Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vancomycin Adult
Vancomycin Adult
Uploaded by
Giridhar YadavCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Smoke ABSORBER MachineeDocument8 pagesSmoke ABSORBER MachineeNicole Ramos20% (5)
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingFrom EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo ratings yet
- Micormedex NeoFax Essentials 2014Document8 pagesMicormedex NeoFax Essentials 2014Andreia HirtNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin Dosing Guidelines Adults 2018Document7 pagesVancomycin Dosing Guidelines Adults 2018gabriellaNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin Dosing and Monitoring in AdultsDocument1 pageVancomycin Dosing and Monitoring in AdultsjulialeoNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Vancomycin Use in Adults - 2017Document4 pagesIntravenous Vancomycin Use in Adults - 2017Angy KarakostaNo ratings yet
- Adult Vancomycin Dosing Guidelines DefinitionsDocument2 pagesAdult Vancomycin Dosing Guidelines DefinitionsPhạm DuyênNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guideline For Vancomycin Prescribing and Therapeutic Drug MonitoringDocument11 pagesClinical Guideline For Vancomycin Prescribing and Therapeutic Drug MonitoringFate ChanNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin MylaninfDocument13 pagesVancomycin MylaninfAmanuel GirmayeNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin Nephrology Preferred Dosing StrategyDocument2 pagesVancomycin Nephrology Preferred Dosing StrategyEster Elisabeth WoworNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside & VancomycinDocument10 pagesAminoglycoside & VancomycinKhor Chin PooNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin: Group 5 R.M 2Document31 pagesVancomycin: Group 5 R.M 2vi_wiviaNo ratings yet
- VancoDosingCalculator UCSF 2020 0Document14 pagesVancoDosingCalculator UCSF 2020 0Saul RuizNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Weight & CRCL - StudentDocument4 pagesAssignment-Weight & CRCL - StudentpinkhasovdNo ratings yet
- Vriii PresentationDocument29 pagesVriii Presentationsundance127No ratings yet
- Stanford Hospital & Clinics Antimicrobial Dosing Reference Guide 2013Document3 pagesStanford Hospital & Clinics Antimicrobial Dosing Reference Guide 2013SANCHOSKYNo ratings yet
- Renal Replacement Therapy in Critical Care: Choice of ModeDocument15 pagesRenal Replacement Therapy in Critical Care: Choice of ModePeter AgabaNo ratings yet
- Figure 5-1Document7 pagesFigure 5-1KhaledNo ratings yet
- Ch5 VancomycinDocument14 pagesCh5 Vancomycintiba.qasem2000No ratings yet
- Vancomycin 1. Product Name 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition 3. Pharmaceutical FormDocument11 pagesVancomycin 1. Product Name 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition 3. Pharmaceutical FormVerghese GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Renal Replacement Therapy in Critical Care: Choice of ModeDocument15 pagesRenal Replacement Therapy in Critical Care: Choice of ModeJelena Obrenovic StankovicNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Dosing Guidelines For Renal ImpairmentDocument6 pagesAntibiotic Dosing Guidelines For Renal ImpairmentvitauxianaNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin-Dosing-and-Monitoring-Neonatal.-and-PediatricsDocument5 pagesVancomycin-Dosing-and-Monitoring-Neonatal.-and-Pediatricsf2b9b25kb9No ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis LK, 60 Tahun, Kaki Bengkak, Unilateral, Kemerahan, Riwayat Kanker ParuDocument9 pagesDifferential Diagnosis LK, 60 Tahun, Kaki Bengkak, Unilateral, Kemerahan, Riwayat Kanker ParuArbiantoni 17No ratings yet
- Vancomycin Dosing RecommendationsDocument2 pagesVancomycin Dosing RecommendationsStacey WoodsNo ratings yet
- Most of Cardiac Care Unit (C.C.U) DrugsDocument57 pagesMost of Cardiac Care Unit (C.C.U) DrugsOsama OmarNo ratings yet
- BWH Hyperglycemia GuidelinesDocument7 pagesBWH Hyperglycemia Guidelinespmahesh107100% (1)
- Nursing Orientation Program Intravenous TherapyDocument45 pagesNursing Orientation Program Intravenous TherapyMarianne LayloNo ratings yet
- RENAL DosingDocument8 pagesRENAL Dosingsumayyah995No ratings yet
- SHC Vancomycin Dosing GuideDocument8 pagesSHC Vancomycin Dosing GuidePitchya WangmeesriNo ratings yet
- ClexaneinjDocument25 pagesClexaneinjBobeico TatianaNo ratings yet
- Seasonal Influenza Therapeutic ProtocolDocument4 pagesSeasonal Influenza Therapeutic ProtocolSaleem HamilahNo ratings yet
- SPC 350 0715-03Document19 pagesSPC 350 0715-03lydia kadaNo ratings yet
- VBMC Heparin Protocol FINAL May2004Document3 pagesVBMC Heparin Protocol FINAL May2004Pharmacy OneSource100% (1)
- Vancomycin Protocol: A Protocol To Guide The Dosing and Monitoring of Vancomycin in AdultsDocument5 pagesVancomycin Protocol: A Protocol To Guide The Dosing and Monitoring of Vancomycin in AdultsSaadia MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Problems: 5: VancomycinDocument4 pagesProblems: 5: VancomycinSaul RuizNo ratings yet
- VancomycinDocument5 pagesVancomycintharani1005No ratings yet
- SHC Vancomycin Dosing GuideDocument10 pagesSHC Vancomycin Dosing GuideAlan SmithNo ratings yet
- Enoxaparin Sodium Injection I.PDocument15 pagesEnoxaparin Sodium Injection I.PSuhailansariNo ratings yet
- New Oral Anticoagulants Guidelines: Kai YapDocument23 pagesNew Oral Anticoagulants Guidelines: Kai YapMuhammad Reza FirdausNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation Dosing Recommendations COVID 19 PatientsDocument1 pageAnticoagulation Dosing Recommendations COVID 19 PatientsChalwe HowardNo ratings yet
- Guideline: Antibiotic Drug Monitoring: Aminoglycosides and GlycopeptidesDocument8 pagesGuideline: Antibiotic Drug Monitoring: Aminoglycosides and GlycopeptidesKenRodulfReyesVillaruelNo ratings yet
- Package Insert - NovoSevenRTDocument31 pagesPackage Insert - NovoSevenRTVenu YasarapuNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin - Peds DoseDocument4 pagesVancomycin - Peds DoseIrina UngureanuNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation Protocol For PostDocument8 pagesAnticoagulation Protocol For PostMohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- NICU Drugs GuideDocument49 pagesNICU Drugs GuideArhanNo ratings yet
- Cefepime Kabi DatasheetDocument16 pagesCefepime Kabi Datasheetتوفيق باعبادNo ratings yet
- Pro TaminaDocument2 pagesPro TaminaArcenciel26No ratings yet
- Peramivir Q and A - Updated 11 - 19 - 09 Final CleanDocument10 pagesPeramivir Q and A - Updated 11 - 19 - 09 Final Cleanbenny christantoNo ratings yet
- SHC Vancomycin Dosing GuideDocument9 pagesSHC Vancomycin Dosing GuideDanielVillaNo ratings yet
- New Zealand Data Sheet June 2017Document27 pagesNew Zealand Data Sheet June 2017Eyda JamilNo ratings yet
- Renal PharmacologyDocument52 pagesRenal Pharmacologyashraf0% (1)
- SQC ABx Guidelines 2-21-2011 PDFDocument2 pagesSQC ABx Guidelines 2-21-2011 PDFMinh SteveNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Route of Administration (IV To PO) Therapeutic ConversionDocument1 pageAntimicrobial Route of Administration (IV To PO) Therapeutic ConversiondoodrillNo ratings yet
- Management of Anesthesia: Diabetes MellitusDocument29 pagesManagement of Anesthesia: Diabetes MellitusHari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Vancomicin Guidelines PICUDocument2 pagesVancomicin Guidelines PICUAnonymous 6iwMFwNo ratings yet
- Aciclovir (Zovirax I.V)Document11 pagesAciclovir (Zovirax I.V)asdwasdNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulant Pocket GuideDocument8 pagesAnticoagulant Pocket GuideDrew John Minardi100% (2)
- Stanford Health Care Antimicrobial Dosing Reference GuideDocument7 pagesStanford Health Care Antimicrobial Dosing Reference GuideKarl Martin PinedaNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsFrom EverandDimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsNo ratings yet
- Papich, Mark G. - Saunders Handbook of Veterinary Drugs - Bisoprolol Fumarate (2016, Elsevier) (10.1016 - B978-0-323-24485-5.00107-8) - Libgen - LiDocument2 pagesPapich, Mark G. - Saunders Handbook of Veterinary Drugs - Bisoprolol Fumarate (2016, Elsevier) (10.1016 - B978-0-323-24485-5.00107-8) - Libgen - LibernadethNo ratings yet
- Mental Health EssayDocument5 pagesMental Health Essaycameronbullard2000No ratings yet
- Promoting Mental Health Awareness and Resilience in The Philippine National PoliceDocument2 pagesPromoting Mental Health Awareness and Resilience in The Philippine National PoliceSftts TagapagsanayNo ratings yet
- Ohs-Info Sheet No. 4Document11 pagesOhs-Info Sheet No. 4Ferlyn AboyNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Health & Disease: K.Sagar Asso ProfessorDocument86 pagesConcepts in Health & Disease: K.Sagar Asso Professorkuruvagadda sagarNo ratings yet
- Use of The Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) As A Screening Tool in Prisons: Results of A Preliminary StudyDocument5 pagesUse of The Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) As A Screening Tool in Prisons: Results of A Preliminary StudyRafael MartinsNo ratings yet
- SPECT ScanDocument2 pagesSPECT ScandhruvaNo ratings yet
- Clean Water For AllDocument8 pagesClean Water For AllArgie Joy Marie AmpolNo ratings yet
- Literature Review 1Document7 pagesLiterature Review 1api-743809775No ratings yet
- Euac 125Document23 pagesEuac 125Nicoletta OrphanouNo ratings yet
- Health Grade 10 2nd QTR M4Document5 pagesHealth Grade 10 2nd QTR M4MrLonely Drake Deniel SanchezNo ratings yet
- A Qualitative Study: Campus Bullying in The Senior High SchoolDocument14 pagesA Qualitative Study: Campus Bullying in The Senior High SchoolHouston IbañezNo ratings yet
- TFN PrelimDocument9 pagesTFN PrelimElla ArnocoNo ratings yet
- Exercise:: I. True or False Statements: Put TRUE in Front of The True Sentences and FALSE inDocument6 pagesExercise:: I. True or False Statements: Put TRUE in Front of The True Sentences and FALSE inIssouf BertheNo ratings yet
- 25.signal HIV Immuno DotDocument5 pages25.signal HIV Immuno DotprastacharNo ratings yet
- Medex Academy EssayDocument1 pageMedex Academy Essayapi-592597628No ratings yet
- Essentials of Prosthetics and Orthotics With Mcqs and Disability Assessment Guidelines 1st EditionDocument6 pagesEssentials of Prosthetics and Orthotics With Mcqs and Disability Assessment Guidelines 1st EditionYasir RasoolNo ratings yet
- Breaking Bad NewsDocument33 pagesBreaking Bad Newszonia kilashNo ratings yet
- Nutrition SurveyDocument18 pagesNutrition SurveyMogesNo ratings yet
- Systems-Heart Dissection Lab - Answer KeyDocument1 pageSystems-Heart Dissection Lab - Answer KeyGiorde PasambaNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Bipolar DisorderDocument4 pagesDissertation Bipolar DisorderWhereCanIFindSomeoneToWriteMyPaperSingapore100% (1)
- Localized Dental Abrasion Caused by An Unusually Vicious Habit: Cases Report and Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesLocalized Dental Abrasion Caused by An Unusually Vicious Habit: Cases Report and Literature ReviewTheodora ComanNo ratings yet
- Form Pre Job MeetingDocument2 pagesForm Pre Job Meetingrian1099No ratings yet
- Hematology Blood CollectionDocument3 pagesHematology Blood CollectioncassseeeyyyNo ratings yet
- Health Trends, Issues, and Concerns (Document12 pagesHealth Trends, Issues, and Concerns (Trisha PaclebNo ratings yet
- Ark DownlodDocument39 pagesArk DownlodvkNo ratings yet
- What Is Tummy Time: Is It Necessary For Newborns?: by Joyce Miller, BSC, DC, PHD, and Sharon Vallone, DC, FiccpDocument3 pagesWhat Is Tummy Time: Is It Necessary For Newborns?: by Joyce Miller, BSC, DC, PHD, and Sharon Vallone, DC, FiccpzikmonNo ratings yet
- 1088 in Vitro & in Vivo Evaluation of Dosage Forms - USP 36 PDFDocument10 pages1088 in Vitro & in Vivo Evaluation of Dosage Forms - USP 36 PDFKarlaBadongNo ratings yet
- FINAL DRUG REGISTRATION For Barbados - PpsDocument27 pagesFINAL DRUG REGISTRATION For Barbados - PpsjohnGeberNo ratings yet
Vancomycin Adult
Vancomycin Adult
Uploaded by
Giridhar YadavOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vancomycin Adult
Vancomycin Adult
Uploaded by
Giridhar YadavCopyright:
Available Formats
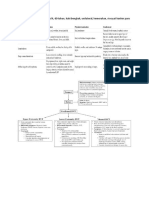
VANCOMYCIN NOMOGRAM FOR ADULT PATIENTS:
GOAL AUC24 400-600
Loading dose (LD): Consider loading dose in morbidly obese patients >125 kg that have stable renal function with clearance above
30 ml/min. Consider loading in patients with documented severe or complicated MRSA infections. Initiation of maintenance dose
should begin at next dosing interval.
• 50-64 kg: 1,250 mg x1, then maintenance schedule as provided below.
• 65-79 kg: 1,500 mg x1, then maintenance schedule as provided below.
• 80-99 kg: 1,750 mg x1, then maintenance schedule as provided below.
• ≥100 kg: 2,000 mg x1, then maintenance schedule as provided below.
Maintenance dose (MD): Based on estimated creatinine clearance and actual body weight.
<25, AKI,
25-34 35-44 45-54 55-64 65-74 75-84 85-94 >95
PD
(mL/min) (mL/min) (mL/min) (mL/min) (mL/min) (mL/min) (mL/min) (mL/min)
(mL/min)
50 kg 500 q24 500 q24 750 q24 750 q24 1000 q24 750 q12 750 q12 750 q12
55 kg 10-15 500 q24 750 q24 750 q24 1000 q24 1000 q24 750 q12 750 q12 750 q8
60 kg mg/kg x1 750 q24 750 q24 750 q24 1000 q24 750 q12 750 q12 750 q12 750 q8
65 kg dose 750 q24 750 q24 1000 q24 750 q12 750 q12 1000 q12 750 q8 750 q8
(rounded to
70 kg 1000 q24 1000 q24 1000 q24 750 q12 1000 q12 1000 q12 750 q8 750 q8
nearest 250
75 kg mg, max 1000 q24 1000 q24 1000 q24 750 q12 1000 q12 1000 q12 1000 q12 750 q8
80 kg dose of 1000 q24 1000 q24 1000 q24 1000 q12 1000 q12 1000 q12 1000 q12 1000 q8
85 kg 1500 mg) 1000 q24 1000 q24 1000 q24 1000 q12 1000 q12 1000 q12 1000 q12 1000 q8
90 kg 1000 q24 1000 q24 1250 q24 1000 q12 1000 q12 1000 q12 1000 q8 1000 q8
95 kg See below 1000 q24 1000 q24 1250 q24 1000 q12 1000 q12 1000 q12 1000 q8 1000 q8
100 kg for dosing 1000 q24 1250 q24 1250 q24 1000 q12 1250 q12 1250 q12 1000 q8 1000 q8
105 kg frequency 1250 q24 1250 q24 1250 q24 1000 q12 1250 q12 1250 q12 1000 q8 1000 q8
and
110 kg 1250 q24 1250 q24 1000 q12 1000 q12 1250 q12 1250 q12 1000 q8 1250 q8
monitoring
115 kg * 1250 q24 1250 q24 1000 q12 1000 q12 1250 q12 1000 q8 1000 q8 1250 q8
120 kg 1250 q24 1250 q24 1250 q12 1250 q12 1250 q12 1000 q8 1000 q8 1250 q8
≥125 kg 1250 q24 1250 q24 1250 q12 1250 q12 1250 q12 1000 q8 1000 q8 1250 q8
* IHD: administer 10-15 mg/kg (max: 1500 mg) after each HD session
*CRRT: administer 10-15 mg/kg (max: 1500 mg) every 24 hours
Initiating Vancomycin Therapy
1. If patient recently received vancomycin, review the previous regimen and patient information when determining an
appropriate current regimen. Consider rounding the nomogram dose up or down based on patient specific factors that have
significant impact on vancomycin distribution or clearance (e.g., pregnancy, severe trauma, ascites, extensive fluid boluses,
etc.). Please reduce total daily vancomycin dose by approximately 30% when treating patients with uncompensated
cirrhosis.
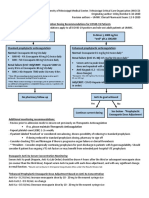
Monitoring within 72 hours of starting vancomycin:
1. Vancomycin levels should be unnecessary if therapy not anticipated to exceed 72 hours.
2. Do not check vancomycin concentrations within the first 72 hours except in the following situations:
Clinical Situation Monitoring Recommendation
Approximately 90% of patients will have vancomycin discontinued within 48-72 hours and most patients do not require levels
Documented gram positive infection requiring • Obtain 2 vancomycin levels at steady state (e.g., around 4th dose) and
vancomycin calculate AUC, and adjust dose to achieve goal AUC of 400-600
Septic shock or ECCMO • Avoid obtaining vanco level during infusion or within 1 hour after
completion of infusion
Weight >150 kg
•
Significant acute changes in renal function, • Obtain a vancomycin level and dose per level
AKI, or CrCl <25 mL/min. • Monitor random levels in patients and re-dose when level <15 mcg/mL
3. AUC is the preferred method of vancomycin monitoring. Trough-based monitoring should not be routinely used. Goal AUC
is 400-600 regardless of MIC and should not be adjusted for MICs less than or equal to 1.
Monitoring after 72 hours of starting vancomycin:
1. Use the following table to guide monitoring of vancomycin based on the patient’s clinical status:
Clinical Situation Monitoring Recommendation
Patients with stable renal function (including • Obtain 2 vancomycin levels at steady state and calculate AUC to achieve
patients with CKD and receiving CRRT) goal AUC of 400-600
• Avoid obtaining vanco level during infusion or within 1 hour after
completion of infusion
• Document individualized trough range that corresponds to AUC of 400-600
for that patient
Patients on conventional dialysis • Check pre-HD level (preferred for floor patients) or 3-hr post-HD level
(preferred for ICU patients)
• Target pre-HD levels of 15-20 mcg/mL, or post-HD level of 10-15 mcg/mL
Patients on peritoneal dialysis • Obtained random level 3-5 days after vancomycin administration
• Target level of 10-15 mcg/mL, and re-dose as necessary
Patients who have fluctuating fluid and/or • Use clinical judgement to determine monitoring strategy
renal status • It is reasonable to perform AUC or trough based monitoring. However, the
instability of renal clearance or volume of distribution should be taken into
account when evaluating levels and subsequent dosing.
Patient on IV vancomycin for post-operative • Target trough goal of 10-15 mcg/mL
prophylaxis
2. Consider ID consult in patients with confirmed MRSA infection who do not improve on vancomycin. ID consult should be
ordered for all patients with MRSA bacteremia.
3. Refer to the following table for recommendations on frequency of ordering vancomycin levels and serum creatinine:
Clinical Situation Monitoring Recommendation
Subsequent levels should be drawn every 2-7 days, and serum creatinine should be monitored at least every 48 hours during
entire course of vancomycin therapy. Avoid evening and overnight levels if clinically stable
Patients with changing fluid status or renal • Obtain levels every 2-3 days
function • Monitor 2 vancomycin levels to facilitate AUC calculation, when possible
• In patients receiving one-time doses (i.e., dosing by level), monitor random
levels and re-dose when level <15 mcg/mL
Patients with stable fluid status and renal • Obtain levels every 5-7 days, after initial level(s) are therapeutic
function requiring long-term therapy • Once a patient is on a stable dose with an AUC between 400 and 600,
monitoring of vancomycin troughs may be acceptable in patients with
stable fluid status and renal function
4. Red Man’s Syndrome is the most common vancomycin reaction, characterized by flushing, redness of the trunk and itching
during or shortly after the infusion. Treatment should include prolonging the infusion time (to 3-4 hours). Could also
consider diphenhydramine.
Michigan Medicine AUC Calculator:
https://www.med.umich.edu/asp/misc/UMich_PK_Calculator.xlsx
Antimicrobial Subcommittee Approval: 10/2021 Originated: Unknown
P&T Approval: 11/2021 Last Revised: 11/2021
Revision History:
03/21: Adjusted loading dose recommendations, added comment on cirrhosis, added post-operative prophylaxis goals
11/21: Adjusted level timing recommendations
The recommendations in this guide are meant to serve as treatment guidelines for use at Michigan Medicine facilities. If you are an individual experiencing a medical
emergency, call 911 immediately. These guidelines should not replace a provider’s professional medical advice based on clinical judgment, or be used in lieu of an
Infectious Diseases consultation when necessary. As a result of ongoing research, practice guidelines may from time to time change. The authors of these guidelines
have made all attempts to ensure the accuracy based on current information, however, due to ongoing research, users of these guidelines are strongly encouraged to
confirm the information contained within them through an independent source.
If obtained from a source other than med.umich.edu/asp, please visit the webpage for the most up-to-date document.
Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Smoke ABSORBER MachineeDocument8 pagesSmoke ABSORBER MachineeNicole Ramos20% (5)
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingFrom EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo ratings yet
- Micormedex NeoFax Essentials 2014Document8 pagesMicormedex NeoFax Essentials 2014Andreia HirtNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin Dosing Guidelines Adults 2018Document7 pagesVancomycin Dosing Guidelines Adults 2018gabriellaNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin Dosing and Monitoring in AdultsDocument1 pageVancomycin Dosing and Monitoring in AdultsjulialeoNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Vancomycin Use in Adults - 2017Document4 pagesIntravenous Vancomycin Use in Adults - 2017Angy KarakostaNo ratings yet
- Adult Vancomycin Dosing Guidelines DefinitionsDocument2 pagesAdult Vancomycin Dosing Guidelines DefinitionsPhạm DuyênNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guideline For Vancomycin Prescribing and Therapeutic Drug MonitoringDocument11 pagesClinical Guideline For Vancomycin Prescribing and Therapeutic Drug MonitoringFate ChanNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin MylaninfDocument13 pagesVancomycin MylaninfAmanuel GirmayeNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin Nephrology Preferred Dosing StrategyDocument2 pagesVancomycin Nephrology Preferred Dosing StrategyEster Elisabeth WoworNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside & VancomycinDocument10 pagesAminoglycoside & VancomycinKhor Chin PooNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin: Group 5 R.M 2Document31 pagesVancomycin: Group 5 R.M 2vi_wiviaNo ratings yet
- VancoDosingCalculator UCSF 2020 0Document14 pagesVancoDosingCalculator UCSF 2020 0Saul RuizNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Weight & CRCL - StudentDocument4 pagesAssignment-Weight & CRCL - StudentpinkhasovdNo ratings yet
- Vriii PresentationDocument29 pagesVriii Presentationsundance127No ratings yet
- Stanford Hospital & Clinics Antimicrobial Dosing Reference Guide 2013Document3 pagesStanford Hospital & Clinics Antimicrobial Dosing Reference Guide 2013SANCHOSKYNo ratings yet
- Renal Replacement Therapy in Critical Care: Choice of ModeDocument15 pagesRenal Replacement Therapy in Critical Care: Choice of ModePeter AgabaNo ratings yet
- Figure 5-1Document7 pagesFigure 5-1KhaledNo ratings yet
- Ch5 VancomycinDocument14 pagesCh5 Vancomycintiba.qasem2000No ratings yet
- Vancomycin 1. Product Name 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition 3. Pharmaceutical FormDocument11 pagesVancomycin 1. Product Name 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition 3. Pharmaceutical FormVerghese GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Renal Replacement Therapy in Critical Care: Choice of ModeDocument15 pagesRenal Replacement Therapy in Critical Care: Choice of ModeJelena Obrenovic StankovicNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Dosing Guidelines For Renal ImpairmentDocument6 pagesAntibiotic Dosing Guidelines For Renal ImpairmentvitauxianaNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin-Dosing-and-Monitoring-Neonatal.-and-PediatricsDocument5 pagesVancomycin-Dosing-and-Monitoring-Neonatal.-and-Pediatricsf2b9b25kb9No ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis LK, 60 Tahun, Kaki Bengkak, Unilateral, Kemerahan, Riwayat Kanker ParuDocument9 pagesDifferential Diagnosis LK, 60 Tahun, Kaki Bengkak, Unilateral, Kemerahan, Riwayat Kanker ParuArbiantoni 17No ratings yet
- Vancomycin Dosing RecommendationsDocument2 pagesVancomycin Dosing RecommendationsStacey WoodsNo ratings yet
- Most of Cardiac Care Unit (C.C.U) DrugsDocument57 pagesMost of Cardiac Care Unit (C.C.U) DrugsOsama OmarNo ratings yet
- BWH Hyperglycemia GuidelinesDocument7 pagesBWH Hyperglycemia Guidelinespmahesh107100% (1)
- Nursing Orientation Program Intravenous TherapyDocument45 pagesNursing Orientation Program Intravenous TherapyMarianne LayloNo ratings yet
- RENAL DosingDocument8 pagesRENAL Dosingsumayyah995No ratings yet
- SHC Vancomycin Dosing GuideDocument8 pagesSHC Vancomycin Dosing GuidePitchya WangmeesriNo ratings yet
- ClexaneinjDocument25 pagesClexaneinjBobeico TatianaNo ratings yet
- Seasonal Influenza Therapeutic ProtocolDocument4 pagesSeasonal Influenza Therapeutic ProtocolSaleem HamilahNo ratings yet
- SPC 350 0715-03Document19 pagesSPC 350 0715-03lydia kadaNo ratings yet
- VBMC Heparin Protocol FINAL May2004Document3 pagesVBMC Heparin Protocol FINAL May2004Pharmacy OneSource100% (1)
- Vancomycin Protocol: A Protocol To Guide The Dosing and Monitoring of Vancomycin in AdultsDocument5 pagesVancomycin Protocol: A Protocol To Guide The Dosing and Monitoring of Vancomycin in AdultsSaadia MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Problems: 5: VancomycinDocument4 pagesProblems: 5: VancomycinSaul RuizNo ratings yet
- VancomycinDocument5 pagesVancomycintharani1005No ratings yet
- SHC Vancomycin Dosing GuideDocument10 pagesSHC Vancomycin Dosing GuideAlan SmithNo ratings yet
- Enoxaparin Sodium Injection I.PDocument15 pagesEnoxaparin Sodium Injection I.PSuhailansariNo ratings yet
- New Oral Anticoagulants Guidelines: Kai YapDocument23 pagesNew Oral Anticoagulants Guidelines: Kai YapMuhammad Reza FirdausNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation Dosing Recommendations COVID 19 PatientsDocument1 pageAnticoagulation Dosing Recommendations COVID 19 PatientsChalwe HowardNo ratings yet
- Guideline: Antibiotic Drug Monitoring: Aminoglycosides and GlycopeptidesDocument8 pagesGuideline: Antibiotic Drug Monitoring: Aminoglycosides and GlycopeptidesKenRodulfReyesVillaruelNo ratings yet
- Package Insert - NovoSevenRTDocument31 pagesPackage Insert - NovoSevenRTVenu YasarapuNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin - Peds DoseDocument4 pagesVancomycin - Peds DoseIrina UngureanuNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation Protocol For PostDocument8 pagesAnticoagulation Protocol For PostMohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- NICU Drugs GuideDocument49 pagesNICU Drugs GuideArhanNo ratings yet
- Cefepime Kabi DatasheetDocument16 pagesCefepime Kabi Datasheetتوفيق باعبادNo ratings yet
- Pro TaminaDocument2 pagesPro TaminaArcenciel26No ratings yet
- Peramivir Q and A - Updated 11 - 19 - 09 Final CleanDocument10 pagesPeramivir Q and A - Updated 11 - 19 - 09 Final Cleanbenny christantoNo ratings yet
- SHC Vancomycin Dosing GuideDocument9 pagesSHC Vancomycin Dosing GuideDanielVillaNo ratings yet
- New Zealand Data Sheet June 2017Document27 pagesNew Zealand Data Sheet June 2017Eyda JamilNo ratings yet
- Renal PharmacologyDocument52 pagesRenal Pharmacologyashraf0% (1)
- SQC ABx Guidelines 2-21-2011 PDFDocument2 pagesSQC ABx Guidelines 2-21-2011 PDFMinh SteveNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Route of Administration (IV To PO) Therapeutic ConversionDocument1 pageAntimicrobial Route of Administration (IV To PO) Therapeutic ConversiondoodrillNo ratings yet
- Management of Anesthesia: Diabetes MellitusDocument29 pagesManagement of Anesthesia: Diabetes MellitusHari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Vancomicin Guidelines PICUDocument2 pagesVancomicin Guidelines PICUAnonymous 6iwMFwNo ratings yet
- Aciclovir (Zovirax I.V)Document11 pagesAciclovir (Zovirax I.V)asdwasdNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulant Pocket GuideDocument8 pagesAnticoagulant Pocket GuideDrew John Minardi100% (2)
- Stanford Health Care Antimicrobial Dosing Reference GuideDocument7 pagesStanford Health Care Antimicrobial Dosing Reference GuideKarl Martin PinedaNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsFrom EverandDimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsNo ratings yet
- Papich, Mark G. - Saunders Handbook of Veterinary Drugs - Bisoprolol Fumarate (2016, Elsevier) (10.1016 - B978-0-323-24485-5.00107-8) - Libgen - LiDocument2 pagesPapich, Mark G. - Saunders Handbook of Veterinary Drugs - Bisoprolol Fumarate (2016, Elsevier) (10.1016 - B978-0-323-24485-5.00107-8) - Libgen - LibernadethNo ratings yet
- Mental Health EssayDocument5 pagesMental Health Essaycameronbullard2000No ratings yet
- Promoting Mental Health Awareness and Resilience in The Philippine National PoliceDocument2 pagesPromoting Mental Health Awareness and Resilience in The Philippine National PoliceSftts TagapagsanayNo ratings yet
- Ohs-Info Sheet No. 4Document11 pagesOhs-Info Sheet No. 4Ferlyn AboyNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Health & Disease: K.Sagar Asso ProfessorDocument86 pagesConcepts in Health & Disease: K.Sagar Asso Professorkuruvagadda sagarNo ratings yet
- Use of The Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) As A Screening Tool in Prisons: Results of A Preliminary StudyDocument5 pagesUse of The Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) As A Screening Tool in Prisons: Results of A Preliminary StudyRafael MartinsNo ratings yet
- SPECT ScanDocument2 pagesSPECT ScandhruvaNo ratings yet
- Clean Water For AllDocument8 pagesClean Water For AllArgie Joy Marie AmpolNo ratings yet
- Literature Review 1Document7 pagesLiterature Review 1api-743809775No ratings yet
- Euac 125Document23 pagesEuac 125Nicoletta OrphanouNo ratings yet
- Health Grade 10 2nd QTR M4Document5 pagesHealth Grade 10 2nd QTR M4MrLonely Drake Deniel SanchezNo ratings yet
- A Qualitative Study: Campus Bullying in The Senior High SchoolDocument14 pagesA Qualitative Study: Campus Bullying in The Senior High SchoolHouston IbañezNo ratings yet
- TFN PrelimDocument9 pagesTFN PrelimElla ArnocoNo ratings yet
- Exercise:: I. True or False Statements: Put TRUE in Front of The True Sentences and FALSE inDocument6 pagesExercise:: I. True or False Statements: Put TRUE in Front of The True Sentences and FALSE inIssouf BertheNo ratings yet
- 25.signal HIV Immuno DotDocument5 pages25.signal HIV Immuno DotprastacharNo ratings yet
- Medex Academy EssayDocument1 pageMedex Academy Essayapi-592597628No ratings yet
- Essentials of Prosthetics and Orthotics With Mcqs and Disability Assessment Guidelines 1st EditionDocument6 pagesEssentials of Prosthetics and Orthotics With Mcqs and Disability Assessment Guidelines 1st EditionYasir RasoolNo ratings yet
- Breaking Bad NewsDocument33 pagesBreaking Bad Newszonia kilashNo ratings yet
- Nutrition SurveyDocument18 pagesNutrition SurveyMogesNo ratings yet
- Systems-Heart Dissection Lab - Answer KeyDocument1 pageSystems-Heart Dissection Lab - Answer KeyGiorde PasambaNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Bipolar DisorderDocument4 pagesDissertation Bipolar DisorderWhereCanIFindSomeoneToWriteMyPaperSingapore100% (1)
- Localized Dental Abrasion Caused by An Unusually Vicious Habit: Cases Report and Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesLocalized Dental Abrasion Caused by An Unusually Vicious Habit: Cases Report and Literature ReviewTheodora ComanNo ratings yet
- Form Pre Job MeetingDocument2 pagesForm Pre Job Meetingrian1099No ratings yet
- Hematology Blood CollectionDocument3 pagesHematology Blood CollectioncassseeeyyyNo ratings yet
- Health Trends, Issues, and Concerns (Document12 pagesHealth Trends, Issues, and Concerns (Trisha PaclebNo ratings yet
- Ark DownlodDocument39 pagesArk DownlodvkNo ratings yet
- What Is Tummy Time: Is It Necessary For Newborns?: by Joyce Miller, BSC, DC, PHD, and Sharon Vallone, DC, FiccpDocument3 pagesWhat Is Tummy Time: Is It Necessary For Newborns?: by Joyce Miller, BSC, DC, PHD, and Sharon Vallone, DC, FiccpzikmonNo ratings yet
- 1088 in Vitro & in Vivo Evaluation of Dosage Forms - USP 36 PDFDocument10 pages1088 in Vitro & in Vivo Evaluation of Dosage Forms - USP 36 PDFKarlaBadongNo ratings yet
- FINAL DRUG REGISTRATION For Barbados - PpsDocument27 pagesFINAL DRUG REGISTRATION For Barbados - PpsjohnGeberNo ratings yet