Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.3.3 - Types of Adjectives
1.3.3 - Types of Adjectives
Uploaded by
Kapco ChallengersCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- New Close Up B1 Plus Teachers BookDocument176 pagesNew Close Up B1 Plus Teachers Booklakoh4161171% (7)
- Nmat Repeated Questions Admito Admito PDFDocument123 pagesNmat Repeated Questions Admito Admito PDFKushal Gangar100% (1)
- Crash Course - Final SyllabusDocument32 pagesCrash Course - Final SyllabusynrNo ratings yet
- Grammar For PPSCDocument22 pagesGrammar For PPSCAlina NoreenNo ratings yet
- ADJECTIV1Document2 pagesADJECTIV1daveashNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de InglesDocument9 pagesTrabajo de InglesGabu DreepNo ratings yet
- Descriptive AdjectivesDocument11 pagesDescriptive AdjectivesitxtryNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Rejoice & Happy After Seeing This Type of Late ST TechnologyDocument18 pagesParts of Speech Rejoice & Happy After Seeing This Type of Late ST TechnologyKrishan GuptaNo ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument6 pagesAdjectivesahmadmuhammadamasNo ratings yet
- What Is Noun?Document4 pagesWhat Is Noun?Christian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and AdverbsDocument4 pagesAdjectives and Adverbspinpollo 507No ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument5 pagesHomeworkraziel castroNo ratings yet
- Guided Writing Part of SpeechDocument4 pagesGuided Writing Part of Speechgurning chanelNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument7 pagesPart of SpeechMaria Alonica Mae BacoyNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument7 pagesParts of SpeechBhavna SinghalNo ratings yet
- Adjective Definition & Meaning - Merriam-WebsterDocument16 pagesAdjective Definition & Meaning - Merriam-WebsteraimarylorenzoizquierdoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document28 pagesChapter 4Nga phạmNo ratings yet
- Classification of Parts of Speech: NounsDocument10 pagesClassification of Parts of Speech: NounsДенис МитрохінNo ratings yet
- Mental VerbsDocument15 pagesMental VerbsHazel Ann Bragado CabacunganNo ratings yet
- A Noun Is A Word Used As The Name of A PersonDocument18 pagesA Noun Is A Word Used As The Name of A PersonSharib SheraziNo ratings yet
- Adjective and Its Kinds: Possessive AdjectivesDocument4 pagesAdjective and Its Kinds: Possessive AdjectivesArsalan QureshiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Eng Jordão Ortega Jemusse ManguenaDocument11 pagesDr. Eng Jordão Ortega Jemusse ManguenajemusseNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech in EnglishDocument13 pagesParts of Speech in EnglishApparel ShopNo ratings yet
- ENG111 Adj Conj PrepDocument22 pagesENG111 Adj Conj PrepjemimaafuapeNo ratings yet
- A Noun Is A Part of Speech That Names A PersonDocument22 pagesA Noun Is A Part of Speech That Names A PersonghshamzarashakaNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Introductor-WPS OfficeDocument6 pages1.0 Introductor-WPS Officebenitamujinga84No ratings yet
- Raysha's SyntaxDocument5 pagesRaysha's SyntaxM. Fauzi ArrasyidNo ratings yet
- Eng Mod1Document26 pagesEng Mod1Tivar VictorNo ratings yet
- Types of NounsDocument5 pagesTypes of NounsnarutothunderjetNo ratings yet
- NounsDocument44 pagesNounsRoger Donoso BarralNo ratings yet
- 2 Forum InglesDocument4 pages2 Forum InglesRaimundo AfonsoNo ratings yet
- Adjectives 140524073135 Phpapp02Document42 pagesAdjectives 140524073135 Phpapp02Donna Rose Malizon ObcianaNo ratings yet
- A Noun Is A Part of Speech That Names A PersonDocument12 pagesA Noun Is A Part of Speech That Names A PersonfarhanalicasNo ratings yet
- Determine RsDocument38 pagesDetermine RsAaron S. Casipe Jr.No ratings yet
- ADJECTIVESDocument3 pagesADJECTIVESKatherine ArcosNo ratings yet
- Types of AdjectivesDocument2 pagesTypes of AdjectivesPaola ParkerNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument12 pagesParts of SpeechKh adijaNo ratings yet
- Adjectives CutieDocument5 pagesAdjectives CutieSweet lea AntonesNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument30 pagesPart of SpeechKaren BlanqueraNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument14 pagesPronounsainhoa.brosaNo ratings yet
- Packet UpdatedDocument70 pagesPacket UpdatedTien Thanh Le,No ratings yet
- Structure of English ModuleDocument26 pagesStructure of English ModuleSai Guyo50% (2)
- PARTS OF SPEECH UpdatedDocument12 pagesPARTS OF SPEECH UpdatedMCC Gilgit-BaltistanNo ratings yet
- Seminar 4Document13 pagesSeminar 4Михаил РешетниковNo ratings yet
- ADJECTIVEDocument5 pagesADJECTIVEdaveashNo ratings yet
- Foundation in Tesol Unit 2: Study of The English LanguageDocument28 pagesFoundation in Tesol Unit 2: Study of The English LanguageMiramar CamachoNo ratings yet
- Placement of AdjectivesDocument5 pagesPlacement of AdjectivesPranalaNo ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument9 pagesAdjectivesAnyeli SantosNo ratings yet
- Grammar Noun PronounsDocument4 pagesGrammar Noun PronounsShane AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- It's Means It Is or It Has While Its Means?Document2 pagesIt's Means It Is or It Has While Its Means?Dardarsky FegiNo ratings yet
- AdjectiveDocument11 pagesAdjectiveTika RogavaNo ratings yet
- Adjectives Are Describing WordsDocument1 pageAdjectives Are Describing Wordsjoy05.alexa.01No ratings yet
- Guide - Words, Phrases, Clauses and SentencesDocument14 pagesGuide - Words, Phrases, Clauses and SentencesTomas G Salazar TNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document6 pagesLecture 5安思吉No ratings yet
- WK5ENGDocument3 pagesWK5ENGAwojuyigbeNo ratings yet
- Grammatical CategoriesDocument6 pagesGrammatical CategoriesBeverlyNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument10 pagesParts of SpeechsalahudinNo ratings yet
- Types of AdjectivesDocument3 pagesTypes of AdjectivesNway Htet Htet AungNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument3 pagesPronounstobizarreNo ratings yet
- Gen Ed Guide English-GrammarDocument12 pagesGen Ed Guide English-GrammarShane AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- NounsDocument42 pagesNounsRoger Donoso Barral100% (1)
- English Adjectives Made Easy: An Essential Guide to Rules and Examples of English AdjectivesFrom EverandEnglish Adjectives Made Easy: An Essential Guide to Rules and Examples of English AdjectivesNo ratings yet
- How To Make Simple Comparisons Lesson 1Document7 pagesHow To Make Simple Comparisons Lesson 1Irene RamirezNo ratings yet
- Voca-Book (Scent of A Woman)Document51 pagesVoca-Book (Scent of A Woman)Анастасия ВознесенскаяNo ratings yet
- Week 009-Module Correct UsageDocument16 pagesWeek 009-Module Correct UsageKenberly DingleNo ratings yet
- A1 - A2 Grammar SyllabusDocument3 pagesA1 - A2 Grammar SyllabusInda AriestiyaNo ratings yet
- Stories About Simple PastDocument3 pagesStories About Simple PastVictor Leonardo BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication School of Liberal Arts Divine Word College of Calapan Week 2 GrammarDocument55 pagesPurposive Communication School of Liberal Arts Divine Word College of Calapan Week 2 GrammarLarahNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Types of Speeches 2Document20 pagesModule 6 Types of Speeches 2Its KenchaNo ratings yet
- BJMC - I & 6th Sem 2012-13Document24 pagesBJMC - I & 6th Sem 2012-13G SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Dafivewavon LifuvosDocument3 pagesDafivewavon LifuvosShubham TyagiNo ratings yet
- Grammar Practice For Elementary StudentsDocument178 pagesGrammar Practice For Elementary StudentsAndreas Karaeng100% (2)
- Iptx 2004 2 0 125576 0 25727Document162 pagesIptx 2004 2 0 125576 0 25727KedarShuklaNo ratings yet
- Excel 6 GR Kaz WB Vnutr p001 050 - 94Document50 pagesExcel 6 GR Kaz WB Vnutr p001 050 - 94Ala ProductionNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Tense - SSDocument18 pagesPresent Perfect Tense - SSloeyan19No ratings yet
- Summary WritingDocument14 pagesSummary WritingAshbirkaurNo ratings yet
- Minggu 28Document18 pagesMinggu 28Heera ShiniNo ratings yet
- C Eng-111Document2 pagesC Eng-111Haris KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan HOW TO TELL WILD ANIMALSDocument4 pagesLesson Plan HOW TO TELL WILD ANIMALSSaritamahesh100% (2)
- 1971-Article Text-5577-1-10-20230731Document16 pages1971-Article Text-5577-1-10-20230731M Husnain RazaNo ratings yet
- Modals: Prepared by Madan Sharma Nexus International AcademyDocument20 pagesModals: Prepared by Madan Sharma Nexus International AcademyMadan SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Linguistic Survey of Adoptives in Venda: Submitted in Fulfilment of The Requirements For The Degree ofDocument301 pagesA Linguistic Survey of Adoptives in Venda: Submitted in Fulfilment of The Requirements For The Degree ofNelcasNo ratings yet
- The Little Girl 3. The Little Girl 3. The Little Girl 3. The Little Girl 3. The Little GirlDocument11 pagesThe Little Girl 3. The Little Girl 3. The Little Girl 3. The Little Girl 3. The Little GirlShrirang ShuklaNo ratings yet
- List of Registered Support OrganizationDocument337 pagesList of Registered Support OrganizationImatsuNo ratings yet
- Learning and Activiating Vocabulary PDFDocument5 pagesLearning and Activiating Vocabulary PDFKamal Kaum Deep SinghNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Questions For HomeDocument2 pagesReading Comprehension Questions For Homeapi-308209207No ratings yet
- May and Might English Grammar WorksheetDocument2 pagesMay and Might English Grammar WorksheetVeronica Vise MenéndezNo ratings yet
- BIODATADocument1 pageBIODATAzspi rotc unitNo ratings yet
- De Thi Hoc Sinh Gioi Tieng Anh Lop 7 Nam Hoc 2022 2023 So 2Document10 pagesDe Thi Hoc Sinh Gioi Tieng Anh Lop 7 Nam Hoc 2022 2023 So 2thuhuong980No ratings yet
- Over Easy: A Sample From All AboutDocument9 pagesOver Easy: A Sample From All AboutNicoleNo ratings yet
1.3.3 - Types of Adjectives
1.3.3 - Types of Adjectives
Uploaded by
Kapco ChallengersOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.3.3 - Types of Adjectives
1.3.3 - Types of Adjectives
Uploaded by
Kapco ChallengersCopyright:
Available Formats
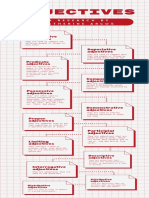
1.3.
3 – Types of Adjectives
Types of Adjectives
These are the most common type of adjectives and are
Descriptive Adjectives: used to describe the attributes or qualities of nouns.
Examples: happy, beautiful, tall, blue, delicious.
These adjectives point out specific nouns or pronouns and
Demonstrative
indicate their proximity in relation to the speaker.
Adjectives: Examples: this, that, these, those.
These adjectives show ownership or possession. They
Possessive Adjectives: indicate that something belongs to someone or something
else. Examples: my, your, his, her, its, our, their.
These adjectives express the quantity or amount of a noun.
Quantitative Adjectives:
Examples: few, many, several, some, all, any, much, little.
These adjectives indicate the number or order of nouns.
Numeral Adjectives: They can be cardinal (one, two, three) or ordinal (first,
second, third).
These adjectives are used in questions to ask about the
Interrogative Adjectives: quality, identity, or type of a noun. Examples: which, what,
whose.
These adjectives are used to give unspecific information
about a noun. They do not point to a specific noun but
Indefinite Adjectives: rather refer to any or all members of a group. Examples:
some, any, several, each, every, all, both, neither.
These adjectives are derived from proper nouns and
describe specific people, places, or things. Examples:
Proper Adjectives:
American (from America), Chinese (from China),
Shakespearean (related to Shakespeare).
These adjectives are used to compare the qualities of two
nouns or pronouns. They are usually formed by adding "-er"
Comparative Adjectives: to the adjective (for short adjectives) or using "more"
before the adjective (for longer adjectives). Examples:
taller, more beautiful, happier.
These adjectives are used to compare three or more nouns
or pronouns, indicating the highest degree of a quality.
They are often formed by adding "-est" to the adjective (for
Superlative Adjectives: short adjectives) or using "most" before the adjective (for
longer adjectives). Examples: tallest, most beautiful,
happiest.
You might also like
- New Close Up B1 Plus Teachers BookDocument176 pagesNew Close Up B1 Plus Teachers Booklakoh4161171% (7)
- Nmat Repeated Questions Admito Admito PDFDocument123 pagesNmat Repeated Questions Admito Admito PDFKushal Gangar100% (1)
- Crash Course - Final SyllabusDocument32 pagesCrash Course - Final SyllabusynrNo ratings yet
- Grammar For PPSCDocument22 pagesGrammar For PPSCAlina NoreenNo ratings yet
- ADJECTIV1Document2 pagesADJECTIV1daveashNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de InglesDocument9 pagesTrabajo de InglesGabu DreepNo ratings yet
- Descriptive AdjectivesDocument11 pagesDescriptive AdjectivesitxtryNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Rejoice & Happy After Seeing This Type of Late ST TechnologyDocument18 pagesParts of Speech Rejoice & Happy After Seeing This Type of Late ST TechnologyKrishan GuptaNo ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument6 pagesAdjectivesahmadmuhammadamasNo ratings yet
- What Is Noun?Document4 pagesWhat Is Noun?Christian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and AdverbsDocument4 pagesAdjectives and Adverbspinpollo 507No ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument5 pagesHomeworkraziel castroNo ratings yet
- Guided Writing Part of SpeechDocument4 pagesGuided Writing Part of Speechgurning chanelNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument7 pagesPart of SpeechMaria Alonica Mae BacoyNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument7 pagesParts of SpeechBhavna SinghalNo ratings yet
- Adjective Definition & Meaning - Merriam-WebsterDocument16 pagesAdjective Definition & Meaning - Merriam-WebsteraimarylorenzoizquierdoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document28 pagesChapter 4Nga phạmNo ratings yet
- Classification of Parts of Speech: NounsDocument10 pagesClassification of Parts of Speech: NounsДенис МитрохінNo ratings yet
- Mental VerbsDocument15 pagesMental VerbsHazel Ann Bragado CabacunganNo ratings yet
- A Noun Is A Word Used As The Name of A PersonDocument18 pagesA Noun Is A Word Used As The Name of A PersonSharib SheraziNo ratings yet
- Adjective and Its Kinds: Possessive AdjectivesDocument4 pagesAdjective and Its Kinds: Possessive AdjectivesArsalan QureshiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Eng Jordão Ortega Jemusse ManguenaDocument11 pagesDr. Eng Jordão Ortega Jemusse ManguenajemusseNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech in EnglishDocument13 pagesParts of Speech in EnglishApparel ShopNo ratings yet
- ENG111 Adj Conj PrepDocument22 pagesENG111 Adj Conj PrepjemimaafuapeNo ratings yet
- A Noun Is A Part of Speech That Names A PersonDocument22 pagesA Noun Is A Part of Speech That Names A PersonghshamzarashakaNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Introductor-WPS OfficeDocument6 pages1.0 Introductor-WPS Officebenitamujinga84No ratings yet
- Raysha's SyntaxDocument5 pagesRaysha's SyntaxM. Fauzi ArrasyidNo ratings yet
- Eng Mod1Document26 pagesEng Mod1Tivar VictorNo ratings yet
- Types of NounsDocument5 pagesTypes of NounsnarutothunderjetNo ratings yet
- NounsDocument44 pagesNounsRoger Donoso BarralNo ratings yet
- 2 Forum InglesDocument4 pages2 Forum InglesRaimundo AfonsoNo ratings yet
- Adjectives 140524073135 Phpapp02Document42 pagesAdjectives 140524073135 Phpapp02Donna Rose Malizon ObcianaNo ratings yet
- A Noun Is A Part of Speech That Names A PersonDocument12 pagesA Noun Is A Part of Speech That Names A PersonfarhanalicasNo ratings yet
- Determine RsDocument38 pagesDetermine RsAaron S. Casipe Jr.No ratings yet
- ADJECTIVESDocument3 pagesADJECTIVESKatherine ArcosNo ratings yet
- Types of AdjectivesDocument2 pagesTypes of AdjectivesPaola ParkerNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument12 pagesParts of SpeechKh adijaNo ratings yet
- Adjectives CutieDocument5 pagesAdjectives CutieSweet lea AntonesNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument30 pagesPart of SpeechKaren BlanqueraNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument14 pagesPronounsainhoa.brosaNo ratings yet
- Packet UpdatedDocument70 pagesPacket UpdatedTien Thanh Le,No ratings yet
- Structure of English ModuleDocument26 pagesStructure of English ModuleSai Guyo50% (2)
- PARTS OF SPEECH UpdatedDocument12 pagesPARTS OF SPEECH UpdatedMCC Gilgit-BaltistanNo ratings yet
- Seminar 4Document13 pagesSeminar 4Михаил РешетниковNo ratings yet
- ADJECTIVEDocument5 pagesADJECTIVEdaveashNo ratings yet
- Foundation in Tesol Unit 2: Study of The English LanguageDocument28 pagesFoundation in Tesol Unit 2: Study of The English LanguageMiramar CamachoNo ratings yet
- Placement of AdjectivesDocument5 pagesPlacement of AdjectivesPranalaNo ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument9 pagesAdjectivesAnyeli SantosNo ratings yet
- Grammar Noun PronounsDocument4 pagesGrammar Noun PronounsShane AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- It's Means It Is or It Has While Its Means?Document2 pagesIt's Means It Is or It Has While Its Means?Dardarsky FegiNo ratings yet
- AdjectiveDocument11 pagesAdjectiveTika RogavaNo ratings yet
- Adjectives Are Describing WordsDocument1 pageAdjectives Are Describing Wordsjoy05.alexa.01No ratings yet
- Guide - Words, Phrases, Clauses and SentencesDocument14 pagesGuide - Words, Phrases, Clauses and SentencesTomas G Salazar TNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document6 pagesLecture 5安思吉No ratings yet
- WK5ENGDocument3 pagesWK5ENGAwojuyigbeNo ratings yet
- Grammatical CategoriesDocument6 pagesGrammatical CategoriesBeverlyNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument10 pagesParts of SpeechsalahudinNo ratings yet
- Types of AdjectivesDocument3 pagesTypes of AdjectivesNway Htet Htet AungNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument3 pagesPronounstobizarreNo ratings yet
- Gen Ed Guide English-GrammarDocument12 pagesGen Ed Guide English-GrammarShane AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- NounsDocument42 pagesNounsRoger Donoso Barral100% (1)
- English Adjectives Made Easy: An Essential Guide to Rules and Examples of English AdjectivesFrom EverandEnglish Adjectives Made Easy: An Essential Guide to Rules and Examples of English AdjectivesNo ratings yet
- How To Make Simple Comparisons Lesson 1Document7 pagesHow To Make Simple Comparisons Lesson 1Irene RamirezNo ratings yet
- Voca-Book (Scent of A Woman)Document51 pagesVoca-Book (Scent of A Woman)Анастасия ВознесенскаяNo ratings yet
- Week 009-Module Correct UsageDocument16 pagesWeek 009-Module Correct UsageKenberly DingleNo ratings yet
- A1 - A2 Grammar SyllabusDocument3 pagesA1 - A2 Grammar SyllabusInda AriestiyaNo ratings yet
- Stories About Simple PastDocument3 pagesStories About Simple PastVictor Leonardo BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication School of Liberal Arts Divine Word College of Calapan Week 2 GrammarDocument55 pagesPurposive Communication School of Liberal Arts Divine Word College of Calapan Week 2 GrammarLarahNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Types of Speeches 2Document20 pagesModule 6 Types of Speeches 2Its KenchaNo ratings yet
- BJMC - I & 6th Sem 2012-13Document24 pagesBJMC - I & 6th Sem 2012-13G SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Dafivewavon LifuvosDocument3 pagesDafivewavon LifuvosShubham TyagiNo ratings yet
- Grammar Practice For Elementary StudentsDocument178 pagesGrammar Practice For Elementary StudentsAndreas Karaeng100% (2)
- Iptx 2004 2 0 125576 0 25727Document162 pagesIptx 2004 2 0 125576 0 25727KedarShuklaNo ratings yet
- Excel 6 GR Kaz WB Vnutr p001 050 - 94Document50 pagesExcel 6 GR Kaz WB Vnutr p001 050 - 94Ala ProductionNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Tense - SSDocument18 pagesPresent Perfect Tense - SSloeyan19No ratings yet
- Summary WritingDocument14 pagesSummary WritingAshbirkaurNo ratings yet
- Minggu 28Document18 pagesMinggu 28Heera ShiniNo ratings yet
- C Eng-111Document2 pagesC Eng-111Haris KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan HOW TO TELL WILD ANIMALSDocument4 pagesLesson Plan HOW TO TELL WILD ANIMALSSaritamahesh100% (2)
- 1971-Article Text-5577-1-10-20230731Document16 pages1971-Article Text-5577-1-10-20230731M Husnain RazaNo ratings yet
- Modals: Prepared by Madan Sharma Nexus International AcademyDocument20 pagesModals: Prepared by Madan Sharma Nexus International AcademyMadan SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Linguistic Survey of Adoptives in Venda: Submitted in Fulfilment of The Requirements For The Degree ofDocument301 pagesA Linguistic Survey of Adoptives in Venda: Submitted in Fulfilment of The Requirements For The Degree ofNelcasNo ratings yet
- The Little Girl 3. The Little Girl 3. The Little Girl 3. The Little Girl 3. The Little GirlDocument11 pagesThe Little Girl 3. The Little Girl 3. The Little Girl 3. The Little Girl 3. The Little GirlShrirang ShuklaNo ratings yet
- List of Registered Support OrganizationDocument337 pagesList of Registered Support OrganizationImatsuNo ratings yet
- Learning and Activiating Vocabulary PDFDocument5 pagesLearning and Activiating Vocabulary PDFKamal Kaum Deep SinghNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Questions For HomeDocument2 pagesReading Comprehension Questions For Homeapi-308209207No ratings yet
- May and Might English Grammar WorksheetDocument2 pagesMay and Might English Grammar WorksheetVeronica Vise MenéndezNo ratings yet
- BIODATADocument1 pageBIODATAzspi rotc unitNo ratings yet
- De Thi Hoc Sinh Gioi Tieng Anh Lop 7 Nam Hoc 2022 2023 So 2Document10 pagesDe Thi Hoc Sinh Gioi Tieng Anh Lop 7 Nam Hoc 2022 2023 So 2thuhuong980No ratings yet
- Over Easy: A Sample From All AboutDocument9 pagesOver Easy: A Sample From All AboutNicoleNo ratings yet