Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules
Uploaded by
Hocine LemlikchiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Jankovic, J. 2001 Tourette's Syndrome. The New England Journal of Medicine 346.16 Pp.1184-1192Document9 pagesJankovic, J. 2001 Tourette's Syndrome. The New England Journal of Medicine 346.16 Pp.1184-1192Jesús Manuel CuevasNo ratings yet
- The Souled StoreDocument8 pagesThe Souled StoreRani DispotaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument8 pagesReported SpeechMAGDALENA MELANIA GHERGHENo ratings yet
- Part VI - Chapter 5 - Fundamentals of Design - Part 1Document176 pagesPart VI - Chapter 5 - Fundamentals of Design - Part 1Pedro Gomes100% (2)
- Reported Speech 1Document3 pagesReported Speech 1Luigi OliNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech RulesDocument14 pagesReported Speech RulessigiryaNo ratings yet
- 18 Reported SpeechDocument4 pages18 Reported SpeechAmanda AbbottNo ratings yet
- Indirect and Direct SpeechDocument4 pagesIndirect and Direct SpeechCharles AndriantoNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Rules: StatementsDocument6 pagesReported Speech Rules: Statementsmnj_gautamNo ratings yet
- Indirect QuestionsDocument15 pagesIndirect Questionsfounè diassanaNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect Speech (2 Mei 2014)Document12 pagesDirect Indirect Speech (2 Mei 2014)A_IntaanNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech: StatementsDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech: StatementsЛеся ЧабаненкоNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech RulesDocument4 pagesReported Speech RulesShaliza MardianaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech.Document4 pagesReported Speech.reebot 666No ratings yet
- Indirect (Reported) Speech in StatementsDocument4 pagesIndirect (Reported) Speech in Statementssenthilr78No ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechIrina MargineanuNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechNoeNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechaphrodisyNo ratings yet
- English - Reported Speech Worksheet Grade 10/11Document10 pagesEnglish - Reported Speech Worksheet Grade 10/11senuthmi dihansaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: English Grammar RulesDocument4 pagesReported Speech: English Grammar RulesCidinha Pinto CarneiroNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechalmurcNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech For FceDocument3 pagesReported Speech For FceIrene Carrion PerezNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported Speechắgdv NguyenNo ratings yet
- Complete These Sentences in The Reported Speech.: Exercise 1Document7 pagesComplete These Sentences in The Reported Speech.: Exercise 1Uyen ChauNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesReported SpeechCharanya GopalNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech RulesDocument2 pagesReported Speech RulescvsosornoNo ratings yet
- 01 Reported Speech 1Document4 pages01 Reported Speech 1katia.khimaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported SpeechChafi DrissNo ratings yet
- 1 Reported SpeechDocument2 pages1 Reported SpeechGianina MihăicăNo ratings yet
- Fce Reported Speech Grammar SummaryDocument4 pagesFce Reported Speech Grammar SummaryMiriam MyriamNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesReported Speechsogharb-1No ratings yet
- TensesDocument53 pagesTensesaichaaitihia2204No ratings yet
- Quá Khứ Đơn vs Quá Khứ Tiếp DiễnDocument14 pagesQuá Khứ Đơn vs Quá Khứ Tiếp Diễnlinh taNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument102 pagesGrammarWad__6674No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Date Teacher Class Number of Students Textbook Lesson Type of Lesson Timing: Methods Materials AimsDocument7 pagesLesson Plan: Date Teacher Class Number of Students Textbook Lesson Type of Lesson Timing: Methods Materials AimsAlexandra MileaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Date Teacher Class Number of Students Textbook Lesson Type of Lesson Timing: Methods Materials AimsDocument7 pagesLesson Plan: Date Teacher Class Number of Students Textbook Lesson Type of Lesson Timing: Methods Materials AimsMagdaBaciuNo ratings yet
- 4 - The - Passive - Voice-Teorie Si ExercitiiDocument9 pages4 - The - Passive - Voice-Teorie Si ExercitiiRoxana Moraru ManicaNo ratings yet
- Revision Grammar 1Document2 pagesRevision Grammar 1kingNo ratings yet
- PastDocument7 pagesPastgeo kemoNo ratings yet
- Estilo Indirecto - TeoríaDocument3 pagesEstilo Indirecto - TeoríaSergio ViñalsNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech PDFDocument3 pagesReported Speech PDFboulaichNo ratings yet
- Future Tense - Futuro I Will Help You. (Eu Ajudei Você.)Document3 pagesFuture Tense - Futuro I Will Help You. (Eu Ajudei Você.)WeltonOSNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechboulouahmouadNo ratings yet
- Sympathy ExpressionDocument7 pagesSympathy ExpressionNindhita Dyah SNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Tests Warmers Coolers - 30453Document1 pageReported Speech Tests Warmers Coolers - 30453English with JamalNo ratings yet
- TP. 2 REVISION PTE SIMPLE - Grammar ExcercisesDocument3 pagesTP. 2 REVISION PTE SIMPLE - Grammar ExcercisesgabyNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument3 pagesPassive VoicePeterNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechamorometeNo ratings yet
- Present SimpleDocument4 pagesPresent SimpleMaddy MariaNo ratings yet
- Modul 4,5,6 InggrisDocument22 pagesModul 4,5,6 InggrisRimaniar DwitaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechSudarshani AyomiNo ratings yet
- English Iv Say and Tell: CICLO 2013-III Módulo:IDocument23 pagesEnglish Iv Say and Tell: CICLO 2013-III Módulo:IAbel QuispeNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR UNIT 2 - Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesGRAMMAR UNIT 2 - Reported SpeechJordan Hernandez VidalNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech PDFDocument2 pagesReported Speech PDFHilde Reis Junior0% (1)
- Revision 4Document9 pagesRevision 4Khedr MohammedNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Ve Cau Tuong Thuat Co Dap An HayDocument12 pagesBai Tap Ve Cau Tuong Thuat Co Dap An HayBích ThuỷNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument11 pagesReported SpeechHongminhNo ratings yet
- Infinitive and GerundDocument7 pagesInfinitive and GerundClases inglés onlineNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech - InglésDocument13 pagesReported Speech - Inglésbrandolin264No ratings yet
- Learn Spanish 26 Day Challenge: For Beginners And Intermediate Includes Grammar Rules, Exercises, Conversation, and Dialogues: Learn Spanish, #2From EverandLearn Spanish 26 Day Challenge: For Beginners And Intermediate Includes Grammar Rules, Exercises, Conversation, and Dialogues: Learn Spanish, #2No ratings yet
- Bac Sample AnswersDocument2 pagesBac Sample AnswersHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term Exam 2023 Junk FoodDocument2 pages2nd Term Exam 2023 Junk FoodHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument1 pageGreenhouse EffectHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- 3 RD Term ExamDocument3 pages3 RD Term ExamHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- 2 AsDocument3 pages2 AsHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- Level 1 Year Literary Stream Duration: 2 Hours Third Term Exam of EnglishDocument4 pagesLevel 1 Year Literary Stream Duration: 2 Hours Third Term Exam of EnglishHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- Vocab - Ethics - Gaps - Docx Filename - UTF-8''vocab Ethics GapsDocument1 pageVocab - Ethics - Gaps - Docx Filename - UTF-8''vocab Ethics GapsHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences 1Document1 pageConditional Sentences 1Hocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- Child LabourDocument1 pageChild LabourHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- Childhood ObesiDocument2 pagesChildhood ObesiHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- Deep Cement Mixing - Tan - etal-2002-SingaporeMarineClaysDocument12 pagesDeep Cement Mixing - Tan - etal-2002-SingaporeMarineClaysmmm_1978No ratings yet
- Nitish-ResumeDocument1 pageNitish-Resumeshariq khanNo ratings yet
- Kundalini YogaDocument153 pagesKundalini Yogaprajjwal singhNo ratings yet
- Xdr2 Memory ArchitectureDocument2 pagesXdr2 Memory ArchitectureElizabethNo ratings yet
- HCM Tentative Timetable CFA Level 1 For May22 ExamDocument1 pageHCM Tentative Timetable CFA Level 1 For May22 ExamKato AkikoNo ratings yet
- PERDEV 3rd Summative TestDocument2 pagesPERDEV 3rd Summative TestPrincess Maiva ValleNo ratings yet
- Villains & Vigilantes Character TemplatesDocument9 pagesVillains & Vigilantes Character TemplatesLink PelcherNo ratings yet
- Career Astrology Analysis As Per Indian Vedic Astrology OmAstrologycomDocument5 pagesCareer Astrology Analysis As Per Indian Vedic Astrology OmAstrologycomSubramanya RaoNo ratings yet
- HVT DS HAEFELY 9231-Capacitor V2206Document4 pagesHVT DS HAEFELY 9231-Capacitor V2206sunilNo ratings yet
- RegressionDocument5 pagesRegressionharpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Giftings TestDocument11 pagesSpiritual Giftings TestKyl M. SrrcNo ratings yet
- ICT-Pedagogy Integration in MathematicsDocument11 pagesICT-Pedagogy Integration in MathematicsKaren Faye LagundayNo ratings yet
- Math - English A Four-Week Recovery Program in Schools Grade 3Document43 pagesMath - English A Four-Week Recovery Program in Schools Grade 3Norma Najem100% (1)
- The Myth of Quantum ConsciousnessDocument10 pagesThe Myth of Quantum ConsciousnessHenry McQualeNo ratings yet
- ByteBlaster InstructionsDocument11 pagesByteBlaster InstructionsildevanNo ratings yet
- WF D02A Energy MeterDocument10 pagesWF D02A Energy MeterfioNo ratings yet
- Tejgyan FoundationDocument2 pagesTejgyan Foundationpradip2190No ratings yet
- Introduction To Information & Communications Technology Introduction ToDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Information & Communications Technology Introduction ToKathleen BorjaNo ratings yet
- Standard Specification: LPG Loading / Unloading ArmDocument19 pagesStandard Specification: LPG Loading / Unloading ArmANIL KUMAR100% (1)
- Service Quality Analysis of SBIDocument38 pagesService Quality Analysis of SBIAkhil BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Efl Teachers Teaching Style On Students Academic Performance and Satisfaction: An Evidence From Public Sector Universities of KarachiDocument27 pagesImpact of Efl Teachers Teaching Style On Students Academic Performance and Satisfaction: An Evidence From Public Sector Universities of KarachiJIECEL FLORESNo ratings yet
- Hollow Fiber Membrane ContactorsDocument47 pagesHollow Fiber Membrane ContactorsEvelyn AntunesNo ratings yet
- 2024 Second-Year WIL Placement LetterDocument3 pages2024 Second-Year WIL Placement LetterleticiaxolileNo ratings yet
- Ccs Assignment 2Document7 pagesCcs Assignment 2VINIKSHA SHREE A CSE studentNo ratings yet
- 29a Catalogo enDocument459 pages29a Catalogo enAndres Felipe GalloNo ratings yet
- Ponce Final Paper - Luis Ramirez-With-Cover-Page-V2Document27 pagesPonce Final Paper - Luis Ramirez-With-Cover-Page-V2Roswitha Klassen0% (1)
- Standards For Mobile Health-Related AppsDocument9 pagesStandards For Mobile Health-Related Appsharsono harsonoNo ratings yet
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules
Uploaded by
Hocine LemlikchiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules
Uploaded by
Hocine LemlikchiCopyright:
Available Formats
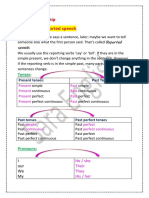
Direct and Reported speech rules
If we want to say what other people said, thought or felt, we can use the direct and indirect speech (reported
speech).
The reported speech is typically introduced by verbs such as say, tell, admit, complain, explain, remind,
reply, think, hope, offer, refuse etc. in the past tense.
He said (that) he didn't want it.
She explained that she had been at the seaside.
If these verbs are in the past tense, we change the following:
A) Verb tenses: We change the tenses in the following way:
Present - past
"I never understand you," she told me. - She told me ........................................................................................
"We are doing exercises," he explained. - He explained that ............................................................................
Present perfect - past perfect
"I have broken the window," he admitted. - He admitted that ...........................................................................
"I have been waiting since the morning," he complained. - He complained that ...............................................
Past - past perfect
"She went to Rome," I thought. - I thought that ..................................................................................................
"He was thinking of buying a new car," she said. - She said .............................................................................
Will - would.
I will come on Sunday," he reminded me. - He reminded me that he .................... ............................................
Notes:
1. May becomes might.
"I may write to him," she promised. - She promised that ............................................................................
Can/ could, must, have to/ had to,
The verb forms remain the same in the following cases:
If we use the past perfect tense.
Eva: "I had never seen him." - Eva claimed that she had never seen him.
If the reporting verb is in the present tense.
Bill: "I am enjoying my holiday." - Bill says he is enjoying his holiday.
Sandy: "I will never go to work." - Sandy says she will never go to work.
When we report something that is still true.
Dan: "Asia is the largest continent." - Dan said Asia is the largest continent.
Emma: "People in Africa are starving." - Emma said people in Africa are starving.
With modal verbs would, might, could, should, ought to, used to.
George: "I would try it." - George said he would try it.
Mimi: "I might come." - Mimi said she might come.
Steve: "I could fail." - Steve said he could fail.
Linda: "He should/ought to stay in bed." - Linda said he should/ought to stay in bed.
Mel: "I used to have a car." - Mel said he used to have a car.
B) Pronouns
We have to change the pronouns to keep the same meaning of a sentence.
"We are the best students," he said. - He said .........................................................
"They called us," he said. - He said ....................................................................
"I can lend you my car," he said. - He said ...................................................
This and these are usually replaced by that and those.
"They will finish it this year," he said. - He said .........................................................................................
"We want these flowers," they said. - They said .........................................................................................
C) Time and place
The time expressions change as follows.
today - that day, tomorrow - the next day/the following day, the day after tomorrow - in two days' time,
yesterday - the day before, the day before yesterday - two days before, next week/month - the following
week/month, last week/month - the previous week/month, a year ago - a year before/the previous year
Bill: "She will leave tomorrow." - Bill said ...........................................................
Sam: "She arrived last week." - Sam said .............................................................
Julie: "He moved a year ago." - Julie said ..........................................................
Here usually becomes there.
At school: "I'll be here at 10 o'clock," he said. - He said ..............................................................
Reported questions
In yes/no questions we use if or whether in questions. If is more common and whether is more formal.
"Will you come?" she asked me. - She asked me if/whether I would come.
"Did he marry Sue?" she said. - She wondered ............................................................................
Reported commands, requests and advice
The commands, requests and advice mostly have the same form in English: verb + object + infinitive
(advise, ask, beg, forbid, order, persuade, recommend, tell, urge, warn etc.).
"Get up!" he said. - He told me to get up.
"Please, revise for the test," he said. - He urged me .........................................................
Negative commands, requests and advice are made by verb + object + not + infinitive.
"Don't hesitate," he said. - He persuaded me not to hesitate.
"Don't smoke," the doctor warned my father. - The doctor warned my father ..........................................
Tell can introduce statements, commands, requests or advice.
Commands, requests or advice with tell
"Leave the room," he told John. - He told John ................................................................
"Don't give up," the teacher told her students. - The teacher told the students ......................................
Similarly ask is used in reported questions, commands, requests or advice in different forms.
Questions with ask
"Will you make coffee?" he said. - He asked me ......................................................................
You might also like
- Jankovic, J. 2001 Tourette's Syndrome. The New England Journal of Medicine 346.16 Pp.1184-1192Document9 pagesJankovic, J. 2001 Tourette's Syndrome. The New England Journal of Medicine 346.16 Pp.1184-1192Jesús Manuel CuevasNo ratings yet
- The Souled StoreDocument8 pagesThe Souled StoreRani DispotaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument8 pagesReported SpeechMAGDALENA MELANIA GHERGHENo ratings yet
- Part VI - Chapter 5 - Fundamentals of Design - Part 1Document176 pagesPart VI - Chapter 5 - Fundamentals of Design - Part 1Pedro Gomes100% (2)
- Reported Speech 1Document3 pagesReported Speech 1Luigi OliNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech RulesDocument14 pagesReported Speech RulessigiryaNo ratings yet
- 18 Reported SpeechDocument4 pages18 Reported SpeechAmanda AbbottNo ratings yet
- Indirect and Direct SpeechDocument4 pagesIndirect and Direct SpeechCharles AndriantoNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Rules: StatementsDocument6 pagesReported Speech Rules: Statementsmnj_gautamNo ratings yet
- Indirect QuestionsDocument15 pagesIndirect Questionsfounè diassanaNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect Speech (2 Mei 2014)Document12 pagesDirect Indirect Speech (2 Mei 2014)A_IntaanNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech: StatementsDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech: StatementsЛеся ЧабаненкоNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech RulesDocument4 pagesReported Speech RulesShaliza MardianaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech.Document4 pagesReported Speech.reebot 666No ratings yet
- Indirect (Reported) Speech in StatementsDocument4 pagesIndirect (Reported) Speech in Statementssenthilr78No ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechIrina MargineanuNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechNoeNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechaphrodisyNo ratings yet
- English - Reported Speech Worksheet Grade 10/11Document10 pagesEnglish - Reported Speech Worksheet Grade 10/11senuthmi dihansaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: English Grammar RulesDocument4 pagesReported Speech: English Grammar RulesCidinha Pinto CarneiroNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechalmurcNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech For FceDocument3 pagesReported Speech For FceIrene Carrion PerezNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported Speechắgdv NguyenNo ratings yet
- Complete These Sentences in The Reported Speech.: Exercise 1Document7 pagesComplete These Sentences in The Reported Speech.: Exercise 1Uyen ChauNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesReported SpeechCharanya GopalNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech RulesDocument2 pagesReported Speech RulescvsosornoNo ratings yet
- 01 Reported Speech 1Document4 pages01 Reported Speech 1katia.khimaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported SpeechChafi DrissNo ratings yet
- 1 Reported SpeechDocument2 pages1 Reported SpeechGianina MihăicăNo ratings yet
- Fce Reported Speech Grammar SummaryDocument4 pagesFce Reported Speech Grammar SummaryMiriam MyriamNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesReported Speechsogharb-1No ratings yet
- TensesDocument53 pagesTensesaichaaitihia2204No ratings yet
- Quá Khứ Đơn vs Quá Khứ Tiếp DiễnDocument14 pagesQuá Khứ Đơn vs Quá Khứ Tiếp Diễnlinh taNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument102 pagesGrammarWad__6674No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Date Teacher Class Number of Students Textbook Lesson Type of Lesson Timing: Methods Materials AimsDocument7 pagesLesson Plan: Date Teacher Class Number of Students Textbook Lesson Type of Lesson Timing: Methods Materials AimsAlexandra MileaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Date Teacher Class Number of Students Textbook Lesson Type of Lesson Timing: Methods Materials AimsDocument7 pagesLesson Plan: Date Teacher Class Number of Students Textbook Lesson Type of Lesson Timing: Methods Materials AimsMagdaBaciuNo ratings yet
- 4 - The - Passive - Voice-Teorie Si ExercitiiDocument9 pages4 - The - Passive - Voice-Teorie Si ExercitiiRoxana Moraru ManicaNo ratings yet
- Revision Grammar 1Document2 pagesRevision Grammar 1kingNo ratings yet
- PastDocument7 pagesPastgeo kemoNo ratings yet
- Estilo Indirecto - TeoríaDocument3 pagesEstilo Indirecto - TeoríaSergio ViñalsNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech PDFDocument3 pagesReported Speech PDFboulaichNo ratings yet
- Future Tense - Futuro I Will Help You. (Eu Ajudei Você.)Document3 pagesFuture Tense - Futuro I Will Help You. (Eu Ajudei Você.)WeltonOSNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechboulouahmouadNo ratings yet
- Sympathy ExpressionDocument7 pagesSympathy ExpressionNindhita Dyah SNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Tests Warmers Coolers - 30453Document1 pageReported Speech Tests Warmers Coolers - 30453English with JamalNo ratings yet
- TP. 2 REVISION PTE SIMPLE - Grammar ExcercisesDocument3 pagesTP. 2 REVISION PTE SIMPLE - Grammar ExcercisesgabyNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument3 pagesPassive VoicePeterNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechamorometeNo ratings yet
- Present SimpleDocument4 pagesPresent SimpleMaddy MariaNo ratings yet
- Modul 4,5,6 InggrisDocument22 pagesModul 4,5,6 InggrisRimaniar DwitaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechSudarshani AyomiNo ratings yet
- English Iv Say and Tell: CICLO 2013-III Módulo:IDocument23 pagesEnglish Iv Say and Tell: CICLO 2013-III Módulo:IAbel QuispeNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR UNIT 2 - Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesGRAMMAR UNIT 2 - Reported SpeechJordan Hernandez VidalNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech PDFDocument2 pagesReported Speech PDFHilde Reis Junior0% (1)
- Revision 4Document9 pagesRevision 4Khedr MohammedNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Ve Cau Tuong Thuat Co Dap An HayDocument12 pagesBai Tap Ve Cau Tuong Thuat Co Dap An HayBích ThuỷNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument11 pagesReported SpeechHongminhNo ratings yet
- Infinitive and GerundDocument7 pagesInfinitive and GerundClases inglés onlineNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech - InglésDocument13 pagesReported Speech - Inglésbrandolin264No ratings yet
- Learn Spanish 26 Day Challenge: For Beginners And Intermediate Includes Grammar Rules, Exercises, Conversation, and Dialogues: Learn Spanish, #2From EverandLearn Spanish 26 Day Challenge: For Beginners And Intermediate Includes Grammar Rules, Exercises, Conversation, and Dialogues: Learn Spanish, #2No ratings yet
- Bac Sample AnswersDocument2 pagesBac Sample AnswersHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term Exam 2023 Junk FoodDocument2 pages2nd Term Exam 2023 Junk FoodHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument1 pageGreenhouse EffectHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- 3 RD Term ExamDocument3 pages3 RD Term ExamHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- 2 AsDocument3 pages2 AsHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- Level 1 Year Literary Stream Duration: 2 Hours Third Term Exam of EnglishDocument4 pagesLevel 1 Year Literary Stream Duration: 2 Hours Third Term Exam of EnglishHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- Vocab - Ethics - Gaps - Docx Filename - UTF-8''vocab Ethics GapsDocument1 pageVocab - Ethics - Gaps - Docx Filename - UTF-8''vocab Ethics GapsHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences 1Document1 pageConditional Sentences 1Hocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- Child LabourDocument1 pageChild LabourHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- Childhood ObesiDocument2 pagesChildhood ObesiHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentHocine LemlikchiNo ratings yet
- Deep Cement Mixing - Tan - etal-2002-SingaporeMarineClaysDocument12 pagesDeep Cement Mixing - Tan - etal-2002-SingaporeMarineClaysmmm_1978No ratings yet
- Nitish-ResumeDocument1 pageNitish-Resumeshariq khanNo ratings yet
- Kundalini YogaDocument153 pagesKundalini Yogaprajjwal singhNo ratings yet
- Xdr2 Memory ArchitectureDocument2 pagesXdr2 Memory ArchitectureElizabethNo ratings yet
- HCM Tentative Timetable CFA Level 1 For May22 ExamDocument1 pageHCM Tentative Timetable CFA Level 1 For May22 ExamKato AkikoNo ratings yet
- PERDEV 3rd Summative TestDocument2 pagesPERDEV 3rd Summative TestPrincess Maiva ValleNo ratings yet
- Villains & Vigilantes Character TemplatesDocument9 pagesVillains & Vigilantes Character TemplatesLink PelcherNo ratings yet
- Career Astrology Analysis As Per Indian Vedic Astrology OmAstrologycomDocument5 pagesCareer Astrology Analysis As Per Indian Vedic Astrology OmAstrologycomSubramanya RaoNo ratings yet
- HVT DS HAEFELY 9231-Capacitor V2206Document4 pagesHVT DS HAEFELY 9231-Capacitor V2206sunilNo ratings yet
- RegressionDocument5 pagesRegressionharpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Giftings TestDocument11 pagesSpiritual Giftings TestKyl M. SrrcNo ratings yet
- ICT-Pedagogy Integration in MathematicsDocument11 pagesICT-Pedagogy Integration in MathematicsKaren Faye LagundayNo ratings yet
- Math - English A Four-Week Recovery Program in Schools Grade 3Document43 pagesMath - English A Four-Week Recovery Program in Schools Grade 3Norma Najem100% (1)
- The Myth of Quantum ConsciousnessDocument10 pagesThe Myth of Quantum ConsciousnessHenry McQualeNo ratings yet
- ByteBlaster InstructionsDocument11 pagesByteBlaster InstructionsildevanNo ratings yet
- WF D02A Energy MeterDocument10 pagesWF D02A Energy MeterfioNo ratings yet
- Tejgyan FoundationDocument2 pagesTejgyan Foundationpradip2190No ratings yet
- Introduction To Information & Communications Technology Introduction ToDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Information & Communications Technology Introduction ToKathleen BorjaNo ratings yet
- Standard Specification: LPG Loading / Unloading ArmDocument19 pagesStandard Specification: LPG Loading / Unloading ArmANIL KUMAR100% (1)
- Service Quality Analysis of SBIDocument38 pagesService Quality Analysis of SBIAkhil BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Efl Teachers Teaching Style On Students Academic Performance and Satisfaction: An Evidence From Public Sector Universities of KarachiDocument27 pagesImpact of Efl Teachers Teaching Style On Students Academic Performance and Satisfaction: An Evidence From Public Sector Universities of KarachiJIECEL FLORESNo ratings yet
- Hollow Fiber Membrane ContactorsDocument47 pagesHollow Fiber Membrane ContactorsEvelyn AntunesNo ratings yet
- 2024 Second-Year WIL Placement LetterDocument3 pages2024 Second-Year WIL Placement LetterleticiaxolileNo ratings yet
- Ccs Assignment 2Document7 pagesCcs Assignment 2VINIKSHA SHREE A CSE studentNo ratings yet
- 29a Catalogo enDocument459 pages29a Catalogo enAndres Felipe GalloNo ratings yet
- Ponce Final Paper - Luis Ramirez-With-Cover-Page-V2Document27 pagesPonce Final Paper - Luis Ramirez-With-Cover-Page-V2Roswitha Klassen0% (1)
- Standards For Mobile Health-Related AppsDocument9 pagesStandards For Mobile Health-Related Appsharsono harsonoNo ratings yet