Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Systems
Human Systems
Uploaded by
maielsherif2020Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Systems
Human Systems
Uploaded by
maielsherif2020Copyright:
Available Formats
EST-ACT-AP
BIOLOGY ACADEMY
Human Systems
Nervous - Immune
Dr. Mina Samuel
drminasamuel@hotmail.com
+2 010 917 111 25
+2 0122 187 70 44
+2 0122 187 70 99
EST-ACT-AP Bio-Academy... Human Systems II-(19) Dr. Mina Samuel
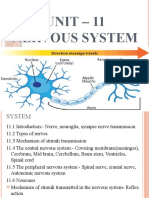
Human Systems II
II. Nervous System
Nervous system is the first to respond to changes in environment
Nervous and Endocrine systems control the human behavior
l
Cerebellum and the semicircular channel in the middle ear maintain the
ue
balance (equilibrium)
Medulla oblongata controls all involuntary action (Respiration rate).
am
Hypothalamus maintain the homeostasis (stable internal environment)
Nerve Impulse:
Sensory neurons start to function when receptors are stimulated
aS
Sensory neurons carry the impulse from sense organs to the CNS
Motor neurons carry the impulse from the CNS to the organs or muscles
Interneuron in CNS connect Sensory and Motor neurons
in
.M
Dr
The
Neuron
- Nerve cell differs from other cells in:
Dendrites, Axon, Myelin sheath (speed impulse transmission)
T.: +20 10 91711125
drminasamuel@hotmail.com Page 1
EST-ACT-AP Bio-Academy... Human Systems II-(19) Dr. Mina Samuel
Nerve Impulse pathway
CNS
Sensation motor order
Skin receptor Spinal cord Brain Spinal cord muscle, organs
Sensory neuron motor neuron
Interneuron
l
ue
Reflex-reflex action (controlled by spinal cord)
am
Sensation motor order
Skin receptor Spinal cord muscle, effector organs (withdraw hand)
(Flame) Sensory neuron motor neuron
Damage to the spinal cord below the waist will most likely interfere with walking.
aS
in
.M
Dr
T.: +20 10 91711125
drminasamuel@hotmail.com Page 2
EST-ACT-AP Bio-Academy... Human Systems II-(19) Dr. Mina Samuel
Nerve Impulse Mechanism:
Neuron is a nerve cell that transmits electrochemical impulses (nerve impulse)
a) In the neuron the impulse is ELECTRICAL
b) while in the synapse (the gap between neurons) (neuromuscular junctions OR motor end plate)
the impulses are CHEMICAL in nature
l
ue
I. Nerve impulse in the neuron (Electrically):
am
aS
There is a difference in electrical charge between the cytoplasm of neuron (-ve) and extracellular fluid
(+ve)
in
1- Resting potential:
.M
neuron is polarized and has membrane potential (-70 Mv)
Na+/K+ pump maintains the polarization
2- Action potential:
Dr
When axon is stimulated a rapid
movement of ions (depolarization)
occurs that is called action potential
Na+ INTO the Cell
K+ floods OUT of the Cell
3- Refractory period:
Na+/K+ pump restore the membrane
to original polarized condition
(Repolarization)
During this period, neuron can NOT respond to another stimulus
T.: +20 10 91711125
drminasamuel@hotmail.com Page 3
EST-ACT-AP Bio-Academy... Human Systems II-(19) Dr. Mina Samuel
II. Nerve impulse in the Synapse (Chemically):
Terminal of neuron has neurotransmitters like ACH stored in vesicles
Release of neurotransmitters by exocytosis into synapse transmit nerve impulse to adjacent neuron
After nerve impulse transmission, neurotransmitters break down by Acetylcholine esterase enzyme to
stop impulse.
l
ue
am
aS
Autonomic Nervous system
in
Sympathetic (Danger- emergency- fear- fight) Parasympathetic (at rest-sleep)
.M
Heart rate (pulse) Heart rate (pulse)
Respiration Respiration
Convert blood from
Convert blood from
Dr
Blood
Blood
Stomach skeletal muscle
skeletal muscle Stomach
Digestion Digestion
Skeletal muscular activity Skeletal muscular activity
Convert glycogen to glucose (energy) Convert glucose to glycogen (store)
Dilate pupil of eye Constrict pupil of eye
Stimulate adrenal medulla gland to release adrenaline
hormone
(adrenaline effect same as sympathetic)
T.: +20 10 91711125
drminasamuel@hotmail.com Page 4
EST-ACT-AP Bio-Academy... Human Systems II-(19) Dr. Mina Samuel
III. Immune System
Immunity
Non Specific immunity Specific immunity
(First Line defense mechanism) (2nd & 3rd Line defense mechanism)
- Normal barrier in the body - By White blood cells
- HCL in stomach Leucocytes
l
- Epidermis of skin (protect us from microorganisms)
ue
- spleen removes damaged cells from blood Phagocyte Lymphocyte
- Tears of eye Macrophage (3rd)
- Mucus, ciliated epithelium in nose (engulf bacteria)
am
(2nd)
B-lymphocyte T- lymphocyte
B-cell T-cell
aS
Antibody Memory Cell Helper Killer
Mature in Bone Marrow Mature in Thymus
in
Humoral and Cell Mediated Response
.M
Humoral Response: Involved with B-cells
which produce antibodies against specific
antigen.
Dr
Cell Mediated Response: Involved with T-cells
which fight pathogen.
T.: +20 10 91711125
drminasamuel@hotmail.com Page 5
EST-ACT-AP Bio-Academy... Human Systems II-(19) Dr. Mina Samuel
Passive and Active immunity
Passive immunity Active immunity
- To get already made antibodies - The body made his own antibodies
Vaccine Proliferation of lymphocytes
Mother milk to her baby
- short term immunity - Long term immunity (some for life time)
l
ue
Inflammatory Response:
Hypersensitivity (allergy) occur due to histamine release (redness, rash, edema and
vasodilatation)
am
IgE is antibody involved in allergy reaction.
Histamine makes capillaries more permeable as part of the inflammatory response to increase
the blood supply to area.
aS
Sever Hypersensitivity Anaphylactic shock
Blood Types
in
.M
Dr
Antigens are proteins that are found on the surfaces of invading viruses and bacteria.
Agglutination Occur when an antibody attacks antigen, result in clumping of anti B antibody B
with red blood cells.
T.: +20 10 91711125
drminasamuel@hotmail.com Page 6
EST-ACT-AP Bio-Academy... Human Systems II-(19) Dr. Mina Samuel
AIDS Virus
AIDS stands for acquired immune deficiency syndrome.
The virus that causes AIDS, HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) mainly attacks helper T cells.
HIV is a retrovirus:
Once inside a cell, it transcribes itself in reverse.
That means that the viral RNA uses the enzyme reverse transcriptase to make DNA.
This is the opposite of the typical DNA transcribing mRNA. The host cell then integrates this newly formed
l
DNA into its own genome.
ue
Antibiotics Vaccines
am
are medicines that kill bacteria or fungi are given to prevent illness caused by viruses
antibiotics are administered after a person is sick They cure the disease
Antibiotic that can block protein synthesis of bacteria without harming its eukaryotic host, when
aS
prokaryotes have ribosomes that are much smaller and simpler than eukaryotes
Strep throat:
Disease that can be treated effectively with antibiotics
in
Smallpox:
.M
Disease for which the causative agent was thought to have been entirely eliminated except for reserves in
two government installations
The first vaccine made from cowpox virus, developed by Edward Jenner in the 1700's, inoculated
Dr
people against smallpox. The development of this vaccine was possible because cowpox and
smallpox viruses are sufficiently similar that cowpox can stimulate the immune system against
smallpox.
Malaria:
Disease that is caused by a Protista parasite and currently responsible for the greatest number of human
deaths worldwide per year
T.: +20 10 91711125
drminasamuel@hotmail.com Page 7
EST-ACT-AP Bio-Academy... Human Systems II-(19) Dr. Mina Samuel
Assignment 19
1. Antibodies in humans are produced by which of the following?
(A) Lymphocyte.
(B) Bone marrow.
(C) Red blood cell.
(D) Platelets.
(E) Macrophage.
l
ue
2. A seven-year-old boy was suffering from chicken pox, and he had high fever and blister rash. His parents took him
to the doctor who decided that the best treatment for him would be
(A) fluids and rash ointment.
am
(B) vaccination against chicken pox.
(C) antibiotics.
(D) expose him to high temperatures to inactivate the disease.
(E) a combination of A and B
aS
3. At the neuromuscular junction, which of the following passes from the nerve cell to the muscle cell?
(A) An electrical signal
(B) A chemical signal
in
(C) A magnetic signal
(D) An axon
.M
(E) A synapse
4. Which of the following body systems responds first to changes in the environment?
(A) Nervous.
(B) Reproductive.
Dr
(C) Circulatory.
(D) Digestive.
(E) Excretory.
5. A person with type B blood should not be given a transfusion of type A blood because
(A) Type AB blood would be formed.
(B) The transfused blood would agglutinate.
(C) Anti-A antibodies destroy anti-B antibodies.
(D) Type A antigens destroy type B antigens.
(E) The type B person would become susceptible to infections.
T.: +20 10 91711125
drminasamuel@hotmail.com Page 8
EST-ACT-AP Bio-Academy... Human Systems II-(19) Dr. Mina Samuel
6. A function of the spleen is to
(A) Remove damaged cells from blood
(B) Produce urea
(C) Manufacture bile
(D) Destroy cholesterol
(E) Control the secretion of digestive juices
7. The function of the myelin sheath is to
(A) Strengthen the action potential of a neuron
l
ue
(B) Speed up the conduction of an action potential along a neuron
(C) Regulate the frequency of action potentials fired along a neuron
(D) Prevent the neuron from firing if the action potential is too weak
(E) Make sure the action potential is traveling in the correct direction along the neuron
am
Questions 8-11 refer to the following diseases
(A) Hemophilia.
(B) Polio.
aS
(C) Smallpox.
(D) Strep throat.
(E) Malaria.
in
8. Disease that can be treated effectively with antibiotics.
9. Disease for which the causative agent was thought to have been entirely eliminated government installations
.M
except for reserves in two.
10. Disease currently responsible for the greatest number of human deaths worldwide per year.
11. Disease that is caused by a protistan parasite.
12. Sensory neurons send impulses down their axons when
Dr
(A) They are stimulated by impulses from the spinal cord.
(B) Their cell body releases a neurotransmitter.
(C) They are stimulated by a receptor.
(D) The brain sends signals to them.
(E) The organism is about to do something dangerous.
13. When humans run during a marathon, their rate of breathing increases. This is primarily controlled by:
(A) Lungs
(B) Cerebrum
(C) Medulla oblongata
(D) Cerebellum
(E) Pleura
T.: +20 10 91711125
drminasamuel@hotmail.com Page 9
EST-ACT-AP Bio-Academy... Human Systems II-(19) Dr. Mina Samuel
14. The behavior of mammals is regulated by which of the following systems?
I. Nervous.
II. Circulatory.
III. Endocrine.
(A) I only.
(B) II only.
(C) III only.
(D) I and II only.
(E) I and III only.
l
ue
Questions 15-17 refer to the following structures
(A) Nephron.
(B) Red blood cell.
am
(C) Epidermis.
(D) Microfilament.
(E) Neuron.
aS
15. Protects organism from desiccation and from invasion by microorganisms.
16. Filters blood to make urine.
17. Transmits electrical impulses away from sensory structures.
in
18. The ABO blood type system is a system that codes for agglutinogen at the level of red blood cells thus
.M
determining the blood type. Blood transfusions are conducted in several cases such as bleeding. The possible
transfusion according to the ABO blood type system is
(A) A => AB
(B) AB => A
(C) A => O
Dr
(D) AB => O
(E) AB => B
T.: +20 10 91711125
drminasamuel@hotmail.com Page 10
EST-ACT-AP Bio-Academy... Human Systems II-(19) Dr. Mina Samuel
Assignment 19 Answers
Human Systems II
1 A 11 E
l
2 A 12 C
ue
3 B 13 C
4 A
am
14 E
aS
5 B 15 C
in
6 A 16 A
.M
7 B 17 E
8 D 18 A
Dr
9 C
10 E
With My best wishes dears
Dr. Mina Samuel
T.: +20 10 91711125
drminasamuel@hotmail.com Page 11
EST-ACT-AP Bio-Academy... Human Systems II-(19) Dr. Mina Samuel
Assignment 19 Student Answers
Student Name: .
Human Systems II
1 11
l
ue
2 12
am
3 13
aS
4 14
5 15
in
.M
6 16
7 17
Dr
8 18
10
With My best wishes dears
Dr. Mina Samuel
T.: +20 10 91711125
drminasamuel@hotmail.com Page 12
You might also like
- Agri 21Document11 pagesAgri 21Nicole UayanNo ratings yet
- Control and Cordination Notes ADocument9 pagesControl and Cordination Notes Ause6118No ratings yet
- Sheniblog-10 Biology (Eng Med) Revision Notes by Rasheed OdakkalDocument14 pagesSheniblog-10 Biology (Eng Med) Revision Notes by Rasheed OdakkalhadiyxxNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7-Control and CoordinationDocument9 pagesChapter-7-Control and Coordinationapi-400692183No ratings yet
- Control and Coordination: Chapter - 7Document9 pagesControl and Coordination: Chapter - 7milind dhamaniya100% (1)
- SHENIBLOG-Class 10 Biology Focus Area Covered Notes (Eng Med) All Chapters 2022Document16 pagesSHENIBLOG-Class 10 Biology Focus Area Covered Notes (Eng Med) All Chapters 2022kailaskrishnaushusNo ratings yet
- Nervous System1Document43 pagesNervous System1human anatomy100% (1)
- Integration and Coordination - SG3Document180 pagesIntegration and Coordination - SG3Marcos AlbaridaNo ratings yet
- Review of Peripheral Nervous System: Dr. Syed Atif AbbasDocument31 pagesReview of Peripheral Nervous System: Dr. Syed Atif AbbasAfif HalimNo ratings yet
- General Psychology: The Biological Basis of Psychological FunctioningDocument62 pagesGeneral Psychology: The Biological Basis of Psychological Functioningtracy_jNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesAutonomic Nervous Systemmaun04No ratings yet
- Unit 12Document30 pagesUnit 12aritrayeebarman05No ratings yet
- Interaction - The Nervous SystemDocument35 pagesInteraction - The Nervous SystemhelenafuertestoranNo ratings yet
- Pharma 2Document12 pagesPharma 2MARIEMIL FOLLOSONo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1wakaopakao2No ratings yet
- Science 8 PDFDocument172 pagesScience 8 PDFaftab khanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesIntroduction To The Nervous SystemVal F. VilarNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument22 pagesControl and CoordinationMozibor RahmanNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 14: Nervous TissueDocument3 pagesHuman Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 14: Nervous TissueSuperjunior8No ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - Part 1Document8 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - Part 1karageeNo ratings yet
- Control & Coordination Part - 1Document35 pagesControl & Coordination Part - 1Dance is LifeNo ratings yet
- Biology F4 Review Summary NoteDocument117 pagesBiology F4 Review Summary NoteSocdal AbdiNo ratings yet
- Points To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationDocument107 pagesPoints To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationRagheNo ratings yet
- Organisation of The Upper MotorneuroneDocument30 pagesOrganisation of The Upper MotorneuroneDanny XuNo ratings yet
- Nervous System PPT StudentsDocument43 pagesNervous System PPT StudentsAce Buenafe AdamosNo ratings yet
- Ch12 OL SummaryDocument47 pagesCh12 OL Summaryzuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- CoordiantionDocument56 pagesCoordiantionvijayp22No ratings yet
- Neurology Week 1 Trans 01 31 23Document3 pagesNeurology Week 1 Trans 01 31 23anime listNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordination in HumansDocument14 pagesCo-Ordination in HumansRahulBansumanNo ratings yet
- Grade Viii: Human Nervous SystemviiiDocument33 pagesGrade Viii: Human Nervous SystemviiiSmash UpNo ratings yet
- Biology 30 Student Notes Nervous ReproductionDocument53 pagesBiology 30 Student Notes Nervous ReproductionDennis Limosnero MayorNo ratings yet
- Neurologic NursingDocument181 pagesNeurologic NursingArcee Feb Dela PazNo ratings yet
- Unit-9 NERVOUS SYSTEMDocument37 pagesUnit-9 NERVOUS SYSTEMAmrita RanaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesNervous SystemJulie Ann SaquilayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Points To RememberDocument6 pagesChapter 22 Points To RememberSaksham YadavNo ratings yet
- Medical SurgicalDocument119 pagesMedical SurgicalNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- 15 Peripheral Nervous InjuryDocument8 pages15 Peripheral Nervous Injury楊畯凱No ratings yet
- StimuliDocument9 pagesStimuliJAZEEL ASLAMI PANDIKKADNo ratings yet
- Autonomic and Systemic Pharmacology DR DahalDocument119 pagesAutonomic and Systemic Pharmacology DR Dahalअविनाश भाल्टरNo ratings yet
- BS10003 Lecture7 NeurobiologyDocument37 pagesBS10003 Lecture7 Neurobiologyanirudhagrawal575No ratings yet
- ICSE Biology Notes Nervous System For 20 PDFDocument25 pagesICSE Biology Notes Nervous System For 20 PDFMmt RdcNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesAnaphy Nervous SystemFraiza BirowaNo ratings yet
- Mini-Lectures 1 - 3 Biological Psychology 2023 03 08Document40 pagesMini-Lectures 1 - 3 Biological Psychology 2023 03 08eeNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous and Glandular SystemDocument33 pagesHuman Nervous and Glandular Systemaanchal1203sharmaNo ratings yet
- Co6 ReviewerDocument10 pagesCo6 ReviewerKaren BritanicoNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument12 pagesCoordination and ResponsemandonaldboikanyoNo ratings yet
- The Spinal Cord and Spinal NervesDocument40 pagesThe Spinal Cord and Spinal NervesMona Mentari PagiNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Nervous SystemDocument117 pagesUnit 11 Nervous SystemChandan Shah100% (1)
- Nervous System - All NotesDocument6 pagesNervous System - All NotesJNo ratings yet
- 3 QTR Notes - Biology: Functions of The Nervous System Nervous System Histology Neurons Nerve CellsDocument4 pages3 QTR Notes - Biology: Functions of The Nervous System Nervous System Histology Neurons Nerve CellsHazel Kristy CatagueNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: AP BiologyDocument65 pagesThe Nervous System: AP BiologyaiswiftNo ratings yet
- Neurology - Saif.wesmosis.2013 104907Document68 pagesNeurology - Saif.wesmosis.2013 104907Helene AlawamiNo ratings yet
- CSE485 Lec3 Neurons SensationPerception M2021Document30 pagesCSE485 Lec3 Neurons SensationPerception M2021Monica PonnamNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemneotwiceskzNo ratings yet
- 06controlandcoordination 240314094029 5e232dbaDocument20 pages06controlandcoordination 240314094029 5e232dbaCrazyMindNo ratings yet
- Bio LabW5Document8 pagesBio LabW5iloveacuandtuinaNo ratings yet
- Week 10 BioDocument7 pagesWeek 10 BioTaze UtoroNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Neuro AnatpathoDocument28 pagesMedsurg Neuro Anatpathoj UNo ratings yet
- Med Surg NotesDocument65 pagesMed Surg NotesAthena ShylaNo ratings yet
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.From EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.No ratings yet
- Urban HierarchyDocument12 pagesUrban HierarchyNafisa Irina100% (1)
- PreliminariesDocument11 pagesPreliminariesGhabbFloresPalNo ratings yet
- Instant PotDocument48 pagesInstant PotCatrinescu Oana100% (1)
- DJ10Document4 pagesDJ10rahulNo ratings yet
- Maths Coursework Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesMaths Coursework Mark Schemef5d7ejd0100% (2)
- Answer:: Free Exam/Cram Practice Materials - Best Exam Practice MaterialsDocument3 pagesAnswer:: Free Exam/Cram Practice Materials - Best Exam Practice MaterialsAmine BoubakeurNo ratings yet
- List of Society Latest PDFDocument42 pagesList of Society Latest PDFDr Tilak Raj MeenaNo ratings yet
- Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, Indore Takshashila Campus: Vigyan BhawanDocument1 pageDevi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, Indore Takshashila Campus: Vigyan BhawankapasNo ratings yet
- Facility Preventive Maintenance ChecklistDocument5 pagesFacility Preventive Maintenance ChecklistFaisalNo ratings yet
- Company LawDocument15 pagesCompany Lawpreetibajaj100% (2)
- Starcraft - (1999) Hybrid - Chris Metzen PDFDocument10 pagesStarcraft - (1999) Hybrid - Chris Metzen PDFHawk RangerNo ratings yet
- Bandas PDFDocument3 pagesBandas PDFClaudia DiazNo ratings yet
- Start-Up Report Warranty Registration - EDITABLEDocument1 pageStart-Up Report Warranty Registration - EDITABLESAED ALAWNEHNo ratings yet
- Ero / Bheemadevarapally Ero / Bheemadevarapally Ero / Bheemadevarapally Sub Ero Gudur & Ero MahabubabadDocument59 pagesEro / Bheemadevarapally Ero / Bheemadevarapally Ero / Bheemadevarapally Sub Ero Gudur & Ero MahabubabadHARSHAVARDHAN REDDY MYADADHANo ratings yet
- Responsibility AccountingDocument14 pagesResponsibility AccountingJignesh TogadiyaNo ratings yet
- Acupressure Animal SheltersDocument1 pageAcupressure Animal SheltersIoana SavaNo ratings yet
- Sika CoolCoat BrochureDocument2 pagesSika CoolCoat BrochureSanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Ibrahim Raja August 2022 Theraplay ReportDocument6 pagesIbrahim Raja August 2022 Theraplay Reportfatma522No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 14Document3 pagesLesson Plan 14api-268829047No ratings yet
- SPM30 PDF Eng PDFDocument0 pagesSPM30 PDF Eng PDFValdemar Miguel SilvaNo ratings yet
- An Argument For Working Capital AdjustmentsDocument4 pagesAn Argument For Working Capital AdjustmentschristianNo ratings yet
- One Time Registration For TNPSCDocument2 pagesOne Time Registration For TNPSCtrismaheshNo ratings yet
- St. Jerome Would Be Shocked-St. Francis de Sales Delighted! Bible Study and Research SoftwareDocument3 pagesSt. Jerome Would Be Shocked-St. Francis de Sales Delighted! Bible Study and Research SoftwareRamelfebea MontedelobeniaNo ratings yet
- Company Profile PDFDocument9 pagesCompany Profile PDFSamir WalunjNo ratings yet
- Employee Turnover & It's Impact On Apparel Industry in Bangladesh: A Case Study of Mondol GroupDocument6 pagesEmployee Turnover & It's Impact On Apparel Industry in Bangladesh: A Case Study of Mondol GroupChristiady PurbaNo ratings yet
- AC Traction ManualDocument162 pagesAC Traction ManualBiju MenonNo ratings yet
- Lección 11 - How MuchDocument4 pagesLección 11 - How Muchyo no fuiNo ratings yet
- CTDI Phantom User's GuideDocument18 pagesCTDI Phantom User's GuideAida Cristiana SanduNo ratings yet
- Contec CMS800G - User Manual PDFDocument31 pagesContec CMS800G - User Manual PDFDea GarNo ratings yet
- Four Spheres and Apple CaseDocument2 pagesFour Spheres and Apple CaseGks06No ratings yet