Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Redox Reaction
Redox Reaction
Uploaded by
gnanavishaljonnalagaddaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Chem 16.1 ReviewerDocument7 pagesChem 16.1 ReviewerCindy ChengNo ratings yet
- ACS Study GuideDocument7 pagesACS Study GuideRachel Garner100% (1)
- CH 19 - Electrochemistry - Chem163 Outline - S2016-1Document34 pagesCH 19 - Electrochemistry - Chem163 Outline - S2016-1Nguyễn Tương QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Ragnar's Homemade Detonators - H - Ragnar BensonDocument68 pagesRagnar's Homemade Detonators - H - Ragnar BensonFrederico WernerNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionDocument1 pageRedox ReactionPARAMBATH ANUP KUMARNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction and Electrochemistry (C-Inpo)Document25 pagesRedox Reaction and Electrochemistry (C-Inpo)Biggos businessNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: 2Mg 2Mg + 4eDocument10 pagesElectrochemistry: 2Mg 2Mg + 4eIvyy Joyce BuanNo ratings yet
- GCSE KO Formuale and EquationsDocument1 pageGCSE KO Formuale and EquationsPaulina MugutiNo ratings yet
- (4469) Sheet Basic Inorganic Nomenclature Theory eDocument6 pages(4469) Sheet Basic Inorganic Nomenclature Theory eboom rangNo ratings yet
- Section (A) : Oxidation Number Halogen Atom:: Basic Inorganic NomenclatureDocument8 pagesSection (A) : Oxidation Number Halogen Atom:: Basic Inorganic NomenclaturewanderedNo ratings yet
- Chem 1011Document4 pagesChem 1011Arfa Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- L Oss of E Lectrons Is O Xidation G Ain of E Lectrons Is R EductionDocument10 pagesL Oss of E Lectrons Is O Xidation G Ain of E Lectrons Is R Eductionherman lewisNo ratings yet
- Lect 7 CHE 142 Energy Production From Electrochemical SystemDocument21 pagesLect 7 CHE 142 Energy Production From Electrochemical Systemytr8bwjch2No ratings yet
- Aa 220619 180412Document1 pageAa 220619 180412KeasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ChemistryDocument33 pagesChapter 3 ChemistryMaticsNo ratings yet
- 5 2 3 Revision Guide Redox and Electrode PotentialsDocument10 pages5 2 3 Revision Guide Redox and Electrode PotentialsGarret GordonNo ratings yet
- REDOXDocument1 pageREDOXeiyda_idrisNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 REDOXDocument5 pagesTopic 3 REDOXskywalkerNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument17 pagesRedox ReactionsThamizharuvi. ANo ratings yet
- Share CE-112-MODULE-3-ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument18 pagesShare CE-112-MODULE-3-ELECTROCHEMISTRYAngelo GranadaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IIDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry IIRoberto SIlvaNo ratings yet
- Httpswww2 Chemistry Msu Educoursescem152Chap20lect PDFDocument48 pagesHttpswww2 Chemistry Msu Educoursescem152Chap20lect PDFAli AllamNo ratings yet
- BMAT CHEMISTRY-c5-Oxidation, reduction and redoxDocument10 pagesBMAT CHEMISTRY-c5-Oxidation, reduction and redoxNapassorn WongduangpaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation ADocument25 pagesOxidation Aaminah hameedNo ratings yet
- 3 Yr Level 3 Eng. ModuleDocument4 pages3 Yr Level 3 Eng. ModulePooja SainiNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry: JEE SyllabusDocument8 pagesRedox Reactions and Electrochemistry: JEE SyllabusIhtisham Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Lessons 1 RM StsDocument18 pagesOxidation Lessons 1 RM Stskocaxi9358No ratings yet
- Ethers: Diethyl Ether Was Commonly Used As A Local AnestheticDocument12 pagesEthers: Diethyl Ether Was Commonly Used As A Local Anestheticelizabethli23No ratings yet
- REDOXDocument10 pagesREDOXPROFFESSORNo ratings yet
- 05 - Group 2 & Redox CORNELLDocument8 pages05 - Group 2 & Redox CORNELLGeorge SolomouNo ratings yet
- L3 AromaticsDocument22 pagesL3 AromaticsCheng FuNo ratings yet
- CHM1-7.5 Like D LikeDocument16 pagesCHM1-7.5 Like D Likeadrian nenengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document24 pagesChapter 13abubakarabubakarbah563No ratings yet
- Week 8 - Redox ReactionDocument4 pagesWeek 8 - Redox ReactionThanni AkanbiNo ratings yet
- Titration (A Volumetric Method of Analysis)Document71 pagesTitration (A Volumetric Method of Analysis)Alleyah May GiducosNo ratings yet
- Organometallic ReactionsDocument7 pagesOrganometallic Reactionszahara99121No ratings yet
- Co Ordination CompoundDocument16 pagesCo Ordination Compounddhruvsoni8905No ratings yet
- Redox Equilibria IDocument5 pagesRedox Equilibria ILisa DentonNo ratings yet
- CHEM131 ElectrochemistryDocument38 pagesCHEM131 ElectrochemistryAngel Rose AriasNo ratings yet
- E5 Lewis Acids and Bases Acids: Bronsted: Acids Are Proton DonorsDocument9 pagesE5 Lewis Acids and Bases Acids: Bronsted: Acids Are Proton DonorsJohn HenricksNo ratings yet
- Redox & Equivalent Concepts (PQRS & J)Document20 pagesRedox & Equivalent Concepts (PQRS & J)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Cac Phan Ung Cua AncolDocument1 pageCac Phan Ung Cua AncolVy Na Ngo100% (1)
- Redox Reaction by AKansha KarnwalDocument66 pagesRedox Reaction by AKansha Karnwalkrishnarewani11No ratings yet
- Course 201N 1 Semester 2006-2007 Inorganic Chemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. BeraDocument10 pagesCourse 201N 1 Semester 2006-2007 Inorganic Chemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. BeraNITU KUMARINo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesElectrochemistry Lecture NotesLyra GurimbaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Red OxDocument1 pageChapter 4 Red OxShriya ParthasarathiNo ratings yet
- Theory (Volumetric Analysis)Document18 pagesTheory (Volumetric Analysis)smitvartakNo ratings yet
- 4.7 Types of Chemical Reactions Student PDFDocument6 pages4.7 Types of Chemical Reactions Student PDFSyed RazaNo ratings yet
- Non-Metallic Assigned: Fe, AgDocument5 pagesNon-Metallic Assigned: Fe, AgAarya DubeyNo ratings yet
- Mitochondriju Gener Lais RadikalaiDocument22 pagesMitochondriju Gener Lais RadikalaiTed McgintyNo ratings yet
- Coordinaiton CompoundsDocument41 pagesCoordinaiton Compoundsjacksparrow16204No ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument120 pagesIonic EquilibriumUdbhav DikshitNo ratings yet
- E5 Lewis Acids and Bases (Session 1) November 5 - 11Document8 pagesE5 Lewis Acids and Bases (Session 1) November 5 - 11KIMIA Ronald Ivan WijayaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 ElectrochemistryDocument39 pagesUnit 4 ElectrochemistryElaiza Angelene NacarioNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument14 pagesRedoxamitaggarwal78No ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDocument13 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedGod is every whereNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and Ketone ReactionsDocument21 pagesAldehyde and Ketone ReactionsAinsssNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Lets Fall in Love With ChemistryDocument68 pagesChemistry: Lets Fall in Love With ChemistryAnay SahuNo ratings yet
- Valence ElectronsDocument3 pagesValence ElectronsGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors TheoryDocument22 pagesSemiconductors Theoryjit_72No ratings yet
- SSSSDocument9 pagesSSSSAkhmad DairobiNo ratings yet
- Zirconia MaterialsDocument2 pagesZirconia MaterialsFlexiblecsiNo ratings yet
- Additives For Drilling FluidsDocument3 pagesAdditives For Drilling FluidsGeorge Liberty0% (1)
- Chemical Stock UpdatedDocument21 pagesChemical Stock UpdatedPraise and worshipNo ratings yet
- Beacon 3000 Process Nir AnalyserDocument2 pagesBeacon 3000 Process Nir AnalyserSiddhartha MitraNo ratings yet
- MIG WeldingDocument17 pagesMIG WeldingAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNo ratings yet
- MDSReport 1039818470Document154 pagesMDSReport 1039818470javier ortizNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual Makita Rp0900Document12 pagesInstruction Manual Makita Rp0900Jonathan Pascua CamachoNo ratings yet
- 01 Atomic Structures N PDFDocument15 pages01 Atomic Structures N PDFElongated SausageNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Schedule - Equipment TemplateDocument2 pagesCleaning Schedule - Equipment TemplateEduyNo ratings yet
- Reactor Kinetics of Urea Formation: November 2015Document21 pagesReactor Kinetics of Urea Formation: November 2015thaeNo ratings yet
- Syllabus MtechDocument75 pagesSyllabus Mtechamit64007No ratings yet
- CLW Vendor DirectoryDocument41 pagesCLW Vendor DirectoryNilanjan Sen100% (1)
- Electrochemistry 494 PDFDocument55 pagesElectrochemistry 494 PDFakashNo ratings yet
- Global Warming PotentialDocument24 pagesGlobal Warming PotentialMotaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium-Constant NOTESDocument5 pagesEquilibrium-Constant NOTESAlex Jethro TigoyNo ratings yet
- Grabner InstrumentDocument2 pagesGrabner InstrumentEgie WijaksonoNo ratings yet
- (Special Publication) S.D. Jackson, J.S.J. Hargreaves, D. Lennon-Catalysis in Application_ [Proceedings of the International Symposium on Applied Catalysis to Be Held at the University of Glasgow on 1Document332 pages(Special Publication) S.D. Jackson, J.S.J. Hargreaves, D. Lennon-Catalysis in Application_ [Proceedings of the International Symposium on Applied Catalysis to Be Held at the University of Glasgow on 1Abdi Nemera EmanaNo ratings yet
- Role of Steam in Partial Oxidation of Propylene Over A PD/SDB CatalystDocument7 pagesRole of Steam in Partial Oxidation of Propylene Over A PD/SDB CatalystAlyaNo ratings yet
- Yakima Bait 2018 Catalog PDFDocument96 pagesYakima Bait 2018 Catalog PDFPenta AlfaNo ratings yet
- The Art and Science of Organic andDocument34 pagesThe Art and Science of Organic andWalter RamirezNo ratings yet
- Volume Correction MethanolDocument2 pagesVolume Correction MethanolLisiLxNo ratings yet
- Flexible Concrete Sheet PDFDocument6 pagesFlexible Concrete Sheet PDFNavanit KumarNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy WKST KEYDocument4 pagesEnthalpy WKST KEYمحمد گراوندNo ratings yet
- Furniture - Guideline For USA and CALIFORNIADocument27 pagesFurniture - Guideline For USA and CALIFORNIAENRIQUE CABRIA DEL OLMONo ratings yet
- High Range Water-Reducing Concrete Admixture: Chemrite - NN (A)Document5 pagesHigh Range Water-Reducing Concrete Admixture: Chemrite - NN (A)ghazanfarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Premium Motor Spirit (PMS) Distributed in Lagos Metropolis, NigeriaDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Premium Motor Spirit (PMS) Distributed in Lagos Metropolis, Nigerialuk4ezyNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesLiterature ReviewSK 119 ENGLISH LANGUAGE SCHOOLNo ratings yet
Redox Reaction
Redox Reaction
Uploaded by
gnanavishaljonnalagaddaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Redox Reaction
Redox Reaction
Uploaded by
gnanavishaljonnalagaddaCopyright:
Available Formats
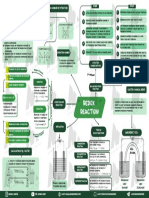
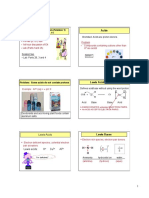
STEPS STEPS
RULES FOR ARRANGING OXIDATION NUMBERS BY STRUCTURE
OXIDATION NUMBER (ON)
1 Write the correct formula of the reaction 1 Seperate equation into two half reaction.
a) Oxidation Number of single element Identify atoms undergoing change in 2 Balance atoms other than O and H
2
is always O. b) Chromium (VI) peroxide Oxidation number
b) Oxidation Number of ions only one a) Earo's acidb(H2SO5) For reaction occuring in acidic medium,
O-1 O
-1
atom, ON is equal to charge on ion O-2 Calculate i9ncrease or decrease in 3 Add H2O to balance O atoms and H+ to
+6
c) Oxidation Number of oxygen in most +1 -2 -1 -1 +1 Cr 3 Oxidation number per atom amd for entire balance H atoms.
HO - S - O - OH ion or molecule. If unequal, multiply by
compound is -2 O -2 -1
d) Oxidation Number of hydrogen is +1, O O suitable number to make equal. Balance charges by adding e- to one
O -2
4
except when it is bonded to metals in side of the half reaction.
binary compounds. Add H+/OH- ion to make total ionic charges
4 Add two half reactions and cancel the
e) Halogens have an oxidation number of of reactants and product equal 5
-1, when they occur as halide ions in their e- on each side.
c) Earo's acidb(H2SO5)
compounds. -2 -2 -2 5 Equalize H+ on two sides by adding water.
f) Algebric sum of oxidation number all the O O O OXIDATION NUMBER 6 Scale the equation has same type and no.
atoms in a compounds must be zero
-2 +6 +4 +6 -2 of atoms and same charges on both sides
O = Br - Br - Br = O
-2 of the equation.
-2
O -2 O It indicates the number
O of electron gained or lost OXIDATION
by a particular atom. NUMBER METHOD
HALF REACTION
1 Oxidation is loss of electrons. Modern METHOD
They are considered as reducing
1st method
2
agents.
OXIDATION 2nd Method
Classical
3 Lower oxidation number.
BALANCING REDOX
Addition of oxygen or
REACTION ELECTRO-CHEMICAL SERIES
removal of hydrogen
from a substance.
REDOX IN DAILY LIFE C + O 2
→ CO 2 + Heat
Photosynthesis
Electron of metals
OXIDATION AND
REDUCTION REDOX A series of electrodes on half cells arranged in
order of their increasing standard oxidation
potentials or in the decreasing order of their
REDUCTION
REACTION
Classical
Combination process standard reduction potential.
Electrochemical cells
Removal of oxygen or
addition of hydrogen
from a substance.
1 Reduction is gain of electrons. H 2 + S → H2 S
APPLICATION
They are considered as oxidising TYPES OF
2
agents.
REDOX REACTIONS GALVENIC CELL
M odern + +
3 Increases Oxidation Number. + +
Two reactants combine to
COMBINATION
form single products
REACTION
H 2 (g) + O 2 (g)
→ H 2 O(l)
Salt
CALCULATION OF N- FACTOR
DECOMPOSITION Breakdown of a compound Bridge
REACTION into two or more compounds
∆
CaCO 3 (s) → CaO(s) + CO 2 (g)
n-factor of oxidising agent/reducing agent
= Change in oxidation number per molecule An ion/atom in a compound, is
DISPLACEMENT replaced by an ion/atom of
Change = 5 × 1 REACTION another elements.
+7 +7 (nf = 5)
CuSO 4 (aq) + Zn(s)
→ ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu
MnO44- Mn2+
Change = 1 × 2 DISPROPORTIONATION An element in one oxidation stateis Oxidation Reduction
+3 +4 (nf = 2) Study of electrode simultaneously oxidised and reduced half half
C2O42- CO2 processes and cells 2H 2 O 2 (l)
→ 2H 2 O(l) + O 2 (g) (Anode) (Cathode)
You might also like
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Chem 16.1 ReviewerDocument7 pagesChem 16.1 ReviewerCindy ChengNo ratings yet
- ACS Study GuideDocument7 pagesACS Study GuideRachel Garner100% (1)
- CH 19 - Electrochemistry - Chem163 Outline - S2016-1Document34 pagesCH 19 - Electrochemistry - Chem163 Outline - S2016-1Nguyễn Tương QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Ragnar's Homemade Detonators - H - Ragnar BensonDocument68 pagesRagnar's Homemade Detonators - H - Ragnar BensonFrederico WernerNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionDocument1 pageRedox ReactionPARAMBATH ANUP KUMARNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction and Electrochemistry (C-Inpo)Document25 pagesRedox Reaction and Electrochemistry (C-Inpo)Biggos businessNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: 2Mg 2Mg + 4eDocument10 pagesElectrochemistry: 2Mg 2Mg + 4eIvyy Joyce BuanNo ratings yet
- GCSE KO Formuale and EquationsDocument1 pageGCSE KO Formuale and EquationsPaulina MugutiNo ratings yet
- (4469) Sheet Basic Inorganic Nomenclature Theory eDocument6 pages(4469) Sheet Basic Inorganic Nomenclature Theory eboom rangNo ratings yet
- Section (A) : Oxidation Number Halogen Atom:: Basic Inorganic NomenclatureDocument8 pagesSection (A) : Oxidation Number Halogen Atom:: Basic Inorganic NomenclaturewanderedNo ratings yet
- Chem 1011Document4 pagesChem 1011Arfa Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- L Oss of E Lectrons Is O Xidation G Ain of E Lectrons Is R EductionDocument10 pagesL Oss of E Lectrons Is O Xidation G Ain of E Lectrons Is R Eductionherman lewisNo ratings yet
- Lect 7 CHE 142 Energy Production From Electrochemical SystemDocument21 pagesLect 7 CHE 142 Energy Production From Electrochemical Systemytr8bwjch2No ratings yet
- Aa 220619 180412Document1 pageAa 220619 180412KeasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ChemistryDocument33 pagesChapter 3 ChemistryMaticsNo ratings yet
- 5 2 3 Revision Guide Redox and Electrode PotentialsDocument10 pages5 2 3 Revision Guide Redox and Electrode PotentialsGarret GordonNo ratings yet
- REDOXDocument1 pageREDOXeiyda_idrisNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 REDOXDocument5 pagesTopic 3 REDOXskywalkerNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument17 pagesRedox ReactionsThamizharuvi. ANo ratings yet
- Share CE-112-MODULE-3-ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument18 pagesShare CE-112-MODULE-3-ELECTROCHEMISTRYAngelo GranadaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IIDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry IIRoberto SIlvaNo ratings yet
- Httpswww2 Chemistry Msu Educoursescem152Chap20lect PDFDocument48 pagesHttpswww2 Chemistry Msu Educoursescem152Chap20lect PDFAli AllamNo ratings yet
- BMAT CHEMISTRY-c5-Oxidation, reduction and redoxDocument10 pagesBMAT CHEMISTRY-c5-Oxidation, reduction and redoxNapassorn WongduangpaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation ADocument25 pagesOxidation Aaminah hameedNo ratings yet
- 3 Yr Level 3 Eng. ModuleDocument4 pages3 Yr Level 3 Eng. ModulePooja SainiNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry: JEE SyllabusDocument8 pagesRedox Reactions and Electrochemistry: JEE SyllabusIhtisham Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Lessons 1 RM StsDocument18 pagesOxidation Lessons 1 RM Stskocaxi9358No ratings yet
- Ethers: Diethyl Ether Was Commonly Used As A Local AnestheticDocument12 pagesEthers: Diethyl Ether Was Commonly Used As A Local Anestheticelizabethli23No ratings yet
- REDOXDocument10 pagesREDOXPROFFESSORNo ratings yet
- 05 - Group 2 & Redox CORNELLDocument8 pages05 - Group 2 & Redox CORNELLGeorge SolomouNo ratings yet
- L3 AromaticsDocument22 pagesL3 AromaticsCheng FuNo ratings yet
- CHM1-7.5 Like D LikeDocument16 pagesCHM1-7.5 Like D Likeadrian nenengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document24 pagesChapter 13abubakarabubakarbah563No ratings yet
- Week 8 - Redox ReactionDocument4 pagesWeek 8 - Redox ReactionThanni AkanbiNo ratings yet
- Titration (A Volumetric Method of Analysis)Document71 pagesTitration (A Volumetric Method of Analysis)Alleyah May GiducosNo ratings yet
- Organometallic ReactionsDocument7 pagesOrganometallic Reactionszahara99121No ratings yet
- Co Ordination CompoundDocument16 pagesCo Ordination Compounddhruvsoni8905No ratings yet
- Redox Equilibria IDocument5 pagesRedox Equilibria ILisa DentonNo ratings yet
- CHEM131 ElectrochemistryDocument38 pagesCHEM131 ElectrochemistryAngel Rose AriasNo ratings yet
- E5 Lewis Acids and Bases Acids: Bronsted: Acids Are Proton DonorsDocument9 pagesE5 Lewis Acids and Bases Acids: Bronsted: Acids Are Proton DonorsJohn HenricksNo ratings yet
- Redox & Equivalent Concepts (PQRS & J)Document20 pagesRedox & Equivalent Concepts (PQRS & J)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Cac Phan Ung Cua AncolDocument1 pageCac Phan Ung Cua AncolVy Na Ngo100% (1)
- Redox Reaction by AKansha KarnwalDocument66 pagesRedox Reaction by AKansha Karnwalkrishnarewani11No ratings yet
- Course 201N 1 Semester 2006-2007 Inorganic Chemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. BeraDocument10 pagesCourse 201N 1 Semester 2006-2007 Inorganic Chemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. BeraNITU KUMARINo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesElectrochemistry Lecture NotesLyra GurimbaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Red OxDocument1 pageChapter 4 Red OxShriya ParthasarathiNo ratings yet
- Theory (Volumetric Analysis)Document18 pagesTheory (Volumetric Analysis)smitvartakNo ratings yet
- 4.7 Types of Chemical Reactions Student PDFDocument6 pages4.7 Types of Chemical Reactions Student PDFSyed RazaNo ratings yet
- Non-Metallic Assigned: Fe, AgDocument5 pagesNon-Metallic Assigned: Fe, AgAarya DubeyNo ratings yet
- Mitochondriju Gener Lais RadikalaiDocument22 pagesMitochondriju Gener Lais RadikalaiTed McgintyNo ratings yet
- Coordinaiton CompoundsDocument41 pagesCoordinaiton Compoundsjacksparrow16204No ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument120 pagesIonic EquilibriumUdbhav DikshitNo ratings yet
- E5 Lewis Acids and Bases (Session 1) November 5 - 11Document8 pagesE5 Lewis Acids and Bases (Session 1) November 5 - 11KIMIA Ronald Ivan WijayaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 ElectrochemistryDocument39 pagesUnit 4 ElectrochemistryElaiza Angelene NacarioNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument14 pagesRedoxamitaggarwal78No ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDocument13 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedGod is every whereNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and Ketone ReactionsDocument21 pagesAldehyde and Ketone ReactionsAinsssNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Lets Fall in Love With ChemistryDocument68 pagesChemistry: Lets Fall in Love With ChemistryAnay SahuNo ratings yet
- Valence ElectronsDocument3 pagesValence ElectronsGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors TheoryDocument22 pagesSemiconductors Theoryjit_72No ratings yet
- SSSSDocument9 pagesSSSSAkhmad DairobiNo ratings yet
- Zirconia MaterialsDocument2 pagesZirconia MaterialsFlexiblecsiNo ratings yet
- Additives For Drilling FluidsDocument3 pagesAdditives For Drilling FluidsGeorge Liberty0% (1)
- Chemical Stock UpdatedDocument21 pagesChemical Stock UpdatedPraise and worshipNo ratings yet
- Beacon 3000 Process Nir AnalyserDocument2 pagesBeacon 3000 Process Nir AnalyserSiddhartha MitraNo ratings yet
- MIG WeldingDocument17 pagesMIG WeldingAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNo ratings yet
- MDSReport 1039818470Document154 pagesMDSReport 1039818470javier ortizNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual Makita Rp0900Document12 pagesInstruction Manual Makita Rp0900Jonathan Pascua CamachoNo ratings yet
- 01 Atomic Structures N PDFDocument15 pages01 Atomic Structures N PDFElongated SausageNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Schedule - Equipment TemplateDocument2 pagesCleaning Schedule - Equipment TemplateEduyNo ratings yet
- Reactor Kinetics of Urea Formation: November 2015Document21 pagesReactor Kinetics of Urea Formation: November 2015thaeNo ratings yet
- Syllabus MtechDocument75 pagesSyllabus Mtechamit64007No ratings yet
- CLW Vendor DirectoryDocument41 pagesCLW Vendor DirectoryNilanjan Sen100% (1)
- Electrochemistry 494 PDFDocument55 pagesElectrochemistry 494 PDFakashNo ratings yet
- Global Warming PotentialDocument24 pagesGlobal Warming PotentialMotaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium-Constant NOTESDocument5 pagesEquilibrium-Constant NOTESAlex Jethro TigoyNo ratings yet
- Grabner InstrumentDocument2 pagesGrabner InstrumentEgie WijaksonoNo ratings yet
- (Special Publication) S.D. Jackson, J.S.J. Hargreaves, D. Lennon-Catalysis in Application_ [Proceedings of the International Symposium on Applied Catalysis to Be Held at the University of Glasgow on 1Document332 pages(Special Publication) S.D. Jackson, J.S.J. Hargreaves, D. Lennon-Catalysis in Application_ [Proceedings of the International Symposium on Applied Catalysis to Be Held at the University of Glasgow on 1Abdi Nemera EmanaNo ratings yet
- Role of Steam in Partial Oxidation of Propylene Over A PD/SDB CatalystDocument7 pagesRole of Steam in Partial Oxidation of Propylene Over A PD/SDB CatalystAlyaNo ratings yet
- Yakima Bait 2018 Catalog PDFDocument96 pagesYakima Bait 2018 Catalog PDFPenta AlfaNo ratings yet
- The Art and Science of Organic andDocument34 pagesThe Art and Science of Organic andWalter RamirezNo ratings yet
- Volume Correction MethanolDocument2 pagesVolume Correction MethanolLisiLxNo ratings yet
- Flexible Concrete Sheet PDFDocument6 pagesFlexible Concrete Sheet PDFNavanit KumarNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy WKST KEYDocument4 pagesEnthalpy WKST KEYمحمد گراوندNo ratings yet
- Furniture - Guideline For USA and CALIFORNIADocument27 pagesFurniture - Guideline For USA and CALIFORNIAENRIQUE CABRIA DEL OLMONo ratings yet
- High Range Water-Reducing Concrete Admixture: Chemrite - NN (A)Document5 pagesHigh Range Water-Reducing Concrete Admixture: Chemrite - NN (A)ghazanfarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Premium Motor Spirit (PMS) Distributed in Lagos Metropolis, NigeriaDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Premium Motor Spirit (PMS) Distributed in Lagos Metropolis, Nigerialuk4ezyNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesLiterature ReviewSK 119 ENGLISH LANGUAGE SCHOOLNo ratings yet