Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled Document
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
Emily Richards0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThe First Law of Thermodynamics, also known as the Law of Conservation of Energy, states that the total energy of an isolated system is constant. Energy may be exchanged between a system and its surroundings, but the total amount of energy remains the same. If energy is lost from the system, an equal amount must be gained by the surroundings, and vice versa.
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled document (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe First Law of Thermodynamics, also known as the Law of Conservation of Energy, states that the total energy of an isolated system is constant. Energy may be exchanged between a system and its surroundings, but the total amount of energy remains the same. If energy is lost from the system, an equal amount must be gained by the surroundings, and vice versa.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageUntitled Document
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
Emily RichardsThe First Law of Thermodynamics, also known as the Law of Conservation of Energy, states that the total energy of an isolated system is constant. Energy may be exchanged between a system and its surroundings, but the total amount of energy remains the same. If energy is lost from the system, an equal amount must be gained by the surroundings, and vice versa.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
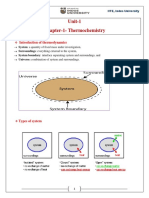
First Law of Thermodynamics (also called the Law of Conservation of Energy):
Energy may be exchanged between a system and its surroundings but the total
energy of the
system and the surroundings remains constant, that is, energy must be conserved.
Any energy
lost from the system must be gained by the surroundings and any energy gained by
the system is
lost from the surroundings.
The system is that part of the environment that we are concerned with. The
surroundings are
everything outside of the system. For example, a chem
Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics (also called the Law of Conservation
of Energy): Energy may be exchanged between a system and its surroundings but
the total energy of the system and the surroundings remains constant, that is, energy
must be conserved. Any energy lost from the system must be gained by the
surroundings and any energy gained by the system is lost from the surroundings.
The system is that part of the environment that we are concerned with. The
surroundings are everything outside of the system. For example, a chemical reaction
is a system and the atmosphere outside of the reaction is the surroundings. Energy
terms: Endothermic – the system absorbs energy/ heat from the surroundings
Exothermic – the system loses energy/ heat to the surroundings Enthalpy (H) – a
thermodynamic function/ term used to describe the energy/ heat content of a system
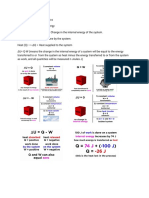
ΔH = Hfinal – Hinitial For a chemical reaction: ΔH = Hproducts – Hreactants The
enthalpy (heat) change that accompanies a reaction is called the enthalpy of reaction
or heat of reaction (ΔHrxn) If ∆H > 0 (i.e. a positive value) the reaction is
endothermic That is, energy must be supplied in order for the reaction to proceed. If
∆H < 0 (i.e. a negative value) the reaction is exothermic That is, energy is released
from the reaction. No energy is required for the reaction to proceed. This means that
exothermic reactions are quite feasible/ favorable as no additional energy is
required. The reactants possess enough energy and the reaction is
thermodynamically spontaneous.
You might also like
- Physical Biochemistry Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesPhysical Biochemistry Lecture Noteschc300No ratings yet
- Elementary Thermochemistry UnidelDocument5 pagesElementary Thermochemistry UnidelFamous IteNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics ShubhaDocument17 pagesThermodynamics ShubhaShubhajyoti KarmakarNo ratings yet
- ENERGY CHANGEs IN CHEMICAL REACTIONsDocument20 pagesENERGY CHANGEs IN CHEMICAL REACTIONsKristan RialaNo ratings yet
- The Laws of Thermodynamics - Boundless Chemistry - pdf1Document4 pagesThe Laws of Thermodynamics - Boundless Chemistry - pdf1booyemahemehrNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Fix KF 2.3Document12 pagesJurnal Fix KF 2.3Diky Dwi SugiartoNo ratings yet
- Internal Energy and ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesInternal Energy and ThermodynamicsVISWANATHAN GNo ratings yet
- BCH 201 - DR Olalekan BakareDocument11 pagesBCH 201 - DR Olalekan BakareIbrahim AkindapoNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesBasic Concepts of ThermodynamicsAADIL AHMED ANo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument9 pagesThermodynamicsMohammed FahadNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - Chapter-1 Thermochemistry PDFDocument26 pagesUnit-1 - Chapter-1 Thermochemistry PDFAshwin JhaNo ratings yet
- 3thermodynamics 2020Document55 pages3thermodynamics 2020Montassar Dridi100% (1)
- LO.15-Elfayoum Chemi Club: Made By: Ali AtefDocument55 pagesLO.15-Elfayoum Chemi Club: Made By: Ali Atefbebo atefNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: Thermochemistry: Heat and EnthalpyDocument2 pagesThermochemistry: Thermochemistry: Heat and EnthalpyJames Patrick TorresNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument10 pagesThermodynamicsThe amateurNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument11 pagesThermodynamicsMohammed FahadNo ratings yet
- Chemical Thermodynamics HandoutDocument8 pagesChemical Thermodynamics HandoutKyle Cedric MitalNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 (References)Document10 pagesCHAPTER 8 (References)JeromeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.2 Chemistry As Book EditedDocument20 pagesUnit 1.2 Chemistry As Book EditedJamsheed KakarNo ratings yet
- The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesThe First Law of ThermodynamicsIan Dimayuga100% (1)
- Thermochemistry. .Document2 pagesThermochemistry. .shadnawazkhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To ThermodynamicsParivesh LuniaNo ratings yet
- Phase TransitionDocument25 pagesPhase TransitionGordon YapNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document10 pagesModule 1Shefana RajaNo ratings yet
- The Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesThe Laws of ThermodynamicsAnila zafarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Is Defined As The Branch of Science That Deals With The RelationshipDocument8 pagesThermodynamics Is Defined As The Branch of Science That Deals With The Relationshipibro4khadNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Its ImplicationDocument5 pagesThermodynamics and Its ImplicationMadan ThapaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics - Thermodynamic TermsDocument3 pagesBasic Concepts of Thermodynamics - Thermodynamic Termsanas khanNo ratings yet
- Introductory Physical Chemistry (CHM 113) 2024 Final Final Correction To Be PrintedDocument21 pagesIntroductory Physical Chemistry (CHM 113) 2024 Final Final Correction To Be Printedcharlesdeezer2006No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics in BiochemistryDocument16 pagesThermodynamics in BiochemistrySurya DoleyNo ratings yet
- THERMODYNAMICSDocument3 pagesTHERMODYNAMICSAngelene Nova MondaresNo ratings yet
- PHY101 Introduction To ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesPHY101 Introduction To Thermodynamicsidrisaminuabdullahi26No ratings yet
- PDF Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument173 pagesPDF Chemical ThermodynamicsAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- 03 Chapter 2 Part 2 ThermochemistryDocument58 pages03 Chapter 2 Part 2 ThermochemistryAko si GianNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Specific Learning Objective at The End of The Session The Student Should Be Able To ExplainDocument67 pagesThermodynamics: Specific Learning Objective at The End of The Session The Student Should Be Able To ExplainfitriNo ratings yet
- Energetics of Chemical ReactionDocument68 pagesEnergetics of Chemical ReactionSolar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Zaporozhye State Medical University Department of Physical and Colloid ChemistryDocument54 pagesThermodynamics: Zaporozhye State Medical University Department of Physical and Colloid ChemistryTrần Nhật Khánh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 7 Chapter 6Document58 pages7 Chapter 6azizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1Zaki BedraniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Official Reporting ThermodynamicsDocument54 pagesChemistry Official Reporting ThermodynamicsJohn Kennly SimNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument13 pagesThermodynamicsNitin BeniwalNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument21 pagesThermodynamicsXenon ClassesNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Tut. 1Document4 pagesThermodynamics Tut. 1Atif MohamedNo ratings yet
- First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesFirst Law of ThermodynamicsFlorecel CaudillaNo ratings yet
- SCHX1014 - Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics - Unit 1: EnergyDocument18 pagesSCHX1014 - Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics - Unit 1: EnergyShanmuga PriyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ThermodynamicsDocument65 pagesIntroduction To ThermodynamicsNafisa AnikaNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument7 pagesThermochemistryLover BoyNo ratings yet
- EI UuiujDocument4 pagesEI UuiujJegr AbasNo ratings yet
- Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument28 pagesEngineering Thermodynamicsnagu nagaNo ratings yet
- THERMOODocument3 pagesTHERMOOKisha KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument43 pagesLecture 3 Laws of Thermodynamicsjackson mathiasNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesThermodynamicsliezyl_15No ratings yet
- XI CH 5 NotesDocument4 pagesXI CH 5 Notesiroonmaan123No ratings yet
- Zeroth Law of ThermodynamicsDocument16 pagesZeroth Law of ThermodynamicsSatyendra VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 ThermochemistryDocument10 pagesChapter 11 Thermochemistrymiraniwaqar16No ratings yet
- DP ThermodynamicsDocument24 pagesDP ThermodynamicsYash AkhauriNo ratings yet
- S ThermodynamicsDocument15 pagesS ThermodynamicsJoselito UbaldoNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 8: Exothermic vs. EndothermicDocument5 pagesLESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 8: Exothermic vs. Endothermicrigie.divinagraciaNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergeticsDocument11 pagesChemical EnergeticsMerab FarooqNo ratings yet