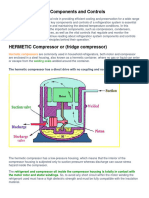
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
G02, Compressor Faults
G02, Compressor Faults
Uploaded by
byronblake80Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Erc .507-515 ManualDocument33 pagesErc .507-515 ManualJoseph Geraci50% (6)
- Oxygen Booster ManualDocument27 pagesOxygen Booster ManualAldo Tolaba Quiroga100% (3)
- Carrier Refrigerant Piping SystemsDocument57 pagesCarrier Refrigerant Piping Systemsrpiland2100% (5)
- Oxysystems 2v3x 172 4.1 ManualDocument21 pagesOxysystems 2v3x 172 4.1 ManualDavid GarciaNo ratings yet
- Poseidon High Pressure Compressor (P 135)Document5 pagesPoseidon High Pressure Compressor (P 135)rmaffireschoolNo ratings yet
- Overhauling Air Compressor On ShipsDocument12 pagesOverhauling Air Compressor On ShipsTun Lin Naing100% (3)
- Компрессор 1Document13 pagesКомпрессор 1momoyomotaNo ratings yet
- Marine Compressors: Operation, Maintenance, and TroubleshootingDocument5 pagesMarine Compressors: Operation, Maintenance, and TroubleshootingRj VermaNo ratings yet
- Bright Hub Engineering: Civil Engineering Electrical Engineering Marine Engineering Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 pagesBright Hub Engineering: Civil Engineering Electrical Engineering Marine Engineering Mechanical EngineeringRavi VikneshNo ratings yet
- Marine CompressorsDocument7 pagesMarine CompressorsAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Best Practice Guide For Power Transformer Maintenance EEPDocument1 pageBest Practice Guide For Power Transformer Maintenance EEPashutosh ambeyNo ratings yet
- Drains On Engine Room MachineryDocument11 pagesDrains On Engine Room MachineryReeta SingjNo ratings yet
- Preventive Maintenance - Keeping Refrigeration Equipment in ShapeDocument5 pagesPreventive Maintenance - Keeping Refrigeration Equipment in ShapeSanjay RanaNo ratings yet
- Mep March 2023Document17 pagesMep March 2023Subham SamantarayNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 FRL UnitDocument10 pagesExperiment No. 4 FRL UnitsbkulkNo ratings yet
- Tex Leugner Hydraulic TroubleshootingDocument29 pagesTex Leugner Hydraulic TroubleshootingMehmet ErbekNo ratings yet
- Brake SystemDocument6 pagesBrake SystemSumit KatwalNo ratings yet
- Compressor FailureDocument14 pagesCompressor FailureJose ThomNo ratings yet
- Notes On Maintenance of TransformersDocument19 pagesNotes On Maintenance of Transformersamer4411100% (2)
- Compressor GuideDocument11 pagesCompressor GuideJack O'LearyNo ratings yet
- DsairelimDocument10 pagesDsairelimGerman Felipe TorresNo ratings yet
- Refrigerated Air Dryer Manual - 1Document24 pagesRefrigerated Air Dryer Manual - 1Darshana AbeyratneNo ratings yet
- Boiler Q&A FurtherDocument7 pagesBoiler Q&A FurtherRachitNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Lab ReportDocument27 pagesRefrigeration Lab ReportLeejat Pradhan78% (27)
- MaxAir 90 PBACDocument23 pagesMaxAir 90 PBACV ZNo ratings yet
- Rotary Manual Screw KompDocument28 pagesRotary Manual Screw KompsebastianNo ratings yet
- General Engineering Knowledge For Marine EngineersDocument31 pagesGeneral Engineering Knowledge For Marine EngineersSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Laboratory Manual 2011Document19 pagesRefrigeration Laboratory Manual 2011Himanshu Uniyal0% (1)
- TT Hydraulic System Care and MaintenanceDocument2 pagesTT Hydraulic System Care and MaintenanceMariglen KurtiNo ratings yet
- I. Choose The Most Appropriate Answer From The Choices Given Below: - (15 Marks)Document4 pagesI. Choose The Most Appropriate Answer From The Choices Given Below: - (15 Marks)indusampathNo ratings yet
- 16 Injection SystemDocument4 pages16 Injection SystemigorNo ratings yet
- Air Eliminators and Combination Air Eliminators Strainers: Descrip OnDocument10 pagesAir Eliminators and Combination Air Eliminators Strainers: Descrip OnvendsrbNo ratings yet
- Scavanging and TurbochargingDocument38 pagesScavanging and TurbochargingMeghanath AdkonkarNo ratings yet
- CompressorsDocument51 pagesCompressorsReza RahmanudinNo ratings yet
- Screw Compressor Theory 1014Document3 pagesScrew Compressor Theory 1014free_eagle2009100% (1)
- Start Air System ProblemsDocument47 pagesStart Air System Problemshpss77100% (5)
- Why Compressors Fail Part 1 - Refrigerant Flood BackDocument4 pagesWhy Compressors Fail Part 1 - Refrigerant Flood BackvickersNo ratings yet
- All About Marine Enginnering OralsDocument76 pagesAll About Marine Enginnering OralsUdana Hettiarachchi100% (3)
- Air Compressor PresentationDocument34 pagesAir Compressor PresentationBhupender Ramchandani100% (1)
- Materials Used For Construction: 1. Reciprocating CompressorDocument6 pagesMaterials Used For Construction: 1. Reciprocating CompressorEdemNo ratings yet
- Oil SystemDocument22 pagesOil Systemlopesmr100% (1)
- 2.3operator Manual of SDLF-80Document27 pages2.3operator Manual of SDLF-80pachara sarntiyakulNo ratings yet
- Conserv shut off DAROC MY2013Document12 pagesConserv shut off DAROC MY2013RHETT BUTLERNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Rac MaintenanceDocument42 pagesLab Manual Rac Maintenanceonkar kalaskarNo ratings yet
- Boiler Emergencies - 2017Document10 pagesBoiler Emergencies - 2017RAJKUMAR100% (1)
- 9780L12 Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Maintenance and TroubleshootingDocument29 pages9780L12 Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Maintenance and Troubleshootingمعلومة على الماشىNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant System Components and ControlsDocument16 pagesRefrigerant System Components and ControlssrybsantosNo ratings yet
- ReamerDocument37 pagesReamerKeisha Ferreze Ann QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Cooling and Sealing AirDocument3 pagesCooling and Sealing AirKrishna VachaNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor and Starting Air SystemDocument15 pagesAir Compressor and Starting Air SystemAlimul Raji AshiqueNo ratings yet
- Marine Air Compressor Maintenance - Things You Must Know About PDFDocument15 pagesMarine Air Compressor Maintenance - Things You Must Know About PDFHope Ikue-JohnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Compressed Air Treatment (Dryers and Filters)Document34 pagesChapter 3 - Compressed Air Treatment (Dryers and Filters)ppluis90No ratings yet
- Screw CompressorDocument4 pagesScrew Compressordarksun2011100% (2)
- Boiler Questions BtechDocument5 pagesBoiler Questions BtechRishav Raj100% (1)
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SFrom EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNo ratings yet
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
G02, Compressor Faults
G02, Compressor Faults
Uploaded by
byronblake80Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
G02, Compressor Faults
G02, Compressor Faults
Uploaded by
byronblake80Copyright:
Available Formats
G02.
What faults are likely to develop in an air compressor and how are they
remedied.
Most compressor faults can fall into three different categories;
1. Problems with suction and discharge valves.
2. Intercooler and after-cooler problems.
3. Restriction of air supply.
Problems with suction and discharge valves;
By far the greatest item of maintenance concerns are the valve plates. Valve plates are
subject to shock loading and fouling by dirt, dust, oil deposits, and high operating
temperatures. Valve plates must retain their mirror like finish to maintain a good seal and
reduce the “drag” on in-coming air flow, thus improving efficiency and in turn keeping
the temperature of the compressor down.
This problem is remedied by;
a) Regular schedule maintenance on the valves, valve plates and any springs
b) Regular maintenance and monitoring of the intake filter.
c) Use of correct lubricating oil to prevent oil fouling.
Intercooler and after-cooler problems;
Intercoolers and after-coolers need to be cleaned and serviced regularly, especially if
seawater is circulated. For maximum efficiency, compression should follow the
isothermal law as close as possible. Any fouling or decline in efficiency of the cooler
directly affects the efficiency of the entire compressor. In addition if the temperature of
the air is insufficiently cooled, the high temperatures may also affect the lubrication of
the piston and liner resulting in increase wear and damage. If the temperature is allow to
continue to climb it could reach a point where there is a risk of self ignition of any
possible oil vapour in the compressor. During the service of the coolers the following
should also be checked,
a) Condition of any zinc fitted
b) Correct operation/condition of the safety valve or burst disk
c) All coolant pumps and associated drives should also be checked/inspected for
correct operation.
Restriction of air supply;
A restriction of the intake reduces the actual quantity of air that the compressor draws in
and therefore reduces the volumetric efficiency and rate of delivery to the air receivers.
For this reason the intake filter must always be kept clean or replaced. The air compressor
must never be run without an air filter as there is a possibility that abrasive dirt particles
can enter the compressor and damage the piston and liner and possible valves.
You might also like
- Erc .507-515 ManualDocument33 pagesErc .507-515 ManualJoseph Geraci50% (6)
- Oxygen Booster ManualDocument27 pagesOxygen Booster ManualAldo Tolaba Quiroga100% (3)
- Carrier Refrigerant Piping SystemsDocument57 pagesCarrier Refrigerant Piping Systemsrpiland2100% (5)
- Oxysystems 2v3x 172 4.1 ManualDocument21 pagesOxysystems 2v3x 172 4.1 ManualDavid GarciaNo ratings yet
- Poseidon High Pressure Compressor (P 135)Document5 pagesPoseidon High Pressure Compressor (P 135)rmaffireschoolNo ratings yet
- Overhauling Air Compressor On ShipsDocument12 pagesOverhauling Air Compressor On ShipsTun Lin Naing100% (3)
- Компрессор 1Document13 pagesКомпрессор 1momoyomotaNo ratings yet
- Marine Compressors: Operation, Maintenance, and TroubleshootingDocument5 pagesMarine Compressors: Operation, Maintenance, and TroubleshootingRj VermaNo ratings yet
- Bright Hub Engineering: Civil Engineering Electrical Engineering Marine Engineering Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 pagesBright Hub Engineering: Civil Engineering Electrical Engineering Marine Engineering Mechanical EngineeringRavi VikneshNo ratings yet
- Marine CompressorsDocument7 pagesMarine CompressorsAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Best Practice Guide For Power Transformer Maintenance EEPDocument1 pageBest Practice Guide For Power Transformer Maintenance EEPashutosh ambeyNo ratings yet
- Drains On Engine Room MachineryDocument11 pagesDrains On Engine Room MachineryReeta SingjNo ratings yet
- Preventive Maintenance - Keeping Refrigeration Equipment in ShapeDocument5 pagesPreventive Maintenance - Keeping Refrigeration Equipment in ShapeSanjay RanaNo ratings yet
- Mep March 2023Document17 pagesMep March 2023Subham SamantarayNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 FRL UnitDocument10 pagesExperiment No. 4 FRL UnitsbkulkNo ratings yet
- Tex Leugner Hydraulic TroubleshootingDocument29 pagesTex Leugner Hydraulic TroubleshootingMehmet ErbekNo ratings yet
- Brake SystemDocument6 pagesBrake SystemSumit KatwalNo ratings yet
- Compressor FailureDocument14 pagesCompressor FailureJose ThomNo ratings yet
- Notes On Maintenance of TransformersDocument19 pagesNotes On Maintenance of Transformersamer4411100% (2)
- Compressor GuideDocument11 pagesCompressor GuideJack O'LearyNo ratings yet
- DsairelimDocument10 pagesDsairelimGerman Felipe TorresNo ratings yet
- Refrigerated Air Dryer Manual - 1Document24 pagesRefrigerated Air Dryer Manual - 1Darshana AbeyratneNo ratings yet
- Boiler Q&A FurtherDocument7 pagesBoiler Q&A FurtherRachitNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Lab ReportDocument27 pagesRefrigeration Lab ReportLeejat Pradhan78% (27)
- MaxAir 90 PBACDocument23 pagesMaxAir 90 PBACV ZNo ratings yet
- Rotary Manual Screw KompDocument28 pagesRotary Manual Screw KompsebastianNo ratings yet
- General Engineering Knowledge For Marine EngineersDocument31 pagesGeneral Engineering Knowledge For Marine EngineersSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Laboratory Manual 2011Document19 pagesRefrigeration Laboratory Manual 2011Himanshu Uniyal0% (1)
- TT Hydraulic System Care and MaintenanceDocument2 pagesTT Hydraulic System Care and MaintenanceMariglen KurtiNo ratings yet
- I. Choose The Most Appropriate Answer From The Choices Given Below: - (15 Marks)Document4 pagesI. Choose The Most Appropriate Answer From The Choices Given Below: - (15 Marks)indusampathNo ratings yet
- 16 Injection SystemDocument4 pages16 Injection SystemigorNo ratings yet
- Air Eliminators and Combination Air Eliminators Strainers: Descrip OnDocument10 pagesAir Eliminators and Combination Air Eliminators Strainers: Descrip OnvendsrbNo ratings yet
- Scavanging and TurbochargingDocument38 pagesScavanging and TurbochargingMeghanath AdkonkarNo ratings yet
- CompressorsDocument51 pagesCompressorsReza RahmanudinNo ratings yet
- Screw Compressor Theory 1014Document3 pagesScrew Compressor Theory 1014free_eagle2009100% (1)
- Start Air System ProblemsDocument47 pagesStart Air System Problemshpss77100% (5)
- Why Compressors Fail Part 1 - Refrigerant Flood BackDocument4 pagesWhy Compressors Fail Part 1 - Refrigerant Flood BackvickersNo ratings yet
- All About Marine Enginnering OralsDocument76 pagesAll About Marine Enginnering OralsUdana Hettiarachchi100% (3)
- Air Compressor PresentationDocument34 pagesAir Compressor PresentationBhupender Ramchandani100% (1)
- Materials Used For Construction: 1. Reciprocating CompressorDocument6 pagesMaterials Used For Construction: 1. Reciprocating CompressorEdemNo ratings yet
- Oil SystemDocument22 pagesOil Systemlopesmr100% (1)
- 2.3operator Manual of SDLF-80Document27 pages2.3operator Manual of SDLF-80pachara sarntiyakulNo ratings yet
- Conserv shut off DAROC MY2013Document12 pagesConserv shut off DAROC MY2013RHETT BUTLERNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Rac MaintenanceDocument42 pagesLab Manual Rac Maintenanceonkar kalaskarNo ratings yet
- Boiler Emergencies - 2017Document10 pagesBoiler Emergencies - 2017RAJKUMAR100% (1)
- 9780L12 Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Maintenance and TroubleshootingDocument29 pages9780L12 Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Maintenance and Troubleshootingمعلومة على الماشىNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant System Components and ControlsDocument16 pagesRefrigerant System Components and ControlssrybsantosNo ratings yet
- ReamerDocument37 pagesReamerKeisha Ferreze Ann QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Cooling and Sealing AirDocument3 pagesCooling and Sealing AirKrishna VachaNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor and Starting Air SystemDocument15 pagesAir Compressor and Starting Air SystemAlimul Raji AshiqueNo ratings yet
- Marine Air Compressor Maintenance - Things You Must Know About PDFDocument15 pagesMarine Air Compressor Maintenance - Things You Must Know About PDFHope Ikue-JohnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Compressed Air Treatment (Dryers and Filters)Document34 pagesChapter 3 - Compressed Air Treatment (Dryers and Filters)ppluis90No ratings yet
- Screw CompressorDocument4 pagesScrew Compressordarksun2011100% (2)
- Boiler Questions BtechDocument5 pagesBoiler Questions BtechRishav Raj100% (1)
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SFrom EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNo ratings yet
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet