Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7vu683 21
7vu683 21
Uploaded by
tonyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- General Information.: SBC Control Module (A7/3n1)Document4 pagesGeneral Information.: SBC Control Module (A7/3n1)SzekelyGobe75% (4)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- GXT2-10000T230 Service ManualDocument33 pagesGXT2-10000T230 Service ManualMilton Mejia80% (10)
- ATS48 Repair Trouble Shooting ManualDocument248 pagesATS48 Repair Trouble Shooting ManualRodolfoAntonioLeónCárdenas100% (3)
- DGA Furan AnalysisDocument42 pagesDGA Furan AnalysisShefian Md Dom100% (10)
- Interlocking Scheme Transmission Dept PDFDocument40 pagesInterlocking Scheme Transmission Dept PDFSergio Henrique F. CArniettoNo ratings yet
- GXT2U 2000ServiceLiebert PDFDocument28 pagesGXT2U 2000ServiceLiebert PDFhytham.midani.63No ratings yet
- SD70ACe IGBT Safety ManualDocument18 pagesSD70ACe IGBT Safety ManualAlberto Alejandro Sanchez100% (1)
- Host Driver Logs CurrentDocument129 pagesHost Driver Logs CurrenttonyNo ratings yet
- 7vu683 26Document5 pages7vu683 26tonyNo ratings yet
- 7vu683 16Document5 pages7vu683 16tonyNo ratings yet
- High-Speed Busbar TransferDocument8 pagesHigh-Speed Busbar TransferFlo MircaNo ratings yet
- High Speed Bus Transfer Function Block Description Operation ManualDocument27 pagesHigh Speed Bus Transfer Function Block Description Operation ManualSơn PhạmNo ratings yet
- Automatic Gen.-Set Controller For AMF and Mains Parallel OperationDocument56 pagesAutomatic Gen.-Set Controller For AMF and Mains Parallel Operationdudu_vitoria92% (12)
- 3BHS212800 Zab E01Document20 pages3BHS212800 Zab E01Eugen RadulianNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX Seg Nb2Document34 pagesVdocuments - MX Seg Nb2KrzysztofNo ratings yet
- Autochangeover in Power PlantsDocument18 pagesAutochangeover in Power PlantsSukant BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- ABB REL670 V2.2.1 A32 ZMF Line PTT User Manual ENU PDFDocument7 pagesABB REL670 V2.2.1 A32 ZMF Line PTT User Manual ENU PDFWafa Imene BouhaddaNo ratings yet
- Manual of Cdig-310220Document22 pagesManual of Cdig-310220trinath mohapatraNo ratings yet
- C6200 Gencontroller: Function DescriptionDocument17 pagesC6200 Gencontroller: Function DescriptionRajneesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Hat530n en ManualDocument19 pagesHat530n en Manualdario sanchezNo ratings yet
- bq2570x Evaluation Module: User's GuideDocument14 pagesbq2570x Evaluation Module: User's Guideandrey_byNo ratings yet
- Sid-8bt High Speed Transfer Operation ManualDocument29 pagesSid-8bt High Speed Transfer Operation ManualLEK MAN ꦲꦂꦩꦤ꧀ꦱꦸꦱꦤ꧀ꦠꦺꦴNo ratings yet
- 11050011G1 CBCT ConfigurationDocument13 pages11050011G1 CBCT Configurationtha_ansNo ratings yet
- 2021 Seo Primary Side Vs Secondary Side Regulation - r1.0Document4 pages2021 Seo Primary Side Vs Secondary Side Regulation - r1.0宋萌萌No ratings yet
- PW2 MCDDocument5 pagesPW2 MCDUlul AzmiNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument15 pagesReportGavaine MattisonNo ratings yet
- HAT530N enDocument20 pagesHAT530N enRath AsypadenNo ratings yet
- Chloride LINEAR MK II - Service ManualDocument32 pagesChloride LINEAR MK II - Service Manualfabio.perazzoloNo ratings yet
- English Service Manual RAINBOW200HFDocument52 pagesEnglish Service Manual RAINBOW200HFJaroslaw BrzozowskiNo ratings yet
- LNK605 DatasheetDocument18 pagesLNK605 DatasheetdgujarathiNo ratings yet
- TPS6103x EVM-208 For High Efficient Output Current Boost ConverterDocument8 pagesTPS6103x EVM-208 For High Efficient Output Current Boost ConverterRichard GonzalezNo ratings yet
- SCR Based Single Phase CycloconverterDocument6 pagesSCR Based Single Phase Cycloconverterchandra sekhar sahuNo ratings yet
- AN3115Document24 pagesAN3115Heriberto Flores AmpieNo ratings yet
- Altistart 01 TechDocument38 pagesAltistart 01 TechSalim SaadNo ratings yet
- Single-Inductor Multiple-Output Switching Converters With Time-Multiplexing Control in Discontinuous Conduction ModeDocument12 pagesSingle-Inductor Multiple-Output Switching Converters With Time-Multiplexing Control in Discontinuous Conduction ModeZhongpeng LiangNo ratings yet
- An-1048 (1) BLDC Driver LossDocument9 pagesAn-1048 (1) BLDC Driver LossDeepa DevarajNo ratings yet
- AVRDocument42 pagesAVRMaged Mounir100% (1)
- User Manual: HAT560N Series (HAT560N/HAT560NB) Ats ControllerDocument28 pagesUser Manual: HAT560N Series (HAT560N/HAT560NB) Ats ControllerWilmer Alfredo CondeNo ratings yet
- 1 14 PDFDocument7 pages1 14 PDFCarlos Lino Rojas AgüeroNo ratings yet
- XC9235 - 36 - 37 DCDC Study GuideDocument14 pagesXC9235 - 36 - 37 DCDC Study GuideTumenbayar LkhagvatserenNo ratings yet
- Switch Yard REVISEDocument28 pagesSwitch Yard REVISEPratheek ReddyNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study Between Pid and Fuzzy Pid Controller For Speed Control of BLDC Motor IJERTV7IS050098Document6 pagesComparative Study Between Pid and Fuzzy Pid Controller For Speed Control of BLDC Motor IJERTV7IS050098DIVYA PRASOONA CNo ratings yet
- Linear MK II 6kVA Service ManualDocument31 pagesLinear MK II 6kVA Service ManualSry SantosNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Based DC Motor Control: Jayshree Sahu, S.K.Sahu, Jayendra KumarDocument4 pagesMicrocontroller Based DC Motor Control: Jayshree Sahu, S.K.Sahu, Jayendra KumarJagdish PatankarNo ratings yet
- Buck-Boost Converter For Battery ChargersDocument16 pagesBuck-Boost Converter For Battery Chargersdowny44No ratings yet
- Controlled Switching of Circuit Breaker and Its Site MeasurementDocument4 pagesControlled Switching of Circuit Breaker and Its Site MeasurementprabhuNo ratings yet
- ABB RET630 PG 756978 ENbDocument72 pagesABB RET630 PG 756978 ENbjppreciadomNo ratings yet
- HAT560N HAT560NB enDocument28 pagesHAT560N HAT560NB enChhoan NhunNo ratings yet
- 2002apr08 Icd Amd Pow TacDocument9 pages2002apr08 Icd Amd Pow TacMihaela CaciumarciucNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Hat530 Ats ControllerDocument26 pagesUser Manual: Hat530 Ats Controllerrjcp01No ratings yet
- Service Manual RAINBOW 180E EnglishDocument54 pagesService Manual RAINBOW 180E EnglishJaroslaw BrzozowskiNo ratings yet
- Application of DC/DC Buck Power Converter in DC Motor For Speed Controlling Using PI ControllerDocument5 pagesApplication of DC/DC Buck Power Converter in DC Motor For Speed Controlling Using PI ControllerShreeji ExportsNo ratings yet
- Function cw1500 Semikron Rev05 07gb PDFDocument13 pagesFunction cw1500 Semikron Rev05 07gb PDFNguyen HoangNo ratings yet
- AN1114 - Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Topologies (Part I) - MicrochipDocument48 pagesAN1114 - Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Topologies (Part I) - MicrochipbmmostefaNo ratings yet
- Prekidačka NapajanjaDocument48 pagesPrekidačka NapajanjaDamir PranjkovicNo ratings yet
- Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Topologies (Part I) - MicrochipDocument48 pagesSwitch Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Topologies (Part I) - MicrochipGhulam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Power Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignFrom EverandPower Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignBruno AllardNo ratings yet
- 7vu683 26Document5 pages7vu683 26tonyNo ratings yet
- Metrahit Im Serie Ba - GB - 2Document1 pageMetrahit Im Serie Ba - GB - 2tonyNo ratings yet
- (IT) 1 Introduction: Figure 1 - Functional DiagramDocument3 pages(IT) 1 Introduction: Figure 1 - Functional DiagramtonyNo ratings yet
- 7vu683 11Document5 pages7vu683 11tonyNo ratings yet
- 7vu683 6Document5 pages7vu683 6tonyNo ratings yet
- Manu 1Document1 pageManu 1tonyNo ratings yet
- Manu 3Document1 pageManu 3tonyNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument1 pagePDFtonyNo ratings yet
- (TD) 2 Technical Data: Only The Following Combinations of Software Version and Hardware SuffixDocument3 pages(TD) 2 Technical Data: Only The Following Combinations of Software Version and Hardware SuffixtonyNo ratings yet
- Manu 2Document1 pageManu 2tonyNo ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To MicomDocument3 pages2 Introduction To MicomtonyNo ratings yet
- 3.3.3 Information Required With Order For P143: Product ScopeDocument3 pages3.3.3 Information Required With Order For P143: Product ScopetonyNo ratings yet
- 5 De-Commissioning and Disposal: (SI) Safety InformationDocument3 pages5 De-Commissioning and Disposal: (SI) Safety InformationtonyNo ratings yet
- Only The Following Combinations of Software Version and Hardware SuffixDocument3 pagesOnly The Following Combinations of Software Version and Hardware SuffixtonyNo ratings yet
- 1 5 2 Health and Safety 6 3 Symbols and Labels On The Equipment 8Document3 pages1 5 2 Health and Safety 6 3 Symbols and Labels On The Equipment 8tonyNo ratings yet
- Micom P120/P121/P122 & P123 Overcurrent Relays Technical GuideDocument1 pageMicom P120/P121/P122 & P123 Overcurrent Relays Technical GuidetonyNo ratings yet
- Installing, Commissioning and ServicingDocument3 pagesInstalling, Commissioning and ServicingtonyNo ratings yet
- 2 Health and SafetyDocument3 pages2 Health and SafetytonyNo ratings yet
- Battery Testing Test Battery Discharge 110 TestDocument3 pagesBattery Testing Test Battery Discharge 110 TesttonyNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Labels On The EquipmentDocument1 pageSymbols and Labels On The EquipmenttonyNo ratings yet
- Batteries Discharge Test Batteries Discharge Test Batteries SubstationDocument2 pagesBatteries Discharge Test Batteries Discharge Test Batteries SubstationtonyNo ratings yet
- Part7 p122 PDFDocument1 pagePart7 p122 PDFtonyNo ratings yet
- De-Commissioning and Disposal: CleaningDocument1 pageDe-Commissioning and Disposal: CleaningtonyNo ratings yet
- Accidental Touching of Exposed TerminalsDocument1 pageAccidental Touching of Exposed TerminalstonyNo ratings yet
- Standard Safety Statements For Areva T&D EquipmentDocument1 pageStandard Safety Statements For Areva T&D EquipmenttonyNo ratings yet
- APN-056 Application-Low-voltageDocument8 pagesAPN-056 Application-Low-voltageANTONIO SOLISNo ratings yet
- Protection Relay ANSI StandardsDocument7 pagesProtection Relay ANSI Standardskondareddy100% (1)
- Thermal Overload Relays With Current Transformer CTXL: T16 and Tf42 With Ct4L185R/4, Ct4L310R/4, Ct5L500R/4, Ct5L850R/4Document6 pagesThermal Overload Relays With Current Transformer CTXL: T16 and Tf42 With Ct4L185R/4, Ct4L310R/4, Ct5L500R/4, Ct5L850R/4rio_olNo ratings yet
- 193 - 035 Ac500 Owners ManualDocument30 pages193 - 035 Ac500 Owners ManualE Abadt DLNo ratings yet
- CH 3 PDFDocument80 pagesCH 3 PDFmuhammad saeedNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument36 pagesInternship ReportDhruv Patel100% (1)
- Smart Grid ReportDocument27 pagesSmart Grid ReportLovelesh MalavNo ratings yet
- As Built Drawings 33kv PanelDocument44 pagesAs Built Drawings 33kv Panellalitendu jenaNo ratings yet
- Protection and Relay SchemesDocument44 pagesProtection and Relay SchemesSaeed Mahmood Gul Khan67% (6)
- Practical Example of Arrester and TransformerDocument6 pagesPractical Example of Arrester and Transformerdeepthik27No ratings yet
- Eaton Harmonic Problems & Solutions AnnotatedDocument16 pagesEaton Harmonic Problems & Solutions AnnotatedGMCaselNo ratings yet
- Protection of Motors, Busbar, FeedersDocument33 pagesProtection of Motors, Busbar, FeedersViswanathanBalaji100% (1)
- IEEE Guide For Partial Discharge Measurement in Power SwitchgearDocument24 pagesIEEE Guide For Partial Discharge Measurement in Power SwitchgearHafiziAhmadNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Examination: Engineering Mathematics - IIDocument34 pagesScheme of Examination: Engineering Mathematics - IIvamsiNo ratings yet
- 512 International Enquiry On Reliability of High Voltage Equipment Part 4 - Instrument TransformersDocument193 pages512 International Enquiry On Reliability of High Voltage Equipment Part 4 - Instrument Transformersepri100% (1)
- Unit 11 Electricity & MagnetismDocument60 pagesUnit 11 Electricity & Magnetismtheswag9876No ratings yet
- T921A, B, E-G Proportional Control ThermostatsDocument8 pagesT921A, B, E-G Proportional Control ThermostatsAudi eko susatyoNo ratings yet
- Testing of TransformerDocument130 pagesTesting of TransformerRohit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Air Insulated Switchboard: Mcset 17.5 KVDocument76 pagesAir Insulated Switchboard: Mcset 17.5 KVMIGUEL ALVARO BLASCO MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- HVAC Electrical ControlDocument47 pagesHVAC Electrical ControlAurelio Jr TambigaNo ratings yet
- Reference DPDDocument66 pagesReference DPDAmmar Syahid RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Emd QPDocument6 pagesEmd QPrubyviswanathanNo ratings yet
- Haramaya UniversityDocument10 pagesHaramaya UniversityAlex MekoNo ratings yet
- DC Microgride ProtectionDocument7 pagesDC Microgride ProtectionSuco MuzenzaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Braking SystemDocument33 pagesElectromagnetic Braking SystemArpit7867756% (9)
- UG EEE - FINAL - ACADEMIC - HANDBOOK - NIT - GOA - Revised-1Document69 pagesUG EEE - FINAL - ACADEMIC - HANDBOOK - NIT - GOA - Revised-1qwerNo ratings yet
- Wind TB GeneratorDocument26 pagesWind TB GeneratorbinhNo ratings yet
- Electrical Substation Components List - Diagram, Working & FunctionsDocument15 pagesElectrical Substation Components List - Diagram, Working & FunctionsPanner2009100% (1)
7vu683 21
7vu683 21
Uploaded by
tonyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7vu683 21
7vu683 21
Uploaded by
tonyCopyright:
Available Formats
Function
2.1 General
Figure 2-2 VT Installation Illustration at HV Side of in-feeding Transformer
Calculation example for Figure 2-2:
0283 Balancing factor of line1: = (38.5/35*0.1) / (6/6*0.1) = 1.10
Default setting: 1.00
0284 Angle adjustment of line1: = 1 * 30° = 30°
Default setting: 0.0°
2.1.2 CT Installation
Line current is helpful for reliable self-start which can be used as the additional criteria, e.g, for under-voltage
starting condition. Only 1-ph current is required for line side.
3-ph bus current is only required if protective functions for tie-CB under primary diagram of sectionalized single
busbar with 3-CB are configured.
SIPROTEC, 7VU683, User Manual 21
C53000-G1176-C369-4, Release Date 07.2016
Function
2.1 General
Figure 2-3 shows the current connection example.
Figure 2-3 CT Connection Illustration
Line current is only essential for self-auto starting condition of reverse power. Then, the connection must be
parameterized under Power System Data 1, e.g, 0280 CT connection of Line 1 = IB.
2.1.3 Remote ON/OFF
The device 7VU683 supports to remotely switch on/off functions over protocol if parameter 0650 Remote setting
ON/OFF is set to YES.
Below functions can be remotely switched on/off over protocol,
• HSBT function;
• Protection function;
• Kinds of switching direction;
• Kinds of transfer mode;
22 SIPROTEC, 7VU683, User Manual
C53000-G1176-C369-4, Release Date 07.2016
Function
2.2 HSBT
2.2 HSBT
2.2.1 General
After power loss of running source, the decaying residual voltage on bus is there which is produced by induction
motors. To transfer the motor bus to alternative source, the asynchronous switching must occur. Special
consideration must be taken into account to avoid any damages to motors.
Key points are to secure the safe but fast transfer for motor bus to minimize the impact to motor winding and
processing loads. All relevance to fast transfer will be described in below chapters, for example, starting
conditions, switching sequences, transfer modes, etc.
2.2.1.1 Bus Residual Voltage
After power loss, residual voltage will be there on motor bus which is induced by rotating motors with
remanence. Figure 2-4 shows the simulation results.
Figure 2-4 Residual Voltage Simulation on Motor Bus
Key conclusions regarding the simulation,
SIPROTEC, 7VU683, User Manual 23
C53000-G1176-C369-4, Release Date 07.2016
Function
2.2 HSBT
• The amplitude of residual voltage is decaying;
• The frequency of residual voltage is decaying;
• The phase angle difference between the residual voltage and alternative source is bigger and bigger;
• The differential voltage across the alternative source CB is swinging, i.e, from -180to 180.
2.2.1.2 Philosophy
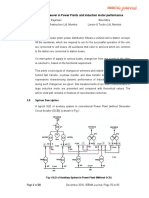
Some attentions must be paid to the co-ordination between HSBT and protective relays. Figure 2-5 shows the
overview.
Figure 2-5 Co-ordination Philosophy between HSBT and Protective Relays
Some basic rules can be drawn from Figure 2-5,
• Protective relay will detect and clear any system fault or HV bus fault, and result at CB4 (CB6) trip. This leads
to power loss of motor bus. Normally there is not any indication routed to HSBT. HSBT can only be self-
started by integrated abnormal detection criterions, e.g, under-voltage, under-frequency, etc.
• Protective relay, for example, differential protection (ANSI 87), will detect and clear any fault on in-feeding
transformer, and result at CB1 trip. Meanwhile, HSBT should be externally started by protective relay.
• Protective relay, for example, over-current protection (ANSI 50), will detect and clear any fault on motor bus,
and result at CB1 trip. Meanwhile, HSBT should be externally blocked by protective relay.
HSBT should be externally started under planned operation, for example, starting up of generator. This can be
actualized via binary input, for example, push the external button of OPEN CB1. It will also be externally started
24 SIPROTEC, 7VU683, User Manual
C53000-G1176-C369-4, Release Date 07.2016
Function
2.2 HSBT
under fault, e.g, in-feeding transformer over-loading, this can be actualized via binary input, e.g, the indication
from protective relays. HSBT should be internally self-started under power loss of motor bus, e.g, up-stream
CB is tripped.
Switching sequence means the operating sequence of running source CB and alternative source CB. Three
possible sequences are there. PARALLEL sequence is to send the CLOSE command to alternative source CB
first, then send the OPEN command to running source CB. That is, the two sources will over-lap for short time
on motor bus. SIMULTANEOUS sequence is to send the OPEN and CLOSE command at the same time. Very
short source dead time caused by the operating time difference of two CBs could be there. The last
SEQUENTIAL sequence is to send the OPEN command to running source CB first, then the CLOSE command
to alternative source CB. That is, a significant source dead time on motor bus will be there.
PARALLEL sequence is actually to make synchro-check to alternative source CB under steady condition. It's
only available for planned operation if over-lapping is allowed. The OPEN command can be automatically sent
out after the alternative source CB is switched on under switching sequence PARALLEL Auto. It can also be
manually sent out after the alternative source CB is switched on under switching sequence PARALLEL Half-
Auto.
Special attentions have to be paid for both SIMUTANEOUS and SEQUENTIAL sequence under dynamic
condition. Then, various transfer modes are applied. Each mode acts as different criterions and has different
action time. Both FAST and REAL-TIME FAST modes are designed according to the fast transfer definition in
ANSI C50.41-2012. The other three slow modes serve as the backup transfer. Each mode has to be
parameterized.
To avoid the possible over-loading of alternative source during the low voltage re-starting of bus motors after
transfer, it's helpful to deploy the low voltage load-shedding function before transfer mode RES-VOLT.
The overall workflow in HSBT 7VU683 is shown in Figure 2-6.
SIPROTEC, 7VU683, User Manual 25
C53000-G1176-C369-4, Release Date 07.2016
You might also like
- General Information.: SBC Control Module (A7/3n1)Document4 pagesGeneral Information.: SBC Control Module (A7/3n1)SzekelyGobe75% (4)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- GXT2-10000T230 Service ManualDocument33 pagesGXT2-10000T230 Service ManualMilton Mejia80% (10)
- ATS48 Repair Trouble Shooting ManualDocument248 pagesATS48 Repair Trouble Shooting ManualRodolfoAntonioLeónCárdenas100% (3)
- DGA Furan AnalysisDocument42 pagesDGA Furan AnalysisShefian Md Dom100% (10)
- Interlocking Scheme Transmission Dept PDFDocument40 pagesInterlocking Scheme Transmission Dept PDFSergio Henrique F. CArniettoNo ratings yet
- GXT2U 2000ServiceLiebert PDFDocument28 pagesGXT2U 2000ServiceLiebert PDFhytham.midani.63No ratings yet
- SD70ACe IGBT Safety ManualDocument18 pagesSD70ACe IGBT Safety ManualAlberto Alejandro Sanchez100% (1)
- Host Driver Logs CurrentDocument129 pagesHost Driver Logs CurrenttonyNo ratings yet
- 7vu683 26Document5 pages7vu683 26tonyNo ratings yet
- 7vu683 16Document5 pages7vu683 16tonyNo ratings yet
- High-Speed Busbar TransferDocument8 pagesHigh-Speed Busbar TransferFlo MircaNo ratings yet
- High Speed Bus Transfer Function Block Description Operation ManualDocument27 pagesHigh Speed Bus Transfer Function Block Description Operation ManualSơn PhạmNo ratings yet
- Automatic Gen.-Set Controller For AMF and Mains Parallel OperationDocument56 pagesAutomatic Gen.-Set Controller For AMF and Mains Parallel Operationdudu_vitoria92% (12)
- 3BHS212800 Zab E01Document20 pages3BHS212800 Zab E01Eugen RadulianNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX Seg Nb2Document34 pagesVdocuments - MX Seg Nb2KrzysztofNo ratings yet
- Autochangeover in Power PlantsDocument18 pagesAutochangeover in Power PlantsSukant BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- ABB REL670 V2.2.1 A32 ZMF Line PTT User Manual ENU PDFDocument7 pagesABB REL670 V2.2.1 A32 ZMF Line PTT User Manual ENU PDFWafa Imene BouhaddaNo ratings yet
- Manual of Cdig-310220Document22 pagesManual of Cdig-310220trinath mohapatraNo ratings yet
- C6200 Gencontroller: Function DescriptionDocument17 pagesC6200 Gencontroller: Function DescriptionRajneesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Hat530n en ManualDocument19 pagesHat530n en Manualdario sanchezNo ratings yet
- bq2570x Evaluation Module: User's GuideDocument14 pagesbq2570x Evaluation Module: User's Guideandrey_byNo ratings yet
- Sid-8bt High Speed Transfer Operation ManualDocument29 pagesSid-8bt High Speed Transfer Operation ManualLEK MAN ꦲꦂꦩꦤ꧀ꦱꦸꦱꦤ꧀ꦠꦺꦴNo ratings yet
- 11050011G1 CBCT ConfigurationDocument13 pages11050011G1 CBCT Configurationtha_ansNo ratings yet
- 2021 Seo Primary Side Vs Secondary Side Regulation - r1.0Document4 pages2021 Seo Primary Side Vs Secondary Side Regulation - r1.0宋萌萌No ratings yet
- PW2 MCDDocument5 pagesPW2 MCDUlul AzmiNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument15 pagesReportGavaine MattisonNo ratings yet
- HAT530N enDocument20 pagesHAT530N enRath AsypadenNo ratings yet
- Chloride LINEAR MK II - Service ManualDocument32 pagesChloride LINEAR MK II - Service Manualfabio.perazzoloNo ratings yet
- English Service Manual RAINBOW200HFDocument52 pagesEnglish Service Manual RAINBOW200HFJaroslaw BrzozowskiNo ratings yet
- LNK605 DatasheetDocument18 pagesLNK605 DatasheetdgujarathiNo ratings yet
- TPS6103x EVM-208 For High Efficient Output Current Boost ConverterDocument8 pagesTPS6103x EVM-208 For High Efficient Output Current Boost ConverterRichard GonzalezNo ratings yet
- SCR Based Single Phase CycloconverterDocument6 pagesSCR Based Single Phase Cycloconverterchandra sekhar sahuNo ratings yet
- AN3115Document24 pagesAN3115Heriberto Flores AmpieNo ratings yet
- Altistart 01 TechDocument38 pagesAltistart 01 TechSalim SaadNo ratings yet
- Single-Inductor Multiple-Output Switching Converters With Time-Multiplexing Control in Discontinuous Conduction ModeDocument12 pagesSingle-Inductor Multiple-Output Switching Converters With Time-Multiplexing Control in Discontinuous Conduction ModeZhongpeng LiangNo ratings yet
- An-1048 (1) BLDC Driver LossDocument9 pagesAn-1048 (1) BLDC Driver LossDeepa DevarajNo ratings yet
- AVRDocument42 pagesAVRMaged Mounir100% (1)
- User Manual: HAT560N Series (HAT560N/HAT560NB) Ats ControllerDocument28 pagesUser Manual: HAT560N Series (HAT560N/HAT560NB) Ats ControllerWilmer Alfredo CondeNo ratings yet
- 1 14 PDFDocument7 pages1 14 PDFCarlos Lino Rojas AgüeroNo ratings yet
- XC9235 - 36 - 37 DCDC Study GuideDocument14 pagesXC9235 - 36 - 37 DCDC Study GuideTumenbayar LkhagvatserenNo ratings yet
- Switch Yard REVISEDocument28 pagesSwitch Yard REVISEPratheek ReddyNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study Between Pid and Fuzzy Pid Controller For Speed Control of BLDC Motor IJERTV7IS050098Document6 pagesComparative Study Between Pid and Fuzzy Pid Controller For Speed Control of BLDC Motor IJERTV7IS050098DIVYA PRASOONA CNo ratings yet
- Linear MK II 6kVA Service ManualDocument31 pagesLinear MK II 6kVA Service ManualSry SantosNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Based DC Motor Control: Jayshree Sahu, S.K.Sahu, Jayendra KumarDocument4 pagesMicrocontroller Based DC Motor Control: Jayshree Sahu, S.K.Sahu, Jayendra KumarJagdish PatankarNo ratings yet
- Buck-Boost Converter For Battery ChargersDocument16 pagesBuck-Boost Converter For Battery Chargersdowny44No ratings yet
- Controlled Switching of Circuit Breaker and Its Site MeasurementDocument4 pagesControlled Switching of Circuit Breaker and Its Site MeasurementprabhuNo ratings yet
- ABB RET630 PG 756978 ENbDocument72 pagesABB RET630 PG 756978 ENbjppreciadomNo ratings yet
- HAT560N HAT560NB enDocument28 pagesHAT560N HAT560NB enChhoan NhunNo ratings yet
- 2002apr08 Icd Amd Pow TacDocument9 pages2002apr08 Icd Amd Pow TacMihaela CaciumarciucNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Hat530 Ats ControllerDocument26 pagesUser Manual: Hat530 Ats Controllerrjcp01No ratings yet
- Service Manual RAINBOW 180E EnglishDocument54 pagesService Manual RAINBOW 180E EnglishJaroslaw BrzozowskiNo ratings yet
- Application of DC/DC Buck Power Converter in DC Motor For Speed Controlling Using PI ControllerDocument5 pagesApplication of DC/DC Buck Power Converter in DC Motor For Speed Controlling Using PI ControllerShreeji ExportsNo ratings yet
- Function cw1500 Semikron Rev05 07gb PDFDocument13 pagesFunction cw1500 Semikron Rev05 07gb PDFNguyen HoangNo ratings yet
- AN1114 - Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Topologies (Part I) - MicrochipDocument48 pagesAN1114 - Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Topologies (Part I) - MicrochipbmmostefaNo ratings yet
- Prekidačka NapajanjaDocument48 pagesPrekidačka NapajanjaDamir PranjkovicNo ratings yet
- Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Topologies (Part I) - MicrochipDocument48 pagesSwitch Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Topologies (Part I) - MicrochipGhulam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Power Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignFrom EverandPower Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignBruno AllardNo ratings yet
- 7vu683 26Document5 pages7vu683 26tonyNo ratings yet
- Metrahit Im Serie Ba - GB - 2Document1 pageMetrahit Im Serie Ba - GB - 2tonyNo ratings yet
- (IT) 1 Introduction: Figure 1 - Functional DiagramDocument3 pages(IT) 1 Introduction: Figure 1 - Functional DiagramtonyNo ratings yet
- 7vu683 11Document5 pages7vu683 11tonyNo ratings yet
- 7vu683 6Document5 pages7vu683 6tonyNo ratings yet
- Manu 1Document1 pageManu 1tonyNo ratings yet
- Manu 3Document1 pageManu 3tonyNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument1 pagePDFtonyNo ratings yet
- (TD) 2 Technical Data: Only The Following Combinations of Software Version and Hardware SuffixDocument3 pages(TD) 2 Technical Data: Only The Following Combinations of Software Version and Hardware SuffixtonyNo ratings yet
- Manu 2Document1 pageManu 2tonyNo ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To MicomDocument3 pages2 Introduction To MicomtonyNo ratings yet
- 3.3.3 Information Required With Order For P143: Product ScopeDocument3 pages3.3.3 Information Required With Order For P143: Product ScopetonyNo ratings yet
- 5 De-Commissioning and Disposal: (SI) Safety InformationDocument3 pages5 De-Commissioning and Disposal: (SI) Safety InformationtonyNo ratings yet
- Only The Following Combinations of Software Version and Hardware SuffixDocument3 pagesOnly The Following Combinations of Software Version and Hardware SuffixtonyNo ratings yet
- 1 5 2 Health and Safety 6 3 Symbols and Labels On The Equipment 8Document3 pages1 5 2 Health and Safety 6 3 Symbols and Labels On The Equipment 8tonyNo ratings yet
- Micom P120/P121/P122 & P123 Overcurrent Relays Technical GuideDocument1 pageMicom P120/P121/P122 & P123 Overcurrent Relays Technical GuidetonyNo ratings yet
- Installing, Commissioning and ServicingDocument3 pagesInstalling, Commissioning and ServicingtonyNo ratings yet
- 2 Health and SafetyDocument3 pages2 Health and SafetytonyNo ratings yet
- Battery Testing Test Battery Discharge 110 TestDocument3 pagesBattery Testing Test Battery Discharge 110 TesttonyNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Labels On The EquipmentDocument1 pageSymbols and Labels On The EquipmenttonyNo ratings yet
- Batteries Discharge Test Batteries Discharge Test Batteries SubstationDocument2 pagesBatteries Discharge Test Batteries Discharge Test Batteries SubstationtonyNo ratings yet
- Part7 p122 PDFDocument1 pagePart7 p122 PDFtonyNo ratings yet
- De-Commissioning and Disposal: CleaningDocument1 pageDe-Commissioning and Disposal: CleaningtonyNo ratings yet
- Accidental Touching of Exposed TerminalsDocument1 pageAccidental Touching of Exposed TerminalstonyNo ratings yet
- Standard Safety Statements For Areva T&D EquipmentDocument1 pageStandard Safety Statements For Areva T&D EquipmenttonyNo ratings yet
- APN-056 Application-Low-voltageDocument8 pagesAPN-056 Application-Low-voltageANTONIO SOLISNo ratings yet
- Protection Relay ANSI StandardsDocument7 pagesProtection Relay ANSI Standardskondareddy100% (1)
- Thermal Overload Relays With Current Transformer CTXL: T16 and Tf42 With Ct4L185R/4, Ct4L310R/4, Ct5L500R/4, Ct5L850R/4Document6 pagesThermal Overload Relays With Current Transformer CTXL: T16 and Tf42 With Ct4L185R/4, Ct4L310R/4, Ct5L500R/4, Ct5L850R/4rio_olNo ratings yet
- 193 - 035 Ac500 Owners ManualDocument30 pages193 - 035 Ac500 Owners ManualE Abadt DLNo ratings yet
- CH 3 PDFDocument80 pagesCH 3 PDFmuhammad saeedNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument36 pagesInternship ReportDhruv Patel100% (1)
- Smart Grid ReportDocument27 pagesSmart Grid ReportLovelesh MalavNo ratings yet
- As Built Drawings 33kv PanelDocument44 pagesAs Built Drawings 33kv Panellalitendu jenaNo ratings yet
- Protection and Relay SchemesDocument44 pagesProtection and Relay SchemesSaeed Mahmood Gul Khan67% (6)
- Practical Example of Arrester and TransformerDocument6 pagesPractical Example of Arrester and Transformerdeepthik27No ratings yet
- Eaton Harmonic Problems & Solutions AnnotatedDocument16 pagesEaton Harmonic Problems & Solutions AnnotatedGMCaselNo ratings yet
- Protection of Motors, Busbar, FeedersDocument33 pagesProtection of Motors, Busbar, FeedersViswanathanBalaji100% (1)
- IEEE Guide For Partial Discharge Measurement in Power SwitchgearDocument24 pagesIEEE Guide For Partial Discharge Measurement in Power SwitchgearHafiziAhmadNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Examination: Engineering Mathematics - IIDocument34 pagesScheme of Examination: Engineering Mathematics - IIvamsiNo ratings yet
- 512 International Enquiry On Reliability of High Voltage Equipment Part 4 - Instrument TransformersDocument193 pages512 International Enquiry On Reliability of High Voltage Equipment Part 4 - Instrument Transformersepri100% (1)
- Unit 11 Electricity & MagnetismDocument60 pagesUnit 11 Electricity & Magnetismtheswag9876No ratings yet
- T921A, B, E-G Proportional Control ThermostatsDocument8 pagesT921A, B, E-G Proportional Control ThermostatsAudi eko susatyoNo ratings yet
- Testing of TransformerDocument130 pagesTesting of TransformerRohit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Air Insulated Switchboard: Mcset 17.5 KVDocument76 pagesAir Insulated Switchboard: Mcset 17.5 KVMIGUEL ALVARO BLASCO MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- HVAC Electrical ControlDocument47 pagesHVAC Electrical ControlAurelio Jr TambigaNo ratings yet
- Reference DPDDocument66 pagesReference DPDAmmar Syahid RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Emd QPDocument6 pagesEmd QPrubyviswanathanNo ratings yet
- Haramaya UniversityDocument10 pagesHaramaya UniversityAlex MekoNo ratings yet
- DC Microgride ProtectionDocument7 pagesDC Microgride ProtectionSuco MuzenzaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Braking SystemDocument33 pagesElectromagnetic Braking SystemArpit7867756% (9)
- UG EEE - FINAL - ACADEMIC - HANDBOOK - NIT - GOA - Revised-1Document69 pagesUG EEE - FINAL - ACADEMIC - HANDBOOK - NIT - GOA - Revised-1qwerNo ratings yet
- Wind TB GeneratorDocument26 pagesWind TB GeneratorbinhNo ratings yet
- Electrical Substation Components List - Diagram, Working & FunctionsDocument15 pagesElectrical Substation Components List - Diagram, Working & FunctionsPanner2009100% (1)