Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inbound 1467816154223714815
Inbound 1467816154223714815
Uploaded by
Shiemarie Santos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesThe document is a study guide that provides definitions and explanations of key cell biology concepts. It covers topics like cell theory, organelles like the cell membrane and golgi apparatus, microscopy techniques, tissues like epithelial and connective tissues, and the stages of mitosis. Specifically, it discusses Theodor Schwann's contributions to cell theory, that organelles provide structure and protection to cells, and the functions of the golgi apparatus and chloroplast.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document is a study guide that provides definitions and explanations of key cell biology concepts. It covers topics like cell theory, organelles like the cell membrane and golgi apparatus, microscopy techniques, tissues like epithelial and connective tissues, and the stages of mitosis. Specifically, it discusses Theodor Schwann's contributions to cell theory, that organelles provide structure and protection to cells, and the functions of the golgi apparatus and chloroplast.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesInbound 1467816154223714815
Inbound 1467816154223714815
Uploaded by
Shiemarie SantosThe document is a study guide that provides definitions and explanations of key cell biology concepts. It covers topics like cell theory, organelles like the cell membrane and golgi apparatus, microscopy techniques, tissues like epithelial and connective tissues, and the stages of mitosis. Specifically, it discusses Theodor Schwann's contributions to cell theory, that organelles provide structure and protection to cells, and the functions of the golgi apparatus and chloroplast.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Study Guide
How did Theodor Schwann contribute to the development of cell theory?
Schwann stated that the new cells in an organism are produced by preexisting cells.
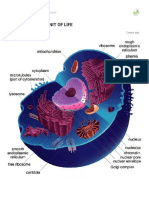
Organelle gives the protection, support and structure.
Cell wall
Applies the theory that cell comes from free existing cell.
Virus reproduces drastically causing infection in chicken.
Omnis cellulae cellula in English means.
New cells come from already pre-existing cell.
Organelle that allows only essential substances to pass through.
Cell membrane
Function of golgi apparatus
It sorts, tag, package and distribute lipids and proteins.
The building block of life discovered.
Robert Hooke- 1665
Three major parts of cell
Cell membrane, Cytoplasm and Nucleus
First invested microscope to view the cell.
Compound microscope
Branch of biology dealing with the structure, function, multiplication, pathology and life history of cells.
Cytology
Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden has been recognized for their discovery of cell.
Yes, because Schwann and Schleiden proposed the cell theory and coined its term “cell”.
It means little organs.
Organelles
Functions of neurons
Accept impulse from sensory receptors
Convey nerve impulse between various parts of the CNS
Accept nerve impulse from Central Nervous System (CNS)
Xylem tissue important to plants.
Transport water and minerals
Which of the following tissues do the following parts belong: tendon, ligaments, and cartilage?
Connective
Specialized for covering or lining of all internal and external body surface.
Epithelial tissue
Provide support and strength to the plant.
Sclerenchyma
Chemical equation for photosynthesis.
C6H12O6 + + 6 O2 = 6 H2O + 6 CO2
Products of the light reactions that are needed for the Calvin Cycle.
ATP and NADPH
Primary function of the light reactions of photosynthesis.
To produce NADPH and ATP
Supplies the electrons that are lost in photosystem I (PSI).
The electron from PS II
Light dependent reaction take place
Thylakoids
Organelle that performs in photosynthesis.
Chloroplast
Characteristics of permanent tissues.
Matured tissues which are already differentiated
Mature tissues that are undergoing differentiation
Categorized into epidermal tissue, ground tissue and vascular tissue
Refers to the change in an organism in response to some environmental factors.
Cell Modification
Short, hair-like structures that beat in a coordinated rhythmical wave-like manner.
Cilia
Show the difference between cilia and flagella.
Cilia and flagella are both locomotory organelles.
Cilia are long whiplike structures while flagella are short hair-like projections that arise from the
body of the microorganism.
Function of guard cells in plants.
Site for cellular respiration
It monitors the plant’s internal condition.
When an individual is diagnosed to be anemic, does it affect the function of the red blood cell.
Yes, having a low RBC affects the poor circulation of oxygen in the blood.
The “S” phase stand for and its function.
Synthesis phase where DNA is copied
A cell cycle, when is a cell’s DNA replicated.
S phase
Phase of mitosis do the chromosomes line up along the middle of the dividing cell.
Metaphase
Role of the spindle fibers during mitosis.
They help separate the chromosomes
The chromosomes are seen as a pair of sister chromatids joined together at the centromere.
Prophase
Stage of mitosis when chromosomes reach the pole of the spindle.
Telophase
Spindle microtubules not attached to the chromosome grow longer during anaphase.
To pull the chromosomes towards each other
You might also like
- Year 10 Edexcel IGCSE Human Biology Cells Unit 1 NotesDocument49 pagesYear 10 Edexcel IGCSE Human Biology Cells Unit 1 NotesZoonieFR0% (1)
- Cellular Basis of LifeDocument4 pagesCellular Basis of Lifemarc7victor7salesNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument32 pagesCell TheorySumana BasuNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument20 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of LifeShivansh Shrivastava100% (1)
- Science 5 Quiz Bee ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience 5 Quiz Bee ReviewerRommel Urbano Yabis50% (2)
- Lesson Plan-Body PiercingDocument4 pagesLesson Plan-Body PiercingAime Jeanne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Science Quiz BeeDocument7 pagesScience Quiz BeerieNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 2016 - 2017Document8 pagesReviewer 2016 - 2017VivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument12 pagesFundamental Unit of LifeAdil KhanNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument40 pagesEarth and Life ScienceGraceEstoleCaloNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument40 pagesCellsemo mHAYNo ratings yet
- Senior High School - STEMDocument85 pagesSenior High School - STEMMary Grace MacadiniNo ratings yet
- Biology-9 (U1 Tutorial) 2020-21Document10 pagesBiology-9 (U1 Tutorial) 2020-21fahad darNo ratings yet
- What Is A CellDocument12 pagesWhat Is A CellMaries San PedroNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life: CEL LDocument18 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life: CEL LSubiksha A.R.ANo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Cell and Its StructureDocument6 pagesIntroduction To The Cell and Its StructureMary Ann Leona SelgaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 18-19 Cells Reference PPT1Document68 pagesGen Bio 1 18-19 Cells Reference PPT1Ciena GaddiNo ratings yet
- Cytology Full Notes NcertDocument20 pagesCytology Full Notes NcertAftab100% (1)
- Unit 2 Study Guide - TeacherDocument11 pagesUnit 2 Study Guide - Teacherapi-198603477No ratings yet
- Cellular StructureDocument6 pagesCellular StructureVela STEM Naron, Claire KylaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 NotesDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology 1 NotesKrisha GatocNo ratings yet
- Beed1 - Rejano, Mary Grace M.Document6 pagesBeed1 - Rejano, Mary Grace M.GraceNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Basic Cell BiologyDocument116 pagesUnit-I Basic Cell Biologyvishav sharmaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document11 pagesLesson 1remshopNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument6 pagesGeneral BiologywellingtotakeNo ratings yet
- Gen. BioDocument6 pagesGen. BioMarxinne PajarinNo ratings yet
- Jilbert B. Gumaru, LPTDocument85 pagesJilbert B. Gumaru, LPTJulius MacaballugNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology - Cell StructureDocument44 pagesMolecular Biology - Cell StructureArzo AnumNo ratings yet
- The Cell: by DR - Hikmat Fatima HashmiDocument53 pagesThe Cell: by DR - Hikmat Fatima Hashmibeverly brittoNo ratings yet
- The Cell - ZoologyDocument7 pagesThe Cell - ZoologyEthel May GranilNo ratings yet
- Cell 2Document27 pagesCell 2Crissa CruzNo ratings yet
- Senior High School - STEMDocument93 pagesSenior High School - STEMMaam Elle CruzNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 3-4Document6 pagesGen Bio 3-4Honey Joy Leopando SabadoNo ratings yet
- Btec Biology New RevisionDocument53 pagesBtec Biology New RevisionGemma WrigleyNo ratings yet
- The Cell Theory: Presented By: Rickyla Vien A. VienteDocument25 pagesThe Cell Theory: Presented By: Rickyla Vien A. VienteRickyla VienteNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology: Topic: The CellsDocument121 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology: Topic: The CellsJoan Ano CaneteNo ratings yet
- CellDocument3 pagesCellFrama Intan MiguelNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Life and Levels of Organization: in Skin)Document3 pagesCharacteristics of Life and Levels of Organization: in Skin)AngelieBadarNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO CELLS - EditedDocument11 pagesINTRODUCTION TO CELLS - EditedSammel SevillaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Genbio1 Melc 1 2Document6 pagesWeek 1 Genbio1 Melc 1 2silvajunjosephNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Q1Document11 pagesGen Bio Q1jessy silva (Lynsy)No ratings yet
- Biology Lecture Notes: (Stemer'S Guide)Document24 pagesBiology Lecture Notes: (Stemer'S Guide)Magdy Mohamed Abdallah AbdelkaderNo ratings yet
- Stem 11 Genbio 1 NotesDocument1 pageStem 11 Genbio 1 NotesKalila MckenzieNo ratings yet
- Biology 1 Reviewer Quarter 1Document18 pagesBiology 1 Reviewer Quarter 1Angela Kim S. BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Sciencia Du Gaia - Introduccion Du Sciencia BioDocument56 pagesSciencia Du Gaia - Introduccion Du Sciencia BioRETLAWNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument5 pagesCell TheoryJett Xyrich RositNo ratings yet
- Animals and Plant CellsDocument17 pagesAnimals and Plant CellshiroantiojoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument100 pagesChapter-5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeNodiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The CellDocument3 pagesChapter 1: The CellGIAN CARLONo ratings yet
- Cell Structures 2: Hamilton High School Biology Chapter 3Document27 pagesCell Structures 2: Hamilton High School Biology Chapter 3PiereNo ratings yet
- !gen Bio Notes!Document14 pages!gen Bio Notes!Eyvette GoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cytology or Cell BiologyDocument63 pagesIntroduction To Cytology or Cell BiologyChemMANo ratings yet
- Biochem Module1Document12 pagesBiochem Module1ShannNo ratings yet
- Gen. Bio. 1 Module 1st QuarterDocument24 pagesGen. Bio. 1 Module 1st QuarterjoyNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument39 pagesCell Structure and Functionsshilpa SNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell?: Cells: Size & ShapeDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Cell?: Cells: Size & ShapePedro SuyuNo ratings yet
- Cells NotesDocument26 pagesCells Notesapi-293063607No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument17 pagesCell DivisionAnika FerolinNo ratings yet
- Celll BioDocument6 pagesCelll BioDharmveer kumarNo ratings yet
- WJEC GCSE Biology - Cells & Cell MembranesDocument4 pagesWJEC GCSE Biology - Cells & Cell MembranesMegan TaylorNo ratings yet
- 2017 Infectious Diseases Society of America Clinical Practice Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Management of Infectious DiarrheaDocument36 pages2017 Infectious Diseases Society of America Clinical Practice Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Management of Infectious Diarrheagrady janitraNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument74 pagesCirculatory Systemmathvin thummalaNo ratings yet
- Krok - 1 Angliyskiy 2017Document22 pagesKrok - 1 Angliyskiy 2017ДарьяNo ratings yet
- Rodaks 6th Ed. Hema Lab Midterm ReviewerDocument30 pagesRodaks 6th Ed. Hema Lab Midterm ReviewerGerald SorianoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 4Document6 pagesLaboratory Exercise 4Dane Ashley RubinoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To SerologyDocument13 pagesAn Introduction To SerologyLeydi Yudith Angarita Bautista100% (1)
- Nisebj 21 2 2021Document39 pagesNisebj 21 2 2021Clement BewajiNo ratings yet
- Aqa Y2 P2 Jun 19 MSDocument19 pagesAqa Y2 P2 Jun 19 MSestee.onyeNo ratings yet
- Phytochemicals From Phyllanthus Niruri Linn. and Their Pharmacological Properties: A ReviewDocument12 pagesPhytochemicals From Phyllanthus Niruri Linn. and Their Pharmacological Properties: A ReviewAnand KirtiNo ratings yet
- FEBS Letters - 2020 - Eastman - The Palette of Techniques For Cell Cycle AnalysisDocument15 pagesFEBS Letters - 2020 - Eastman - The Palette of Techniques For Cell Cycle Analysissigmafranco8No ratings yet
- Biology S.1, Mid TermDocument3 pagesBiology S.1, Mid TermEMMANUEL BIRUNGINo ratings yet
- Human Papilloma Virus HPV PSPD PDFDocument11 pagesHuman Papilloma Virus HPV PSPD PDFHenok Nugrahawanto100% (1)
- Soalsoal StanDocument2 pagesSoalsoal StanRifqi MartinNo ratings yet
- Cabletow2020 2Document104 pagesCabletow2020 2Noble KnightNo ratings yet
- Galectin-3 Binding Protein Links Circulating Microparticles With Electron Dense Glomerular Deposits in Lupus NephritisDocument11 pagesGalectin-3 Binding Protein Links Circulating Microparticles With Electron Dense Glomerular Deposits in Lupus NephritisRina kriswiastinyNo ratings yet
- Class Notes: Human Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesClass Notes: Human Circulatory SystemAnurag SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Nukleus Dan NukleolusDocument63 pagesNukleus Dan NukleolusKarin NakajimaNo ratings yet
- Virology User ManualDocument24 pagesVirology User ManualMedo2012No ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument34 pagesIlovepdf MergedSheen LegsNo ratings yet
- 10 - Basic Recombinant DNA TechniquesDocument77 pages10 - Basic Recombinant DNA TechniquesNguyenHongThamNo ratings yet
- Advanced Wound Care Awc Industry in IndiaDocument15 pagesAdvanced Wound Care Awc Industry in IndiaSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Bio Ip Xii RKDocument19 pagesBio Ip Xii RKdohajed656No ratings yet
- Daphne Agnp Paper UpdatedDocument7 pagesDaphne Agnp Paper Updatedapi-355514096No ratings yet
- Lecture 23 - EicosanoidsDocument22 pagesLecture 23 - Eicosanoidsapi-3703352100% (1)
- PACK Global Adult Ebook 2018Document128 pagesPACK Global Adult Ebook 2018Gabriel DutraNo ratings yet
- Envenomations: Wonder Abotsi, PHDDocument123 pagesEnvenomations: Wonder Abotsi, PHDKofi Frimpong-Manson100% (1)
- Correspondence: Broad-And Narrow-Spectrum Antibiotics: A Different ApproachDocument2 pagesCorrespondence: Broad-And Narrow-Spectrum Antibiotics: A Different ApproachJulio Andro ArtamulandikaNo ratings yet
- FGF21 Activates AMPK Signaling: Impact On Metabolic Regulation and The Aging ProcessDocument9 pagesFGF21 Activates AMPK Signaling: Impact On Metabolic Regulation and The Aging ProcessaginaNo ratings yet