Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsMost Important Questions and Answers Related To India and Constitution of India
Most Important Questions and Answers Related To India and Constitution of India
Uploaded by
harishmbmlk2003This document discusses several important topics related to India's constitution and history. It covers the concepts of religion, contributions of key nationalist leaders, reforms like the Montague-Chelmsford Reforms and Government of India Act 1935, provisions of the Indian Independence Act 1947, and key features of the Indian constitution including fundamental rights and the relationships between central and state governments. It also summarizes the roles and powers of important government bodies like the Rajya Sabha, Lok Sabha, President, Prime Minister, Supreme Court, and Election Commission of India.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Toussaint Louverture by C. L. R. JamesDocument51 pagesToussaint Louverture by C. L. R. JamesDuke University Press83% (6)
- Constitutional Law - II - Important Questions LBDocument1 pageConstitutional Law - II - Important Questions LBbalaji67% (3)
- Blonde and Blue EyesDocument2 pagesBlonde and Blue EyesMikel Arispe78% (9)
- Our ConstitutionDocument10 pagesOur ConstitutionAnkith RudreshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Our ConstitutionDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Our ConstitutionaavishfaizNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity Chapter 2 - Making of The Constitution MCQ PDFDocument13 pagesIndian Polity Chapter 2 - Making of The Constitution MCQ PDFmurthy gNo ratings yet
- Class 9 - Total History & Civics SolutionsDocument10 pagesClass 9 - Total History & Civics Solutionstanveer1976No ratings yet
- 10th Civics Must KnowDocument6 pages10th Civics Must KnowAryan MishraNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument16 pagesUntitled Documentgagangautamedu.officialNo ratings yet
- PT #1 - Question Paper + Answer KeyDocument57 pagesPT #1 - Question Paper + Answer KeyDevaraj BillaNo ratings yet
- 11th Notes AdilDocument50 pages11th Notes Adilfastfollow accountsNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge Final Lecture: by Anil Sir..!!Document124 pagesGeneral Knowledge Final Lecture: by Anil Sir..!!deepakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Indian ConstitutionDocument3 pagesChapter 1: The Indian ConstitutionnancyNo ratings yet
- Polity Question BankDocument66 pagesPolity Question BankTanisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Constitutional DesignDocument6 pagesConstitutional DesignAbheeram PatilNo ratings yet
- Pol - SC 1st ChapDocument7 pagesPol - SC 1st ChapRoshniNo ratings yet
- MCN202 Imp QuestionsDocument3 pagesMCN202 Imp QuestionsMohammed AsifNo ratings yet
- History ICSE Questions Class 10Document4 pagesHistory ICSE Questions Class 10Ankita Anand100% (1)
- NOTESDocument13 pagesNOTESst62452No ratings yet
- Fayaz SirDocument72 pagesFayaz Sirhaleem malikNo ratings yet
- Day-1 - Polity PDFDocument6 pagesDay-1 - Polity PDFAkash DeepNo ratings yet
- DAY 01 POLITY (Shashidthakur23.Wordpress - Com)Document6 pagesDAY 01 POLITY (Shashidthakur23.Wordpress - Com)AbhishekKurilNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Design Part B AnswersDocument4 pagesConstitutional Design Part B Answersrupayan majumderNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Design NotesDocument6 pagesConstitutional Design Notestindutt life timeNo ratings yet
- UPSC Mains General Studies Indian Polity and ConstitutionDocument10 pagesUPSC Mains General Studies Indian Polity and ConstitutionPankaj ChetryNo ratings yet
- Making of Constitution: Useful LinksDocument23 pagesMaking of Constitution: Useful Linksvivek kumarNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Neeed A GovernmentDocument8 pagesWhy Do We Neeed A GovernmentNeelNo ratings yet
- C8CCh1 The Indian ConstitutionDocument13 pagesC8CCh1 The Indian ConstitutionPieNo ratings yet
- The Union Legislature - WorksheetDocument1 pageThe Union Legislature - WorksheetRishta PorwalNo ratings yet
- IASbabas 60 Day Plan 2017 Day 1Document19 pagesIASbabas 60 Day Plan 2017 Day 1sabirNo ratings yet
- IASbaba's 60 Day Plan 2017 - Day 01 To Day 36Document681 pagesIASbaba's 60 Day Plan 2017 - Day 01 To Day 36Tapas SwainNo ratings yet
- (Gkmojo) Indian Polity Notes: 1. Framing of The ConstitutionDocument9 pages(Gkmojo) Indian Polity Notes: 1. Framing of The Constitutionananyaverma695No ratings yet
- Indian Polity Notes PDFDocument9 pagesIndian Polity Notes PDFUnmesh MitraNo ratings yet
- Polity LaxmikanthDocument35 pagesPolity LaxmikanthS100% (1)
- 2017-18 Hist Must Know QnsDocument6 pages2017-18 Hist Must Know QnsAdvait BhoreNo ratings yet
- POLITY 1.0 by Abhas SainiDocument39 pagesPOLITY 1.0 by Abhas SainiKeshav BhartiNo ratings yet
- 11th Class PaperDocument2 pages11th Class PaperAshutosh jabotraNo ratings yet
- Polity Set 5Document51 pagesPolity Set 5Manish ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Political Science Class XiDocument3 pagesSample Paper Political Science Class XisumeghaonlineNo ratings yet
- Political Science March 2020 STD 12th Arts HSC Maharashtra Board Question PaperDocument2 pagesPolitical Science March 2020 STD 12th Arts HSC Maharashtra Board Question PaperNew Prestige WelfareNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law-IDocument7 pagesConstitutional Law-IthesharemarketlearnerNo ratings yet
- Preamble, Federalism Abb0c53d 88bc 455a Ad11 16ce1401f65aDocument7 pagesPreamble, Federalism Abb0c53d 88bc 455a Ad11 16ce1401f65aaadhiimohan03No ratings yet
- Indian Constitution Exam PaperDocument4 pagesIndian Constitution Exam PaperNahid H Mazumder L15No ratings yet
- Short Answer QuestionsDocument11 pagesShort Answer QuestionsAaromal MaanasNo ratings yet
- UPSC Main Exam Indian Polity and Constitution Previous Years Questions The Pattern and TrendDocument12 pagesUPSC Main Exam Indian Polity and Constitution Previous Years Questions The Pattern and TrendJhansi LaxmiNo ratings yet
- Constitutional LawDocument7 pagesConstitutional LawGaming GodNo ratings yet
- 22ICO17 - Notes - 230511 - 090018Document23 pages22ICO17 - Notes - 230511 - 090018Pravaal Raj MishraNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Class 11 Pol Science Chapter 1Document4 pagesImportant Questions Class 11 Pol Science Chapter 1Prasun AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 2023 2024 Class VIII Social Studies Part 3 AWDocument5 pages2023 2024 Class VIII Social Studies Part 3 AWBRO IT’S DHARAHASNo ratings yet
- CH-3 Parliamentary GovernmentDocument6 pagesCH-3 Parliamentary GovernmentSanjiv BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Constitution of India Chapter 1Document10 pagesConstitution of India Chapter 1mmmmNo ratings yet
- CLAT PG 2019 Solutions Set ADocument26 pagesCLAT PG 2019 Solutions Set ASahana MathpatiNo ratings yet
- 2018 PolDocument16 pages2018 Polnitin pandeyNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law Questions III SemesterDocument4 pagesConstitutional Law Questions III SemesterAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Durga Das BasuDocument3 pagesDurga Das BasuArun Cse0% (1)
- Part B 1. About India-C-EDocument39 pagesPart B 1. About India-C-ESaYani SamaDdarNo ratings yet
- Extra Questions of Constitutional DesignDocument39 pagesExtra Questions of Constitutional Designaditya3421pNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet - Half YearlyDocument12 pagesRevision Worksheet - Half Yearlyrizzie12345.icecreamsNo ratings yet
- Hist8 - 2 Union Executive Drilling QuestionsDocument1 pageHist8 - 2 Union Executive Drilling QuestionsBFF ForeverNo ratings yet
- 7HCC1 The Constitution of IndiaDocument5 pages7HCC1 The Constitution of Indiakilleraarush27No ratings yet
- ISC Political Science 2016Document13 pagesISC Political Science 2016AVNISH PRAKASHNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsFrom EverandIndian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsNo ratings yet
- Komunikasyon at PananaliksikDocument73 pagesKomunikasyon at PananaliksikANGELU RANE BAGARES INTOL100% (2)
- Government Remarks Prime Minister How The Role Was FulfilledDocument2 pagesGovernment Remarks Prime Minister How The Role Was FulfilledTina MarianoNo ratings yet
- 72-74 - 08-4-The Situation in Southern RhodesiaDocument13 pages72-74 - 08-4-The Situation in Southern RhodesiaVasilije BlagojevicNo ratings yet
- Campus/Centre LocationDocument55 pagesCampus/Centre LocationToddy LaiNo ratings yet
- "Men, Women, and Work - Reflections On The Two-Person Career" - Hanna PapanekDocument21 pages"Men, Women, and Work - Reflections On The Two-Person Career" - Hanna PapanekMuseu da MONo ratings yet
- Models of Disability 222Document4 pagesModels of Disability 222ayenew kassahunNo ratings yet
- Adsum Notes - Public Corp Reviewer MidtermDocument13 pagesAdsum Notes - Public Corp Reviewer MidtermRaz SPNo ratings yet
- Somali Women'S Political Participation and Leadership-Evidence and OpportunitiesDocument29 pagesSomali Women'S Political Participation and Leadership-Evidence and OpportunitiesalexNo ratings yet
- Frontier: No Talks, No PeaceDocument16 pagesFrontier: No Talks, No PeaceGovindNo ratings yet
- Spousal Collection - Part 3Document79 pagesSpousal Collection - Part 3Queer OntarioNo ratings yet
- Karakachans in Bulgaria (Sarakatsani)Document6 pagesKarakachans in Bulgaria (Sarakatsani)valer_crushuveanlu100% (1)
- Talisay City, Cebu 6045 June 8, 2020: Roselan LabaoDocument4 pagesTalisay City, Cebu 6045 June 8, 2020: Roselan LabaoMichael MabiniNo ratings yet
- Pensatoryallowance Vide Go Ms 176 dt.15-12-2015 PDFDocument4 pagesPensatoryallowance Vide Go Ms 176 dt.15-12-2015 PDFSRIDHARNo ratings yet
- Midterm ExamDocument3 pagesMidterm ExamIya GadonNo ratings yet
- Footnote 20 - The Carter Center. (N.D.) - Observing Myanmar's 2015 General Elections. in Election Final Report.Document80 pagesFootnote 20 - The Carter Center. (N.D.) - Observing Myanmar's 2015 General Elections. in Election Final Report.Kyaw Zaw LinNo ratings yet
- Kwame Ture InterviewDocument8 pagesKwame Ture InterviewSumayya K AliNo ratings yet
- Final Supervisorial District Map Adopted by Sacramento County Board of SupervisorsDocument3 pagesFinal Supervisorial District Map Adopted by Sacramento County Board of SupervisorsGilbert CordovaNo ratings yet
- LLB 3 YDC COLLEGE LIST FEE-excelDocument5 pagesLLB 3 YDC COLLEGE LIST FEE-excelsumanthNo ratings yet
- FPJ International Epaper-21!08!2023Document21 pagesFPJ International Epaper-21!08!2023sagart817296No ratings yet
- Local Government in England: Structures: Briefing PaperDocument22 pagesLocal Government in England: Structures: Briefing PaperSanya Atta SangharNo ratings yet
- Notice ER16323 13122023Document30 pagesNotice ER16323 13122023Jeet GuptaNo ratings yet
- Partition of Bengal - 1905Document28 pagesPartition of Bengal - 1905Reshan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Afterall. A Journal of Art, Context and Enquiry, (Volume 42. AutumnWinter 2016)Document158 pagesAfterall. A Journal of Art, Context and Enquiry, (Volume 42. AutumnWinter 2016)Sangue CorsárioNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On French RevolutionDocument4 pagesTerm Paper On French Revolutionafmzswxbbbbitf100% (1)
- Critic To Zartman - Rothstein-TimingDocument21 pagesCritic To Zartman - Rothstein-TimingElton TivaneNo ratings yet
- PDF A Pocket Guide To The Us Constitution What Every American Needs To Know Andrew B Arnold Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF A Pocket Guide To The Us Constitution What Every American Needs To Know Andrew B Arnold Ebook Full Chapterjennifer.nye440100% (6)
- Moulding The Socialist Subject: Xiaoning LU - 978-90-04-42352-7 Via Free AccessDocument212 pagesMoulding The Socialist Subject: Xiaoning LU - 978-90-04-42352-7 Via Free Accessjeff tehNo ratings yet
- Allah - Bux.soomro Apostle - Of.secular - Harmony Khadim - Soomro. (2006) .CsDocument205 pagesAllah - Bux.soomro Apostle - Of.secular - Harmony Khadim - Soomro. (2006) .CsAnonymous lviObMpprNo ratings yet
Most Important Questions and Answers Related To India and Constitution of India
Most Important Questions and Answers Related To India and Constitution of India
Uploaded by
harishmbmlk20030 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views9 pagesThis document discusses several important topics related to India's constitution and history. It covers the concepts of religion, contributions of key nationalist leaders, reforms like the Montague-Chelmsford Reforms and Government of India Act 1935, provisions of the Indian Independence Act 1947, and key features of the Indian constitution including fundamental rights and the relationships between central and state governments. It also summarizes the roles and powers of important government bodies like the Rajya Sabha, Lok Sabha, President, Prime Minister, Supreme Court, and Election Commission of India.
Original Description:
Original Title
Most Important Questions and Answers related to India and Constitution of India
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses several important topics related to India's constitution and history. It covers the concepts of religion, contributions of key nationalist leaders, reforms like the Montague-Chelmsford Reforms and Government of India Act 1935, provisions of the Indian Independence Act 1947, and key features of the Indian constitution including fundamental rights and the relationships between central and state governments. It also summarizes the roles and powers of important government bodies like the Rajya Sabha, Lok Sabha, President, Prime Minister, Supreme Court, and Election Commission of India.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views9 pagesMost Important Questions and Answers Related To India and Constitution of India
Most Important Questions and Answers Related To India and Constitution of India
Uploaded by
harishmbmlk2003This document discusses several important topics related to India's constitution and history. It covers the concepts of religion, contributions of key nationalist leaders, reforms like the Montague-Chelmsford Reforms and Government of India Act 1935, provisions of the Indian Independence Act 1947, and key features of the Indian constitution including fundamental rights and the relationships between central and state governments. It also summarizes the roles and powers of important government bodies like the Rajya Sabha, Lok Sabha, President, Prime Minister, Supreme Court, and Election Commission of India.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 9
Most Important Questions and Answers related to India and
Constitution of India
1).Concept of religion And briefly describe the contribution..?
Religion is a concept that directs the duties and responsibilities of an individual
and society
The gift of religion..
1). Reinforcement of sense of duty.
2). A symbol of excellence.
3). An assistant to human isolation.
4). Foundation for state administration.
5). An instrument of peace and legal order.
6). A preference for humanism.
2). The contribution of Rajaram Mohan Roy's liberal outlook..?
1). Assertion of Rights.
2). Support for British rule.
3). Efforts for women's emancipation.
4). Encouragement of western education.
5). Enforcement of Acts of the British Parliament.
2). Nationalist view of Swami Vivekananda..?
1).Concept of humanity and universals.
2). The three pillars are spirituality, patriotism, and religion.
3). An ancient inspiration.
4). Revival of Vedapanishads.
5). Prioritize service and sacrifice.
1). Gandhiji's Concept of Satyagraha...?
1). Disobedience.
2). Haratala.
3). Mass boycott.
4). Prevention
5). Violation of the law.
6). Hijrat.
7). Fasting.
8. Strike.
2. Swadeshi concept of Gandhiji..?
1). Exclusion of foreign materials.
2). Call for establishment of Indian Courts.
3). Advice for National Education.
4). Strengthening of Indian political institutions 5).Consent to violation of laws.
3. Vinoba Bhave's Concept of Swayamseva...?
1). land donation.
2).Village donation.
3). Donation of wealth.
4).Shramadana.
5).Buddhi Dana.
3. Explain the provisions of Marlemento Reform of 1909..?
1). Expansion of Legislative Councils..
2).Appointment of various categories of members to the Legislative Council.
3). Establishment of separate constituencies for Muslims.
4). Opportunity for Indians in the Legislative Council.
5).Opportunity for Indians in Governor General's Council.
2. Key Provisions of Montego Reforms...?
1). Independence from center to provinces.
2).Enforcement of dual government system.
3). Allowance for bicameral legislature.
4).Expansion of communal representation.
5). Limited access to voting.
6). Creation of the post of High Commissioner for India.
7). Increase in representation in the Indian Council.
8). Half of the seats in the Viceroy's Executive Council are for Indians.
9). Allowance for establishment of Public Service Commission.
10).Proposal for Constitution of Legislative Commission.
4. Important provisions of the Government of India Act, 1935...?
1). Establishment of All India Union.
2).Aspiration for power sharing.
3).Autonomy for provinces.
4).Implementation of Dual Government at the Centre.
5).Preference for bicameral legislatures.
6). Preference for communal representation.
7).Abolition of Indian Council.
8).Consolidation of voting.
9). Establishment of Reserve Bank.
10). Preference to Administrative Service Commission.
11). Allow for establishment of Union Court.
12).Re-distribution of land parcels.
3. Indian Independence Act of 1947..?
1). End of British rule.
2). Creation of India and Pakistan.
3). Abolition of the post of Viceroy.
4). Power to the Constituent Assembly.
5). Distribution of legislative power.
6).Abolition of the post of Secretary of State for Indian Affairs.
7). End of British Supremacy over India.
8). Free independence for native states.
9).Instruction for compliance with Act of 1935.
10).Proposal of Constitutional Executive Head.
11). Abolition of the title of Emperor of India.
12).Formation of Boundary Commission.
1). Explain in brief about the proposed Constitution of India..?
A summary of the objectives of the Constitution is called the Preamble.
1). We the citizens of India.
2).Sovereign.
3).Socialism.
4).Secularism.
5).Democracy.
6). Republic.
7).Justice.
8).Independent.
9).Equality.
10).fraternity.
2). Briefly explain the features of the Constitution of India.
1). A written and voluminous constitution.
2). Proposal.
3).Parliamentary model of government.
4).Secular nation.
5).Fundamental Duties.
6).compound system.
7). Flexible and Inflexible Constitution.
8).Directorate Principles of State Policy.
9).Universal Adulthood.
10).Voting system.
11).Emergencies.
12).Independent Judiciary System.
4).Dr. in the constitution of India. Contributions of BR Ambedkar..
1).Drafting Committee Chairman.
2).Succeeded in getting consensus for the constitution.
3).Significant role in the drafting of the Constitution.
4) Addition of special regulations.
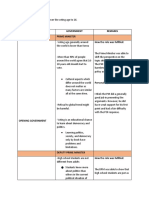
1).Briefly explain Fundamental Rights
1). Right to Equality Article 14 to 18.
2). Article 19 to 22 of the Right to Freedom.
3). Right against exploitation Article 23 to 24.
4). Right to religious freedom Article 25 to 28.
5). Cultural and Educational Right Article 29 to 30.
6).Right to constitutional remedy Article 32.
2. Explain the relationship between center and states in India...?
1). Statutory relations.
2). Administrative relations.
3). Financial relations.
4). International relations.
3). Briefly explain the major amendments to the Constitution of India...?
1). Proposal.
2). National Policy Director Principles.
3). Basic Duties.
4). Parliament.
5). Judiciary.
6). emergency situation.
8). Seventh Schedule.
9). 73rd Constitutional Amendment.
10). 74th Constitutional Amendment.
11). 86th Constitutional Amendment.
1). Explain the structure of Rajya Sabha
Raji Sabha came into existence for the first time on 3rd April 1952.
Convened for the first time on 13 May 1952.
Rajya Sabha is known as the upper house of Parliament.
1). Size.
2). Method of election.
3). Qualifications.
4). Tenure.
5). Sessions.
6). Quorum.
7). President and Vice President.
8). Salary and Exemptions.
2). Functions of Rajya Sabha...
1). Statutory Powers.
2). Executive powers.
3). Financial powers.
4).Judiciary Powers.
5).Powers of election.
6).Power to amend the Constitution.
7). Power to declare emergency.
8). Special powers.
2). Briefly explain the structure and powers of Lok Sabha
1). size
2).Method of Election
3).Qualifications
4).Term of office
5).sessions
6). Quorum
7).Chairman and Vice-Chairman
8).Wage Exemptions
1). Statutory Powers
2). Executive officers
3). Financial powers
4). Criminal officers
5). Electoral powers
6). Amendment powers
7). Powers relating to emergency
8 ).Other Powers
2). Briefly explain the powers and functions of the President
1). Powers of Karengi.
2). Statutory Powers.
3). Financial powers.
4). Judicial officers.
5). Emergency Powers.
6). Selection of ambassadors.
7). Discretionary powers.
2). Powers and Functions of the Prime Minister..
1). Composition of the Cabinet Allocation of accounts
2). Restructuring of the Cabinet.
3). Head of the Cabinet.
4). A review of government policies.
5). Principal Advisor.
6). A bridge between the President and the Cabinet.
7). Leadership for the nation.
8). Leader of Parliament.
3). Briefly explain the Jurisdiction of Supreme Court
1). Original Jurisdiction.
2). Appellate jurisdiction.
3). Advisory jurisdiction .
4).Judicial review.
5).Court of Record.
6). Power to transfer cases.
7). Power to entertain special appeals.
8).Power of Revision.
9).Power to impose penalty for contempt of court.
10). Other Powers.
4). Explain the powers and functions of the Election Commission of India.
1). Conduct of various elections.
2). Determining the boundaries of electoral constituencies.
4). Preparation of Electoral Roll.
5). Publication of election schedule.
5). Registration of parties and allocation of symbols.
6). Power to order re-election
7). the election.
Power of postponement.
8). Power to obtain information on election expenditure.
9). Authority to determine its budget.
10). Power to disqualify candidate.
11). Forming a Model Policy Committee.
1). Explain the Citizenship Act, 1955 and the amendments to the Citizenship
Act...
1). Method of acquiring citizenship.
A). through birth.
b). through blood relation.
c). By registration.
d). By instinctive method.
this ). through land acquisition.
2.) Manner of Loss of Citizenship.
A. By giving up.
B. By canceling.
C. By taking away.
2). Briefly explain the meaning and significance of civil society
A community of people engaged in collective activities to achieve common
objectives is called civil society
Significances...
1). Efforts for public awareness.
2). Social transformation.
3).Assertion of rights.
4).Condemnation of absolutism.
5). Motivating political participation.
6).Protection of environment.
7).Protection of Human Rights.
8).Consolidation of democracy.
9).Cooperation in times of trouble.
10).World Peace.
4). Role of students in national development.
1). Purposeful study.
2). Participation in extracurricular activities.
3). Awareness raising.
4). Adoption of Service Attitude.
5). Upholding moral and constitutional values.
You might also like
- Toussaint Louverture by C. L. R. JamesDocument51 pagesToussaint Louverture by C. L. R. JamesDuke University Press83% (6)
- Constitutional Law - II - Important Questions LBDocument1 pageConstitutional Law - II - Important Questions LBbalaji67% (3)
- Blonde and Blue EyesDocument2 pagesBlonde and Blue EyesMikel Arispe78% (9)
- Our ConstitutionDocument10 pagesOur ConstitutionAnkith RudreshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Our ConstitutionDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Our ConstitutionaavishfaizNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity Chapter 2 - Making of The Constitution MCQ PDFDocument13 pagesIndian Polity Chapter 2 - Making of The Constitution MCQ PDFmurthy gNo ratings yet
- Class 9 - Total History & Civics SolutionsDocument10 pagesClass 9 - Total History & Civics Solutionstanveer1976No ratings yet
- 10th Civics Must KnowDocument6 pages10th Civics Must KnowAryan MishraNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument16 pagesUntitled Documentgagangautamedu.officialNo ratings yet
- PT #1 - Question Paper + Answer KeyDocument57 pagesPT #1 - Question Paper + Answer KeyDevaraj BillaNo ratings yet
- 11th Notes AdilDocument50 pages11th Notes Adilfastfollow accountsNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge Final Lecture: by Anil Sir..!!Document124 pagesGeneral Knowledge Final Lecture: by Anil Sir..!!deepakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Indian ConstitutionDocument3 pagesChapter 1: The Indian ConstitutionnancyNo ratings yet
- Polity Question BankDocument66 pagesPolity Question BankTanisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Constitutional DesignDocument6 pagesConstitutional DesignAbheeram PatilNo ratings yet
- Pol - SC 1st ChapDocument7 pagesPol - SC 1st ChapRoshniNo ratings yet
- MCN202 Imp QuestionsDocument3 pagesMCN202 Imp QuestionsMohammed AsifNo ratings yet
- History ICSE Questions Class 10Document4 pagesHistory ICSE Questions Class 10Ankita Anand100% (1)
- NOTESDocument13 pagesNOTESst62452No ratings yet
- Fayaz SirDocument72 pagesFayaz Sirhaleem malikNo ratings yet
- Day-1 - Polity PDFDocument6 pagesDay-1 - Polity PDFAkash DeepNo ratings yet
- DAY 01 POLITY (Shashidthakur23.Wordpress - Com)Document6 pagesDAY 01 POLITY (Shashidthakur23.Wordpress - Com)AbhishekKurilNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Design Part B AnswersDocument4 pagesConstitutional Design Part B Answersrupayan majumderNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Design NotesDocument6 pagesConstitutional Design Notestindutt life timeNo ratings yet
- UPSC Mains General Studies Indian Polity and ConstitutionDocument10 pagesUPSC Mains General Studies Indian Polity and ConstitutionPankaj ChetryNo ratings yet
- Making of Constitution: Useful LinksDocument23 pagesMaking of Constitution: Useful Linksvivek kumarNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Neeed A GovernmentDocument8 pagesWhy Do We Neeed A GovernmentNeelNo ratings yet
- C8CCh1 The Indian ConstitutionDocument13 pagesC8CCh1 The Indian ConstitutionPieNo ratings yet
- The Union Legislature - WorksheetDocument1 pageThe Union Legislature - WorksheetRishta PorwalNo ratings yet
- IASbabas 60 Day Plan 2017 Day 1Document19 pagesIASbabas 60 Day Plan 2017 Day 1sabirNo ratings yet
- IASbaba's 60 Day Plan 2017 - Day 01 To Day 36Document681 pagesIASbaba's 60 Day Plan 2017 - Day 01 To Day 36Tapas SwainNo ratings yet
- (Gkmojo) Indian Polity Notes: 1. Framing of The ConstitutionDocument9 pages(Gkmojo) Indian Polity Notes: 1. Framing of The Constitutionananyaverma695No ratings yet
- Indian Polity Notes PDFDocument9 pagesIndian Polity Notes PDFUnmesh MitraNo ratings yet
- Polity LaxmikanthDocument35 pagesPolity LaxmikanthS100% (1)
- 2017-18 Hist Must Know QnsDocument6 pages2017-18 Hist Must Know QnsAdvait BhoreNo ratings yet
- POLITY 1.0 by Abhas SainiDocument39 pagesPOLITY 1.0 by Abhas SainiKeshav BhartiNo ratings yet
- 11th Class PaperDocument2 pages11th Class PaperAshutosh jabotraNo ratings yet
- Polity Set 5Document51 pagesPolity Set 5Manish ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Political Science Class XiDocument3 pagesSample Paper Political Science Class XisumeghaonlineNo ratings yet
- Political Science March 2020 STD 12th Arts HSC Maharashtra Board Question PaperDocument2 pagesPolitical Science March 2020 STD 12th Arts HSC Maharashtra Board Question PaperNew Prestige WelfareNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law-IDocument7 pagesConstitutional Law-IthesharemarketlearnerNo ratings yet
- Preamble, Federalism Abb0c53d 88bc 455a Ad11 16ce1401f65aDocument7 pagesPreamble, Federalism Abb0c53d 88bc 455a Ad11 16ce1401f65aaadhiimohan03No ratings yet
- Indian Constitution Exam PaperDocument4 pagesIndian Constitution Exam PaperNahid H Mazumder L15No ratings yet
- Short Answer QuestionsDocument11 pagesShort Answer QuestionsAaromal MaanasNo ratings yet
- UPSC Main Exam Indian Polity and Constitution Previous Years Questions The Pattern and TrendDocument12 pagesUPSC Main Exam Indian Polity and Constitution Previous Years Questions The Pattern and TrendJhansi LaxmiNo ratings yet
- Constitutional LawDocument7 pagesConstitutional LawGaming GodNo ratings yet
- 22ICO17 - Notes - 230511 - 090018Document23 pages22ICO17 - Notes - 230511 - 090018Pravaal Raj MishraNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Class 11 Pol Science Chapter 1Document4 pagesImportant Questions Class 11 Pol Science Chapter 1Prasun AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 2023 2024 Class VIII Social Studies Part 3 AWDocument5 pages2023 2024 Class VIII Social Studies Part 3 AWBRO IT’S DHARAHASNo ratings yet
- CH-3 Parliamentary GovernmentDocument6 pagesCH-3 Parliamentary GovernmentSanjiv BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Constitution of India Chapter 1Document10 pagesConstitution of India Chapter 1mmmmNo ratings yet
- CLAT PG 2019 Solutions Set ADocument26 pagesCLAT PG 2019 Solutions Set ASahana MathpatiNo ratings yet
- 2018 PolDocument16 pages2018 Polnitin pandeyNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law Questions III SemesterDocument4 pagesConstitutional Law Questions III SemesterAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Durga Das BasuDocument3 pagesDurga Das BasuArun Cse0% (1)
- Part B 1. About India-C-EDocument39 pagesPart B 1. About India-C-ESaYani SamaDdarNo ratings yet
- Extra Questions of Constitutional DesignDocument39 pagesExtra Questions of Constitutional Designaditya3421pNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet - Half YearlyDocument12 pagesRevision Worksheet - Half Yearlyrizzie12345.icecreamsNo ratings yet
- Hist8 - 2 Union Executive Drilling QuestionsDocument1 pageHist8 - 2 Union Executive Drilling QuestionsBFF ForeverNo ratings yet
- 7HCC1 The Constitution of IndiaDocument5 pages7HCC1 The Constitution of Indiakilleraarush27No ratings yet
- ISC Political Science 2016Document13 pagesISC Political Science 2016AVNISH PRAKASHNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsFrom EverandIndian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsNo ratings yet
- Komunikasyon at PananaliksikDocument73 pagesKomunikasyon at PananaliksikANGELU RANE BAGARES INTOL100% (2)
- Government Remarks Prime Minister How The Role Was FulfilledDocument2 pagesGovernment Remarks Prime Minister How The Role Was FulfilledTina MarianoNo ratings yet
- 72-74 - 08-4-The Situation in Southern RhodesiaDocument13 pages72-74 - 08-4-The Situation in Southern RhodesiaVasilije BlagojevicNo ratings yet
- Campus/Centre LocationDocument55 pagesCampus/Centre LocationToddy LaiNo ratings yet
- "Men, Women, and Work - Reflections On The Two-Person Career" - Hanna PapanekDocument21 pages"Men, Women, and Work - Reflections On The Two-Person Career" - Hanna PapanekMuseu da MONo ratings yet
- Models of Disability 222Document4 pagesModels of Disability 222ayenew kassahunNo ratings yet
- Adsum Notes - Public Corp Reviewer MidtermDocument13 pagesAdsum Notes - Public Corp Reviewer MidtermRaz SPNo ratings yet
- Somali Women'S Political Participation and Leadership-Evidence and OpportunitiesDocument29 pagesSomali Women'S Political Participation and Leadership-Evidence and OpportunitiesalexNo ratings yet
- Frontier: No Talks, No PeaceDocument16 pagesFrontier: No Talks, No PeaceGovindNo ratings yet
- Spousal Collection - Part 3Document79 pagesSpousal Collection - Part 3Queer OntarioNo ratings yet
- Karakachans in Bulgaria (Sarakatsani)Document6 pagesKarakachans in Bulgaria (Sarakatsani)valer_crushuveanlu100% (1)
- Talisay City, Cebu 6045 June 8, 2020: Roselan LabaoDocument4 pagesTalisay City, Cebu 6045 June 8, 2020: Roselan LabaoMichael MabiniNo ratings yet
- Pensatoryallowance Vide Go Ms 176 dt.15-12-2015 PDFDocument4 pagesPensatoryallowance Vide Go Ms 176 dt.15-12-2015 PDFSRIDHARNo ratings yet
- Midterm ExamDocument3 pagesMidterm ExamIya GadonNo ratings yet
- Footnote 20 - The Carter Center. (N.D.) - Observing Myanmar's 2015 General Elections. in Election Final Report.Document80 pagesFootnote 20 - The Carter Center. (N.D.) - Observing Myanmar's 2015 General Elections. in Election Final Report.Kyaw Zaw LinNo ratings yet
- Kwame Ture InterviewDocument8 pagesKwame Ture InterviewSumayya K AliNo ratings yet
- Final Supervisorial District Map Adopted by Sacramento County Board of SupervisorsDocument3 pagesFinal Supervisorial District Map Adopted by Sacramento County Board of SupervisorsGilbert CordovaNo ratings yet
- LLB 3 YDC COLLEGE LIST FEE-excelDocument5 pagesLLB 3 YDC COLLEGE LIST FEE-excelsumanthNo ratings yet
- FPJ International Epaper-21!08!2023Document21 pagesFPJ International Epaper-21!08!2023sagart817296No ratings yet
- Local Government in England: Structures: Briefing PaperDocument22 pagesLocal Government in England: Structures: Briefing PaperSanya Atta SangharNo ratings yet
- Notice ER16323 13122023Document30 pagesNotice ER16323 13122023Jeet GuptaNo ratings yet
- Partition of Bengal - 1905Document28 pagesPartition of Bengal - 1905Reshan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Afterall. A Journal of Art, Context and Enquiry, (Volume 42. AutumnWinter 2016)Document158 pagesAfterall. A Journal of Art, Context and Enquiry, (Volume 42. AutumnWinter 2016)Sangue CorsárioNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On French RevolutionDocument4 pagesTerm Paper On French Revolutionafmzswxbbbbitf100% (1)
- Critic To Zartman - Rothstein-TimingDocument21 pagesCritic To Zartman - Rothstein-TimingElton TivaneNo ratings yet
- PDF A Pocket Guide To The Us Constitution What Every American Needs To Know Andrew B Arnold Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF A Pocket Guide To The Us Constitution What Every American Needs To Know Andrew B Arnold Ebook Full Chapterjennifer.nye440100% (6)
- Moulding The Socialist Subject: Xiaoning LU - 978-90-04-42352-7 Via Free AccessDocument212 pagesMoulding The Socialist Subject: Xiaoning LU - 978-90-04-42352-7 Via Free Accessjeff tehNo ratings yet
- Allah - Bux.soomro Apostle - Of.secular - Harmony Khadim - Soomro. (2006) .CsDocument205 pagesAllah - Bux.soomro Apostle - Of.secular - Harmony Khadim - Soomro. (2006) .CsAnonymous lviObMpprNo ratings yet