Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antiepileptic Drugs
Antiepileptic Drugs
Uploaded by
Ach Ri Fa ICopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CAT G3500 Gas Engine Maintenance ScheduleDocument3 pagesCAT G3500 Gas Engine Maintenance ScheduleQaiser Iqbal67% (6)
- Antiepileptic Medicines Shanbhag ShenoyDocument9 pagesAntiepileptic Medicines Shanbhag Shenoyshaziashaziashazia2001No ratings yet
- CNS Depressants - Anxiolytics & Sedative HypnoticsDocument4 pagesCNS Depressants - Anxiolytics & Sedative HypnoticsJustin HulinNo ratings yet
- 14-Chapter 17-Drugs For EpilepsyDocument23 pages14-Chapter 17-Drugs For EpilepsyCandilicious10No ratings yet
- AntidepressantsDocument4 pagesAntidepressantsAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- CNS Drugs-2Document34 pagesCNS Drugs-2semessor021245No ratings yet
- GROUP 2: Azuelo, Cano Pacheco, Inoc, Pareja, TejanoDocument5 pagesGROUP 2: Azuelo, Cano Pacheco, Inoc, Pareja, TejanoJesette KhoNo ratings yet
- CNS DrugsDocument57 pagesCNS DrugsHussein Al-jmrawiNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia PharmacologyDocument12 pagesAnesthesia PharmacologyMagy SnowNo ratings yet
- Zalameda CNS-PNSDocument43 pagesZalameda CNS-PNSNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Pharmalab 17Document5 pagesPharmalab 17Medisina StoreNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs 2019 Elearning PDFDocument39 pagesAntiepileptic Drugs 2019 Elearning PDFMalvika BabuNo ratings yet
- 2010 (Chapter19 Final) Epilepsies 2Document20 pages2010 (Chapter19 Final) Epilepsies 2Candilicious10No ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Neuro PharmacologyDocument3 pagesDrugs Used in Neuro PharmacologyNabeel Kouka, MD, DO, MBA, MPH100% (1)
- Farmakologi Dari Obat EpilepsiDocument82 pagesFarmakologi Dari Obat EpilepsiDion SaputraNo ratings yet
- Anti-Epileptic Drugs: Causes of EpilepsyDocument4 pagesAnti-Epileptic Drugs: Causes of EpilepsyElijah ChiumyaNo ratings yet
- Anti DepressantDocument6 pagesAnti Depressantyahyaahmed152000No ratings yet
- AnxiolyticsDocument8 pagesAnxiolyticsAlfie16No ratings yet
- Activity 2 Drug Study LinaoDocument21 pagesActivity 2 Drug Study LinaoNursing ClassNo ratings yet
- DrugofchoiceDocument16 pagesDrugofchoiceAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Obat Anti Konvulsan - CompressedDocument52 pagesObat Anti Konvulsan - CompressedNianurmayanti983278No ratings yet
- Medications TackledDocument3 pagesMedications TackledAl-Khan HadjailNo ratings yet
- Anti-Epileptic DrugsDocument7 pagesAnti-Epileptic DrugsSampada ghodkiNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocument11 pagesAntiepileptic DrugsSalmoon SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Pharmacology - Drug TableDocument2 pagesCholinergic Pharmacology - Drug TableFNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument3 pagesDiazepamGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- CH 28 Nausea/VomitingDocument2 pagesCH 28 Nausea/VomitingkandeeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyVenus April LimonNo ratings yet
- Dimentia EpilepsyDocument7 pagesDimentia EpilepsyoladapoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Tofranil J Zoloft)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Tofranil J Zoloft)alteahmichaella.mintuNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocument3 pagesAntiepileptic DrugsPratham KhairnarNo ratings yet
- Conventional Antiepileptic Drugs: Presented by Dr. Mehnaz MahmoodaDocument41 pagesConventional Antiepileptic Drugs: Presented by Dr. Mehnaz MahmoodaMehediNo ratings yet
- I. Drug Study: Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesI. Drug Study: Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Considerationscyn yana0723No ratings yet
- PH - Karrar HaderDocument33 pagesPH - Karrar HaderAdnan YassinNo ratings yet
- 2015 AntiepilepticsDocument36 pages2015 AntiepilepticsRumaidhil AbroryNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Class - DrdhritiDocument81 pagesEpilepsy Class - DrdhritidbrahmaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology (All Lectures)Document283 pagesPharmacology (All Lectures)Youssef ElzataryNo ratings yet
- THERAPEUTIC CATEGORIES - Docx 2Document15 pagesTHERAPEUTIC CATEGORIES - Docx 2mqdzpmjp2rNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Cns - Dd22Document29 pagesDrugs Acting On Cns - Dd22vabinh.dd2022No ratings yet
- 13 - Antiseizure AgentsDocument145 pages13 - Antiseizure AgentsALJHON OSORIONo ratings yet
- Null 1Document60 pagesNull 1tbuyinza21apNo ratings yet
- Muscarine & Nicotinic: ReceptorDocument26 pagesMuscarine & Nicotinic: ReceptorCess Lagera Ybanez88% (17)
- AntiepilepticsDocument52 pagesAntiepilepticsAkshay NirwalNo ratings yet
- Er-Drug StudyDocument41 pagesEr-Drug Studyrc_lacampuinganyahooNo ratings yet
- EPILEPSYDocument22 pagesEPILEPSYlakshitataneja1998No ratings yet
- Limos Drug-StudyDocument2 pagesLimos Drug-StudyClaire LimosNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Is Due To Sudden, Excessive Depolarization Of: Some or All Cerebral NeuronsDocument19 pagesEpilepsy Is Due To Sudden, Excessive Depolarization Of: Some or All Cerebral NeuronsMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Case AnalysisDocument7 pagesDrug Study Case AnalysisNine SaguiboNo ratings yet
- Anti ConvulsantDocument42 pagesAnti ConvulsantAkmal SafwanNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Handbook of Pharmacotherapy 1Document26 pagesEpilepsy Handbook of Pharmacotherapy 1Sajia Abedin 1821432649No ratings yet
- Anesthesia Drugs Cheat SheetDocument10 pagesAnesthesia Drugs Cheat Sheetapolan2No ratings yet
- Pharmacology ANS DrugsDocument1 pagePharmacology ANS DrugsCharissa NgNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapeutic RecordDocument10 pagesDrug Therapeutic RecordstrawberryNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Sedative DrugsDocument55 pagesPharmacology of Sedative DrugswgalalNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology (1) - 104-122Document19 pagesPharmacology (1) - 104-122Dental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- Status EpilepticusDocument3 pagesStatus EpilepticusVandeosNo ratings yet
- Drugs FOR Psychiatric & Neurologic Disorders: Clonazepam (Klonopin, Rivotril) Midazolam (Versed, Dormicum)Document5 pagesDrugs FOR Psychiatric & Neurologic Disorders: Clonazepam (Klonopin, Rivotril) Midazolam (Versed, Dormicum)Noriko MatsumotoNo ratings yet
- AntiConvulsants Drugs in Brief PDFDocument28 pagesAntiConvulsants Drugs in Brief PDFSunilNo ratings yet
- LcetamDocument40 pagesLcetampabitraNo ratings yet
- The Association Between Community-Associated Staphylococcus Aureus Colonization and Disease: A Meta-AnalysisDocument11 pagesThe Association Between Community-Associated Staphylococcus Aureus Colonization and Disease: A Meta-AnalysisAch Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Anti DepressentsDocument2 pagesAnti DepressentsAch Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Nutrition Support and Dietary Interventions For Patients With Lung Cancer Current InsightsDocument10 pagesNutrition Support and Dietary Interventions For Patients With Lung Cancer Current InsightsAch Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Diabetes 1Document14 pagesDiabetes 1Ach Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Coping Strategies, Optimism, and Life SatisfactionDocument12 pagesCoping Strategies, Optimism, and Life SatisfactionNurulAtiqahAbRajiNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Principles and Practices 20CS44P: WEEK-6: Requirement Engineering & ModelingDocument9 pagesSoftware Engineering Principles and Practices 20CS44P: WEEK-6: Requirement Engineering & ModelingManjunatha OkNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Model ExamDocument20 pagesAnalog Communication Model ExamwalternampimadomNo ratings yet
- GCT LTE Module Software Development Guide: Aquila Solutions IncDocument26 pagesGCT LTE Module Software Development Guide: Aquila Solutions IncLionel MusonzaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Enterprise Asset ManagementDocument4 pagesOracle Enterprise Asset ManagementMH.SezanNo ratings yet
- TQ UcspDocument11 pagesTQ UcspDeron C. De CastroNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0039914010004352 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0039914010004352 MainHesti HariantiNo ratings yet
- VT572 Microwave Radar Motion Movement Sensor Detector Datasheet (Vutlan)Document16 pagesVT572 Microwave Radar Motion Movement Sensor Detector Datasheet (Vutlan)gm4984371No ratings yet
- Recognition and Extinction of StatesDocument4 pagesRecognition and Extinction of StatesCristy C. BangayanNo ratings yet
- BI Strategy Roadmap Final v1.3Document201 pagesBI Strategy Roadmap Final v1.3Ange OraudNo ratings yet
- Comandos de ScilabDocument11 pagesComandos de ScilabAlejandro Galindo Vega0% (1)
- AN1184 Application Note: Bu808Dfi in The Horizontal Deflection StageDocument13 pagesAN1184 Application Note: Bu808Dfi in The Horizontal Deflection StagetrmnmyNo ratings yet
- Physica Medica: Slobodan Devic, Nada Tomic, David LewisDocument16 pagesPhysica Medica: Slobodan Devic, Nada Tomic, David LewisFrederico GomesNo ratings yet
- Silvia Rey Resume OkDocument3 pagesSilvia Rey Resume Okapi-489656705No ratings yet
- Mikala Conway - Meal PlanDocument3 pagesMikala Conway - Meal Planmikala conwayNo ratings yet
- The Word Wall: Chants and Cheers ActivitiesDocument5 pagesThe Word Wall: Chants and Cheers Activitieseva.bensonNo ratings yet
- Arun Saldanha - Psychedelic White - Goa Trance and The Viscosity of Race (2007)Document252 pagesArun Saldanha - Psychedelic White - Goa Trance and The Viscosity of Race (2007)Pulse DemonNo ratings yet
- Implicit and Explicit InformationDocument3 pagesImplicit and Explicit InformationAbbas GholamiNo ratings yet
- Part EM - Classical ElectrodynamicsDocument415 pagesPart EM - Classical Electrodynamicsapoorva singhNo ratings yet
- Joint Summary SheetDocument1 pageJoint Summary Sheetchandana kumarNo ratings yet
- About EthiopianDocument7 pagesAbout EthiopianTiny GechNo ratings yet
- Super VIP Cheat Sheet: Arti Cial IntelligenceDocument18 pagesSuper VIP Cheat Sheet: Arti Cial IntelligenceAthaurRahmanNo ratings yet
- Ingovern Series Electronic Engine Speed Governor Instruction ManualDocument44 pagesIngovern Series Electronic Engine Speed Governor Instruction Manualfelipe floresNo ratings yet
- The Ascent and Decline of A Great Balneological Resort: PucioasaDocument6 pagesThe Ascent and Decline of A Great Balneological Resort: PucioasaStefan RaduNo ratings yet
- Globalization and Human RightsDocument13 pagesGlobalization and Human Rightsjeffcohen04No ratings yet
- When Things Go Wrong, Reach For Devcon: Maintenance RepairDocument20 pagesWhen Things Go Wrong, Reach For Devcon: Maintenance RepairJuanNo ratings yet
- Practicallist11 1Document1 pagePracticallist11 1vikas_2No ratings yet
- Cyclotron PDFDocument5 pagesCyclotron PDFRaju YadavNo ratings yet
- Argumentative Essay: The Willingness of The Community To Participate in Nationwide VaccinationDocument3 pagesArgumentative Essay: The Willingness of The Community To Participate in Nationwide VaccinationKathleen JimenezNo ratings yet
Antiepileptic Drugs
Antiepileptic Drugs
Uploaded by
Ach Ri Fa IOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antiepileptic Drugs
Antiepileptic Drugs
Uploaded by
Ach Ri Fa ICopyright:
Available Formats
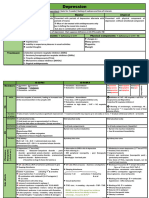
Antiepileptic drugs
Types of epilepsy (reading only)
1- Partial Seizures ( Focal Seizures ) 2- Generalized Seizures
- NO loss of conscious Tonic clonic - loss of consciousness - tonic spasm (1 min) clonic jerking
Simple - Clonic jerking of single limb or a muscle group lasting for about 2 min. seizures - Flaccid relaxation - confusion & fatigue - sleep
partial - there maybe some sensory disturbances. Absence - there is brief loss of consciousness lasting only for 10 to 15 sec. with mild or no motor
seizures disturbances.
Complex - there is brief loss of consciousness followed by amnesia.
partial - Purposeless movements & sensory hallucinations. Myoclonic - NO loss of conscious
seizures - Short jerking of the whole body or one of the extremities.
Partial with Partial seizures that is followed immediately by generalized attack due to spread of discharge.
secondarily Atonic
- Sudden loss of posture tone Fall.
seizures seizures
3- Status Epilepticus
Epilepticus - Severe sustained seizures without period or recovery. - It occurs in all types of epilepsy especially if treatment is irregular or suddenly stopped.
Mechanism of action of antiepileptic drugs Drug Choice
- First choice: Carbamazapine & Phenytoin
Tonic clonic
- Alternative : Valproate.
seizures
Drugs that are effective in seizure reduction accomplish this by - Phenobarbital & primidone (Barbiturates)
variety of mechanisms: - First choice: Carbamazapine & Phenytoin
Simple partial - Alternative : Valproate - Lamotrigine , Vigabatrin , Gabapentin ( mono or add on )
1- blockade of voltage-gated channels (Na+ or Ca2+), - Phenobarbital & primidone
2- enhancement of inhibitory GABAergic impulses, - First choice: Ethosuximide
3- interference with excitatory glutamate transmission. Absence seizures - Alternative : Valproat - Lamotrigine - clonazepam
- Acetazolamide.
The antiepilepsy drugs suppress seizures but do not recur or prevent - Mixed :
Absence seizures + Tonic clonic - First choice: Valproate
epilepsy. - Alternative : clonazepam
- Myoclonic seizures
Status Epilepticus Diazepam – clonazepam – Phenytoin – Phenobarbiton - Paraldehyde
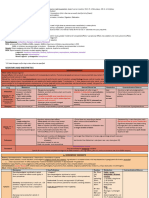
Antiepileptic Drugs
Phenytoin Carbamazepine Barbiturates & Benzodiazepines
- Normal concentration of drug : (check Ahmados sedatives & hypnotics papers)
It blocks voltage-gated sodium channels by selectively binding
to the channel in the inactive state thereby inhibiting the
generation of repetitive action potentials in the epileptic focus The primary mechanism of action is the enhancement of
and preventing their spread. Mechanism like phenytoin inhibitory effects of GABA-mediated neurons, via
increase the frequency of chloride channel opening by
- At very high concentrations, binding to the GABAA receptor.
phenytoin can block voltage-dependent calcium channels and
interfere with the release of monoaminergic neurotransmitters. Diazepam, and lorazepam are most often used as an therapy for :
1- myoclonic 2- partial 3- generalized tonic-clonic seizures.
Side effects Side effects Side effects
- Depression of the CNS occurs particularly in the cerebellum
and vestibular system, causing : - nystagmus , ataxia - Rash - Anorexia
- peripheral neuropathies - osteoporosis. - Nystagmus - anti-diuretic
- confusion & Hallucinations. - Hepatotoxicity. - Ataxia - Hepatitis
- Teratogenic - Bone marrow inhibition (check Ahmados sedatives & hypnotics papers)
- Hormones: release of A.D.H & insulin (hyperglycemia)
- Hirsutism. - Teratogenic.
Fosphenytoin Oxcarbazepine
It is a prodrug and is rapidly converted to phenytoin in It is a prodrug that is rapidly reduced to the 10-monohydroxy
the blood, providing high levels of phenytoin within min. (MHD) MHD blocks sodium channels preventing the spread of
the abnormal discharge producing anticonvulsant activity.
Phernytoin , Carbamazepine & Barbiturates 1-Hepatic microsomal enzyme inducer (drug interactions) 2-Treat Tonic clonic & partial seizures 3-wosens Absence
Ethosuximide Divalproex Acetazolamide
It blocks T-type calcium channels so, reduces Divalproex sodium is a combination of: It's carbonic anhydrase inhibitor Increase CO2
propagation of abnormal electrical activity in the brain sodium valproate + valproic acid & Acidosis decrease CNS excitability
and is reduced to valproate when it reaches the gastrointestinal tract.
It is effective in treating only primary generalized
absence seizures. Usefula in Absence seizures
- Proposed mechanisms of action include:
1-sodium channel blockade,
Side effects 2- blockade of GABA transaminase, Side effects
- CNS Drowsiness , Lethargy , behavioral changes 3- action at the T-type calcium channels. - Hypokalemia - alkaline urine
- GIT upset - Sedation - acidosis
These many mechanisms provide a broad spectrum of activity
- Allergy against seizures.
Trimethadione Side effects
- GI distress,
- hepatotoxicity due to formation of toxic metabolite,
Mechanism like Ethosuximide - pancreatitis
Side effects - alopecia,
- tremor,
- CNS Drowsiness , Lethargy , behavioral changes - Photosensitivity
- GIT upset - Hepatic microsomal enzyme inhibitor.
- Allergy
- Hepatotoxicity – Nephrotoxicity – Bone marrow depression
New Anti-Epileptic Drugs
Lamotrigine Topiramate Felbamate Gabapentin Tiagabin Vigabatrin
The drug blocks : 1- It blocks sodium channels; 1- It blocks sodium channels;
Tiagabine blocks GABA uptake
1- sodium channels 2- The primary mechanism of 2- The primary mechanism of Gabapentin is an analog of GABA. It's irreversible inhibitor of
into presynaptic neurons,
2- voltage dependent action is the enhancement of action is the enhancement of GABA transaminase
inhibitory effects of GABA- inhibitory effects of GABA- permitting more GABA to be
calcium channels. It increases the release of resulting in increase the GABA
mediated neurons mediated neurons available for receptor binding
GABA
3- antagonize the excitatory 3- antagonize the excitatory thus, enhanced inhibitory
transmitters e.g: glutamate . transmitters e.g: glutamate activity.
Side effect : Side effect : Side effect : Side effect : Side effect : Side effect :
Rash - Dermatits Sedation - confusion Fatal aplastic anemia Sedation - ataxia tiredness, dizziness, GIT upset. Depression - Psychosis
You might also like
- CAT G3500 Gas Engine Maintenance ScheduleDocument3 pagesCAT G3500 Gas Engine Maintenance ScheduleQaiser Iqbal67% (6)
- Antiepileptic Medicines Shanbhag ShenoyDocument9 pagesAntiepileptic Medicines Shanbhag Shenoyshaziashaziashazia2001No ratings yet
- CNS Depressants - Anxiolytics & Sedative HypnoticsDocument4 pagesCNS Depressants - Anxiolytics & Sedative HypnoticsJustin HulinNo ratings yet
- 14-Chapter 17-Drugs For EpilepsyDocument23 pages14-Chapter 17-Drugs For EpilepsyCandilicious10No ratings yet
- AntidepressantsDocument4 pagesAntidepressantsAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- CNS Drugs-2Document34 pagesCNS Drugs-2semessor021245No ratings yet
- GROUP 2: Azuelo, Cano Pacheco, Inoc, Pareja, TejanoDocument5 pagesGROUP 2: Azuelo, Cano Pacheco, Inoc, Pareja, TejanoJesette KhoNo ratings yet
- CNS DrugsDocument57 pagesCNS DrugsHussein Al-jmrawiNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia PharmacologyDocument12 pagesAnesthesia PharmacologyMagy SnowNo ratings yet
- Zalameda CNS-PNSDocument43 pagesZalameda CNS-PNSNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Pharmalab 17Document5 pagesPharmalab 17Medisina StoreNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs 2019 Elearning PDFDocument39 pagesAntiepileptic Drugs 2019 Elearning PDFMalvika BabuNo ratings yet
- 2010 (Chapter19 Final) Epilepsies 2Document20 pages2010 (Chapter19 Final) Epilepsies 2Candilicious10No ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Neuro PharmacologyDocument3 pagesDrugs Used in Neuro PharmacologyNabeel Kouka, MD, DO, MBA, MPH100% (1)
- Farmakologi Dari Obat EpilepsiDocument82 pagesFarmakologi Dari Obat EpilepsiDion SaputraNo ratings yet
- Anti-Epileptic Drugs: Causes of EpilepsyDocument4 pagesAnti-Epileptic Drugs: Causes of EpilepsyElijah ChiumyaNo ratings yet
- Anti DepressantDocument6 pagesAnti Depressantyahyaahmed152000No ratings yet
- AnxiolyticsDocument8 pagesAnxiolyticsAlfie16No ratings yet
- Activity 2 Drug Study LinaoDocument21 pagesActivity 2 Drug Study LinaoNursing ClassNo ratings yet
- DrugofchoiceDocument16 pagesDrugofchoiceAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Obat Anti Konvulsan - CompressedDocument52 pagesObat Anti Konvulsan - CompressedNianurmayanti983278No ratings yet
- Medications TackledDocument3 pagesMedications TackledAl-Khan HadjailNo ratings yet
- Anti-Epileptic DrugsDocument7 pagesAnti-Epileptic DrugsSampada ghodkiNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocument11 pagesAntiepileptic DrugsSalmoon SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Pharmacology - Drug TableDocument2 pagesCholinergic Pharmacology - Drug TableFNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument3 pagesDiazepamGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- CH 28 Nausea/VomitingDocument2 pagesCH 28 Nausea/VomitingkandeeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyVenus April LimonNo ratings yet
- Dimentia EpilepsyDocument7 pagesDimentia EpilepsyoladapoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Tofranil J Zoloft)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Tofranil J Zoloft)alteahmichaella.mintuNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocument3 pagesAntiepileptic DrugsPratham KhairnarNo ratings yet
- Conventional Antiepileptic Drugs: Presented by Dr. Mehnaz MahmoodaDocument41 pagesConventional Antiepileptic Drugs: Presented by Dr. Mehnaz MahmoodaMehediNo ratings yet
- I. Drug Study: Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesI. Drug Study: Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Considerationscyn yana0723No ratings yet
- PH - Karrar HaderDocument33 pagesPH - Karrar HaderAdnan YassinNo ratings yet
- 2015 AntiepilepticsDocument36 pages2015 AntiepilepticsRumaidhil AbroryNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Class - DrdhritiDocument81 pagesEpilepsy Class - DrdhritidbrahmaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology (All Lectures)Document283 pagesPharmacology (All Lectures)Youssef ElzataryNo ratings yet
- THERAPEUTIC CATEGORIES - Docx 2Document15 pagesTHERAPEUTIC CATEGORIES - Docx 2mqdzpmjp2rNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Cns - Dd22Document29 pagesDrugs Acting On Cns - Dd22vabinh.dd2022No ratings yet
- 13 - Antiseizure AgentsDocument145 pages13 - Antiseizure AgentsALJHON OSORIONo ratings yet
- Null 1Document60 pagesNull 1tbuyinza21apNo ratings yet
- Muscarine & Nicotinic: ReceptorDocument26 pagesMuscarine & Nicotinic: ReceptorCess Lagera Ybanez88% (17)
- AntiepilepticsDocument52 pagesAntiepilepticsAkshay NirwalNo ratings yet
- Er-Drug StudyDocument41 pagesEr-Drug Studyrc_lacampuinganyahooNo ratings yet
- EPILEPSYDocument22 pagesEPILEPSYlakshitataneja1998No ratings yet
- Limos Drug-StudyDocument2 pagesLimos Drug-StudyClaire LimosNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Is Due To Sudden, Excessive Depolarization Of: Some or All Cerebral NeuronsDocument19 pagesEpilepsy Is Due To Sudden, Excessive Depolarization Of: Some or All Cerebral NeuronsMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Case AnalysisDocument7 pagesDrug Study Case AnalysisNine SaguiboNo ratings yet
- Anti ConvulsantDocument42 pagesAnti ConvulsantAkmal SafwanNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Handbook of Pharmacotherapy 1Document26 pagesEpilepsy Handbook of Pharmacotherapy 1Sajia Abedin 1821432649No ratings yet
- Anesthesia Drugs Cheat SheetDocument10 pagesAnesthesia Drugs Cheat Sheetapolan2No ratings yet
- Pharmacology ANS DrugsDocument1 pagePharmacology ANS DrugsCharissa NgNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapeutic RecordDocument10 pagesDrug Therapeutic RecordstrawberryNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Sedative DrugsDocument55 pagesPharmacology of Sedative DrugswgalalNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology (1) - 104-122Document19 pagesPharmacology (1) - 104-122Dental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- Status EpilepticusDocument3 pagesStatus EpilepticusVandeosNo ratings yet
- Drugs FOR Psychiatric & Neurologic Disorders: Clonazepam (Klonopin, Rivotril) Midazolam (Versed, Dormicum)Document5 pagesDrugs FOR Psychiatric & Neurologic Disorders: Clonazepam (Klonopin, Rivotril) Midazolam (Versed, Dormicum)Noriko MatsumotoNo ratings yet
- AntiConvulsants Drugs in Brief PDFDocument28 pagesAntiConvulsants Drugs in Brief PDFSunilNo ratings yet
- LcetamDocument40 pagesLcetampabitraNo ratings yet
- The Association Between Community-Associated Staphylococcus Aureus Colonization and Disease: A Meta-AnalysisDocument11 pagesThe Association Between Community-Associated Staphylococcus Aureus Colonization and Disease: A Meta-AnalysisAch Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Anti DepressentsDocument2 pagesAnti DepressentsAch Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Nutrition Support and Dietary Interventions For Patients With Lung Cancer Current InsightsDocument10 pagesNutrition Support and Dietary Interventions For Patients With Lung Cancer Current InsightsAch Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Diabetes 1Document14 pagesDiabetes 1Ach Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Coping Strategies, Optimism, and Life SatisfactionDocument12 pagesCoping Strategies, Optimism, and Life SatisfactionNurulAtiqahAbRajiNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Principles and Practices 20CS44P: WEEK-6: Requirement Engineering & ModelingDocument9 pagesSoftware Engineering Principles and Practices 20CS44P: WEEK-6: Requirement Engineering & ModelingManjunatha OkNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Model ExamDocument20 pagesAnalog Communication Model ExamwalternampimadomNo ratings yet
- GCT LTE Module Software Development Guide: Aquila Solutions IncDocument26 pagesGCT LTE Module Software Development Guide: Aquila Solutions IncLionel MusonzaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Enterprise Asset ManagementDocument4 pagesOracle Enterprise Asset ManagementMH.SezanNo ratings yet
- TQ UcspDocument11 pagesTQ UcspDeron C. De CastroNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0039914010004352 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0039914010004352 MainHesti HariantiNo ratings yet
- VT572 Microwave Radar Motion Movement Sensor Detector Datasheet (Vutlan)Document16 pagesVT572 Microwave Radar Motion Movement Sensor Detector Datasheet (Vutlan)gm4984371No ratings yet
- Recognition and Extinction of StatesDocument4 pagesRecognition and Extinction of StatesCristy C. BangayanNo ratings yet
- BI Strategy Roadmap Final v1.3Document201 pagesBI Strategy Roadmap Final v1.3Ange OraudNo ratings yet
- Comandos de ScilabDocument11 pagesComandos de ScilabAlejandro Galindo Vega0% (1)
- AN1184 Application Note: Bu808Dfi in The Horizontal Deflection StageDocument13 pagesAN1184 Application Note: Bu808Dfi in The Horizontal Deflection StagetrmnmyNo ratings yet
- Physica Medica: Slobodan Devic, Nada Tomic, David LewisDocument16 pagesPhysica Medica: Slobodan Devic, Nada Tomic, David LewisFrederico GomesNo ratings yet
- Silvia Rey Resume OkDocument3 pagesSilvia Rey Resume Okapi-489656705No ratings yet
- Mikala Conway - Meal PlanDocument3 pagesMikala Conway - Meal Planmikala conwayNo ratings yet
- The Word Wall: Chants and Cheers ActivitiesDocument5 pagesThe Word Wall: Chants and Cheers Activitieseva.bensonNo ratings yet
- Arun Saldanha - Psychedelic White - Goa Trance and The Viscosity of Race (2007)Document252 pagesArun Saldanha - Psychedelic White - Goa Trance and The Viscosity of Race (2007)Pulse DemonNo ratings yet
- Implicit and Explicit InformationDocument3 pagesImplicit and Explicit InformationAbbas GholamiNo ratings yet
- Part EM - Classical ElectrodynamicsDocument415 pagesPart EM - Classical Electrodynamicsapoorva singhNo ratings yet
- Joint Summary SheetDocument1 pageJoint Summary Sheetchandana kumarNo ratings yet
- About EthiopianDocument7 pagesAbout EthiopianTiny GechNo ratings yet
- Super VIP Cheat Sheet: Arti Cial IntelligenceDocument18 pagesSuper VIP Cheat Sheet: Arti Cial IntelligenceAthaurRahmanNo ratings yet
- Ingovern Series Electronic Engine Speed Governor Instruction ManualDocument44 pagesIngovern Series Electronic Engine Speed Governor Instruction Manualfelipe floresNo ratings yet
- The Ascent and Decline of A Great Balneological Resort: PucioasaDocument6 pagesThe Ascent and Decline of A Great Balneological Resort: PucioasaStefan RaduNo ratings yet
- Globalization and Human RightsDocument13 pagesGlobalization and Human Rightsjeffcohen04No ratings yet
- When Things Go Wrong, Reach For Devcon: Maintenance RepairDocument20 pagesWhen Things Go Wrong, Reach For Devcon: Maintenance RepairJuanNo ratings yet
- Practicallist11 1Document1 pagePracticallist11 1vikas_2No ratings yet
- Cyclotron PDFDocument5 pagesCyclotron PDFRaju YadavNo ratings yet
- Argumentative Essay: The Willingness of The Community To Participate in Nationwide VaccinationDocument3 pagesArgumentative Essay: The Willingness of The Community To Participate in Nationwide VaccinationKathleen JimenezNo ratings yet