Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Py 1679789071
Py 1679789071
Uploaded by
sicherheitchecken0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesThis document provides a summary of key Python concepts including:
1. Python was created by Guido van Rossum in 1991 and the latest version is 3.7.4. It includes popular libraries like TensorFlow, Scikit-Learn, NumPy, Keras, PyTorch, Pandas, and SciPy.
2. NumPy allows for efficient manipulation of numeric data through N-dimensional arrays and matrices. Pandas allows working with labeled data in data structures called DataFrames.
3. Common operations include reading/writing CSV files, aggregating and grouping data, merging DataFrames, applying lambda functions or custom functions to modify columns of data, and sorting data.
Original Description:
Original Title
py_1679789071
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a summary of key Python concepts including:
1. Python was created by Guido van Rossum in 1991 and the latest version is 3.7.4. It includes popular libraries like TensorFlow, Scikit-Learn, NumPy, Keras, PyTorch, Pandas, and SciPy.
2. NumPy allows for efficient manipulation of numeric data through N-dimensional arrays and matrices. Pandas allows working with labeled data in data structures called DataFrames.
3. Common operations include reading/writing CSV files, aggregating and grouping data, merging DataFrames, applying lambda functions or custom functions to modify columns of data, and sorting data.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesPy 1679789071
Py 1679789071
Uploaded by
sicherheitcheckenThis document provides a summary of key Python concepts including:
1. Python was created by Guido van Rossum in 1991 and the latest version is 3.7.4. It includes popular libraries like TensorFlow, Scikit-Learn, NumPy, Keras, PyTorch, Pandas, and SciPy.
2. NumPy allows for efficient manipulation of numeric data through N-dimensional arrays and matrices. Pandas allows working with labeled data in data structures called DataFrames.
3. Common operations include reading/writing CSV files, aggregating and grouping data, merging DataFrames, applying lambda functions or custom functions to modify columns of data, and sorting data.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
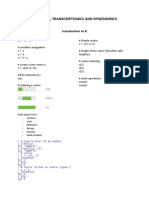
PYTHON 3
INT/FLOAT OPERATORS 3 + 2.56 DICT. OPERATORS {ky1: “A”, ky2: list}
int(“25“) > String to integer dic[key] = val > Add a key
CHEET SHEET BY @CHARLSTOWN
type() > Returns type dic.update({ky: v, ky: v}) > Add multiple keys
A//B > Returns ratio dic[key] = val > Overwrites value
CREATOR: GUIDO VAN ROSSUM A&B > Returns reminder dic[key] > Extracts a value I
YEAR: 1991 divmod(A, B) > Ratio/reminder dic.get(key) > Extracts a value II
LATEST VERSION (2019): 3.7.4 len() > Returns lenght dic.get(key, DefVal) > Extracts a value III
TOP LIBRARIES: TENSORFLOW, SCIKIT-LEARN, max() > Max. value dic.pop(key) > Delete K and V I
NUMPY, KERAS, PYTORCH, PANDAS, SCIPY min() > Min. value del dic[k] > Delete K and V II
abs() > Absolute value dic.keys() > Keys List
ELEMENTAL LIBRARIES import * pow(5, 2) > 5 powered by 2 dic.values() > Values list
import lib > Import all from lib 5**2 > 5 powered by 2 dic.items() > Returns K and V
from lib import function > Import function I round(A, 3) > Round 3 decimals key in dict > Checks key
lib.function() > Import function II sum(list) > Sum all list items dict(zip(lst_1, lst_2)) > Pair lists to Dict.
dir(math) > Show all functions LOOPS LIST & DICT COMPREHENSIONS
import library as lb >Library shortcut
for item in list: > for loop LIST COMPREHENSION
STRING OPERATORS “Hello world” print(item) > Iterate by items lst_A = [i for i in lst_B if i < 0]
str(29) > Int/Float to string LIST COMPREHENSION NESTED
len(“string”) > Total string length while limit <= 5 : > while loop
lst_A = [i if i < 0 else i-5 for i in lst_B]
“My” + “age is:” + “28” > Sum strings limit += 1 > Iterate by condition
“Hey!” * 3 > Repeat string by 3 LIST COMPREHENSION NESTED
LIST OPERATORS [“A”, “B”, 5, True]
“a“ in “chartlstown“ > True if str in str lst_A = [[i+1 for i in x] for x in lst_B]
‘letters‘.isalpha() > Check only letters len(list) > Count items in list
‘string’.upper() > STR to CAPS-CASE list(range(0,10,2)) > List from range DICT COMPREHENSION
‘string‘.lower() > STR to lower-case list.reverse() > Reverse the list {key: value for key, value in dict.items()}
‘string‘.title() > First letter to CAPS lst[idx] > Element index FUNCTION & LAMBDA:
list(“string“) > Letters to list lst[idx] = “item” > Change item
‘my string‘.split() > Words to List lst.append(‘item’) > Add item def switch(in1, in 2): > Code as function
““.join(list) > List to String by ““ lst[-5:] > Slicing list return (in2, in1) > Switch variables
“AB“.replace(“A”, “B”) > Replace AB > BB list.index(“B”) > Position index switch(“a”, “b”) > Run function on a,b
string.find(“A”) > Index from match list.insert(0, A) > Insert item by index
“ A “.strip() > No leading spaces list.remove(5) > Remove element plus_one = lambda x: x+1 > Code as expression
f”My age: {28}” > Insert in string list.count(A) > A frequency plus_one(5) > Number plus 1
“”My age: {}”.format(28) > Old insert in string list.sort() > Sort in same list
“AB\”CD” > Include symbol “ sorted(lst) > Sort in new list TIMING THE CODE
“\n” > New line in string lst.pop() > Last item time.time() > Get elapsed time
“\t” > Tabulator in string list(zip(lst_1, lst_2)) > Entwine pair of lists time.sleep(s) > Pause code s secs.
var = input(‘question?’) >Input string form enumerate(list) > Add index to list time.localtime() > Get local time
NUMPY_LIBRARY PANDAS_LIBRARY PANDAS AGGREGATES (COMANDS)
BASIC FUNCTIONS import numpy as np DATA FRAMES import pandas as pd df.c1.unique() >> Extracts the set
IMPORTING CSV FILES: IMPORTING CSV FILES: df.c1.nunique() >> Extracts len(set)
np.getfromtxt(‘f.csv’, delimiter = ‘,’) pd.read_csv(‘f.csv’) df.c1.mean() >> Average of the column
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - df.c1.median() >> Median of the column
np.mean(lst) >> Average pd.DataFrame(Dict) >> Create a DF I df.c1.std() >> Standard deviation
np.sort(lst) >> Sort the list columns = [list] >> Create a DF II df.c1.max() >> Max number
np.median(lst) >> Median - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - df.c1.min() >> Min number
np.percentile(lst, n) >> Percentil n% df.head(n) >> shows first n rows df.c1.count() >> len of the set
np.std(lst) >> Standard devi. df.info() >> entries and data P.A. (GROOPING)
np.mean(mtx < n) >> Conditions
np.var() >> Variance EXTRACTING COLUMNS AND ROWS df.groupby(c1).c2.mean()* >> Groups c1
df.column.values >> Extract column df.groupby(c1).id.count()* >> Counter
MATRIX import numpy as np df.groupby(c1).c2.apply(lb)* >> lambda
df[‘colum’] >> Extract multiple clmns
mtx = np.array(lst1, lst2, lst3) df[[c1, c2]] >> Extracts columns as df df.groupby([c1,c2]).c3* >> Multiple g
np.mean(mtx) >>Total data mean df.iloc[index] >> Extracts the Row by idx * > .reset_index() >> To reset df
np.mean(mtx, axis = 0) >> Columns mean df.iloc[i:i] >> Extracts Rows as df - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
np.mean(mtx, axis = 1) >> Rows mean df[df.c1 > n] >> Extracts Row by cond. I df.pivot(columns = c2, index = c1, values = v)
df[df.c1.condition] >> Extracts Row by cond. II MERGE METHODS
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
df.reset_index() >> Reset the index pd.merge(df1, df2*) >> Merge method I
drop = True >> Without inserting it df1.merge(df2) >> Merge method II
inplace = True >> Modify overwriting df1.merge(df2).merge(df3)
* > how = ‘outer’ \ ‘inner’ \ ‘right’ \ ‘left’
ADD AND RENAME COLUMNS - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
df[columns] = list >> Adding a column pd.merge(df1, df2, left_on = c1, right_on = c3)*
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - >> To merge 2 data frame with same column
RENAMING COLUMNS: * > suffixes = [name1, name2]
df.columns = list >> Modifying names - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
df.rename(columns = {old:new}, inplace=True) pd.concat([df1, df2])
APPLY MODIFICATIONS & LAMBDA SORTING METHODS
df[col] = df.c1.apply() >> Modify column df.sort_values(by = [‘c1‘, ‘c2‘], ascending = False)
df[col] = df.c1-apply(lb) >> lb = lambda
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
lb = lambda row: row.c1 >> Lambda in rows
df[col] = df.apply(lb, axis = 1)
You might also like
- Understanding The Information System DepartmentDocument9 pagesUnderstanding The Information System DepartmentSazzad Chowdhury0% (4)
- Chatgpt An Ai NLP Model PovDocument11 pagesChatgpt An Ai NLP Model PovLEGEND OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- Modules 1Document9 pagesModules 1karthiyayani umashankarNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Lists, Tuples, Dictionaries Insertion SortDocument12 pagesUnit Iv Lists, Tuples, Dictionaries Insertion SortnancypeterNo ratings yet
- Library Functions - PracticeDocument53 pagesLibrary Functions - PracticeTejasvini YadavNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat Sheet 8 PagesDocument8 pagesPython Cheat Sheet 8 PagesarcukvanaNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument74 pagesPythonNandhini VimalNo ratings yet
- Cheatsheet Python A4Document7 pagesCheatsheet Python A4bobe100% (1)
- PYTHON Chapter 2 PDFDocument11 pagesPYTHON Chapter 2 PDFAkNo ratings yet
- 21.3 Get List Size: Ring Documentation, Release 1.2Document10 pages21.3 Get List Size: Ring Documentation, Release 1.2Mahmoud Samir FayedNo ratings yet
- PYTHON For Coding InterviewsDocument11 pagesPYTHON For Coding InterviewsSangeeta YadavNo ratings yet
- Lists 8Document17 pagesLists 8singh.harsh233001No ratings yet
- Assignment 1701572062Document38 pagesAssignment 1701572062sowmeya veeraraghavanNo ratings yet
- Computer Science WorksheetDocument6 pagesComputer Science WorksheetAman RajNo ratings yet
- Class XI (As Per CBSE Board) : Computer ScienceDocument17 pagesClass XI (As Per CBSE Board) : Computer SciencecodingNo ratings yet
- Tutorial TCLDocument27 pagesTutorial TCLfrfewfewNo ratings yet
- List 12Document17 pagesList 12Abhijeet AmetaNo ratings yet
- List 12Document17 pagesList 12B durga PrasadNo ratings yet
- List and DictionariesDocument36 pagesList and DictionariesEgi LikardoNo ratings yet
- Python Question SetDocument3 pagesPython Question SetAlireza KafaeiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document12 pagesUnit 4Gowri rajuNo ratings yet
- The Ring Programming Language Version 1.5.1 Book - Part 21 of 180Document10 pagesThe Ring Programming Language Version 1.5.1 Book - Part 21 of 180Mahmoud Samir FayedNo ratings yet
- 23CS101T PSPP - Unit 4Document34 pages23CS101T PSPP - Unit 4p rajeshwariNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONS - WorkksheetDocument6 pagesFUNCTIONS - Workksheetmoshikaa.pNo ratings yet
- Assignment Functions in PythonDocument6 pagesAssignment Functions in Pythonsaumya dhayalNo ratings yet
- Python2 Cheat Sheet v2Document2 pagesPython2 Cheat Sheet v2h4ckm3omgNo ratings yet
- Class XI (As Per CBSE Board) : Informatics PracticesDocument17 pagesClass XI (As Per CBSE Board) : Informatics PracticesprithiksNo ratings yet
- 12 ListDocument21 pages12 ListAdhiraj LahonNo ratings yet
- Python - Module 3Document86 pagesPython - Module 3Syed MustafaNo ratings yet
- List - PracticeDocument3 pagesList - PracticeTheAncient01No ratings yet
- File 1680321120 GUSCSE202232165 ArrayandRandomDocument12 pagesFile 1680321120 GUSCSE202232165 ArrayandRandomsumit kumarNo ratings yet
- Programming and Problem Solving With PythonDocument23 pagesProgramming and Problem Solving With PythonRishika AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Python Tutorial 3Document7 pagesPython Tutorial 3queen setiloNo ratings yet
- Python Notes ch3Document22 pagesPython Notes ch3Bharat Khuman100% (1)
- ListDocument15 pagesListshivam0402008No ratings yet
- Lists 8Document17 pagesLists 8AvinashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document50 pagesChapter 3Rohit KhobareNo ratings yet
- JANMEJAY SINGH PROJECT CS - Sanjai SinghDocument24 pagesJANMEJAY SINGH PROJECT CS - Sanjai SinghHungry-- JoyNo ratings yet
- While Loop: Fibonacci SeriesDocument21 pagesWhile Loop: Fibonacci SeriesAnuj RuhelaNo ratings yet
- Breaking Barriers: Micro-Mortgage AnalyticsDocument121 pagesBreaking Barriers: Micro-Mortgage AnalyticsCYRIAC JOSE MBANo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-TuplesDocument15 pagesLecture 2-Tuplesahmed arabNo ratings yet
- PWP Practical PDFDocument13 pagesPWP Practical PDFPiyush SahaneNo ratings yet
- Module Lists Dic TuplesDocument50 pagesModule Lists Dic TuplesPrachi SharmaNo ratings yet
- C:/Users/Rafe/Appdata/Local/Programs/Python/Python35-32/Scripts Object and Data Structures BasicsDocument16 pagesC:/Users/Rafe/Appdata/Local/Programs/Python/Python35-32/Scripts Object and Data Structures BasicsrafeNo ratings yet
- ListDocument17 pagesListMafnitha KKNo ratings yet
- Exp7 PythonDocument6 pagesExp7 PythonradhaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RDocument11 pagesIntroduction To RMaddy IlNo ratings yet
- 21CS202 - Lab ManualDocument18 pages21CS202 - Lab ManualkavithaChinnaduraiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 PPTsDocument110 pagesUnit 3 PPTsrajputaditi2022No ratings yet
- MOO Programming Cheat SheetDocument9 pagesMOO Programming Cheat SheetJeannie MunroNo ratings yet
- CS 12 MS Set-HDocument13 pagesCS 12 MS Set-Hvikas_2No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1Utkarsh SinghNo ratings yet
- CS Answers - 2019-20 - SET2Document13 pagesCS Answers - 2019-20 - SET2-Uddipan BagchiNo ratings yet
- E.G. - If Input Is (12, 54, 49, 86, 23, 36) Then Modified List Is (32, 18, 16, 106, 43, 12)Document6 pagesE.G. - If Input Is (12, 54, 49, 86, 23, 36) Then Modified List Is (32, 18, 16, 106, 43, 12)Tanisha JenaNo ratings yet
- ES 26: Quiz 2 (30 PTS.) : ObjectiveDocument2 pagesES 26: Quiz 2 (30 PTS.) : ObjectiveKarlNo ratings yet
- Write A Python Program Using List and Their Built in FunctionsDocument11 pagesWrite A Python Program Using List and Their Built in Functions18bcs097 M. SanthiyaNo ratings yet
- Samanyu Kaushal-Program FileDocument26 pagesSamanyu Kaushal-Program Filekunal.1214155669No ratings yet
- Python Practice Questions 2Document29 pagesPython Practice Questions 2Shanice ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Python 41 AM2Document8 pagesPython 41 AM2Jonathan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Python Programming: Lecture 3 Functions: Lili DworkinDocument45 pagesPython Programming: Lecture 3 Functions: Lili DworkinMehrdadNo ratings yet
- Scan - and - Share - 1.07 - Printer (How To Scan and Create Quality DJVU Books)Document23 pagesScan - and - Share - 1.07 - Printer (How To Scan and Create Quality DJVU Books)gyl201No ratings yet
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9: Performing A Standard RHEL 9 InstallationDocument183 pagesRed Hat Enterprise Linux 9: Performing A Standard RHEL 9 InstallationMichał GabryelskiNo ratings yet
- 3 1 1 A Vex InputsoutputsDocument12 pages3 1 1 A Vex Inputsoutputsapi-325609401No ratings yet
- Gsmartcontrol StderrDocument1 pageGsmartcontrol StderrBen IkhsanNo ratings yet
- Mapreduce: Simpli - Ed Data Processing On Large ClustersDocument4 pagesMapreduce: Simpli - Ed Data Processing On Large ClustersIbrahim HamzaNo ratings yet
- Solr PPTDocument30 pagesSolr PPTAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- DM Openwrt Wds How ToDocument5 pagesDM Openwrt Wds How ToAlfonso Delgado OlleroNo ratings yet
- Mobile Application Protection Suite (MAPS)Document3 pagesMobile Application Protection Suite (MAPS)신동조No ratings yet
- 24.2 CAD System Hardware: Output Devices Digital Computer Secondary StorageDocument7 pages24.2 CAD System Hardware: Output Devices Digital Computer Secondary StorageAlberto OreaNo ratings yet
- D-LX 201 InformationCentre 3 - 0 ReadMeDocument2 pagesD-LX 201 InformationCentre 3 - 0 ReadMeLuiz HopathaNo ratings yet
- Bonk Physics FileDocument194 pagesBonk Physics FilePranav KNo ratings yet
- AuxiliarDocument9 pagesAuxiliarFelix Malo ANo ratings yet
- Li Fi Data Transmit Using Ardunio WordDocument38 pagesLi Fi Data Transmit Using Ardunio Wordsriranganathan120No ratings yet
- Cookbookv2 0Document171 pagesCookbookv2 0Tania FabrelloNo ratings yet
- CCH1D4 Struktur Data: Modularity and Data AbstractionDocument20 pagesCCH1D4 Struktur Data: Modularity and Data AbstractionSITI KHOTIJAHNo ratings yet
- MemTest86 User Guide UEFIDocument70 pagesMemTest86 User Guide UEFIdjkfkdfjsdfgjNo ratings yet
- Leet CodeDocument12 pagesLeet CodeAkhilesh AsareNo ratings yet
- Primavera Lab Manual 2nd LectureDocument13 pagesPrimavera Lab Manual 2nd LecturelitrakhanNo ratings yet
- Certificate in IT SyllabusDocument2 pagesCertificate in IT SyllabusKareemAdams9029No ratings yet
- Scrum Institute Promo Code - Register Scrum and Kanban CertificationsDocument27 pagesScrum Institute Promo Code - Register Scrum and Kanban CertificationsCath TesoroNo ratings yet
- Autonic SCM RS485 ConverterDocument7 pagesAutonic SCM RS485 ConverterkrisadiNo ratings yet
- #1 Backup, Ransomware Protection and Site Recovery For Virtual, Physical, Cloud, and Saas EnvironmentsDocument5 pages#1 Backup, Ransomware Protection and Site Recovery For Virtual, Physical, Cloud, and Saas Environmentsjuan.pasion3696No ratings yet
- UgcnetDocument613 pagesUgcnet14 - Vinay Singh - XII ANo ratings yet
- Creating A VBA Login Box For Smart ViewDocument8 pagesCreating A VBA Login Box For Smart ViewCaio Leonardo LimaNo ratings yet
- SBC Scz730 AcliconfigurationDocument1,583 pagesSBC Scz730 AcliconfigurationmsantacruzrNo ratings yet
- SCSJ2203 - Assignment 1Document11 pagesSCSJ2203 - Assignment 1teuku hanifNo ratings yet
- LIBR BatchCommandRef ENUDocument160 pagesLIBR BatchCommandRef ENUblazewhiteNo ratings yet
- SolidCAM 2015 Turning and Mill Turn Training CourseDocument282 pagesSolidCAM 2015 Turning and Mill Turn Training Coursehaclongdaica1987100% (2)