Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basel III
Basel III
Uploaded by
Aashish MainkarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Business Economics Notes For KTU StudentsDocument27 pagesBusiness Economics Notes For KTU StudentsAbdu Samad MNo ratings yet
- BASEL III Is A Global Regulatory Standard On Bank Capital AdequacyDocument4 pagesBASEL III Is A Global Regulatory Standard On Bank Capital AdequacyMituNo ratings yet
- BASEL III Is A Global Regulatory Standard On Bank: Bank Liquidity Bank LeverageDocument5 pagesBASEL III Is A Global Regulatory Standard On Bank: Bank Liquidity Bank LeverageLjubodrag LjumovicNo ratings yet
- Basel IIIDocument3 pagesBasel IIIainnocentNo ratings yet
- RAROCDocument6 pagesRAROCvishalchigaleNo ratings yet
- Basel 3Document10 pagesBasel 3sampathfriendNo ratings yet
- Basel Iii: Basel III Is A Global Regulatory Standard On BankDocument6 pagesBasel Iii: Basel III Is A Global Regulatory Standard On BankShipra SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Basil 3 AssignmentDocument27 pagesBasil 3 AssignmentSadia Islam MouNo ratings yet
- The Reforms TargetDocument8 pagesThe Reforms TargetPrachi PawarNo ratings yet
- Bbo Basel IiiDocument4 pagesBbo Basel Iiidas.suchitra991No ratings yet
- Summary of Proposed Changes: Tier 1 Capital Tier 2 CapitalDocument5 pagesSummary of Proposed Changes: Tier 1 Capital Tier 2 CapitalTrupti RayNo ratings yet
- Leverage Ratios Reserve Capital: Basel IiiDocument5 pagesLeverage Ratios Reserve Capital: Basel IiiroshanNo ratings yet
- Basel IIIDocument6 pagesBasel IIIgauravgoluNo ratings yet
- Basel 3 NormsDocument2 pagesBasel 3 Normsnayan8295patelNo ratings yet
- Basel 3Document5 pagesBasel 3Ratan DehuryNo ratings yet
- Basel III Comparison Between BII & B III: Mayuri Jatale Sarita Shah Abhijeet HelodeyDocument20 pagesBasel III Comparison Between BII & B III: Mayuri Jatale Sarita Shah Abhijeet HelodeyDiwakar LakhotiyaNo ratings yet
- Basel 3 NormsDocument14 pagesBasel 3 Normsnidazaidi1989No ratings yet
- Basel 3Document129 pagesBasel 3maneesh pNo ratings yet
- Basel III Important SectionsDocument22 pagesBasel III Important SectionsGeorge Lekatis100% (1)
- ProQuestDocuments 2015-04-22 KDDocument11 pagesProQuestDocuments 2015-04-22 KDKais NandoliaNo ratings yet
- Framework For More Resilient Banks and Banking SystemsDocument115 pagesFramework For More Resilient Banks and Banking SystemsBastab MishraNo ratings yet
- Basel Iii: The Future in BankingDocument7 pagesBasel Iii: The Future in BankingTariq Motiwala100% (1)
- 2 - Banking Regulation and Basel IIIDocument5 pages2 - Banking Regulation and Basel IIIdaniel sakaiNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter 2Document20 pages09 - Chapter 2BEPF 32 Sharma RohitNo ratings yet
- Basel IiiDocument44 pagesBasel IiiƦƛj Thålèswäř100% (2)
- Sos InfoDocument97 pagesSos InfoSailesh NgangbamNo ratings yet
- Basel I I I Presentation 1Document32 pagesBasel I I I Presentation 1madhusudhananNo ratings yet
- Basel 3 PPT OfficialDocument32 pagesBasel 3 PPT OfficialNEERAJA N JNo ratings yet
- Basel III Accord - Basel 3 Norms: Contributed byDocument25 pagesBasel III Accord - Basel 3 Norms: Contributed bysamyumuthuNo ratings yet
- Basel IIIDocument18 pagesBasel IIIPayal SawhneyNo ratings yet
- Basel-III Norms - Highlights: Atul Kumar ThakurDocument9 pagesBasel-III Norms - Highlights: Atul Kumar ThakurJosephin DynaNo ratings yet
- Basel Norms For BankingDocument5 pagesBasel Norms For BankingAkshat PrakashNo ratings yet
- Basel - I, II & IIIDocument31 pagesBasel - I, II & IIILoraNo ratings yet
- Overview of Basel IIIDocument3 pagesOverview of Basel IIIseamhasankhan04No ratings yet
- Basel-IIIDocument3 pagesBasel-IIIJayesh RupaniNo ratings yet
- Bulletin Finanza: Basel Iii NormsDocument2 pagesBulletin Finanza: Basel Iii Normskaran_w3No ratings yet
- Basel - I, II & III - Session 2 PDFDocument31 pagesBasel - I, II & III - Session 2 PDFAzim HossainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 MGT of Equity CapitalDocument29 pagesChapter 16 MGT of Equity CapitalRafiur Rahman100% (1)
- Basel Banking Norms: Their Efficacy, Analysis in The Global Context & Future DirectionDocument13 pagesBasel Banking Norms: Their Efficacy, Analysis in The Global Context & Future DirectionvivekNo ratings yet
- Archa - M180017MS Assgnmnet 2Document5 pagesArcha - M180017MS Assgnmnet 2Archa ShajiNo ratings yet
- Basel Committee On Banking Supervision Reforms - Basel IIIDocument1 pageBasel Committee On Banking Supervision Reforms - Basel IIISunlight FoundationNo ratings yet
- The Impact of The Basel 3 Capital and Liquidity RequirementsDocument64 pagesThe Impact of The Basel 3 Capital and Liquidity Requirementsalicefriends_27No ratings yet
- Comparative Discussion Among BASEL I, BASEL II & BASEL IIIDocument4 pagesComparative Discussion Among BASEL I, BASEL II & BASEL IIIRajesh PaulNo ratings yet
- Basel 3Document8 pagesBasel 3Shuvo SDNo ratings yet
- What Is Basel IIIDocument3 pagesWhat Is Basel IIIshaharyarkhan100% (1)
- Basel Iii: Presented By: Purshottam Singh Rahul Bagla Sandeep S. Sharma Vipul JainDocument10 pagesBasel Iii: Presented By: Purshottam Singh Rahul Bagla Sandeep S. Sharma Vipul JainRahul JainNo ratings yet
- Biggie 1Document4 pagesBiggie 1Neoline Chipo DzirutsvaNo ratings yet
- Basel II Vs Basel III NormsDocument3 pagesBasel II Vs Basel III NormsNaman Sharma0% (1)
- Stefan Ingves Basel III: Are We Done Now?Document5 pagesStefan Ingves Basel III: Are We Done Now?aditya saiNo ratings yet
- Basel 3 News July 2011Document33 pagesBasel 3 News July 2011George LekatisNo ratings yet
- Banking Regulation - Basel IIIDocument51 pagesBanking Regulation - Basel IIIanastasyadustirani100% (1)
- Basel 3 Summary TableDocument1 pageBasel 3 Summary TableIzian SherwaniNo ratings yet
- International BankingDocument5 pagesInternational Bankingaditi singhNo ratings yet
- Basel III News June 2011Document46 pagesBasel III News June 2011George LekatisNo ratings yet
- Banking in Crisis: How strategic trends will change the banking business of the futureFrom EverandBanking in Crisis: How strategic trends will change the banking business of the futureNo ratings yet
- International Public Sector Accounting Standards Implementation Road Map for UzbekistanFrom EverandInternational Public Sector Accounting Standards Implementation Road Map for UzbekistanNo ratings yet
- Credit Risk Management In and Out of the Financial Crisis: New Approaches to Value at Risk and Other ParadigmsFrom EverandCredit Risk Management In and Out of the Financial Crisis: New Approaches to Value at Risk and Other ParadigmsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- The Basel Ii "Use Test" - a Retail Credit Approach: Developing and Implementing Effective Retail Credit Risk Strategies Using Basel IiFrom EverandThe Basel Ii "Use Test" - a Retail Credit Approach: Developing and Implementing Effective Retail Credit Risk Strategies Using Basel IiNo ratings yet
- Asset and Liability Management for Banks and Insurance CompaniesFrom EverandAsset and Liability Management for Banks and Insurance CompaniesNo ratings yet
- CV of Md. Nazrul Islam ACADocument3 pagesCV of Md. Nazrul Islam ACANazrul IslamNo ratings yet
- New Keynesian Model - Week 6 LectureDocument3 pagesNew Keynesian Model - Week 6 LectureAlex LancashireNo ratings yet
- Financials - Biomass Briquetting - 5 YearsDocument14 pagesFinancials - Biomass Briquetting - 5 YearsSHARMA TRAVELS LATURNo ratings yet
- The Fall of Global Trust Bank': BY: Rajeev Kumar Akash Jain Shashidhar Ashwani Atul AgrawalDocument35 pagesThe Fall of Global Trust Bank': BY: Rajeev Kumar Akash Jain Shashidhar Ashwani Atul AgrawalDipesh JainNo ratings yet
- Invoice CookerDocument2 pagesInvoice Cookermankena1973No ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument11 pagesSyllabusMuhammad Qaisar LatifNo ratings yet
- Banking Laws - Villanueva-CastroDocument7 pagesBanking Laws - Villanueva-Castrojade123_129No ratings yet
- Laurus LabsDocument32 pagesLaurus LabsAkash GowdaNo ratings yet
- How To Buy CryptocurrenciesDocument2 pagesHow To Buy CryptocurrenciesObinna ObiefuleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-2Document70 pagesChapter 1-2Dion Bonaventura ManaluNo ratings yet
- 151025-891852 20191231 PDFDocument1 page151025-891852 20191231 PDFArina KhairuzanNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement Receipt: The Ark Vehicle Trading & General Merchandise IncDocument1 pageAcknowledgement Receipt: The Ark Vehicle Trading & General Merchandise IncJoseph S. Palileo Jr.No ratings yet
- Petrobras of Brazil and The CostDocument3 pagesPetrobras of Brazil and The CostIoana PunctNo ratings yet
- Types of BankingDocument123 pagesTypes of BankingSuvankar Nandi100% (1)
- History of BankingDocument2 pagesHistory of BankingJitendra VirahyasNo ratings yet
- Prudential Regulations For Corporate / Commercial BankingDocument53 pagesPrudential Regulations For Corporate / Commercial BankingMUNTHA ARSHADNo ratings yet
- CLMB Food Corp Notes To FSDocument12 pagesCLMB Food Corp Notes To FSSharah Del T. TudeNo ratings yet
- Steps For Trading On Your OwnDocument2 pagesSteps For Trading On Your OwnArunrajNo ratings yet
- Micro Credit PresentationDocument33 pagesMicro Credit PresentationHassan AzizNo ratings yet
- Stupid Economy PDFDocument27 pagesStupid Economy PDFAndrea PérezNo ratings yet
- BUSANA1 Chapter 4: Sinking FundDocument17 pagesBUSANA1 Chapter 4: Sinking Fund7 bitNo ratings yet
- Shri Salman Khurshid Minister For Law and JusticeDocument4 pagesShri Salman Khurshid Minister For Law and JusticeNetwork18No ratings yet
- Investment PaperDocument3 pagesInvestment Paperapi-583759965No ratings yet
- Cost of Capital Exercise ProblemDocument4 pagesCost of Capital Exercise ProblemDhruv MahajanNo ratings yet
- Mass DOTDocument3 pagesMass DOTremolacha147No ratings yet
- Final Non Budgetary KrasDocument548 pagesFinal Non Budgetary KrasRakesh KushwahaNo ratings yet
- MHABJG00118Document1 pageMHABJG00118Gaurav GujrathiNo ratings yet
- ch#5 of CFDocument2 pagesch#5 of CFAzeem KhalidNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet of Bajaj AutoDocument6 pagesBalance Sheet of Bajaj Autogurjit20No ratings yet
Basel III
Basel III
Uploaded by
Aashish MainkarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basel III
Basel III
Uploaded by
Aashish MainkarCopyright:
Available Formats
Basel III
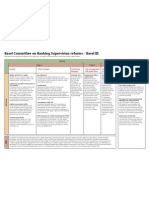
Basel III is a now a global regulatory stanadard on bank capital adequacy and liquid agreed by the members of the basel committee on banking supervision . the third of the basel accord was deelop in a response to the deficiencies in financial regulation revealed by the global fianancial crises. Basel III strengthens bank capital requirement and introduces new regulatory requirements on bank liquidity and bank leverage. The Organisation for economics co-operation and development (OECD) estimates that the implementation of basel III will decrease annual GDP growth by 0.05 to 0.15 percent point. BaselIII will require banks to hold 4.5% fo common equity (up from 2% in basel II) AND 6% of tier I caoitak (up from 4% in basel II) of risk-weighted assets (RWA). BaselII also introduces additional capital buffers,(i) a mandatory capital conservation buffer of 2.5% and (ii) a discretionary counter-cyclical buffer ,which allows national regulators to require up to another 2.5% of capital during period of high credit growth. The liquidity coverage ratio requires a bank to hold sufficient high quantity liquid asset to cover its total net cash flow over 30 days; the stable funding ratio requires the available amount of stable funding to exceed the required amount of stable funding over a one year period of extended stress. Summary of proposed changes First the quality ,consistency an transpersancy of capital base will be raised. Tier 1 capital : the predominant form of tier 1capital must be common share and retained earnings. Tier 2 capital instrument will be harmonised. Tier 3 capital will be eliminated. Second the risk coverage of capital framework will be strengthened. Promote more integrated management of market and counterparty credit risk. Add the CAV(credit valuation adjustment )-risk due to deterioration in counterpartys credit Rating Strengthen the capital requirement for counterparty credit exposure arising from banks derivatives, repo and decurities financing transactions. Provide additional incentives to move OTC derivatives to central counterparties (probably clearing house ) Third, the committee will introduce a leverage ratio as a supplementary measure to the basel II risk-based framework.
The committee therefore is introducing a leverage ratio requirement that is intended to achieve the following objectives : The committee therefore is introducing a leverage ratio requirement that is intended to achieve the following objectives Put a floor under the build up of leverage in the banking sector Introduce additional safeguards against model risk and measurement error by supplementing the risk based measures with a simpler measures that is based on gross explosure. Fourth the committee is introducing a service of measures to promote the build up of capital buffers in good times that can be drawn upon in periods of stress (reducing procyclicality and promoting counter cyclical buffers)
Reforms in indian banking sector leads to increase competition between various industries such as banking, insurance, financial institutions and so on. It helps to enhance the economic growth of the country. Inclusion would also emerge as the key issues for a country like india, art this stage of socio-economic development.
You might also like
- Business Economics Notes For KTU StudentsDocument27 pagesBusiness Economics Notes For KTU StudentsAbdu Samad MNo ratings yet
- BASEL III Is A Global Regulatory Standard On Bank Capital AdequacyDocument4 pagesBASEL III Is A Global Regulatory Standard On Bank Capital AdequacyMituNo ratings yet
- BASEL III Is A Global Regulatory Standard On Bank: Bank Liquidity Bank LeverageDocument5 pagesBASEL III Is A Global Regulatory Standard On Bank: Bank Liquidity Bank LeverageLjubodrag LjumovicNo ratings yet
- Basel IIIDocument3 pagesBasel IIIainnocentNo ratings yet
- RAROCDocument6 pagesRAROCvishalchigaleNo ratings yet
- Basel 3Document10 pagesBasel 3sampathfriendNo ratings yet
- Basel Iii: Basel III Is A Global Regulatory Standard On BankDocument6 pagesBasel Iii: Basel III Is A Global Regulatory Standard On BankShipra SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Basil 3 AssignmentDocument27 pagesBasil 3 AssignmentSadia Islam MouNo ratings yet
- The Reforms TargetDocument8 pagesThe Reforms TargetPrachi PawarNo ratings yet
- Bbo Basel IiiDocument4 pagesBbo Basel Iiidas.suchitra991No ratings yet
- Summary of Proposed Changes: Tier 1 Capital Tier 2 CapitalDocument5 pagesSummary of Proposed Changes: Tier 1 Capital Tier 2 CapitalTrupti RayNo ratings yet
- Leverage Ratios Reserve Capital: Basel IiiDocument5 pagesLeverage Ratios Reserve Capital: Basel IiiroshanNo ratings yet
- Basel IIIDocument6 pagesBasel IIIgauravgoluNo ratings yet
- Basel 3 NormsDocument2 pagesBasel 3 Normsnayan8295patelNo ratings yet
- Basel 3Document5 pagesBasel 3Ratan DehuryNo ratings yet
- Basel III Comparison Between BII & B III: Mayuri Jatale Sarita Shah Abhijeet HelodeyDocument20 pagesBasel III Comparison Between BII & B III: Mayuri Jatale Sarita Shah Abhijeet HelodeyDiwakar LakhotiyaNo ratings yet
- Basel 3 NormsDocument14 pagesBasel 3 Normsnidazaidi1989No ratings yet
- Basel 3Document129 pagesBasel 3maneesh pNo ratings yet
- Basel III Important SectionsDocument22 pagesBasel III Important SectionsGeorge Lekatis100% (1)
- ProQuestDocuments 2015-04-22 KDDocument11 pagesProQuestDocuments 2015-04-22 KDKais NandoliaNo ratings yet
- Framework For More Resilient Banks and Banking SystemsDocument115 pagesFramework For More Resilient Banks and Banking SystemsBastab MishraNo ratings yet
- Basel Iii: The Future in BankingDocument7 pagesBasel Iii: The Future in BankingTariq Motiwala100% (1)
- 2 - Banking Regulation and Basel IIIDocument5 pages2 - Banking Regulation and Basel IIIdaniel sakaiNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter 2Document20 pages09 - Chapter 2BEPF 32 Sharma RohitNo ratings yet
- Basel IiiDocument44 pagesBasel IiiƦƛj Thålèswäř100% (2)
- Sos InfoDocument97 pagesSos InfoSailesh NgangbamNo ratings yet
- Basel I I I Presentation 1Document32 pagesBasel I I I Presentation 1madhusudhananNo ratings yet
- Basel 3 PPT OfficialDocument32 pagesBasel 3 PPT OfficialNEERAJA N JNo ratings yet
- Basel III Accord - Basel 3 Norms: Contributed byDocument25 pagesBasel III Accord - Basel 3 Norms: Contributed bysamyumuthuNo ratings yet
- Basel IIIDocument18 pagesBasel IIIPayal SawhneyNo ratings yet
- Basel-III Norms - Highlights: Atul Kumar ThakurDocument9 pagesBasel-III Norms - Highlights: Atul Kumar ThakurJosephin DynaNo ratings yet
- Basel Norms For BankingDocument5 pagesBasel Norms For BankingAkshat PrakashNo ratings yet
- Basel - I, II & IIIDocument31 pagesBasel - I, II & IIILoraNo ratings yet
- Overview of Basel IIIDocument3 pagesOverview of Basel IIIseamhasankhan04No ratings yet
- Basel-IIIDocument3 pagesBasel-IIIJayesh RupaniNo ratings yet
- Bulletin Finanza: Basel Iii NormsDocument2 pagesBulletin Finanza: Basel Iii Normskaran_w3No ratings yet
- Basel - I, II & III - Session 2 PDFDocument31 pagesBasel - I, II & III - Session 2 PDFAzim HossainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 MGT of Equity CapitalDocument29 pagesChapter 16 MGT of Equity CapitalRafiur Rahman100% (1)
- Basel Banking Norms: Their Efficacy, Analysis in The Global Context & Future DirectionDocument13 pagesBasel Banking Norms: Their Efficacy, Analysis in The Global Context & Future DirectionvivekNo ratings yet
- Archa - M180017MS Assgnmnet 2Document5 pagesArcha - M180017MS Assgnmnet 2Archa ShajiNo ratings yet
- Basel Committee On Banking Supervision Reforms - Basel IIIDocument1 pageBasel Committee On Banking Supervision Reforms - Basel IIISunlight FoundationNo ratings yet
- The Impact of The Basel 3 Capital and Liquidity RequirementsDocument64 pagesThe Impact of The Basel 3 Capital and Liquidity Requirementsalicefriends_27No ratings yet
- Comparative Discussion Among BASEL I, BASEL II & BASEL IIIDocument4 pagesComparative Discussion Among BASEL I, BASEL II & BASEL IIIRajesh PaulNo ratings yet
- Basel 3Document8 pagesBasel 3Shuvo SDNo ratings yet
- What Is Basel IIIDocument3 pagesWhat Is Basel IIIshaharyarkhan100% (1)
- Basel Iii: Presented By: Purshottam Singh Rahul Bagla Sandeep S. Sharma Vipul JainDocument10 pagesBasel Iii: Presented By: Purshottam Singh Rahul Bagla Sandeep S. Sharma Vipul JainRahul JainNo ratings yet
- Biggie 1Document4 pagesBiggie 1Neoline Chipo DzirutsvaNo ratings yet
- Basel II Vs Basel III NormsDocument3 pagesBasel II Vs Basel III NormsNaman Sharma0% (1)
- Stefan Ingves Basel III: Are We Done Now?Document5 pagesStefan Ingves Basel III: Are We Done Now?aditya saiNo ratings yet
- Basel 3 News July 2011Document33 pagesBasel 3 News July 2011George LekatisNo ratings yet
- Banking Regulation - Basel IIIDocument51 pagesBanking Regulation - Basel IIIanastasyadustirani100% (1)
- Basel 3 Summary TableDocument1 pageBasel 3 Summary TableIzian SherwaniNo ratings yet
- International BankingDocument5 pagesInternational Bankingaditi singhNo ratings yet
- Basel III News June 2011Document46 pagesBasel III News June 2011George LekatisNo ratings yet
- Banking in Crisis: How strategic trends will change the banking business of the futureFrom EverandBanking in Crisis: How strategic trends will change the banking business of the futureNo ratings yet
- International Public Sector Accounting Standards Implementation Road Map for UzbekistanFrom EverandInternational Public Sector Accounting Standards Implementation Road Map for UzbekistanNo ratings yet
- Credit Risk Management In and Out of the Financial Crisis: New Approaches to Value at Risk and Other ParadigmsFrom EverandCredit Risk Management In and Out of the Financial Crisis: New Approaches to Value at Risk and Other ParadigmsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- The Basel Ii "Use Test" - a Retail Credit Approach: Developing and Implementing Effective Retail Credit Risk Strategies Using Basel IiFrom EverandThe Basel Ii "Use Test" - a Retail Credit Approach: Developing and Implementing Effective Retail Credit Risk Strategies Using Basel IiNo ratings yet
- Asset and Liability Management for Banks and Insurance CompaniesFrom EverandAsset and Liability Management for Banks and Insurance CompaniesNo ratings yet
- CV of Md. Nazrul Islam ACADocument3 pagesCV of Md. Nazrul Islam ACANazrul IslamNo ratings yet
- New Keynesian Model - Week 6 LectureDocument3 pagesNew Keynesian Model - Week 6 LectureAlex LancashireNo ratings yet
- Financials - Biomass Briquetting - 5 YearsDocument14 pagesFinancials - Biomass Briquetting - 5 YearsSHARMA TRAVELS LATURNo ratings yet
- The Fall of Global Trust Bank': BY: Rajeev Kumar Akash Jain Shashidhar Ashwani Atul AgrawalDocument35 pagesThe Fall of Global Trust Bank': BY: Rajeev Kumar Akash Jain Shashidhar Ashwani Atul AgrawalDipesh JainNo ratings yet
- Invoice CookerDocument2 pagesInvoice Cookermankena1973No ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument11 pagesSyllabusMuhammad Qaisar LatifNo ratings yet
- Banking Laws - Villanueva-CastroDocument7 pagesBanking Laws - Villanueva-Castrojade123_129No ratings yet
- Laurus LabsDocument32 pagesLaurus LabsAkash GowdaNo ratings yet
- How To Buy CryptocurrenciesDocument2 pagesHow To Buy CryptocurrenciesObinna ObiefuleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-2Document70 pagesChapter 1-2Dion Bonaventura ManaluNo ratings yet
- 151025-891852 20191231 PDFDocument1 page151025-891852 20191231 PDFArina KhairuzanNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement Receipt: The Ark Vehicle Trading & General Merchandise IncDocument1 pageAcknowledgement Receipt: The Ark Vehicle Trading & General Merchandise IncJoseph S. Palileo Jr.No ratings yet
- Petrobras of Brazil and The CostDocument3 pagesPetrobras of Brazil and The CostIoana PunctNo ratings yet
- Types of BankingDocument123 pagesTypes of BankingSuvankar Nandi100% (1)
- History of BankingDocument2 pagesHistory of BankingJitendra VirahyasNo ratings yet
- Prudential Regulations For Corporate / Commercial BankingDocument53 pagesPrudential Regulations For Corporate / Commercial BankingMUNTHA ARSHADNo ratings yet
- CLMB Food Corp Notes To FSDocument12 pagesCLMB Food Corp Notes To FSSharah Del T. TudeNo ratings yet
- Steps For Trading On Your OwnDocument2 pagesSteps For Trading On Your OwnArunrajNo ratings yet
- Micro Credit PresentationDocument33 pagesMicro Credit PresentationHassan AzizNo ratings yet
- Stupid Economy PDFDocument27 pagesStupid Economy PDFAndrea PérezNo ratings yet
- BUSANA1 Chapter 4: Sinking FundDocument17 pagesBUSANA1 Chapter 4: Sinking Fund7 bitNo ratings yet
- Shri Salman Khurshid Minister For Law and JusticeDocument4 pagesShri Salman Khurshid Minister For Law and JusticeNetwork18No ratings yet
- Investment PaperDocument3 pagesInvestment Paperapi-583759965No ratings yet
- Cost of Capital Exercise ProblemDocument4 pagesCost of Capital Exercise ProblemDhruv MahajanNo ratings yet
- Mass DOTDocument3 pagesMass DOTremolacha147No ratings yet
- Final Non Budgetary KrasDocument548 pagesFinal Non Budgetary KrasRakesh KushwahaNo ratings yet
- MHABJG00118Document1 pageMHABJG00118Gaurav GujrathiNo ratings yet
- ch#5 of CFDocument2 pagesch#5 of CFAzeem KhalidNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet of Bajaj AutoDocument6 pagesBalance Sheet of Bajaj Autogurjit20No ratings yet