Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geography Notes
Geography Notes
Uploaded by
MinethegroundCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Help Your Kids With GeographyDocument259 pagesHelp Your Kids With GeographyopenfileNo ratings yet
- How Plates MoveDocument5 pagesHow Plates Movelucasjorgelindo6335No ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics and Plate BoundariesDocument35 pagesPlate Tectonics and Plate BoundariesBENJ AMINNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review in ScienceDocument2 pagesPointers To Review in SciencePj JavierNo ratings yet
- Tectonic PlatesDocument7 pagesTectonic PlatesAmit 786No ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument5 pagesPlate TectonicsAmelia KaisersinghNo ratings yet
- Tectonic PlatesDocument6 pagesTectonic PlatesSamim AkhtarNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument3 pagesScienceShairene DimaculanganNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument2 pagesScienceShairene DimaculanganNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 6 PPT Q3 - Plate Tectonics and Plate BoundariesDocument35 pagesSCIENCE 6 PPT Q3 - Plate Tectonics and Plate Boundariesmar galiaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Notes Pt-IIDocument9 pagesPlate Tectonics Notes Pt-II19rikenNo ratings yet
- Caribbean Studies - Plate TectonicsDocument24 pagesCaribbean Studies - Plate TectonicsJamion Knight100% (1)
- G10 Science Notes - Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesG10 Science Notes - Plate TectonicsCairo DiazNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument8 pagesSCIENCEMico Angelo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics and Plate BoundariesDocument35 pagesPlate Tectonics and Plate BoundariesHara Shelle AcompaniadoNo ratings yet
- Article On What Forms in Divergent Boundaries and TransformDocument2 pagesArticle On What Forms in Divergent Boundaries and TransformGUILLER BELENNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Power PointDocument22 pagesPlate Tectonics Power PointGuia GoopioNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics - Chapter 1Document12 pagesPlate Tectonics - Chapter 1ellahbrackenNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries: Sir PadillaDocument32 pagesPlate Boundaries: Sir PadillaMille GrayNo ratings yet
- Movement of Earth CrustDocument22 pagesMovement of Earth CrustJake Condes LiquiganNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument8 pagesReviewerMelody Bong ZitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Plate BoundariesDocument37 pagesLesson 4 Plate Boundarieslaizy998No ratings yet
- Origin of Continents & OceansDocument30 pagesOrigin of Continents & Oceansamanamu436No ratings yet
- ELECT1-week 9 CHAPTER 5 ENDOGENIC PROCESSESDocument12 pagesELECT1-week 9 CHAPTER 5 ENDOGENIC PROCESSESRenNo ratings yet
- Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms: Structure of The EarthDocument25 pagesEarth Movement and Resultant Landforms: Structure of The EarthEmille Grace NistalNo ratings yet
- A Level Geography NotesDocument71 pagesA Level Geography NotesAndrew mulabbiNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries: Quarter 4 Reference: The New Science LinksDocument19 pagesPlate Boundaries: Quarter 4 Reference: The New Science LinksRobieDeLeonNo ratings yet
- شرح تيكتونكس - ٠٥١٨٣٨Document27 pagesشرح تيكتونكس - ٠٥١٨٣٨Mohammed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics TheoryDocument24 pagesPlate Tectonics TheoryBernice CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Boundary Types 1Document22 pagesBoundary Types 1Apple Grace Marie SebastianNo ratings yet
- Notes On Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesNotes On Plate BoundariesDaniel HarrisNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument43 pagesPlate Tectonicspaulopasker80No ratings yet
- Are Rocks StressDocument17 pagesAre Rocks StressArniel CatubigNo ratings yet
- Sci10 Plate TectonicsDocument44 pagesSci10 Plate TectonicsStill into youNo ratings yet
- SYNTHESIS: Theory of Plate TectonicsDocument27 pagesSYNTHESIS: Theory of Plate TectonicsMarvin SantosNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Tectonic Plates 7.3Document23 pagesThe Theory of Tectonic Plates 7.3JAY-R PALLEGANo ratings yet
- Science 1st QuartDocument6 pagesScience 1st QuartArisa h.No ratings yet
- Earths MechanismDocument25 pagesEarths MechanismCyree ElishaNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift TheoryDocument35 pagesContinental Drift TheoryCarmela Del MarNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document91 pagesSession 2Shimaa MohammedNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics by Zeeshan AnsariDocument21 pagesPlate Tectonics by Zeeshan AnsariZeeshan AnsariNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument17 pagesPlate TectonicsDharel Joy AbongNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Quiz 5 ReviewerDocument2 pagesEarth and Life Quiz 5 Revieweririshpajarillaga13No ratings yet
- 5 Continental Drift, Group Plants-AnimalsDocument22 pages5 Continental Drift, Group Plants-Animalssakibhasandu3846No ratings yet
- 3 Plate-TechtonicsDocument33 pages3 Plate-TechtonicsSakshi BhalewadikarNo ratings yet
- Science Q1 ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience Q1 ReviewerAaron John BautistaNo ratings yet
- How Do Plate Tectonics WorkDocument7 pagesHow Do Plate Tectonics WorkFrancois LiletteNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Plate Boundaries and Geological ProcessesDocument3 pagesRelationship Between Plate Boundaries and Geological ProcessesAh FeNo ratings yet
- Continantal Drift TheoryDocument4 pagesContinantal Drift TheoryBasetsana BoikanyoNo ratings yet
- Plate MovementDocument49 pagesPlate Movementapi-25965024No ratings yet
- Science 10 First Quarter ReviewerDocument6 pagesScience 10 First Quarter ReviewerPlayer 456No ratings yet
- Earth Processes: Plate Tectonics: Lecture 7 and 8Document23 pagesEarth Processes: Plate Tectonics: Lecture 7 and 8Mangam RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics PPDocument30 pagesPlate Tectonics PPdazwerk123No ratings yet
- Geography Paper 1 NotesDocument262 pagesGeography Paper 1 NotesKayemba AndrewNo ratings yet
- Geo111 Part III 2021-22 CorDocument9 pagesGeo111 Part III 2021-22 CorgiovanniissakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Plate Tectonics) PlatesDocument28 pagesChapter 1 (Plate Tectonics) PlatesIatan Eugen MihaiNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument12 pagesGeographyshivambhardwajscribdNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Engineering GeologyDocument64 pagesPlate Tectonics Engineering GeologyChiranjaya Hulangamuwa50% (2)
- Module 3 ScienceDocument2 pagesModule 3 ScienceSunoo KimNo ratings yet
- CIV 442 Hydrology: Brief Geology of The UaeDocument22 pagesCIV 442 Hydrology: Brief Geology of The UaeMohammed ZiadNo ratings yet
- Folding MountainsDocument2 pagesFolding MountainsMinethegroundNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Sowing and ReseedingDocument6 pagesChapter 19 Sowing and ReseedingMinethegroundNo ratings yet
- Why Do Schools Feel DisconnectedDocument1 pageWhy Do Schools Feel DisconnectedMinethegroundNo ratings yet
- 5thyearbooklist 2023 24Document2 pages5thyearbooklist 2023 24MinethegroundNo ratings yet
- Weirdest Year of My LifeDocument6 pagesWeirdest Year of My LifeMinethegroundNo ratings yet
- Earth Science SHS 4.3 Sedimentary RocksDocument12 pagesEarth Science SHS 4.3 Sedimentary Rockssteven irvine alampayNo ratings yet
- 11 Glaciers and GlaciationsDocument4 pages11 Glaciers and GlaciationsMUHAMMAD NUMANNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle QuestionsDocument13 pagesRock Cycle Questionseeloadewole15No ratings yet
- Natural Environment - WikipediaDocument1 pageNatural Environment - Wikipediamerissacustarddy346No ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN - The Internal Structure of The EarthDocument4 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN - The Internal Structure of The Earthmaybelle100% (1)
- Mass WastingDocument10 pagesMass WastingAbhinav RajeevanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Environmental Geology 5Th Edition Keller Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Environmental Geology 5Th Edition Keller Test Bank Full Chapter PDFnathanmelanie53f18f100% (12)
- 24-Article Text-47-1-10-20180926Document18 pages24-Article Text-47-1-10-20180926irfandy andy17No ratings yet
- What Is Geomorphology? Why Study Geomorphology - 10 Reasons? Geomorphology Categories The Geomorphic SystemDocument20 pagesWhat Is Geomorphology? Why Study Geomorphology - 10 Reasons? Geomorphology Categories The Geomorphic Systemuapfa khomolaNo ratings yet
- Geology Honours (Revised)Document85 pagesGeology Honours (Revised)Neil PeguNo ratings yet
- Olps Earth Science Lesson 2 Minerals and RocksDocument8 pagesOlps Earth Science Lesson 2 Minerals and RocksJoseph MansionNo ratings yet
- Rock The RockDocument19 pagesRock The RockSavita YadavNo ratings yet
- Week 7 CAUSES OF PLATE MOVEMENTDocument23 pagesWeek 7 CAUSES OF PLATE MOVEMENTJuliever EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Earth MaterialsDocument32 pagesEarth MaterialsalexandereugeneleguaNo ratings yet
- Soil Profile PPT 2Document10 pagesSoil Profile PPT 2Sharmaine MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessesDocument27 pagesEndogenic ProcessesDuane AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Applications of Remote Sensing in GeomorphologyDocument15 pagesApplications of Remote Sensing in Geomorphologyimanfikri025No ratings yet
- Soil Management Montenegro Mirko KnezevicDocument56 pagesSoil Management Montenegro Mirko KnezevicJastouk SuperhNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesPlate TectonicsSophia Shannon D. DeiparineNo ratings yet
- UNIT 8 - Soil ErosionDocument47 pagesUNIT 8 - Soil ErosionMaria Lourdes samontinaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Preliminary and Chapter 1 - PPTDocument28 pagesLecture 1 - Preliminary and Chapter 1 - PPTcrainvictor 45No ratings yet
- Kami Export - EARTH - SCI - 2 - SG - UNIT - 1 PDFDocument16 pagesKami Export - EARTH - SCI - 2 - SG - UNIT - 1 PDFbaileyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18Document18 pagesLecture 18Raza ArshadNo ratings yet
- Earth Scie Peta Group 9Document92 pagesEarth Scie Peta Group 91 Estabillo, Roland Andrew T.No ratings yet
- Analisis Kualitas Sub DAS Citarum Hulu: Astri Mutia Ekasari, Hani Burhanudin, Irland FardaniDocument1 pageAnalisis Kualitas Sub DAS Citarum Hulu: Astri Mutia Ekasari, Hani Burhanudin, Irland FardaniabahaangNo ratings yet
- CIVE2304 C1-1 Hydrological CycleDocument54 pagesCIVE2304 C1-1 Hydrological CyclenaserNo ratings yet
- GEOL 101 Lab 8Document10 pagesGEOL 101 Lab 8Jack ChenNo ratings yet
- The Rock and Fosil RecordDocument45 pagesThe Rock and Fosil Recordmrk2rykbdwNo ratings yet
- Convergent Plate BoundariesDocument45 pagesConvergent Plate Boundariesjherwinperez2007No ratings yet
Geography Notes
Geography Notes
Uploaded by
MinethegroundOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geography Notes
Geography Notes
Uploaded by
MinethegroundCopyright:
Available Formats
Geography Notes
Plate tectonics – Endogenic Force
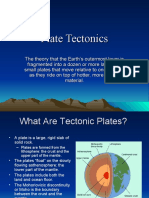
Plates tectonics states that the Earth’s lithosphere is broken into a number of slabs called plates.
These plates float on top of the mantle and are constantly in motion.
Plate boundary: Zone where plates collide, separate or slide past one another.
The earths crust is broken into sections called plates.
Classroom code = wgf7dvo
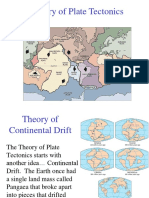
Continental drift
One of the earliest ways geologists thought continents moved over time.
Alferd Wegener was the creator of plate tectonics.
It proposes that all the earth’s continents were once part of a giant single landmass called Pangaea.
After Pangaea it was split into 2 landmasses Laurasia and Gondwana.
Proofs of continental drift.
Continental fit: The continental shelves of the east coast of South America and the west coast of Africa fit
together.
Fossil similarity: fossils of the ancient freshwater reptiles have been found on both the African and south
American continents.
Matching rocks and mountain ranges: mountain ranges of the east coast of the USA and north-western
Europe have similar features.
Ice sheets once covered areas that today are very warm: Evidence of glaciation in equatorial areas
suggest they were at different latitudes before being moved by continental drift.
Transform Plate boundaries.
Passive plate boundaries are created where plates slide past each other.
• The best-known passive boundary in the world exists between the North American
and Pacific Plates.
• Pressure builds over time as the faster-moving Pacific Plate tries to jolt free from
the slower-moving North American Plate.
• This pressure builds until one plate slips or jolts free. The sudden movement of the
plate triggers powerful earthquakes.
• The movement of the plates has created a large crack in the crust that is over 1300
km long. This is known as the San Andreas Fault
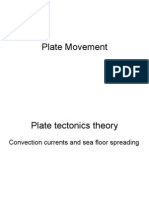
Divergent Plate Boundaries
Constructive -- new crust/land is created here.
Plates separate – pull away from each other due to convection currents within the mantle.
The convection currents in the mantle are flowing away from each other – this splits the
lithosphere and drags the plates apart.
There are 2 types of divergent plate boundaries
Continental Rifting
Sea floor Spreading
Rifting valleys are formed when continental plates are pulled apart by convection currents
East Africa is rifting apart from the rest of the African continent. The Red Sea has formed as a
result of water formed the Indian Ocean rushing in to fill the north part of the rifting valley.
Folding, faulting and doming
Deformation refers to any change in the shape and size of rock as a result of stress.
Forces of deformation
Compression squeezes and shortens the rock. Convergent plate movement. It results in folding
and/or faulting in the rock.
Tension stretches a body of rock.
You might also like
- Help Your Kids With GeographyDocument259 pagesHelp Your Kids With GeographyopenfileNo ratings yet
- How Plates MoveDocument5 pagesHow Plates Movelucasjorgelindo6335No ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics and Plate BoundariesDocument35 pagesPlate Tectonics and Plate BoundariesBENJ AMINNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review in ScienceDocument2 pagesPointers To Review in SciencePj JavierNo ratings yet
- Tectonic PlatesDocument7 pagesTectonic PlatesAmit 786No ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument5 pagesPlate TectonicsAmelia KaisersinghNo ratings yet
- Tectonic PlatesDocument6 pagesTectonic PlatesSamim AkhtarNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument3 pagesScienceShairene DimaculanganNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument2 pagesScienceShairene DimaculanganNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 6 PPT Q3 - Plate Tectonics and Plate BoundariesDocument35 pagesSCIENCE 6 PPT Q3 - Plate Tectonics and Plate Boundariesmar galiaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Notes Pt-IIDocument9 pagesPlate Tectonics Notes Pt-II19rikenNo ratings yet
- Caribbean Studies - Plate TectonicsDocument24 pagesCaribbean Studies - Plate TectonicsJamion Knight100% (1)
- G10 Science Notes - Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesG10 Science Notes - Plate TectonicsCairo DiazNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument8 pagesSCIENCEMico Angelo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics and Plate BoundariesDocument35 pagesPlate Tectonics and Plate BoundariesHara Shelle AcompaniadoNo ratings yet
- Article On What Forms in Divergent Boundaries and TransformDocument2 pagesArticle On What Forms in Divergent Boundaries and TransformGUILLER BELENNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Power PointDocument22 pagesPlate Tectonics Power PointGuia GoopioNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics - Chapter 1Document12 pagesPlate Tectonics - Chapter 1ellahbrackenNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries: Sir PadillaDocument32 pagesPlate Boundaries: Sir PadillaMille GrayNo ratings yet
- Movement of Earth CrustDocument22 pagesMovement of Earth CrustJake Condes LiquiganNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument8 pagesReviewerMelody Bong ZitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Plate BoundariesDocument37 pagesLesson 4 Plate Boundarieslaizy998No ratings yet
- Origin of Continents & OceansDocument30 pagesOrigin of Continents & Oceansamanamu436No ratings yet
- ELECT1-week 9 CHAPTER 5 ENDOGENIC PROCESSESDocument12 pagesELECT1-week 9 CHAPTER 5 ENDOGENIC PROCESSESRenNo ratings yet
- Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms: Structure of The EarthDocument25 pagesEarth Movement and Resultant Landforms: Structure of The EarthEmille Grace NistalNo ratings yet
- A Level Geography NotesDocument71 pagesA Level Geography NotesAndrew mulabbiNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries: Quarter 4 Reference: The New Science LinksDocument19 pagesPlate Boundaries: Quarter 4 Reference: The New Science LinksRobieDeLeonNo ratings yet
- شرح تيكتونكس - ٠٥١٨٣٨Document27 pagesشرح تيكتونكس - ٠٥١٨٣٨Mohammed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics TheoryDocument24 pagesPlate Tectonics TheoryBernice CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Boundary Types 1Document22 pagesBoundary Types 1Apple Grace Marie SebastianNo ratings yet
- Notes On Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesNotes On Plate BoundariesDaniel HarrisNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument43 pagesPlate Tectonicspaulopasker80No ratings yet
- Are Rocks StressDocument17 pagesAre Rocks StressArniel CatubigNo ratings yet
- Sci10 Plate TectonicsDocument44 pagesSci10 Plate TectonicsStill into youNo ratings yet
- SYNTHESIS: Theory of Plate TectonicsDocument27 pagesSYNTHESIS: Theory of Plate TectonicsMarvin SantosNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Tectonic Plates 7.3Document23 pagesThe Theory of Tectonic Plates 7.3JAY-R PALLEGANo ratings yet
- Science 1st QuartDocument6 pagesScience 1st QuartArisa h.No ratings yet
- Earths MechanismDocument25 pagesEarths MechanismCyree ElishaNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift TheoryDocument35 pagesContinental Drift TheoryCarmela Del MarNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document91 pagesSession 2Shimaa MohammedNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics by Zeeshan AnsariDocument21 pagesPlate Tectonics by Zeeshan AnsariZeeshan AnsariNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument17 pagesPlate TectonicsDharel Joy AbongNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Quiz 5 ReviewerDocument2 pagesEarth and Life Quiz 5 Revieweririshpajarillaga13No ratings yet
- 5 Continental Drift, Group Plants-AnimalsDocument22 pages5 Continental Drift, Group Plants-Animalssakibhasandu3846No ratings yet
- 3 Plate-TechtonicsDocument33 pages3 Plate-TechtonicsSakshi BhalewadikarNo ratings yet
- Science Q1 ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience Q1 ReviewerAaron John BautistaNo ratings yet
- How Do Plate Tectonics WorkDocument7 pagesHow Do Plate Tectonics WorkFrancois LiletteNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Plate Boundaries and Geological ProcessesDocument3 pagesRelationship Between Plate Boundaries and Geological ProcessesAh FeNo ratings yet
- Continantal Drift TheoryDocument4 pagesContinantal Drift TheoryBasetsana BoikanyoNo ratings yet
- Plate MovementDocument49 pagesPlate Movementapi-25965024No ratings yet
- Science 10 First Quarter ReviewerDocument6 pagesScience 10 First Quarter ReviewerPlayer 456No ratings yet
- Earth Processes: Plate Tectonics: Lecture 7 and 8Document23 pagesEarth Processes: Plate Tectonics: Lecture 7 and 8Mangam RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics PPDocument30 pagesPlate Tectonics PPdazwerk123No ratings yet
- Geography Paper 1 NotesDocument262 pagesGeography Paper 1 NotesKayemba AndrewNo ratings yet
- Geo111 Part III 2021-22 CorDocument9 pagesGeo111 Part III 2021-22 CorgiovanniissakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Plate Tectonics) PlatesDocument28 pagesChapter 1 (Plate Tectonics) PlatesIatan Eugen MihaiNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument12 pagesGeographyshivambhardwajscribdNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Engineering GeologyDocument64 pagesPlate Tectonics Engineering GeologyChiranjaya Hulangamuwa50% (2)
- Module 3 ScienceDocument2 pagesModule 3 ScienceSunoo KimNo ratings yet
- CIV 442 Hydrology: Brief Geology of The UaeDocument22 pagesCIV 442 Hydrology: Brief Geology of The UaeMohammed ZiadNo ratings yet
- Folding MountainsDocument2 pagesFolding MountainsMinethegroundNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Sowing and ReseedingDocument6 pagesChapter 19 Sowing and ReseedingMinethegroundNo ratings yet
- Why Do Schools Feel DisconnectedDocument1 pageWhy Do Schools Feel DisconnectedMinethegroundNo ratings yet
- 5thyearbooklist 2023 24Document2 pages5thyearbooklist 2023 24MinethegroundNo ratings yet
- Weirdest Year of My LifeDocument6 pagesWeirdest Year of My LifeMinethegroundNo ratings yet
- Earth Science SHS 4.3 Sedimentary RocksDocument12 pagesEarth Science SHS 4.3 Sedimentary Rockssteven irvine alampayNo ratings yet
- 11 Glaciers and GlaciationsDocument4 pages11 Glaciers and GlaciationsMUHAMMAD NUMANNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle QuestionsDocument13 pagesRock Cycle Questionseeloadewole15No ratings yet
- Natural Environment - WikipediaDocument1 pageNatural Environment - Wikipediamerissacustarddy346No ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN - The Internal Structure of The EarthDocument4 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN - The Internal Structure of The Earthmaybelle100% (1)
- Mass WastingDocument10 pagesMass WastingAbhinav RajeevanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Environmental Geology 5Th Edition Keller Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Environmental Geology 5Th Edition Keller Test Bank Full Chapter PDFnathanmelanie53f18f100% (12)
- 24-Article Text-47-1-10-20180926Document18 pages24-Article Text-47-1-10-20180926irfandy andy17No ratings yet
- What Is Geomorphology? Why Study Geomorphology - 10 Reasons? Geomorphology Categories The Geomorphic SystemDocument20 pagesWhat Is Geomorphology? Why Study Geomorphology - 10 Reasons? Geomorphology Categories The Geomorphic Systemuapfa khomolaNo ratings yet
- Geology Honours (Revised)Document85 pagesGeology Honours (Revised)Neil PeguNo ratings yet
- Olps Earth Science Lesson 2 Minerals and RocksDocument8 pagesOlps Earth Science Lesson 2 Minerals and RocksJoseph MansionNo ratings yet
- Rock The RockDocument19 pagesRock The RockSavita YadavNo ratings yet
- Week 7 CAUSES OF PLATE MOVEMENTDocument23 pagesWeek 7 CAUSES OF PLATE MOVEMENTJuliever EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Earth MaterialsDocument32 pagesEarth MaterialsalexandereugeneleguaNo ratings yet
- Soil Profile PPT 2Document10 pagesSoil Profile PPT 2Sharmaine MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessesDocument27 pagesEndogenic ProcessesDuane AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Applications of Remote Sensing in GeomorphologyDocument15 pagesApplications of Remote Sensing in Geomorphologyimanfikri025No ratings yet
- Soil Management Montenegro Mirko KnezevicDocument56 pagesSoil Management Montenegro Mirko KnezevicJastouk SuperhNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesPlate TectonicsSophia Shannon D. DeiparineNo ratings yet
- UNIT 8 - Soil ErosionDocument47 pagesUNIT 8 - Soil ErosionMaria Lourdes samontinaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Preliminary and Chapter 1 - PPTDocument28 pagesLecture 1 - Preliminary and Chapter 1 - PPTcrainvictor 45No ratings yet
- Kami Export - EARTH - SCI - 2 - SG - UNIT - 1 PDFDocument16 pagesKami Export - EARTH - SCI - 2 - SG - UNIT - 1 PDFbaileyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18Document18 pagesLecture 18Raza ArshadNo ratings yet
- Earth Scie Peta Group 9Document92 pagesEarth Scie Peta Group 91 Estabillo, Roland Andrew T.No ratings yet
- Analisis Kualitas Sub DAS Citarum Hulu: Astri Mutia Ekasari, Hani Burhanudin, Irland FardaniDocument1 pageAnalisis Kualitas Sub DAS Citarum Hulu: Astri Mutia Ekasari, Hani Burhanudin, Irland FardaniabahaangNo ratings yet
- CIVE2304 C1-1 Hydrological CycleDocument54 pagesCIVE2304 C1-1 Hydrological CyclenaserNo ratings yet
- GEOL 101 Lab 8Document10 pagesGEOL 101 Lab 8Jack ChenNo ratings yet
- The Rock and Fosil RecordDocument45 pagesThe Rock and Fosil Recordmrk2rykbdwNo ratings yet
- Convergent Plate BoundariesDocument45 pagesConvergent Plate Boundariesjherwinperez2007No ratings yet