Professional Documents
Culture Documents
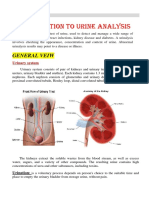
Urinary Lithiasis
Urinary Lithiasis
Uploaded by
eutamène ramziCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 47-49Document78 pagesChapter 47-49Lupita Solorzano100% (1)
- Test Bank For Introductory Maternity and Pediatric Nursing 2nd Edition by KlossnerDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Introductory Maternity and Pediatric Nursing 2nd Edition by KlossnerJulieJacobsrkozw100% (89)
- Renal NursingDocument11 pagesRenal NursingFreeNursingNotes100% (10)
- Small Animal Surgery (Group)Document15 pagesSmall Animal Surgery (Group)Uttam RoyNo ratings yet
- Diseases o F Urinary System 5 LevelDocument6 pagesDiseases o F Urinary System 5 LevelABDULLAH AMROONNo ratings yet
- Urolithiasis: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesUrolithiasis: ObjectivesOkki Masitah Syahfitri NasutionNo ratings yet
- Meat Pract 03 - NephrolithiasisDocument9 pagesMeat Pract 03 - NephrolithiasisKetty MupakwaNo ratings yet
- Vol - 61-3-4 Cystine Urolithiasis in A CatDocument5 pagesVol - 61-3-4 Cystine Urolithiasis in A CatCak AnangNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Urinary SystemDocument39 pagesDiseases of Urinary SystemRupak PandeyNo ratings yet
- Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis PDFDocument5 pagesCalcium Oxalate Urolithiasis PDFpriscimasNo ratings yet
- Report On Etiological Structure and Epidemiology of The Acute Intestinal Infections. Pa Tho Genesis of Diarrohea Caused by Infectious Agents.Document3 pagesReport On Etiological Structure and Epidemiology of The Acute Intestinal Infections. Pa Tho Genesis of Diarrohea Caused by Infectious Agents.Adnan Akram, MD (Latvia)No ratings yet
- UrolithiasisDocument8 pagesUrolithiasisvictor zhefaNo ratings yet
- Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) - CatDocument5 pagesFeline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) - CatAndrexixNo ratings yet
- Urolithiasis in Cattle, Sheep and GoatDocument34 pagesUrolithiasis in Cattle, Sheep and GoatAnkit kumar singh100% (2)
- Understanding StoolDocument6 pagesUnderstanding StoolJonni Arianto RangkutyNo ratings yet
- Avian Urolithiasis EngDocument4 pagesAvian Urolithiasis Engwaseem234No ratings yet
- Urolithiasis PowerpointDocument41 pagesUrolithiasis PowerpointPinkrose Chiong FabellaNo ratings yet
- Blocked CatDocument9 pagesBlocked CatBê LagoNo ratings yet
- 4 Obstructive UropathyDocument37 pages4 Obstructive UropathyCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- UROLITHIASISDocument25 pagesUROLITHIASISPaulo ManlangitNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Urolithiasis: Nursing Faculty Chatolic University of Widya Mandala Surabaya 2014Document11 pagesNursing Care of Urolithiasis: Nursing Faculty Chatolic University of Widya Mandala Surabaya 2014victor zhefaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Kidney Stone - Kul - Lecture - CompressedDocument36 pagesNursing Care Kidney Stone - Kul - Lecture - CompressedAlrinal Oktafiandi100% (1)
- Urine AnalysisDocument16 pagesUrine Analysismdhamidkarim399No ratings yet
- Urinalysis - Fundamentals of Nursing CliDocument30 pagesUrinalysis - Fundamentals of Nursing CliJessica BeanNo ratings yet
- MoniDocument15 pagesMoniH.M. AriyanNo ratings yet
- Small Bowel and Large Bowel DisordersDocument43 pagesSmall Bowel and Large Bowel DisordersDanielle FosterNo ratings yet
- 1 Urinary StonesDocument11 pages1 Urinary StonesMohamed Al-zichrawyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Urine Analysis: General VeiwDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Urine Analysis: General Veiwبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterizationDocument17 pagesUrinary CatheterizationLeofe CorregidorNo ratings yet
- DiarrhoeaDocument22 pagesDiarrhoeaMonika aryaNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis Pre LabDocument6 pagesUrinalysis Pre LabbobbyNo ratings yet
- General Stool ExaminationDocument6 pagesGeneral Stool Examinationزكريا خالدNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Urine Analysis: General VeiwDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Urine Analysis: General Veiwبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Bladder Stones Obstruct WebDocument3 pagesBladder Stones Obstruct WebRi'ayat AlzamendaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation UrolithiasisDocument13 pagesCase Presentation UrolithiasisTeguh Soni ReksaNo ratings yet
- Cholera: Fadillah Alma PutraDocument18 pagesCholera: Fadillah Alma Putrafadil almaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System Notes1Document30 pagesGastrointestinal System Notes1freak009No ratings yet
- Stones in The BodyDocument14 pagesStones in The BodyMichaelNo ratings yet
- Av Av Av Av Av Av Av Av Av Av Av AvDocument4 pagesAv Av Av Av Av Av Av Av Av Av Av AvJoyce Ramos CadondonNo ratings yet
- Acute If 4 Weeks in DurationDocument9 pagesAcute If 4 Weeks in DurationSalsabila Rahma FadlillahNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument18 pagesUrinary SystemAbdusaburNo ratings yet
- Renalcalculi 190912083750Document39 pagesRenalcalculi 190912083750Asadur MollaNo ratings yet
- Acute Watery Diarrhea (1399-05-22)Document31 pagesAcute Watery Diarrhea (1399-05-22)Shams Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Renal CalculiDocument5 pagesRenal CalculiRufus Raj100% (1)
- Urinary System DisordersDocument14 pagesUrinary System DisordersGideon P. CasasNo ratings yet
- Renal Stone and Renal FailureDocument14 pagesRenal Stone and Renal FailurereboNo ratings yet
- BCH 376 (Urinalysis Lecture Notes)Document7 pagesBCH 376 (Urinalysis Lecture Notes)biddyusmc100% (1)
- Aka: Urolithiasis, Kidney Stone, Renal Calculi, Ureteral Calculus, Renal ColicDocument4 pagesAka: Urolithiasis, Kidney Stone, Renal Calculi, Ureteral Calculus, Renal ColicMarlin Nouelle Agpalza SacramedNo ratings yet
- Renal CalculiDocument28 pagesRenal Calculihailleyann33% (3)
- Portosystemic ShuntsDocument5 pagesPortosystemic ShuntsAnaNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document16 pagesModule 4Lib PalmaresNo ratings yet
- 13 CholecystitisDocument11 pages13 CholecystitisdorajuangaterNo ratings yet
- Acute Diarrhoea and VomitingDocument43 pagesAcute Diarrhoea and VomitingAdriana AfiqahNo ratings yet
- VanMetre Urolith Surgery 04Document11 pagesVanMetre Urolith Surgery 04MHD SuryanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-09 - Examination of Digestive SystemDocument16 pagesChapter-09 - Examination of Digestive SystemAnnahi BcNo ratings yet
- (Urogenital) Obstructive Bacterial Cystitis Following Cystotomy in A Persian CatDocument5 pages(Urogenital) Obstructive Bacterial Cystitis Following Cystotomy in A Persian CatErlangga ReeNo ratings yet
- Faecal AnalysisDocument83 pagesFaecal AnalysisJoseph SabidoNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Urinary TractDocument13 pagesPathology of The Urinary Tractesther-mwakaleNo ratings yet
- Colibacillosis: Cause: E. ColiDocument37 pagesColibacillosis: Cause: E. ColiDianventi RiandaniNo ratings yet
- Bartter Syndrom-WPS OfficeDocument29 pagesBartter Syndrom-WPS OfficeMuhammad SaqlainNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandLiver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Kidney - 2Document6 pagesKidney - 2eutamène ramziNo ratings yet
- Salmonellos RuminantsDocument4 pagesSalmonellos Ruminantseutamène ramziNo ratings yet
- Foot and Mouth DiseasesDocument3 pagesFoot and Mouth Diseaseseutamène ramziNo ratings yet
- Lumpy Skin Disease Treatment ProtocoL SK&MRDocument2 pagesLumpy Skin Disease Treatment ProtocoL SK&MReutamène ramziNo ratings yet
- ActinobacilloseDocument4 pagesActinobacilloseeutamène ramziNo ratings yet
- Case Study Acute PyelonephritisDocument52 pagesCase Study Acute PyelonephritisJohn Mark ObreroNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive Surgery in Gynecological Practice: Ertan Sarıdoğan, Gokhan Sami Kilic, Kubilay Ertan (Ed.)Document332 pagesMinimally Invasive Surgery in Gynecological Practice: Ertan Sarıdoğan, Gokhan Sami Kilic, Kubilay Ertan (Ed.)salah subbahNo ratings yet
- Male Female Catheterization Rle 30Document95 pagesMale Female Catheterization Rle 30HoneylouAzOpondaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanCARRAO, Samuel Jr.No ratings yet
- Dog Dissection ProcedureDocument20 pagesDog Dissection ProcedureChristine Joyce NavarroNo ratings yet
- 3 FINAL LESSON PLAN ON UTI in PREGNANCYDocument24 pages3 FINAL LESSON PLAN ON UTI in PREGNANCYAkansha gandharvNo ratings yet
- BPH Case PresentationDocument15 pagesBPH Case PresentationxxandraNo ratings yet
- Vesicolithotomy - RenDocument23 pagesVesicolithotomy - RenjimNo ratings yet
- Whole Abdomen (Female)Document35 pagesWhole Abdomen (Female)Eftekharul IslamNo ratings yet
- Eva Bolton Haematuria Presentation WebDocument52 pagesEva Bolton Haematuria Presentation WebereczkieNo ratings yet
- Bladder InjuriesDocument13 pagesBladder InjuriesSchoeb MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Physiology Chapter 13 Urinary System NotesDocument10 pagesHuman Anatomy Physiology Chapter 13 Urinary System NotesVGH CREATIONS Lucky's.lyrical.statusNo ratings yet
- HIPERPLASIADocument4 pagesHIPERPLASIArstheresia17No ratings yet
- Development of The Urinary SystemDocument32 pagesDevelopment of The Urinary SystemPaulin AmanNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment SAS Session 16Document5 pagesHealth Assessment SAS Session 16Mary Maxiluch TabudlongNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument22 pagesLesson PlanPramila AdhikariNo ratings yet
- BPH and HematuriaDocument40 pagesBPH and HematuriaJohn LeeNo ratings yet
- Mod 8 ZooDocument10 pagesMod 8 ZooLM Tricia T. DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- 2.lower Limb, Abdomen and Pelvis: Section 1Document12 pages2.lower Limb, Abdomen and Pelvis: Section 1Labana LabanaNo ratings yet
- NCERT - Exemplar - Life ProcessesDocument26 pagesNCERT - Exemplar - Life ProcessesRagini BaghelNo ratings yet
- Renal UroDocument120 pagesRenal UroMazharul IslamNo ratings yet
- DLP - ScienceDocument7 pagesDLP - ScienceJUDE ABBUNo ratings yet
- RGU and MCU PPT Final For 18.9.23, BsmmuDocument46 pagesRGU and MCU PPT Final For 18.9.23, BsmmuMd.AlauddinNo ratings yet
- Notes 22 - Orientation in para Clinical Science Unit - IiiDocument88 pagesNotes 22 - Orientation in para Clinical Science Unit - Iiiswapneelshirsat.ssNo ratings yet
- Preface and Table of Contents - WordDocument18 pagesPreface and Table of Contents - WordAashima BhallaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Medical Terminology Simplified A Programmed Learning Approach by Body System 6th Edition Barbara A Gylys Regina M Masters DownloadDocument15 pagesTest Bank For Medical Terminology Simplified A Programmed Learning Approach by Body System 6th Edition Barbara A Gylys Regina M Masters Downloadchristinemays21121993bgw100% (29)
- Psychosocial Wellbeing SeriesDocument30 pagesPsychosocial Wellbeing SeriesPAOLA148No ratings yet
- Scrotal Sonography Us אשכיםDocument116 pagesScrotal Sonography Us אשכיםOded YanaNo ratings yet
Urinary Lithiasis
Urinary Lithiasis
Uploaded by
eutamène ramziOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Urinary Lithiasis
Urinary Lithiasis
Uploaded by
eutamène ramziCopyright:
Available Formats
Urolithiasis
It's a dangerous disease recorded in all animal species and
human especially dog and castrated male of ruminant ,
character by urethral obstruction with complete retention of
urine which lead to filling and swelling of urinary bladder and
finally the urethral perforation and rupture of urinary bladder
occur .
Etiology :
The source of urolith is from precipitates the urinary solutes (
especially inorganic ) as crystal or amphorous depositions which
need for longer time .
The precipitates accumulated around of nidus which either
sloughing cells or any necrotic cells .
Factors enhanced the urolith conformation :-
1 – Conformation the nidus :
The probality of nidus conformation increase in :
A – Infection in any part of urinary tract .
B – Vit . A . deficiency .
C – Give animals high doses of oestrogens ( 20% of urolithiasis
recorded due to intake 30 mg / stilbestrol hormone )
2 – Precipitation the solutes :
The urine in nature as fluid with high concentration of solutes
which normally don't precipitate due to found the protective
colloids mechanism which convert the urine to gel like .
The factors causes to precipitate the urinary solutes :
A – pH
The high alkaline pH of urine stimulate the conformation of
urolith which contain salts of Ca and P .
B – Degree of solutes concentration and density in urine .
of concentration and density enhanced the precipitate the
salts which occur in :
1 – Deprivation animals ( repeated ) from water .
2 – Excessive losing of body fluid as in sever sweating ,
diarrhea .
3 – Drinking a water which contain high percentage of Ca salts
as from water have different levels of salts .
4 – Metabolic defects
5 – Excessive intake vit . D. and diet rich in oxalic acid which
they are increase Ca concentration in urine .
Clinical signs : depend on urolith location
1 – If calculi present in urinary bladder caused cystitis which
accompanied by specific clinical signs of cystitis .
– rectal palpation exhibited a calculi in bladder .
2 – If calculi in urethra caused urethral obstruction ( commonly
in castrated small bull ) with severe abdominal pain ( animal
kicking ground and abdomen by posterior hands and swishing of
tail ) and animal suffering of dysuria ) .
- Urethra and bladder swelling and filling by urine and
palpation of urethra caused to animal sever pain ( Rectal
exam ) .
Diagnosis : -
1 – case history 2 – clinical signs
3 – urine exam :
- The urine contain : - RBCs , epithelial cells , crystals and
sand deposition .
4 – blood exam : BUN .
5-X-rays and ultra –sonic apparatus.
Treatment :
1 – Surgical Operation
2 – Destructive urolith drugs with give muscular relaxants as
Aminopromazine help in urine excretion .
3 – Advised to slaughter animals if diagnosis confirm
urolithiasis .
You might also like
- Chapter 47-49Document78 pagesChapter 47-49Lupita Solorzano100% (1)
- Test Bank For Introductory Maternity and Pediatric Nursing 2nd Edition by KlossnerDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Introductory Maternity and Pediatric Nursing 2nd Edition by KlossnerJulieJacobsrkozw100% (89)
- Renal NursingDocument11 pagesRenal NursingFreeNursingNotes100% (10)
- Small Animal Surgery (Group)Document15 pagesSmall Animal Surgery (Group)Uttam RoyNo ratings yet
- Diseases o F Urinary System 5 LevelDocument6 pagesDiseases o F Urinary System 5 LevelABDULLAH AMROONNo ratings yet
- Urolithiasis: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesUrolithiasis: ObjectivesOkki Masitah Syahfitri NasutionNo ratings yet
- Meat Pract 03 - NephrolithiasisDocument9 pagesMeat Pract 03 - NephrolithiasisKetty MupakwaNo ratings yet
- Vol - 61-3-4 Cystine Urolithiasis in A CatDocument5 pagesVol - 61-3-4 Cystine Urolithiasis in A CatCak AnangNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Urinary SystemDocument39 pagesDiseases of Urinary SystemRupak PandeyNo ratings yet
- Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis PDFDocument5 pagesCalcium Oxalate Urolithiasis PDFpriscimasNo ratings yet
- Report On Etiological Structure and Epidemiology of The Acute Intestinal Infections. Pa Tho Genesis of Diarrohea Caused by Infectious Agents.Document3 pagesReport On Etiological Structure and Epidemiology of The Acute Intestinal Infections. Pa Tho Genesis of Diarrohea Caused by Infectious Agents.Adnan Akram, MD (Latvia)No ratings yet
- UrolithiasisDocument8 pagesUrolithiasisvictor zhefaNo ratings yet
- Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) - CatDocument5 pagesFeline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) - CatAndrexixNo ratings yet
- Urolithiasis in Cattle, Sheep and GoatDocument34 pagesUrolithiasis in Cattle, Sheep and GoatAnkit kumar singh100% (2)
- Understanding StoolDocument6 pagesUnderstanding StoolJonni Arianto RangkutyNo ratings yet
- Avian Urolithiasis EngDocument4 pagesAvian Urolithiasis Engwaseem234No ratings yet
- Urolithiasis PowerpointDocument41 pagesUrolithiasis PowerpointPinkrose Chiong FabellaNo ratings yet
- Blocked CatDocument9 pagesBlocked CatBê LagoNo ratings yet
- 4 Obstructive UropathyDocument37 pages4 Obstructive UropathyCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- UROLITHIASISDocument25 pagesUROLITHIASISPaulo ManlangitNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Urolithiasis: Nursing Faculty Chatolic University of Widya Mandala Surabaya 2014Document11 pagesNursing Care of Urolithiasis: Nursing Faculty Chatolic University of Widya Mandala Surabaya 2014victor zhefaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Kidney Stone - Kul - Lecture - CompressedDocument36 pagesNursing Care Kidney Stone - Kul - Lecture - CompressedAlrinal Oktafiandi100% (1)
- Urine AnalysisDocument16 pagesUrine Analysismdhamidkarim399No ratings yet
- Urinalysis - Fundamentals of Nursing CliDocument30 pagesUrinalysis - Fundamentals of Nursing CliJessica BeanNo ratings yet
- MoniDocument15 pagesMoniH.M. AriyanNo ratings yet
- Small Bowel and Large Bowel DisordersDocument43 pagesSmall Bowel and Large Bowel DisordersDanielle FosterNo ratings yet
- 1 Urinary StonesDocument11 pages1 Urinary StonesMohamed Al-zichrawyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Urine Analysis: General VeiwDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Urine Analysis: General Veiwبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterizationDocument17 pagesUrinary CatheterizationLeofe CorregidorNo ratings yet
- DiarrhoeaDocument22 pagesDiarrhoeaMonika aryaNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis Pre LabDocument6 pagesUrinalysis Pre LabbobbyNo ratings yet
- General Stool ExaminationDocument6 pagesGeneral Stool Examinationزكريا خالدNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Urine Analysis: General VeiwDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Urine Analysis: General Veiwبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Bladder Stones Obstruct WebDocument3 pagesBladder Stones Obstruct WebRi'ayat AlzamendaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation UrolithiasisDocument13 pagesCase Presentation UrolithiasisTeguh Soni ReksaNo ratings yet
- Cholera: Fadillah Alma PutraDocument18 pagesCholera: Fadillah Alma Putrafadil almaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System Notes1Document30 pagesGastrointestinal System Notes1freak009No ratings yet
- Stones in The BodyDocument14 pagesStones in The BodyMichaelNo ratings yet
- Av Av Av Av Av Av Av Av Av Av Av AvDocument4 pagesAv Av Av Av Av Av Av Av Av Av Av AvJoyce Ramos CadondonNo ratings yet
- Acute If 4 Weeks in DurationDocument9 pagesAcute If 4 Weeks in DurationSalsabila Rahma FadlillahNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument18 pagesUrinary SystemAbdusaburNo ratings yet
- Renalcalculi 190912083750Document39 pagesRenalcalculi 190912083750Asadur MollaNo ratings yet
- Acute Watery Diarrhea (1399-05-22)Document31 pagesAcute Watery Diarrhea (1399-05-22)Shams Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Renal CalculiDocument5 pagesRenal CalculiRufus Raj100% (1)
- Urinary System DisordersDocument14 pagesUrinary System DisordersGideon P. CasasNo ratings yet
- Renal Stone and Renal FailureDocument14 pagesRenal Stone and Renal FailurereboNo ratings yet
- BCH 376 (Urinalysis Lecture Notes)Document7 pagesBCH 376 (Urinalysis Lecture Notes)biddyusmc100% (1)
- Aka: Urolithiasis, Kidney Stone, Renal Calculi, Ureteral Calculus, Renal ColicDocument4 pagesAka: Urolithiasis, Kidney Stone, Renal Calculi, Ureteral Calculus, Renal ColicMarlin Nouelle Agpalza SacramedNo ratings yet
- Renal CalculiDocument28 pagesRenal Calculihailleyann33% (3)
- Portosystemic ShuntsDocument5 pagesPortosystemic ShuntsAnaNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document16 pagesModule 4Lib PalmaresNo ratings yet
- 13 CholecystitisDocument11 pages13 CholecystitisdorajuangaterNo ratings yet
- Acute Diarrhoea and VomitingDocument43 pagesAcute Diarrhoea and VomitingAdriana AfiqahNo ratings yet
- VanMetre Urolith Surgery 04Document11 pagesVanMetre Urolith Surgery 04MHD SuryanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-09 - Examination of Digestive SystemDocument16 pagesChapter-09 - Examination of Digestive SystemAnnahi BcNo ratings yet
- (Urogenital) Obstructive Bacterial Cystitis Following Cystotomy in A Persian CatDocument5 pages(Urogenital) Obstructive Bacterial Cystitis Following Cystotomy in A Persian CatErlangga ReeNo ratings yet
- Faecal AnalysisDocument83 pagesFaecal AnalysisJoseph SabidoNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Urinary TractDocument13 pagesPathology of The Urinary Tractesther-mwakaleNo ratings yet
- Colibacillosis: Cause: E. ColiDocument37 pagesColibacillosis: Cause: E. ColiDianventi RiandaniNo ratings yet
- Bartter Syndrom-WPS OfficeDocument29 pagesBartter Syndrom-WPS OfficeMuhammad SaqlainNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandLiver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Kidney - 2Document6 pagesKidney - 2eutamène ramziNo ratings yet
- Salmonellos RuminantsDocument4 pagesSalmonellos Ruminantseutamène ramziNo ratings yet
- Foot and Mouth DiseasesDocument3 pagesFoot and Mouth Diseaseseutamène ramziNo ratings yet
- Lumpy Skin Disease Treatment ProtocoL SK&MRDocument2 pagesLumpy Skin Disease Treatment ProtocoL SK&MReutamène ramziNo ratings yet
- ActinobacilloseDocument4 pagesActinobacilloseeutamène ramziNo ratings yet
- Case Study Acute PyelonephritisDocument52 pagesCase Study Acute PyelonephritisJohn Mark ObreroNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive Surgery in Gynecological Practice: Ertan Sarıdoğan, Gokhan Sami Kilic, Kubilay Ertan (Ed.)Document332 pagesMinimally Invasive Surgery in Gynecological Practice: Ertan Sarıdoğan, Gokhan Sami Kilic, Kubilay Ertan (Ed.)salah subbahNo ratings yet
- Male Female Catheterization Rle 30Document95 pagesMale Female Catheterization Rle 30HoneylouAzOpondaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanCARRAO, Samuel Jr.No ratings yet
- Dog Dissection ProcedureDocument20 pagesDog Dissection ProcedureChristine Joyce NavarroNo ratings yet
- 3 FINAL LESSON PLAN ON UTI in PREGNANCYDocument24 pages3 FINAL LESSON PLAN ON UTI in PREGNANCYAkansha gandharvNo ratings yet
- BPH Case PresentationDocument15 pagesBPH Case PresentationxxandraNo ratings yet
- Vesicolithotomy - RenDocument23 pagesVesicolithotomy - RenjimNo ratings yet
- Whole Abdomen (Female)Document35 pagesWhole Abdomen (Female)Eftekharul IslamNo ratings yet
- Eva Bolton Haematuria Presentation WebDocument52 pagesEva Bolton Haematuria Presentation WebereczkieNo ratings yet
- Bladder InjuriesDocument13 pagesBladder InjuriesSchoeb MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Physiology Chapter 13 Urinary System NotesDocument10 pagesHuman Anatomy Physiology Chapter 13 Urinary System NotesVGH CREATIONS Lucky's.lyrical.statusNo ratings yet
- HIPERPLASIADocument4 pagesHIPERPLASIArstheresia17No ratings yet
- Development of The Urinary SystemDocument32 pagesDevelopment of The Urinary SystemPaulin AmanNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment SAS Session 16Document5 pagesHealth Assessment SAS Session 16Mary Maxiluch TabudlongNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument22 pagesLesson PlanPramila AdhikariNo ratings yet
- BPH and HematuriaDocument40 pagesBPH and HematuriaJohn LeeNo ratings yet
- Mod 8 ZooDocument10 pagesMod 8 ZooLM Tricia T. DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- 2.lower Limb, Abdomen and Pelvis: Section 1Document12 pages2.lower Limb, Abdomen and Pelvis: Section 1Labana LabanaNo ratings yet
- NCERT - Exemplar - Life ProcessesDocument26 pagesNCERT - Exemplar - Life ProcessesRagini BaghelNo ratings yet
- Renal UroDocument120 pagesRenal UroMazharul IslamNo ratings yet
- DLP - ScienceDocument7 pagesDLP - ScienceJUDE ABBUNo ratings yet
- RGU and MCU PPT Final For 18.9.23, BsmmuDocument46 pagesRGU and MCU PPT Final For 18.9.23, BsmmuMd.AlauddinNo ratings yet
- Notes 22 - Orientation in para Clinical Science Unit - IiiDocument88 pagesNotes 22 - Orientation in para Clinical Science Unit - Iiiswapneelshirsat.ssNo ratings yet
- Preface and Table of Contents - WordDocument18 pagesPreface and Table of Contents - WordAashima BhallaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Medical Terminology Simplified A Programmed Learning Approach by Body System 6th Edition Barbara A Gylys Regina M Masters DownloadDocument15 pagesTest Bank For Medical Terminology Simplified A Programmed Learning Approach by Body System 6th Edition Barbara A Gylys Regina M Masters Downloadchristinemays21121993bgw100% (29)
- Psychosocial Wellbeing SeriesDocument30 pagesPsychosocial Wellbeing SeriesPAOLA148No ratings yet
- Scrotal Sonography Us אשכיםDocument116 pagesScrotal Sonography Us אשכיםOded YanaNo ratings yet