Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 The Trouble With Water - Teacher
2 The Trouble With Water - Teacher
Uploaded by
Louisa LauOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 The Trouble With Water - Teacher
2 The Trouble With Water - Teacher
Uploaded by
Louisa LauCopyright:
Available Formats
3 The trouble with water
3 The trouble with water
3.1
What are the major threats to water resources?
A What are the uses of water?
B What are the major threats to the global water supply?
2 The two major threats are:
a not having enough freshwater for use; and
b lacking clean water.
3 Where do we get freshwater?
We get freshwater from rain , rivers and lakes .
4 The supply of freshwater is continuous. Therefore, it is a renewable resource.
Yet, its supply is still not enough for use, because:
a P opulation Economic Income goes up/
increases activities increase increases
More water is needed Rise in living
standards
© Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012 1
Junior Secondary Exploring Geography
Lesson worksheets
b in some areas, people use more water than the water resources can provide.
c some people use the water (wisely / unwisely).
5 When water demand exceeds water supply, water shortages occur.
6 Why is there a lack of clean water?
This is because water is polluted by toxic or dirty substances such as sewage or
garbage.
2 © Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012
3 The trouble with water
3.2 Where does water come from?
A Where is the water?
1 Water is found in the following places on the earth:
In this 4%,
- 1.7% is frozen in glaciers and polar
ice caps ;
- 1.7% is ground water in rocks;
- Less than 1% is water in lakes, rivers,
plants and in the air .
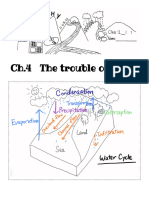
B What is a water cycle?
2 Water goes round and round in the form of a cycle. The movement of water is called the
water cycle . Refer to your textbook (p. 11 Figure 5). Add arrows and fill in the
blanks to complete the diagram below.
© Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012 3
Junior Secondary Exploring Geography
Lesson worksheets
3.3
What and where are China’s water resources?
A Where are the major rivers in China?
1 A river basin is the area drained by a river and its tributaries .
2 The following map shows the major river basins in China. Name the rivers of these basins
under the map. Find your answers in the box below.
Chang Jiang Hai He Huai He Huang He
Liao He Songhua Jiang Zhu Jiang
1 Songhua Jiang 2 Liao He
3 Hai He 4 Huang He
5 Huai He 6 Chang Jiang
7 Zhu Jiang
4 © Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012
3 The trouble with water
3 Complete the following information about the three most important rivers in China.
a Chang Jiang : This is the longest and largest river in China
Dongting Hu Poyang Hu Tai Hu
b Huang He : This is the second longest river in China. It is muddy
c Zhu Jiang : It is formed by three rivers, namely
Xi Jiang Bei Jiang Dong Jiang .
Hong Kong is at its mouth
© Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012 5
Junior Secondary Exploring Geography
Lesson worksheets
B What is the relationship between the relief of China and the
direction of flow of major rivers?
4 Water flows from ( high / low ) levels to ( high / low ) levels.
5 In China, there are ( highlands / lowlands ) in the east (the coast) and ( highlands / lowlands )
in the west (the inland). Therefore, the major rivers of China flow from west to
east towards the sea.
Examples of highland in inland China Examples of lowland in coastal China
a Qing Zang Gaoyuan f Huabei Pingyuan
b Yungui Gaoyuan g Middle and Lower Chang Jiang Pingyuan
6 © Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012
3 The trouble with water
c Kunlun Shan h Zhu Jiang Delta
d Huangtu Gaoyuan
e Himalayas
© Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012 7
Junior Secondary Exploring Geography
Lesson worksheets
C What is the climate of China?
6 A large part of China has a m onsoon climate.
7 Winds blowing in opposite directions during different seasons are called
m onsoons .
1 In summer Land
The land is heated up by the sun .
Air becomes ( hot / cold ) and it rises.
Air pressure over the land is ( high / low ).
Sea
Water absorbs heat more ( quickly / slowly ) than land.
Air over the sea is relatively cooler than air over the land.
Cool air is denser than warm air.
Air pressure over the sea is ( higher / lower ) than over the land.
Air moves from high-pressure areas to low-
pressure areas.
Therefore, wind blows from the
Pacific Ocean towards the
southern and eastern parts of Asia.
This is the s ummer m onsoon .
8 © Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012
3 The trouble with water
Winds blowing from the sea to the land are called onshore winds. They carry a lot of
moisture and bring rain to coastal regions.
Therefore, places affected by these winds are ( dry / wet ) in summer.
2 In winter Land
The land loses heat more ( quickly / slowly ) than
the sea.
The land surface is colder than the sea surface.
Cold air over the land ( rises / sinks ).
Air pressure over the land is ( high / low ).
Sea
Water releases heat more ( quickly / slowly ) than land.
Air over the sea is relatively warmer than air over the land.
Warm air is lighter than cool air.
Air pressure over the sea is ( higher / lower ) than over the land.
© Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012 9
Junior Secondary Exploring Geography
Lesson worksheets
Air moves from high-pressure areas to
low-pressure areas.
Therefore, wind blows from the
land towards the sea
(Pacific Ocean) .
This is the w inter m onsoon .
Winds blowing from the land to the sea are called offshore winds. They carry little
moisture.
Therefore, they bring dry weather to the affected regions in winter.
10 © Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012
3 The trouble with water
8 The inland region has less rain than the coastal area in China.
Winds blowing from the sea bring
moisture. But as they move inland,
the amount of moisture carried by
them ( increases / decreases ).
D Where are China’s water resources?
9 Where are the wet and dry regions in China? Finish the descriptions below.
a There are four major wet and dry regions. They are:
1 Humid region (>800 mm) 3 Semi-arid region (200-400 mm)
2 Semi-humid region (400-800 mm) 4 Arid region (<200 mm)
Region 1 is mainly found in the southern part Regions 3 and 4 are mainly found in the
of China. Region 2 is mainly found in northern and the
southern and north-eastern China north-western parts of China
© Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012 11
Junior Secondary Exploring Geography
Lesson worksheets
More precipitation means more water in the The annual flow of water in rivers of these
river. The annual flow of water in rivers of these regions is ( great / small )
regions is ( great / small )
b In general, the amount of water resources in China decreases from south-east to
north-west . Their distribution is ( even / uneven ).
E How do monsoons affect water resources in China?
10 Refer to the following climatic graphs of places along the Chang Jiang.
Monsoon climate affects these places in the following ways:
Summer monsoons prevail Winter monsoons prevail between
between May and September. They November and March. They bring low
bring high rainfall during the wet rainfall during the dry season.
season.
Chengdu May to September, about 800 mm November to March, about 60 mm
Wuhan May to September, about 720 mm November to March, about 270 mm
Hangzhou May to September, about 830 mm November to March, about 400 mm
12 © Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012
3 The trouble with water
( More / Fewer ) water resources are ( More / Fewer ) water resources are
available during the wet season. available during the dry season.
11 Water resources in China also vary greatly yearly.
During wet years, the high rainfall may cause f looding .
During dry years, the low rainfall may result in d rought .
Both of them can cause serious damage to farming and other economic activities.
© Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012 13
Junior Secondary Exploring Geography
Lesson worksheets
F What are the major human activities in a river basin?
12 Human activities are often found in river basins. What are these activities?
Deforestation : People cut down trees for timber and fuel wood.
Building dams : People use them to control the river flow. Water in the river is used
for irrigation .
Modifying channels and lakes:
People straighten the river channel for flood control.
People convert lakes to land for fishery , farmland and s ettlement .
Drawing ground water for various uses, e.g. for industrial and domestic uses.
14 © Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012
3 The trouble with water
3.4 What are the major water problems in China?
A What and where are China’s major water problems?
1 What are China’s major water problems?
a Flooding
It occurs when rainfall is very
heavy, rivers become full and
water flows over the channel.
Sometimes, strong typhoons push
seawater onto the shore. This
causes storm
surges and leads to severe
coastal flooding .
b Drought
It occurs when there is a long
period without any rain, or when
rainfall is much lower than
normal.
© Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012 15
Junior Secondary Exploring Geography
Lesson worksheets
c Pollution
When a river is polluted, the water
becomes unusable.
16 © Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012
3 The trouble with water
2 Where do China’s water problems occur? Refer to the following maps showing the
distribution of the three major water problems in China. Fill in the blanks and circle the
correct answer (there can be more than one answer) to show their distribution.
Distribution of flooding:
It occurs mainly in low-lying areas such
as coastal flat land and river basins. These
areas are found in ( western / central /
eastern ) China
Distribution of drought (can choose more
than one):
Mainly found in ( western / central /
eastern ) China
© Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012 17
Junior Secondary Exploring Geography
Lesson worksheets
Distribution of water pollution (can choose
more than one):
Mainly found along the ( upper / middle /
lower ) parts of rivers in China. Many of
these rivers flow past major cities in
( western / central / eastern ) China
18 © Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012
3 The trouble with water
B What are the harmful effects of flooding?
3 Flooding causes great damage. The damage includes:
a On structures
i Damaging buildings
ii Damaging transport networks such as roads, rail lines
and bridges
b On services
iii Stopping the supply of water , electricity and In sum, flooding causes
gas the following losses:
iv Disrupting transport services - E conomic loss
c On health of people - Loss of lives and
v Loss of lives and injuries property
vi Causing water pollution, and the polluted water may
cause diseases on people
d On crops
vii Damaging crops causing crop f ailure
© Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012 19
Junior Secondary Exploring Geography
Lesson worksheets
20 © Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012
3 The trouble with water
C What is the impact of drought?
1 Impact on the environment
4 a Serious drought may cause no water flow in a river
channel. It is called the cut-off of a river.
b The sediment in the river will stay in the river. This
causes silting and results in a rise of river
bed .
5 Dry condition does not favour vegetation growth. The
topsoil may be blown away more easily. This will intensify
d esertification and s andstorms may become more
common.
2 Impact on people
6 Drought
Industry Agriculture Daily life of people
Fall in Crop HEP generation
Electricity Insufficient water for
production failure daily use
generation is
because of food inconvenience and
affected
insufficient water shortages affecting health
D How does serious water pollution in China worsen the water
shortage problem?
7
Waste water from factories may Excess chemicals from farms Sewage
contain heavy metals and toxic e.g. pesticides and from home
chemicals fertilizers
Not treated
Discharged into rivers and lakes
Water pollution
Reduces the Intensifies the water
quality of water shortage problem
© Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012 21
Junior Secondary Exploring Geography
Lesson worksheets
3.5 Is nature to blame?
A What are the causes of flooding in China?
1 Flooding occurs when:
There is a sudden and large increase in The river bed becomes shallow and the
river flow river cannot hold the large amount of flow
Factor A: Factor B:
The amount of river flow increases The capacity of the river decreases
Natural causes Factor Human causes Factor
Heavy rainfall and typhoons bring Deforestation results in more soil and
heavy rain rocks washed into the rivers
A B
When the slope of the channel Poor farming methods and too much
becomes gentle, the water flow livestock grazing on the slopes causes
slows down. Sediment in the river soil erosion. Silting becomes more
stays in the river bed. This raises serious
the river bed
B B
22 © Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012
3 The trouble with water
Lakes are changed to different uses.
They cannot store as much water as
before
Dykes are poorly kept. They may fail
if river flow increases rapidly
© Oxford University Press (China) Ltd 2012 23
You might also like
- Map Reading Skills - Booklet p.9-15Document7 pagesMap Reading Skills - Booklet p.9-15Lai Sum YinNo ratings yet
- S3 - Geo - 2nd Term Exam Revision Industry 2Document8 pagesS3 - Geo - 2nd Term Exam Revision Industry 2Billy LauNo ratings yet
- Uf Toray PresentationDocument54 pagesUf Toray PresentationPrateek VermaNo ratings yet
- Geog. C4 Unit 1 & 2 WSDocument4 pagesGeog. C4 Unit 1 & 2 WSHayleyNo ratings yet
- (NEW) F.2 - Ch.4 The Trouble With Water Notes (ANS.) - 2ND TERM TESTDocument16 pages(NEW) F.2 - Ch.4 The Trouble With Water Notes (ANS.) - 2ND TERM TESTxhy44142677No ratings yet
- WS Part4 TE eDocument41 pagesWS Part4 TE emramesng.spamNo ratings yet
- WS Part4 SB eDocument41 pagesWS Part4 SB emramesng.spamNo ratings yet
- Ho Lap College Second Revision Test (2018-19) F.1 Integrated Science Time Allowed: 20 MinutesDocument5 pagesHo Lap College Second Revision Test (2018-19) F.1 Integrated Science Time Allowed: 20 Minutes冷燄No ratings yet
- Queen's College Half-Yearly Examination 2016-2017 English Language I General EnglishDocument52 pagesQueen's College Half-Yearly Examination 2016-2017 English Language I General EnglishTimmy SzeNo ratings yet
- Scicent SQ U8 3-4 SetB Final eDocument7 pagesScicent SQ U8 3-4 SetB Final eApple Lou100% (1)
- Assignment AC U6 Final eDocument26 pagesAssignment AC U6 Final eYuenHei Kwok0% (1)
- Assignment AC U2 Final eDocument28 pagesAssignment AC U2 Final eYuenHei KwokNo ratings yet
- S1 GE PaperDocument8 pagesS1 GE PapermelanieplchanNo ratings yet
- 1718 2nd Exan F3 Geog QPDocument11 pages1718 2nd Exan F3 Geog QP惜靈靜雅No ratings yet
- 2223-IS-S2-T1-Exam - Question PaperDocument12 pages2223-IS-S2-T1-Exam - Question PaperviclaukkNo ratings yet
- 1415 - S1 - Using Urban Space Wisely - Unit 1.1Document5 pages1415 - S1 - Using Urban Space Wisely - Unit 1.1DickyNo ratings yet
- Aristo Science Workbook 1A (Answer) PDF Solubility EvaporationDocument1 pageAristo Science Workbook 1A (Answer) PDF Solubility Evaporationntlroblox870% (1)
- S3 Biology First Term Exam MockDocument17 pagesS3 Biology First Term Exam Mockharis RehmanNo ratings yet
- WS E6 U1 Eng AnsDocument5 pagesWS E6 U1 Eng AnsMatthew LongNo ratings yet
- S3T1 2016DBQ Elementary eDocument37 pagesS3T1 2016DBQ Elementary eSharon TaoNo ratings yet
- Maximum Marks: 100Document35 pagesMaximum Marks: 100Yu HoyanNo ratings yet
- 2020-21-S2 HistoryDocument12 pages2020-21-S2 HistorywuhoyinNo ratings yet
- Scicent SQ U2 5-6 SetA Final eDocument4 pagesScicent SQ U2 5-6 SetA Final esteve LNo ratings yet
- 1415 - S1 - Using Urban Space Wisely - Unit 1.4Document8 pages1415 - S1 - Using Urban Space Wisely - Unit 1.4DickyNo ratings yet
- 3A 2017 Test eDocument15 pages3A 2017 Test eSharon TaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter5-Food and HumansDocument15 pagesChapter5-Food and HumansLisa TeddyNo ratings yet
- ENG S3 HY Composition QPDocument6 pagesENG S3 HY Composition QPtkh rjlinNo ratings yet
- Form 2 History Mid Term ExaminationDocument12 pagesForm 2 History Mid Term ExaminationTse LingNo ratings yet
- Mock Test 31 English Language Paper 4: Re: Hong Kong Minibus Hits Two Double-Deckers On Congested RoadDocument3 pagesMock Test 31 English Language Paper 4: Re: Hong Kong Minibus Hits Two Double-Deckers On Congested RoadFung AlexNo ratings yet
- Math Club 22-23 F1 Mock Paper - SolDocument17 pagesMath Club 22-23 F1 Mock Paper - Soltrach88347No ratings yet
- 3 Geog T2, Q 1819Document6 pages3 Geog T2, Q 1819Sze Ying HuiNo ratings yet
- Scicent SQ U8 3-4 SetA Final eDocument7 pagesScicent SQ U8 3-4 SetA Final eApple LouNo ratings yet
- 2021 S.3 1st Term TestDocument11 pages2021 S.3 1st Term Testirene fungNo ratings yet
- BAFS 1011 Midyear F4 ExamDocument8 pagesBAFS 1011 Midyear F4 Examqsoss433No ratings yet
- 1920 F3 Chem First Exam AnswerDocument2 pages1920 F3 Chem First Exam AnswerElsaaaNo ratings yet
- 1718 F4 - First - Term - ExamDocument11 pages1718 F4 - First - Term - ExamLo JustinNo ratings yet
- Questions: World History Express 3Document77 pagesQuestions: World History Express 3Vincent NGNo ratings yet
- F3 Phy Test 2 19-20Document5 pagesF3 Phy Test 2 19-20Carina WongNo ratings yet
- S.2 Integrated Science Worksheet Chapter 7 (7.4 - 7.7) : Part A: Concept Checking (10 Marks)Document7 pagesS.2 Integrated Science Worksheet Chapter 7 (7.4 - 7.7) : Part A: Concept Checking (10 Marks)Wong YanNo ratings yet
- 2009 Longman Book 1A Mock PaperDocument43 pages2009 Longman Book 1A Mock PaperVictor NgNo ratings yet
- ST - Stephen - Girl - College - F3 Math P1 17 18 Final ExamDocument13 pagesST - Stephen - Girl - College - F3 Math P1 17 18 Final ExamTommy UwuuwuNo ratings yet
- S1 - History - Ancient Greece Project - 2223Document4 pagesS1 - History - Ancient Greece Project - 22231F-17 Li Jasmine Tin YanNo ratings yet
- Kwun Tong Government SecondaryDocument15 pagesKwun Tong Government SecondaryRebeNo ratings yet
- 1a DBQDocument25 pages1a DBQVincent NGNo ratings yet
- English Language Paper 1 Reading PassageDocument9 pagesEnglish Language Paper 1 Reading PassageToby ChengNo ratings yet
- WS 10.1-10.4 With AnsDocument7 pagesWS 10.1-10.4 With Anselephantn63No ratings yet
- Answers To 2017-2018 F3-CHEM Final Examination: Section A: Multiple ChoicesDocument13 pagesAnswers To 2017-2018 F3-CHEM Final Examination: Section A: Multiple Choicesjonas hoNo ratings yet
- Sir Edward Youde Memorial Scholarships For Undergraduate and Diploma Students 2023/24 Nomination ReportDocument16 pagesSir Edward Youde Memorial Scholarships For Undergraduate and Diploma Students 2023/24 Nomination ReporthydrogenburningsplintNo ratings yet
- 英華女學校 2020 Mock Paper 1B Marking Scheme Part 1 - TikadoDocument11 pages英華女學校 2020 Mock Paper 1B Marking Scheme Part 1 - TikadoOof GucciNo ratings yet
- F2 IS Exam 1 (15-16)Document10 pagesF2 IS Exam 1 (15-16)羅天佑No ratings yet
- 2020-21-S2 GeographyDocument13 pages2020-21-S2 GeographywuhoyinNo ratings yet
- Physics: Question-Answer BookDocument16 pagesPhysics: Question-Answer Bookjonas hoNo ratings yet
- f1 Geog NotesDocument12 pagesf1 Geog NotesTse LingNo ratings yet
- CHMS3Y20E2Document13 pagesCHMS3Y20E2no nameNo ratings yet
- 2022-23-F1 Maths-1st Exam - Paper I-Questions OnlyDocument12 pages2022-23-F1 Maths-1st Exam - Paper I-Questions OnlyngayingchangNo ratings yet
- Good Hope School - 13 18 2A Ch.5 Angles Related To Rectilinear Figures MCDocument5 pagesGood Hope School - 13 18 2A Ch.5 Angles Related To Rectilinear Figures MCbot 2No ratings yet
- 1718 2nd Ut f3 Geog QPDocument8 pages1718 2nd Ut f3 Geog QP惜靈靜雅No ratings yet
- Unit 7 Living Things and Air (Question)Document7 pagesUnit 7 Living Things and Air (Question)usbdetailsNo ratings yet
- St. Louis School: 2019-20 Internal Test and Exam Syllabus (Final Examination)Document27 pagesSt. Louis School: 2019-20 Internal Test and Exam Syllabus (Final Examination)GG Hi100% (1)
- 19-20 Math Section A2 Answer KeyDocument6 pages19-20 Math Section A2 Answer KeyChad Aristo CHIMNo ratings yet
- The HydrosphereDocument5 pagesThe HydrosphereAnshul VermaNo ratings yet
- Technical Datasheet: MBR Wastewater Treatment Pilot System For Water Recovery & ReuseDocument3 pagesTechnical Datasheet: MBR Wastewater Treatment Pilot System For Water Recovery & Reusekesavaganesan58No ratings yet
- Plumbing Layout: General NotesDocument1 pagePlumbing Layout: General NotesMiiNo ratings yet
- Water Supply and Sanitary Engineering PDFDocument3 pagesWater Supply and Sanitary Engineering PDFVinod Kumar56% (16)
- L-2 Housedrainage SystemDocument69 pagesL-2 Housedrainage SystemLumbini DuddeNo ratings yet
- Water Supply CalculationsDocument8 pagesWater Supply CalculationsAshiq NishmaNo ratings yet
- People and Earth'S Ecosystem Ge - Elective BSME-3 Final Exam OutputDocument2 pagesPeople and Earth'S Ecosystem Ge - Elective BSME-3 Final Exam Outputjessie sandoyNo ratings yet
- Main Report Hapur STPDocument121 pagesMain Report Hapur STPManoj PatneNo ratings yet
- Vws Oil GasDocument8 pagesVws Oil GasFabricio TrosarelloNo ratings yet
- Energy: TERI Energy & Environment Data Diary and Yearbook (TEDDY) 2017/18Document30 pagesEnergy: TERI Energy & Environment Data Diary and Yearbook (TEDDY) 2017/18sereneNo ratings yet
- CIE4485 Wastewater Treatment: DR - Ir. M.K. de KreukDocument21 pagesCIE4485 Wastewater Treatment: DR - Ir. M.K. de KreukPragathees WaranNo ratings yet
- Vineet Tex FabDocument7 pagesVineet Tex FabSharon SusmithaNo ratings yet
- Interim National Water Quality Standards For MalaysiaDocument5 pagesInterim National Water Quality Standards For MalaysiaunknownNo ratings yet
- Soak Pit ParametersDocument2 pagesSoak Pit ParametersmmduuNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Water ManagementDocument38 pagesSustainable Water ManagementPallavi JagtapNo ratings yet
- Rainwater Harvesting - A Need of The Hour in Yemen Final 25 AugDocument101 pagesRainwater Harvesting - A Need of The Hour in Yemen Final 25 AugKasivajjula Sreeram ViswanathamNo ratings yet
- Ardelyn Paybano Activity Plumbing QuestionDocument3 pagesArdelyn Paybano Activity Plumbing QuestionArdelyn PaybanoNo ratings yet
- Progress On Drinking-Water and Sanitation Special Focus On SanitationDocument58 pagesProgress On Drinking-Water and Sanitation Special Focus On SanitationSTBM IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- Plumbing (AutoRecovered)Document3 pagesPlumbing (AutoRecovered)nicsNo ratings yet
- Analisa Kandungan Limbah Cair Tempe Air Rebusan Dan Air Rendaman KedelaiDocument6 pagesAnalisa Kandungan Limbah Cair Tempe Air Rebusan Dan Air Rendaman KedelaiPoco M3No ratings yet
- Department of Education: June 17, 2019 School MemorandumDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: June 17, 2019 School MemorandumZan OjedaNo ratings yet
- Job Corps Employment HandbookDocument72 pagesJob Corps Employment HandbookJobCorps LivesNo ratings yet
- South-to-North Water Transfer Project: F3 GeographyDocument15 pagesSouth-to-North Water Transfer Project: F3 GeographyYu Hang FUNGNo ratings yet
- Septic Tank DesignDocument3 pagesSeptic Tank DesignAnjo BalucasNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Water QualityDocument47 pagesIrrigation Water QualityfarzanNo ratings yet
- MECO - Biopharm - MASTERpure™ - Case StudyDocument9 pagesMECO - Biopharm - MASTERpure™ - Case Studyoussara1979No ratings yet
- Sewage and Excreta DisposalDocument61 pagesSewage and Excreta DisposalLeila Austria de Villa-MasajoNo ratings yet
- Water Budget and Water BalanceDocument15 pagesWater Budget and Water BalanceLarissa RiveraNo ratings yet
- Storm Water Management Manual For Eastern WashingtonDocument715 pagesStorm Water Management Manual For Eastern WashingtonDan LarsonNo ratings yet
- Mini Project 2Document6 pagesMini Project 2Anurag Dixit100% (1)