Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trig Formulas
Trig Formulas
Uploaded by
Farukh ShaikhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trig Formulas
Trig Formulas
Uploaded by
Farukh ShaikhCopyright:
Available Formats
Special Factoring Arc Length and Angular Speed
( )( )
( )
( )
( )( ) Dimensional analysis conversion factors
( )( )
Converting Between Degree & Radian Measure
To convert from degree to radian measure, Variables
multiply by ( )
( )
To convert from radian to degree measure,
( )
multiply by ( )
Trig Functions of an Acute Angle
Trigonometric Identities
Reciprocal Identities Cofunction Identities
, ( ) , ( )
, ( ) , ( )
, ( ) , ( )
Ratio Identities Double-Angle Identities
,
Odd-Even Identities
( ) , ( ) , ( )
( ) , ( ) , ( )
Half-Angle Identities
Pythagorean Identities
√ √
√
Sum and Difference Identities
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
Solving Triangles
Law of Sines Law of Cosines Area of a Triangle
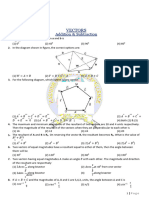
Vectors
The component form of ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ with ( ) and ( ) is ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ 〈 〉
The magnitude of a vector with component form 〈 〉 is |⃗ | √
The reference angle for the direction angle of the vector 〈 〉 is given by . Figure out
which quadrant this angle should be in and measure the angle counterclockwise from the positive x-axis.
The horizontal component of the vector 〈 〉 is | |
The vertical component of the vector 〈 〉 is | |
For a real number and a vector 〈 〉, the scalar product of and is 〈 〉 〈 〉. The vector is a
scalar multiple of the vector .
Vector Addition/Subtraction: If ⃗ 〈 〉 and 〈 〉, then ⃗ ⃗ 〈 〉.
⃗
If is a vector and ⃗ , then is a unit vector (vector with magnitude 1) in the direction of .
|⃗ |
The dot product of two vectors ⃗ 〈 〉 and 〈 〉 is ⃗ ⃗ .
⃗⃗ ⃗
If is the angle between two nonzero vectors ⃗ and , then |⃗⃗ ||⃗ |
.
Trigonometric Form of Complex Numbers
A complex number , where √ can be written in trigonometric form as
( ) or , where √ is the modulus of and direction angle is referred to as the argument.
[ ( ) ( )]
[ ( ) ( )]
[ ( ) ( )] ( )
You might also like
- Geometry Transformation Guided Notes 1Document18 pagesGeometry Transformation Guided Notes 1api-287816312100% (1)
- Montessori Constructive Triangle Command CardsDocument5 pagesMontessori Constructive Triangle Command CardsJennifer Norman Oliver100% (2)
- Shapes Worsheet PDFDocument31 pagesShapes Worsheet PDFCarmenEnidOrtizNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: "The Established Leader in Ee Review" Legit Multivector Review and Training CenterDocument6 pagesTrigonometry: "The Established Leader in Ee Review" Legit Multivector Review and Training CenterJohn RatillaNo ratings yet
- DIFFCAL FormulaDocument7 pagesDIFFCAL FormulaRocelle Andrea BelandresNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric FunctionsDocument11 pagesTrigonometric FunctionssatyajitadrijaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Vectors and The Geometry of SpaceDocument4 pagesChapter 12: Vectors and The Geometry of SpaceBenjamin Benicarlo Juanillo IIINo ratings yet
- MR Harish Chandra Rajpoot: M.M.M. University of Technology, Gorakhpur-273010 (UP), IndiaDocument11 pagesMR Harish Chandra Rajpoot: M.M.M. University of Technology, Gorakhpur-273010 (UP), IndiaSherlock_GrzegorjNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematcs MH201E Unit 4. TrigonometryDocument10 pagesEngineering Mathematcs MH201E Unit 4. TrigonometrySamir GedamNo ratings yet
- Vector Algebra NotesDocument11 pagesVector Algebra Notesketaki.mahajanNo ratings yet
- Differential Geometry M Usman HamidDocument125 pagesDifferential Geometry M Usman HamidKalaiNo ratings yet
- Numerical Problem F.Sc. Physics, Chapter # 2: Vectors and EquilibriumDocument6 pagesNumerical Problem F.Sc. Physics, Chapter # 2: Vectors and EquilibriumAli hassanNo ratings yet
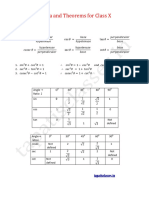
- Formula and Theorems For Class XDocument12 pagesFormula and Theorems For Class XPraneel .SNo ratings yet
- Differential Geometry M Usman HamidDocument126 pagesDifferential Geometry M Usman HamidLuqman ArshadNo ratings yet
- Electrodynamics (Gradient, Divergence and Curl)Document6 pagesElectrodynamics (Gradient, Divergence and Curl)Jay NahataNo ratings yet
- Answer of Final Exam Geometry May 2014 For Preparatory Year QuestionDocument4 pagesAnswer of Final Exam Geometry May 2014 For Preparatory Year QuestionMhmdÁbdóNo ratings yet
- Phy 4201 (2) 1Document4 pagesPhy 4201 (2) 1Emon HossainNo ratings yet
- CC Domain Math - 5 FNDocument14 pagesCC Domain Math - 5 FNpranit shankarNo ratings yet
- AS Maths Pure ChecklistDocument2 pagesAS Maths Pure Checklististvan.szaboNo ratings yet
- Motion in PlaneDocument15 pagesMotion in PlaneKajol HNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - PhyDocument13 pagesCh3 - Phylarasamen1997No ratings yet
- Control Chapter 6Document15 pagesControl Chapter 6Ali MadridNo ratings yet
- 1st Year NumercialsDocument4 pages1st Year Numercialspaggal janNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Coordinate System FDocument14 pagesCylindrical Coordinate System FRajeshNo ratings yet
- Math Word Wall Words Course 3Document18 pagesMath Word Wall Words Course 3Taleese WalshNo ratings yet
- Dama50 Unit2Document27 pagesDama50 Unit2apostolosNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Math (India) : Con Nue Number SystemsDocument2 pagesClass 9 Math (India) : Con Nue Number Systemsavijitcu2007No ratings yet
- IB HL Math Exam ReviewDocument5 pagesIB HL Math Exam ReviewPrashanth Srinivasan100% (2)
- Patter Recognition (Spring 2012) Midterm Exam SolutionDocument4 pagesPatter Recognition (Spring 2012) Midterm Exam SolutionranaNo ratings yet
- Directional Drilling EquationDocument4 pagesDirectional Drilling EquationMufti Ghazali67% (3)
- Introduction To Computer GraphicsDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Computer GraphicsRajasekharReddyGajulapaalliNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Final 18 EE 555Document6 pagesFormula Sheet Final 18 EE 555Ali KumailNo ratings yet
- Long LineDocument27 pagesLong Linekhushi03122002No ratings yet
- 5.8. Some Definitions Involving Div, Curl and GradDocument1 page5.8. Some Definitions Involving Div, Curl and GradRubensVilhenaFonsecaNo ratings yet
- Vectors 2023-24 Without KeysDocument14 pagesVectors 2023-24 Without Keyszmir3970No ratings yet
- Harmonic OscillatorDocument9 pagesHarmonic OscillatorLinNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Complex NumbersDocument8 pagesChap 1 Complex NumbersVĩnh PhongNo ratings yet
- Mega PP - V2Document112 pagesMega PP - V2Tanvir ButaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation ReglerDocument1 pageDifferentiation ReglerHans Brix HansenNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument288 pagesInverse Trigonometric FunctionsJennifer BanteNo ratings yet
- Finals New Part 1Document13 pagesFinals New Part 1Hygeia Knoll Cloa BorjaNo ratings yet
- Maths Formulae 2Unit/3Unit/4UnitDocument10 pagesMaths Formulae 2Unit/3Unit/4UnitEdward YangNo ratings yet
- Vectors TheoryDocument45 pagesVectors TheoryNavin RaiNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument8 pages1 PBad_mih7867No ratings yet
- ON THE Calculation OF Deflection of A Semitrailer Chassis Under Various Loading Conditions: An Experimental and Numerical InvestigationDocument11 pagesON THE Calculation OF Deflection of A Semitrailer Chassis Under Various Loading Conditions: An Experimental and Numerical InvestigationYãbeçk MâmNo ratings yet
- BB202 Lecture 2 PDFDocument7 pagesBB202 Lecture 2 PDFUyên PhạmNo ratings yet
- 2 Miscellaneous MathematicsDocument22 pages2 Miscellaneous MathematicssokhaNo ratings yet
- 02 TrigonometryDocument23 pages02 TrigonometryAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Udvash-23 Bio Weekly SolnDocument44 pagesUdvash-23 Bio Weekly Solnredgamer0056No ratings yet
- Checklist c1Document3 pagesChecklist c1Arwa HamdiNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesDocument33 pagesCylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesAbraham ZawierNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument11 pagesInverse Trigonometric FunctionsSamir GedamNo ratings yet
- Appendix BDocument60 pagesAppendix BRJ Wakefield-CarlNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-03-13 at 9.04.23 PMDocument6 pagesScreenshot 2024-03-13 at 9.04.23 PMzeinab.nazhaNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical CoordinatesDocument5 pagesCylindrical Coordinatesatanus788No ratings yet
- 1 Introduction 2009 PetrelDocument35 pages1 Introduction 2009 PetreltadeitosNo ratings yet
- Two Dimensional Computer Graphics: Exploring the Visual Realm: Two Dimensional Computer Graphics in Computer VisionFrom EverandTwo Dimensional Computer Graphics: Exploring the Visual Realm: Two Dimensional Computer Graphics in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Robot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlFrom EverandRobot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlNo ratings yet
- Report Usemo 2022Document30 pagesReport Usemo 2022au auNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Revision Notes Three Dimensional GeometryDocument10 pagesClass 12 Revision Notes Three Dimensional GeometryAmaan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Ellipse Narayana Pyq 2Document4 pagesEllipse Narayana Pyq 2vallabha kaustubhaNo ratings yet
- Math 4-Quarter 3 Week 3-Module 3Document18 pagesMath 4-Quarter 3 Week 3-Module 3jgorpiaNo ratings yet
- (Booklet) KS4 Mastery Higher 1 - Answers - Single PagesDocument36 pages(Booklet) KS4 Mastery Higher 1 - Answers - Single PagesZahra JamilNo ratings yet
- AMC Formula Sheet Portrait 6Document15 pagesAMC Formula Sheet Portrait 6UdayNo ratings yet
- Plane and Solid GeometryDocument8 pagesPlane and Solid GeometrydftgryhthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 NotesDocument15 pagesChapter 4 Notesapi-271061830No ratings yet
- Posl DPP MathsDocument23 pagesPosl DPP Mathsuday.grossboy.200407No ratings yet
- Grade 8 LAS 3rdquarter W3Document5 pagesGrade 8 LAS 3rdquarter W3OLIVIA LIRIONo ratings yet
- The Incenter/Excenter Lemma: August 6, 2016Document4 pagesThe Incenter/Excenter Lemma: August 6, 2016johnsonNo ratings yet
- PDF PDFDocument30 pagesPDF PDFHassan YounasNo ratings yet
- Answers For 6.6: 6.6 Skill Practice 1. 12.) ) 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. A-B. S CDocument4 pagesAnswers For 6.6: 6.6 Skill Practice 1. 12.) ) 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. A-B. S CsisikaNo ratings yet
- Math10 - Q2 - Week 4Document20 pagesMath10 - Q2 - Week 4Venice Gwyn ChavezNo ratings yet
- Final Project - Trigonometric Functions and Its Connection To Similar TrianglesDocument19 pagesFinal Project - Trigonometric Functions and Its Connection To Similar Trianglesapi-294634416No ratings yet
- Trigonometry Past Paper 2 (1) 2Document11 pagesTrigonometry Past Paper 2 (1) 2Erinç ÇamurdanNo ratings yet
- Prim Maths 6 2ed TR Unit Test AnswersDocument23 pagesPrim Maths 6 2ed TR Unit Test AnswersMelvinder KaurNo ratings yet
- Formulae Mat For P6Document17 pagesFormulae Mat For P6Chelsea Chee Ching IianNo ratings yet
- 2010 UPSR Practice Mathematcs Paper 2 - Shape & SpaceDocument6 pages2010 UPSR Practice Mathematcs Paper 2 - Shape & SpacePuworkUtara OnScribd100% (1)
- Geometry Final Review AnswersDocument8 pagesGeometry Final Review Answersapi-293880973No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya, - Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya, - Lesson PlanHARSH BAJPAI 10bNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13.2Document24 pagesExercise 13.2Himanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 4 VisualsDocument16 pagesCH 4 VisualsDwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- Volume of A Cylinder, Cone, and SphereDocument27 pagesVolume of A Cylinder, Cone, and SphereiLearnMathNo ratings yet
- Tournament of Towns 2007Document10 pagesTournament of Towns 2007OklaNo ratings yet
- 120 Geometry Exercises by Romantics of Geometry Vol.1, Issues 01-10Document149 pages120 Geometry Exercises by Romantics of Geometry Vol.1, Issues 01-10Marcos PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Congruent Triangles Packet 2013 With Correct Answers1Document87 pagesCongruent Triangles Packet 2013 With Correct Answers1光No ratings yet