Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 viewsNervous System
Nervous System
Uploaded by
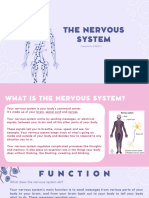
faresalesa2005The nervous system is responsible for reactions like moving your hand away from something hot or your heart beating faster when scared. It has two main divisions - the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord which controls and interprets signals, and the peripheral nervous system consisting of nerves that connect to sensory receptors and muscles. The peripheral system is further divided into sensory nerves that bring information to the brain and motor nerves that carry commands from the brain to muscles and organs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chuchi Andres Social Case Study ReportDocument2 pagesChuchi Andres Social Case Study Reportrafael solam89% (9)
- 3D Implant Position Esquivel 2021Document9 pages3D Implant Position Esquivel 2021Lamis MagdyNo ratings yet
- Health Talk On AnemiaDocument15 pagesHealth Talk On Anemiasimonjosan89% (64)
- Big in Baltimore (Chapter 11, Letter 1)Document4 pagesBig in Baltimore (Chapter 11, Letter 1)LynnNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesNervous SystemShayu ShaNo ratings yet
- PERDEV Q4M5 The Brain Parts Function Societal RelationshipDocument68 pagesPERDEV Q4M5 The Brain Parts Function Societal Relationshipnickybts09No ratings yet
- Influence of Nervous System On BehaviorDocument2 pagesInfluence of Nervous System On BehaviorcynthiasenNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyWiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesModule 7 Nervous SystemMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Hemisphere Is Divided Into LobesDocument2 pagesCerebral Hemisphere Is Divided Into LobesWiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Perdev StephanieDocument4 pagesPerdev StephaniemallarijiannaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesThe Nervous System868.CapalotNo ratings yet
- The-Nervous-System-Written ReportDocument5 pagesThe-Nervous-System-Written ReportHeileen S. San GabrielNo ratings yet
- PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT - 2nd Batch LASDocument16 pagesPERSONAL DEVELOPMENT - 2nd Batch LASJustin JoshNo ratings yet
- Health PresentationDocument20 pagesHealth Presentationapi-214728543No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument1 pageThe Nervous SystemNaomi FenechNo ratings yet
- Ballaran-Anatomy-Bsess-Fsc 2aDocument3 pagesBallaran-Anatomy-Bsess-Fsc 2aMary Joy BallaranNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-THE NERVOUS SYSTEMDocument6 pagesLesson 1-THE NERVOUS SYSTEMNatoya RichardsNo ratings yet
- Neurons: Cells of The Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNeurons: Cells of The Nervous SystemItpixels OfficebackdoorNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE VI Module 10Document5 pagesSCIENCE VI Module 10JHUDIELLE ANNE JANSOLNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNervous Systemjanssen.azagra.basalloteNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemshhhNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument3 pagesSCIENCENel BorniaNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument17 pagesHuman BrainAkbota KuanishkyzyNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNervous SystemCerene denzinNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Que Fransis A.Document5 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Kepy 01 09 37 EtextDocument9 pagesKepy 01 09 37 Etextmradul guptaNo ratings yet
- STEM 12 ERYTHRON Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesSTEM 12 ERYTHRON Nervous SystemJhon Philip ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology: Explain The Functions of The Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology: Explain The Functions of The Nervous SystemJay-ar BarquerosNo ratings yet
- q3 w2 Science 10Document63 pagesq3 w2 Science 10dejaveusNo ratings yet
- The Biological Perspective 2Document11 pagesThe Biological Perspective 2Radhey SurveNo ratings yet
- Group 1B OutlineDocument3 pagesGroup 1B Outlinejackclaudefajardo15No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument6 pagesBiologyExtreme gaming buddyNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Overview: FunctionDocument11 pagesNervous System - Overview: FunctionAadil JuttNo ratings yet
- Reporting Module 5Document12 pagesReporting Module 5Emarre BaronNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Nervous System Part 2Document25 pagesTopic 3 Nervous System Part 2fauzi ariffinNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination Do You Know Which Organs Make Up The Nervous System?Document22 pagesControl and Coordination Do You Know Which Organs Make Up The Nervous System?So TemptedNo ratings yet
- Brain and Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesBrain and Nervous SystemBrenda LizarragaNo ratings yet
- General Psychology Notes Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesGeneral Psychology Notes Nervous SystemRj BengilNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesParts of The Nervous SystemRonel AsuncionNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesThe Nervous Systemhajra0325No ratings yet
- Biology For Engineers Module 2Document82 pagesBiology For Engineers Module 2moaaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- The Amazing Human Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Amazing Human Nervous SystemSenio, Lexis Jan A.No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesThe Nervous Systemvedansh duttNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesHuman Nervous SystemSridevi NadipalliNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System Is The BodyDocument18 pagesThe Nervous System Is The Bodyvedansh duttNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReportingDocument5 pagesAnaphy ReportingZyra Kim ResareNo ratings yet
- ANATOMYDocument4 pagesANATOMYChristine IgnasNo ratings yet
- The BrainDocument35 pagesThe BrainKuriok BurnikNo ratings yet
- What Is Neuron?Document8 pagesWhat Is Neuron?Shaekh Maruf Skder 1912892630No ratings yet
- Anatomy Analogy ProjectDocument2 pagesAnatomy Analogy Projectapi-251525028No ratings yet
- KSG-Brain ActivityDocument10 pagesKSG-Brain ActivitySyahirah ZackNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous Systemkrista2007xxNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System (Edited)Document27 pagesThe Nervous System (Edited)Kiarana Fleischer100% (1)
- General Biology 2 Finals ExamDocument32 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Finals ExamJohn Lloyd BallaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesNervous SystemBarangay Onefourseven CaloocanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document109 pagesChapter 3amala raviNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Science NotesDocument45 pagesYear 10 Science NotesAmal VivekNo ratings yet
- Presentation Biology in Healthcare Stage4Document29 pagesPresentation Biology in Healthcare Stage4alanmauriciohdzNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between The Brain and The Nervous System - 2328 Words - Term Paper ExampleDocument4 pagesRelationship Between The Brain and The Nervous System - 2328 Words - Term Paper ExampleObi TomaNo ratings yet
- Bases of Human Behaviour: How Neurons Transmit Information?Document5 pagesBases of Human Behaviour: How Neurons Transmit Information?Ritu DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyNo ratings yet
- Brain Health - How to Have a Healthy Memory and a Healthy BrainFrom EverandBrain Health - How to Have a Healthy Memory and a Healthy BrainNo ratings yet
- Msds BenzenaDocument7 pagesMsds BenzenaRezaPratamaNo ratings yet
- Loneliness Ncp2Document2 pagesLoneliness Ncp2milcah_castillo100% (4)
- Frequently Asked Questions: How Many Women and Girls Are Victims of Violence?Document4 pagesFrequently Asked Questions: How Many Women and Girls Are Victims of Violence?Favour Toluwanimi ADETOUNNo ratings yet
- Poor Hygiene Practices in Hospitals May Lead To Antibiotic ResistanceDocument2 pagesPoor Hygiene Practices in Hospitals May Lead To Antibiotic ResistancePearl NoconNo ratings yet
- Sohail Updated Thesis 13-June-2022-1Document246 pagesSohail Updated Thesis 13-June-2022-1Quratulain BilalNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma NCLEX Questions QuizDocument22 pagesGlaucoma NCLEX Questions QuizGabrielle G. MaldoNo ratings yet
- Coconut Oil CapsulesDocument13 pagesCoconut Oil CapsulesShouvik DasNo ratings yet
- Pulmonology: C R P - C - 1) All of The Following Are The Causes of Clubbing of Fingers, ExceptDocument30 pagesPulmonology: C R P - C - 1) All of The Following Are The Causes of Clubbing of Fingers, ExceptZaid ZayedNo ratings yet
- Git MCQ Valume DDocument39 pagesGit MCQ Valume DAhmed ElwassiefNo ratings yet
- Essay About Women RightsDocument7 pagesEssay About Women Rightsvqrhuwwhd100% (2)
- RABIES Causative Agent: Rhabdovirus Mode of Transmission: Bite of RabidDocument1 pageRABIES Causative Agent: Rhabdovirus Mode of Transmission: Bite of RabidFreeNursingNotes100% (1)
- Prolonged Postpartum Urinary Retention A Case RepoDocument3 pagesProlonged Postpartum Urinary Retention A Case RepoeeeNo ratings yet
- Walking Aids - PhysiopediaDocument6 pagesWalking Aids - PhysiopediaNana Ann PaaNo ratings yet
- Cry Internship Application Form 1Document3 pagesCry Internship Application Form 1Tanya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Trauma Informed ABADocument23 pagesTrauma Informed ABAGiuli KumeNo ratings yet
- Immunological Tolerance, Pregnancy, and Preeclampsia: The Roles of Semen Microbes and The FatherDocument39 pagesImmunological Tolerance, Pregnancy, and Preeclampsia: The Roles of Semen Microbes and The FatherAnanda Yuliastri DewiNo ratings yet
- Jerônimo Et Al., 2021Document6 pagesJerônimo Et Al., 2021Claudia BrilhanteNo ratings yet
- SemenDocument14 pagesSemenjems wattNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: Vanessa Klee MSIVDocument25 pagesArterial Blood Gas Analysis: Vanessa Klee MSIVGarata PutriNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Reading Passage PREDocument4 pagesGrade 9 Reading Passage PREREY VISTAL100% (1)
- Human Nutrition 2 QPDocument11 pagesHuman Nutrition 2 QPRay PeramathevanNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Flash Cards - PDocument37 pagesFinal Exam Flash Cards - PReut shapiraNo ratings yet
- Clinical Evaluation Comparing The Fit of All-Ceramic Crowns Obtained From Silicone and Digital Intraoral ImpressionsDocument8 pagesClinical Evaluation Comparing The Fit of All-Ceramic Crowns Obtained From Silicone and Digital Intraoral ImpressionsCristobalVeraNo ratings yet
- Physiology Paper II - SampleDocument1 pagePhysiology Paper II - Samplerehan athaniNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure and Its Drug ClassificationDocument37 pagesHeart Failure and Its Drug ClassificationMaham AzmatNo ratings yet
- 1699Document3 pages1699Souci RahmadhanyNo ratings yet
Nervous System
Nervous System
Uploaded by
faresalesa20050 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views9 pagesThe nervous system is responsible for reactions like moving your hand away from something hot or your heart beating faster when scared. It has two main divisions - the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord which controls and interprets signals, and the peripheral nervous system consisting of nerves that connect to sensory receptors and muscles. The peripheral system is further divided into sensory nerves that bring information to the brain and motor nerves that carry commands from the brain to muscles and organs.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe nervous system is responsible for reactions like moving your hand away from something hot or your heart beating faster when scared. It has two main divisions - the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord which controls and interprets signals, and the peripheral nervous system consisting of nerves that connect to sensory receptors and muscles. The peripheral system is further divided into sensory nerves that bring information to the brain and motor nerves that carry commands from the brain to muscles and organs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views9 pagesNervous System
Nervous System
Uploaded by
faresalesa2005The nervous system is responsible for reactions like moving your hand away from something hot or your heart beating faster when scared. It has two main divisions - the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord which controls and interprets signals, and the peripheral nervous system consisting of nerves that connect to sensory receptors and muscles. The peripheral system is further divided into sensory nerves that bring information to the brain and motor nerves that carry commands from the brain to muscles and organs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
When you touch something hot, your hand
moves away quickly. When you smell
freshly baked bread, your mouth
waters. When a big dog jumps at
you, you start to sweat and your
heart beats faster. Did you
know that your nervous system is
responsible for all these reactions?
The nervous system is a complex
collection of nerves and cells that
carry messages throughout your body and
controls your actions. It has
two major divisions, the central nervous
system and the peripheral nervous system.
The first major division is the central
nervous system. It consists of the
brain and the spinal cord and is.
responsible for interpreting the
incoming sensory information and
issuing orders. You could
say the central nervous system is like
the system manager or boss.
The brain and spinal cord are the 2 main
organs in the central nervous system. The
brain is the organ responsible for
processing information, making
decisions, and carrying out tasks
such as maintaining
homeostasis, interpreting sensory
information, creating motor responses,
learning, thinking and talking.
These tasks are either conscious or
unconscious processes. The spinal
cord helps transfer sensory information
from sensory receptors in the
body up to the brain. It also
transfers motor information travelling
down from the brain to the motor units.
The spinal cord also operates as a
switchboard for reflexes or movements,
requiring speed. With
reflexes, movements are initiated in
the spinal cord, not the brain. The
reason for this is that precious time
would be lost if the message had to
travel to and from the brain prior to
triggering the reflex or movement.
The second major division is the
peripheral nervous system. It is made-
up of nerves that travel to and from
the central nervous system. This
system reports any sensory changes to the
brain and spinal cord and carry out
orders. This system reports any
sensory changes to the brain and spinal
cord and carries out orders.
You could say the peripheral nervous
system is like the system employees or
workers. The peripheral nervous system
is further divided into two major
subdivisions, the sensory division
and the motor division. The
sensory division or afferent division
is made-up of the nerves that travel
towards the brain. The nerves in this
division take information from the
sensory receptors to the central nervous
system, such as the frightened sound
of a dog barking or the wonderful
smell of a fresh homemade meal.
This division gives you a sense of the
world around you. The nerves that travel
away from the central nervous system make
up the motor division or efferent
division. This system sends messages to
your muscles and glands to carry out
orders from the brain. Some of these
orders you do by choice, but other
actions such as your mouth watering when
you smell something delicious or sweating
when you are frightened, are done
unconsciously. The motive
division of the peripheral nervous system
is further divided into two.
Subdivisions. One is the
somatic nervous system. It is the
subdivision of the motor division that
allows you to consciously control your
skeletal muscles, so
any voluntary movements like brushing
your teeth or swatting a fly off your
arm. The other subdivision is the
autonomic nervous system. This
allows the body to perform tasks that are
not under conscious control.
In other words, it's the system that
regulates involuntary activities
such as digestion, sweating, and your
heartbeat. The autonomic
nervous system also has two parts.
The first part is the sympathetic nervous
system, which is responsible for
responses such as speeding up your heart
rate, constricting your blood vessels and
raising your blood pressure. The 2nd is
the parasympathetic nervous system, which
calms you down once the threat is over.
This includes slowing your heart
rate, which allows you to relax.
Did You Know?
Spinal cord injuries are very common and
have life changing effects on people who
develop such injuries.
Spinal cord injuries can leave you with
no feeling or control of your
body below the injury site.
In a spinal injury that is classified
as complete, you lose all
sensory and motor function below the
sight of the injury. In
a case that is classified as
incomplete, you only lose partial
sensory and motor control.
Car accidents and falls are the leading
causes of spinal injuries, but
diseases such as cancer,
arthritis, osteoporosis
and inflammation of the spinal cord also
lead to spinal cord injuries.
Health care professionals conduct a
number of physical response and
medical tests to diagnose spinal
injuries. Also,
X-rays, CT scans and
Mris are commonly used to diagnose
spinal injuries.
According to the Mayo Clinic, though it
is currently not possible to medically
repair damage to the spinal cord,
treatments to manage the condition and
stop further damage include
prosthesis, electrical
stimulation and medication. The
nervous system has many functions. Two of
its main functions are first, it
detects changes inside and outside the
body. This happens because of the
sensories receptors that exist all over
the body. Most are concentrated in the
sensory organs such as the eyes,
ears, tongue, nose and
skin. Second, the nervous system
also interprets the information it
receives from the sensory receptors
and sends orders to the muscles and
glands and effects a response,
for example, if someone throws the ball
your way. You see the ball with your
eyes, your brain gives you the order to
catch it, and then you move your arm to
catch it. This description simplifies
the way the nervous system operates, but
in fact the nervous system contains
billions of cells that carry out
countless functions every day.
Your body systems interact with
and depend on one another. The
brain receives information from many
organs and sends signals to these
organs to function properly.
Therefore, the nervous system is
associated with a number of
body systems.
Including. The skeletal.
Cardiovascular, Muscular.
Endocrine. Lymphatic,
respiratory, digestive,
reproductive, and urinary
systems.
You might also like
- Chuchi Andres Social Case Study ReportDocument2 pagesChuchi Andres Social Case Study Reportrafael solam89% (9)
- 3D Implant Position Esquivel 2021Document9 pages3D Implant Position Esquivel 2021Lamis MagdyNo ratings yet
- Health Talk On AnemiaDocument15 pagesHealth Talk On Anemiasimonjosan89% (64)
- Big in Baltimore (Chapter 11, Letter 1)Document4 pagesBig in Baltimore (Chapter 11, Letter 1)LynnNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesNervous SystemShayu ShaNo ratings yet
- PERDEV Q4M5 The Brain Parts Function Societal RelationshipDocument68 pagesPERDEV Q4M5 The Brain Parts Function Societal Relationshipnickybts09No ratings yet
- Influence of Nervous System On BehaviorDocument2 pagesInfluence of Nervous System On BehaviorcynthiasenNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyWiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesModule 7 Nervous SystemMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Hemisphere Is Divided Into LobesDocument2 pagesCerebral Hemisphere Is Divided Into LobesWiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Perdev StephanieDocument4 pagesPerdev StephaniemallarijiannaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesThe Nervous System868.CapalotNo ratings yet
- The-Nervous-System-Written ReportDocument5 pagesThe-Nervous-System-Written ReportHeileen S. San GabrielNo ratings yet
- PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT - 2nd Batch LASDocument16 pagesPERSONAL DEVELOPMENT - 2nd Batch LASJustin JoshNo ratings yet
- Health PresentationDocument20 pagesHealth Presentationapi-214728543No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument1 pageThe Nervous SystemNaomi FenechNo ratings yet
- Ballaran-Anatomy-Bsess-Fsc 2aDocument3 pagesBallaran-Anatomy-Bsess-Fsc 2aMary Joy BallaranNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-THE NERVOUS SYSTEMDocument6 pagesLesson 1-THE NERVOUS SYSTEMNatoya RichardsNo ratings yet
- Neurons: Cells of The Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNeurons: Cells of The Nervous SystemItpixels OfficebackdoorNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE VI Module 10Document5 pagesSCIENCE VI Module 10JHUDIELLE ANNE JANSOLNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNervous Systemjanssen.azagra.basalloteNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemshhhNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument3 pagesSCIENCENel BorniaNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument17 pagesHuman BrainAkbota KuanishkyzyNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNervous SystemCerene denzinNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Que Fransis A.Document5 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Kepy 01 09 37 EtextDocument9 pagesKepy 01 09 37 Etextmradul guptaNo ratings yet
- STEM 12 ERYTHRON Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesSTEM 12 ERYTHRON Nervous SystemJhon Philip ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology: Explain The Functions of The Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology: Explain The Functions of The Nervous SystemJay-ar BarquerosNo ratings yet
- q3 w2 Science 10Document63 pagesq3 w2 Science 10dejaveusNo ratings yet
- The Biological Perspective 2Document11 pagesThe Biological Perspective 2Radhey SurveNo ratings yet
- Group 1B OutlineDocument3 pagesGroup 1B Outlinejackclaudefajardo15No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument6 pagesBiologyExtreme gaming buddyNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Overview: FunctionDocument11 pagesNervous System - Overview: FunctionAadil JuttNo ratings yet
- Reporting Module 5Document12 pagesReporting Module 5Emarre BaronNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Nervous System Part 2Document25 pagesTopic 3 Nervous System Part 2fauzi ariffinNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination Do You Know Which Organs Make Up The Nervous System?Document22 pagesControl and Coordination Do You Know Which Organs Make Up The Nervous System?So TemptedNo ratings yet
- Brain and Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesBrain and Nervous SystemBrenda LizarragaNo ratings yet
- General Psychology Notes Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesGeneral Psychology Notes Nervous SystemRj BengilNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesParts of The Nervous SystemRonel AsuncionNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesThe Nervous Systemhajra0325No ratings yet
- Biology For Engineers Module 2Document82 pagesBiology For Engineers Module 2moaaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- The Amazing Human Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Amazing Human Nervous SystemSenio, Lexis Jan A.No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesThe Nervous Systemvedansh duttNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesHuman Nervous SystemSridevi NadipalliNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System Is The BodyDocument18 pagesThe Nervous System Is The Bodyvedansh duttNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReportingDocument5 pagesAnaphy ReportingZyra Kim ResareNo ratings yet
- ANATOMYDocument4 pagesANATOMYChristine IgnasNo ratings yet
- The BrainDocument35 pagesThe BrainKuriok BurnikNo ratings yet
- What Is Neuron?Document8 pagesWhat Is Neuron?Shaekh Maruf Skder 1912892630No ratings yet
- Anatomy Analogy ProjectDocument2 pagesAnatomy Analogy Projectapi-251525028No ratings yet
- KSG-Brain ActivityDocument10 pagesKSG-Brain ActivitySyahirah ZackNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous Systemkrista2007xxNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System (Edited)Document27 pagesThe Nervous System (Edited)Kiarana Fleischer100% (1)
- General Biology 2 Finals ExamDocument32 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Finals ExamJohn Lloyd BallaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesNervous SystemBarangay Onefourseven CaloocanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document109 pagesChapter 3amala raviNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Science NotesDocument45 pagesYear 10 Science NotesAmal VivekNo ratings yet
- Presentation Biology in Healthcare Stage4Document29 pagesPresentation Biology in Healthcare Stage4alanmauriciohdzNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between The Brain and The Nervous System - 2328 Words - Term Paper ExampleDocument4 pagesRelationship Between The Brain and The Nervous System - 2328 Words - Term Paper ExampleObi TomaNo ratings yet
- Bases of Human Behaviour: How Neurons Transmit Information?Document5 pagesBases of Human Behaviour: How Neurons Transmit Information?Ritu DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyNo ratings yet
- Brain Health - How to Have a Healthy Memory and a Healthy BrainFrom EverandBrain Health - How to Have a Healthy Memory and a Healthy BrainNo ratings yet
- Msds BenzenaDocument7 pagesMsds BenzenaRezaPratamaNo ratings yet
- Loneliness Ncp2Document2 pagesLoneliness Ncp2milcah_castillo100% (4)
- Frequently Asked Questions: How Many Women and Girls Are Victims of Violence?Document4 pagesFrequently Asked Questions: How Many Women and Girls Are Victims of Violence?Favour Toluwanimi ADETOUNNo ratings yet
- Poor Hygiene Practices in Hospitals May Lead To Antibiotic ResistanceDocument2 pagesPoor Hygiene Practices in Hospitals May Lead To Antibiotic ResistancePearl NoconNo ratings yet
- Sohail Updated Thesis 13-June-2022-1Document246 pagesSohail Updated Thesis 13-June-2022-1Quratulain BilalNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma NCLEX Questions QuizDocument22 pagesGlaucoma NCLEX Questions QuizGabrielle G. MaldoNo ratings yet
- Coconut Oil CapsulesDocument13 pagesCoconut Oil CapsulesShouvik DasNo ratings yet
- Pulmonology: C R P - C - 1) All of The Following Are The Causes of Clubbing of Fingers, ExceptDocument30 pagesPulmonology: C R P - C - 1) All of The Following Are The Causes of Clubbing of Fingers, ExceptZaid ZayedNo ratings yet
- Git MCQ Valume DDocument39 pagesGit MCQ Valume DAhmed ElwassiefNo ratings yet
- Essay About Women RightsDocument7 pagesEssay About Women Rightsvqrhuwwhd100% (2)
- RABIES Causative Agent: Rhabdovirus Mode of Transmission: Bite of RabidDocument1 pageRABIES Causative Agent: Rhabdovirus Mode of Transmission: Bite of RabidFreeNursingNotes100% (1)
- Prolonged Postpartum Urinary Retention A Case RepoDocument3 pagesProlonged Postpartum Urinary Retention A Case RepoeeeNo ratings yet
- Walking Aids - PhysiopediaDocument6 pagesWalking Aids - PhysiopediaNana Ann PaaNo ratings yet
- Cry Internship Application Form 1Document3 pagesCry Internship Application Form 1Tanya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Trauma Informed ABADocument23 pagesTrauma Informed ABAGiuli KumeNo ratings yet
- Immunological Tolerance, Pregnancy, and Preeclampsia: The Roles of Semen Microbes and The FatherDocument39 pagesImmunological Tolerance, Pregnancy, and Preeclampsia: The Roles of Semen Microbes and The FatherAnanda Yuliastri DewiNo ratings yet
- Jerônimo Et Al., 2021Document6 pagesJerônimo Et Al., 2021Claudia BrilhanteNo ratings yet
- SemenDocument14 pagesSemenjems wattNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: Vanessa Klee MSIVDocument25 pagesArterial Blood Gas Analysis: Vanessa Klee MSIVGarata PutriNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Reading Passage PREDocument4 pagesGrade 9 Reading Passage PREREY VISTAL100% (1)
- Human Nutrition 2 QPDocument11 pagesHuman Nutrition 2 QPRay PeramathevanNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Flash Cards - PDocument37 pagesFinal Exam Flash Cards - PReut shapiraNo ratings yet
- Clinical Evaluation Comparing The Fit of All-Ceramic Crowns Obtained From Silicone and Digital Intraoral ImpressionsDocument8 pagesClinical Evaluation Comparing The Fit of All-Ceramic Crowns Obtained From Silicone and Digital Intraoral ImpressionsCristobalVeraNo ratings yet
- Physiology Paper II - SampleDocument1 pagePhysiology Paper II - Samplerehan athaniNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure and Its Drug ClassificationDocument37 pagesHeart Failure and Its Drug ClassificationMaham AzmatNo ratings yet
- 1699Document3 pages1699Souci RahmadhanyNo ratings yet