pagesUnit 4-Applying The Concepts of ArraysLeah RachaelNo ratings yet
- r16 JavaDocument61 pagesr16 Javajani28cse100% (4)
- Array PDFDocument3 pagesArray PDFAnonymous TM75YJysaNo ratings yet
- Arrays in CDocument6 pagesArrays in CShivaraju KoilakondaNo ratings yet
- Java LAB 5 ArraysDocument6 pagesJava LAB 5 Arraysshah rizviNo ratings yet
- Java 2Document52 pagesJava 2mahendar chuphalNo ratings yet
- String OperationsDocument6 pagesString OperationsIngabire FlorenceNo ratings yet
- Java Assigment NewDocument35 pagesJava Assigment Newmohitparihar8786No ratings yet
- Isc ProjectDocument12 pagesIsc ProjectDevanshNo ratings yet
- Q1. Program To Create, Initialize, Assign and Access A Pointer VariableDocument82 pagesQ1. Program To Create, Initialize, Assign and Access A Pointer VariableYouTuBoy AmanNo ratings yet
- Int Int: I I I J J J System Out Print JDocument6 pagesInt Int: I I I J J J System Out Print JLimSiEianNo ratings yet
- 20mia1104 Psoop Ips10Document22 pages20mia1104 Psoop Ips10Sricharan SridharNo ratings yet
- Name: Patel Charmy Tarunkumar Course: MSC - It Subject: Java Programming Roll No.: 11 Faculty Name Assignment: Priti PatelDocument20 pagesName: Patel Charmy Tarunkumar Course: MSC - It Subject: Java Programming Roll No.: 11 Faculty Name Assignment: Priti PatelCharmy PatelNo ratings yet
- Abd JavaDocument13 pagesAbd JavaKriti SinghNo ratings yet
- Fa17 Sample Midterm SolutionDocument6 pagesFa17 Sample Midterm SolutionEliana IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Computer ProgramDocument7 pagesComputer ProgramSilent WarriorNo ratings yet
- ProgramsDocument16 pagesProgramsdeepthi kolliparaNo ratings yet
- Java Lab ManualDocument16 pagesJava Lab ManualJANARDHANA RAO ALAPATINo ratings yet
- JavafileDocument25 pagesJavafileprachiti kirtikudaveNo ratings yet
- JJJJJJJDocument37 pagesJJJJJJJRahul PRAJAPATINo ratings yet
- Advanced Algorithms & Data Structures: Lecturer: Karimzhan Nurlan BerlibekulyDocument23 pagesAdvanced Algorithms & Data Structures: Lecturer: Karimzhan Nurlan BerlibekulyNaski KuafniNo ratings yet
- PL Labexer4 Sacasas ElizaldeDocument7 pagesPL Labexer4 Sacasas Elizaldeapi-565917483No ratings yet
- SME 1013 Programming For Engineers: ArraysDocument9 pagesSME 1013 Programming For Engineers: Arraysjfl2096No ratings yet
- UNIT II Arrays and StringsDocument30 pagesUNIT II Arrays and StringsSivasathiya G100% (1)
- Arrays, Strings & Enum: T.Dhiliphan Rajkumar Assistant Professor Computer Science & EngineeringDocument34 pagesArrays, Strings & Enum: T.Dhiliphan Rajkumar Assistant Professor Computer Science & EngineeringUPPALA BHARATH KUMAR CSEUG-2020 BATCHNo ratings yet
- 1st Part Desktop B8t11omDocument18 pages1st Part Desktop B8t11omSOUMYODEEP SAHANo ratings yet
- 09 Ch8 ArraysDocument122 pages09 Ch8 ArraysSourajit MitraNo ratings yet
- OOP Lab Record DdvdaDocument95 pagesOOP Lab Record DdvdaDevelop with AcelogicNo ratings yet
- NAME-Megha Saxena Registration Number - 20BIT0366 Java Programming Lab - 33+34 Assignment 2Document5 pagesNAME-Megha Saxena Registration Number - 20BIT0366 Java Programming Lab - 33+34 Assignment 2Megha SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Week 3: Import Java - Util.scanner Public Class Sum - Avg - Array (Public Static Void Main (String Args ) (Document23 pagesWeek 3: Import Java - Util.scanner Public Class Sum - Avg - Array (Public Static Void Main (String Args ) (Bikram DeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Introduction To ArraysDocument33 pagesChapter 7 - Introduction To ArraysNUREEN AMIRA HASRUL NIZAMNo ratings yet
- Class X Project Ques - Ans (Last 10 Progs)Document13 pagesClass X Project Ques - Ans (Last 10 Progs)roy.subhojit07No ratings yet
- 21bce7761 Java Assignment 2Document9 pages21bce7761 Java Assignment 2NARENDRANo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document13 pagesAssignment 2Vipul RanaNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Array LabsheetJavaDocument50 pagesAssignment of Array LabsheetJavaNabin GautamNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming Assignment Aman Paniya MBA Tech LL YearDocument16 pagesObject Oriented Programming Assignment Aman Paniya MBA Tech LL YearAman PaniyaNo ratings yet
- Java Programming (Bcse 2333) Lab File: Submitted byDocument61 pagesJava Programming (Bcse 2333) Lab File: Submitted byZiyaul AijazNo ratings yet
- Advanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionFrom EverandAdvanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Art Appreciation Notes MidtermDocument7 pagesArt Appreciation Notes MidtermurielNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Programming - Lab 1Document2 pagesIntermediate Programming - Lab 1urielNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Programming - Lab 2Document2 pagesFundamentals of Programming - Lab 2urielNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Programming - Lab 3Document3 pagesFundamentals of Programming - Lab 3urielNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Programming - Lab 4Document2 pagesFundamentals of Programming - Lab 4urielNo ratings yet
Fundamentals of Programming - Lab 6
Fundamentals of Programming - Lab 6
Uploaded by
urielCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fundamentals of Programming - Lab 6
Fundamentals of Programming - Lab 6
Uploaded by
urielCopyright:
Available Formats
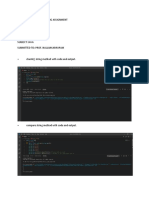
LAB 6
Monday, November 7, 2022 8:36 AM
Legend: code To clear the screen:
normal text System.out.println("\033[H\033[2J");
CALLING OF FUNCTIONS
To make functions, you use;
public static void 'function name'() {
}
To make the variables and utility declarations applicable to all of the
functions or to make global declarations, you use;
public static 'datatype' 'variable name';
for scanner;
public static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
To call out the functions or methods, you use;
'function name'();
ARRAY
Array – stores multiple values in a single variable, instead of multiple
variables for each value
DECLARING ARRAYS
To declare or create arrays, use;
Long method
datatype[] 'array name'= new datatype['number of
values'];
'array name[0] = value;
'array name[1] = value;
'array name[2] = value;
Short method
Datatype 'array name' = {'values'};
ONE DIMENTIONAL ARRAY
Short method
int[] b = {10,20,30};
System.out.println("One Dimensional Array
Elements");
System.out.println(a[0] + ", " + a[1] + ", "
+ a[2] + ".");
Output:
ARRAY FUNCTIONS
to.String() method
FUNDAMENTALS OF PROGRAMMING Page 1
to.String() method
This displays all of the array values without needing to specify the array
indexes.
Use the syntax;
Arrays.toString('Array name');
Example:
int[] n = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
System.out.println("The arrays are: " +
Arrays.toString(n));
How to get rid of the brackets when displaying
to.String()
Use the syntax;
'Array name'.length to loop through every value of an array.
Example:
For (a = 0; a < n.length; a++){
System.out.print(n[a]);
}
TWO DIMENTIONAL ARRAYS
are arrays of arrays
2D ARRAY FUNCTION/S
.deepToString method
Is used for multidimensional Java arrays to be converted in to Strings.
Output:
int[] n = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100};
FUNDAMENTALS OF PROGRAMMING Page 2
int[] n = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100};
Random rn = new Random(n.length);
System.out.println(n[rn.nextInt(n.length)]);
int[] n = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
int res = 0;
for (int a = 0; a < n.length + 1; a++){
res += n[a];
System.out.println("\033[H\033[2J");
System.out.println(res);
}
FUNDAMENTALS OF PROGRAMMING Page 3
You might also like
- Arrays in C#Document8 pagesArrays in C#Manish PushkarNo ratings yet
- EshanDocument19 pagesEshancebex22655No ratings yet
- ArrayDocument27 pagesArrayapexg786No ratings yet
- Java Assignment 2Document18 pagesJava Assignment 2PSNo ratings yet
- JAVA - CodingDocument22 pagesJAVA - CodingManjula OJNo ratings yet
- Computer Project - FinalDocument98 pagesComputer Project - FinalJasmine BhattNo ratings yet
- Java Practical FileDocument44 pagesJava Practical FileKarandeep Singh54% (13)
- Arrays in JavaDocument13 pagesArrays in Javalaxmi bagadeNo ratings yet
- An Array of Arrays Is Known As Double Dimensional ArrayDocument15 pagesAn Array of Arrays Is Known As Double Dimensional ArrayRISHABH YADAVNo ratings yet
- Ood - Lab ManualDocument50 pagesOod - Lab ManualAswin P TNo ratings yet
- 18bce0074 VL2020210504679 Ast01Document26 pages18bce0074 VL2020210504679 Ast01Lakshya SadanaNo ratings yet
- Code To Solve Set of ProblemsDocument17 pagesCode To Solve Set of ProblemsMamta DoliyaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 C# Fundamentals: The Objective of This Lab Is To Understand The Following Concepts: 3 1 ArraysDocument14 pagesLab 3 C# Fundamentals: The Objective of This Lab Is To Understand The Following Concepts: 3 1 Arraysnisrine omriNo ratings yet
- Package Import Public Class Public Static Void: // Auto-Generated Method StubDocument5 pagesPackage Import Public Class Public Static Void: // Auto-Generated Method Stubmaitrayee karNo ratings yet
- Ce127 JT Lab 1Document9 pagesCe127 JT Lab 1CE127 MEET SHAHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Arrays & StringsDocument36 pagesChapter 4 Arrays & Stringsmekuriameku99No ratings yet
- Array, String and VectorDocument39 pagesArray, String and Vectorkaminisarode1507No ratings yet
- Aqsa Lab ManualDocument161 pagesAqsa Lab ManualAqsa TabassumNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument426 pagesJavaBima maulanaNo ratings yet
- Practical Part OneDocument14 pagesPractical Part OneSrijana ShetNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-Applying The Concepts of ArraysDocument43 pagesUnit 4-Applying The Concepts of ArraysLeah RachaelNo ratings yet
- r16 JavaDocument61 pagesr16 Javajani28cse100% (4)
- Array PDFDocument3 pagesArray PDFAnonymous TM75YJysaNo ratings yet
- Arrays in CDocument6 pagesArrays in CShivaraju KoilakondaNo ratings yet
- Java LAB 5 ArraysDocument6 pagesJava LAB 5 Arraysshah rizviNo ratings yet
- Java 2Document52 pagesJava 2mahendar chuphalNo ratings yet
- String OperationsDocument6 pagesString OperationsIngabire FlorenceNo ratings yet
- Java Assigment NewDocument35 pagesJava Assigment Newmohitparihar8786No ratings yet
- Isc ProjectDocument12 pagesIsc ProjectDevanshNo ratings yet
- Q1. Program To Create, Initialize, Assign and Access A Pointer VariableDocument82 pagesQ1. Program To Create, Initialize, Assign and Access A Pointer VariableYouTuBoy AmanNo ratings yet
- Int Int: I I I J J J System Out Print JDocument6 pagesInt Int: I I I J J J System Out Print JLimSiEianNo ratings yet
- 20mia1104 Psoop Ips10Document22 pages20mia1104 Psoop Ips10Sricharan SridharNo ratings yet
- Name: Patel Charmy Tarunkumar Course: MSC - It Subject: Java Programming Roll No.: 11 Faculty Name Assignment: Priti PatelDocument20 pagesName: Patel Charmy Tarunkumar Course: MSC - It Subject: Java Programming Roll No.: 11 Faculty Name Assignment: Priti PatelCharmy PatelNo ratings yet
- Abd JavaDocument13 pagesAbd JavaKriti SinghNo ratings yet
- Fa17 Sample Midterm SolutionDocument6 pagesFa17 Sample Midterm SolutionEliana IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Computer ProgramDocument7 pagesComputer ProgramSilent WarriorNo ratings yet
- ProgramsDocument16 pagesProgramsdeepthi kolliparaNo ratings yet
- Java Lab ManualDocument16 pagesJava Lab ManualJANARDHANA RAO ALAPATINo ratings yet
- JavafileDocument25 pagesJavafileprachiti kirtikudaveNo ratings yet
- JJJJJJJDocument37 pagesJJJJJJJRahul PRAJAPATINo ratings yet
- Advanced Algorithms & Data Structures: Lecturer: Karimzhan Nurlan BerlibekulyDocument23 pagesAdvanced Algorithms & Data Structures: Lecturer: Karimzhan Nurlan BerlibekulyNaski KuafniNo ratings yet
- PL Labexer4 Sacasas ElizaldeDocument7 pagesPL Labexer4 Sacasas Elizaldeapi-565917483No ratings yet
- SME 1013 Programming For Engineers: ArraysDocument9 pagesSME 1013 Programming For Engineers: Arraysjfl2096No ratings yet
- UNIT II Arrays and StringsDocument30 pagesUNIT II Arrays and StringsSivasathiya G100% (1)
- Arrays, Strings & Enum: T.Dhiliphan Rajkumar Assistant Professor Computer Science & EngineeringDocument34 pagesArrays, Strings & Enum: T.Dhiliphan Rajkumar Assistant Professor Computer Science & EngineeringUPPALA BHARATH KUMAR CSEUG-2020 BATCHNo ratings yet
- 1st Part Desktop B8t11omDocument18 pages1st Part Desktop B8t11omSOUMYODEEP SAHANo ratings yet
- 09 Ch8 ArraysDocument122 pages09 Ch8 ArraysSourajit MitraNo ratings yet
- OOP Lab Record DdvdaDocument95 pagesOOP Lab Record DdvdaDevelop with AcelogicNo ratings yet
- NAME-Megha Saxena Registration Number - 20BIT0366 Java Programming Lab - 33+34 Assignment 2Document5 pagesNAME-Megha Saxena Registration Number - 20BIT0366 Java Programming Lab - 33+34 Assignment 2Megha SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Week 3: Import Java - Util.scanner Public Class Sum - Avg - Array (Public Static Void Main (String Args ) (Document23 pagesWeek 3: Import Java - Util.scanner Public Class Sum - Avg - Array (Public Static Void Main (String Args ) (Bikram DeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Introduction To ArraysDocument33 pagesChapter 7 - Introduction To ArraysNUREEN AMIRA HASRUL NIZAMNo ratings yet
- Class X Project Ques - Ans (Last 10 Progs)Document13 pagesClass X Project Ques - Ans (Last 10 Progs)roy.subhojit07No ratings yet
- 21bce7761 Java Assignment 2Document9 pages21bce7761 Java Assignment 2NARENDRANo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document13 pagesAssignment 2Vipul RanaNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Array LabsheetJavaDocument50 pagesAssignment of Array LabsheetJavaNabin GautamNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming Assignment Aman Paniya MBA Tech LL YearDocument16 pagesObject Oriented Programming Assignment Aman Paniya MBA Tech LL YearAman PaniyaNo ratings yet
- Java Programming (Bcse 2333) Lab File: Submitted byDocument61 pagesJava Programming (Bcse 2333) Lab File: Submitted byZiyaul AijazNo ratings yet
- Advanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionFrom EverandAdvanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Art Appreciation Notes MidtermDocument7 pagesArt Appreciation Notes MidtermurielNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Programming - Lab 1Document2 pagesIntermediate Programming - Lab 1urielNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Programming - Lab 2Document2 pagesFundamentals of Programming - Lab 2urielNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Programming - Lab 3Document3 pagesFundamentals of Programming - Lab 3urielNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Programming - Lab 4Document2 pagesFundamentals of Programming - Lab 4urielNo ratings yet